定义:
顺序表存储定义: 把逻辑上相邻的数据元素存储在物理上相邻的存储单元中的存储结构,顺序表功能的实现借助于数组,通过对数组进行封装,从而实现增删查改的功能,严格意义上来说(数组无法实现删除数据的功能)。
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include"seqlist.h"
void initseqlist(SL* p) {
assert(p);
p->arr = NULL;
p->capacity = p->size = 0;
}
void printseqlist(SL* p) {
for (int i = 0; i < p->size; i++) {
printf("%d ", p->arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
void checkcapacity(SL* p) {
assert(p);
if (p->capacity == p->size) {
int newcapacity = p->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * p->capacity;
// if here use malloc,the origin data in this array might be missing
int* temp = (int*)realloc(p->arr,sizeof(int) * newcapacity);
p->arr = temp;
p->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
void pushFront(SL* p, int val) {
assert(p);
checkcapacity(p);
int end = p->size - 1;
while (end >= 0) {
p->arr[end + 1] = p->arr[end];
end--;
}
p->arr[0 ] = val;
p->size++;
}
void pushback(SL* p,int val) {
//assert(p);
checkcapacity(p);
p->arr[p->size] = val;
p->size++;
}
void popfront(SL* p) {
assert(p);
int n = p->arr[0];
printf("将要被pop元素=%d\n", n);
for (int i = 1; i < p->size ; i++) {
p->arr[i - 1] = p->arr[i];
}
p->size--;
}
void insertanyposition(SL* p, int pos, int val) {
assert(p);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= p->size);
int end = p->size - 1;
while (end>=pos) {
p->arr[end + 1] = p->arr[end];
end--;
}
p->arr[pos] = val;
p->size++;
}
int findDataPos(SL* p, int val) {
assert(p);
for (int i = 0; i < p->size; i++) {
if (p->arr[i] == val) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}1、顺序表的初始化:
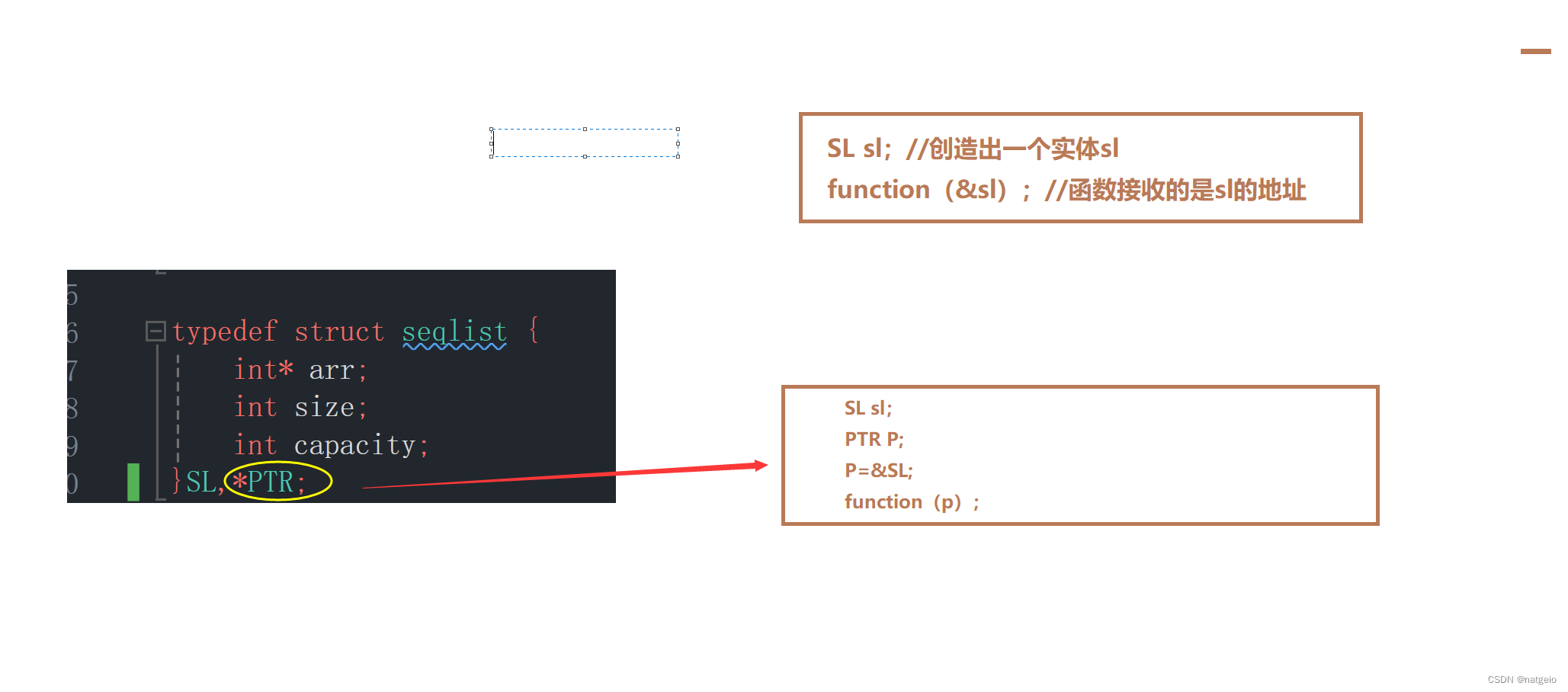
typedef struct seqlist {
int* arr;
int size;
int capacity;
}SL,*PTR;
void initseqlist(SL* p) {
assert(p);
p->arr = NULL;
p->capacity = p->size = 0;
}
2、顺序表容量检测:
当我们要对表里进行相关操作的时候,第一步检测当下该表中size 与 容量的关系,可以写一个checkcapacity函数。
void checkcapacity2(SL* p) {
assert(p);
if (p->capacity == p->size) {
int newcapacity = p->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * p->capacity;
int* temp = (int*)malloc(sizeof(int) * newcapacity);
p->arr = temp;
p->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
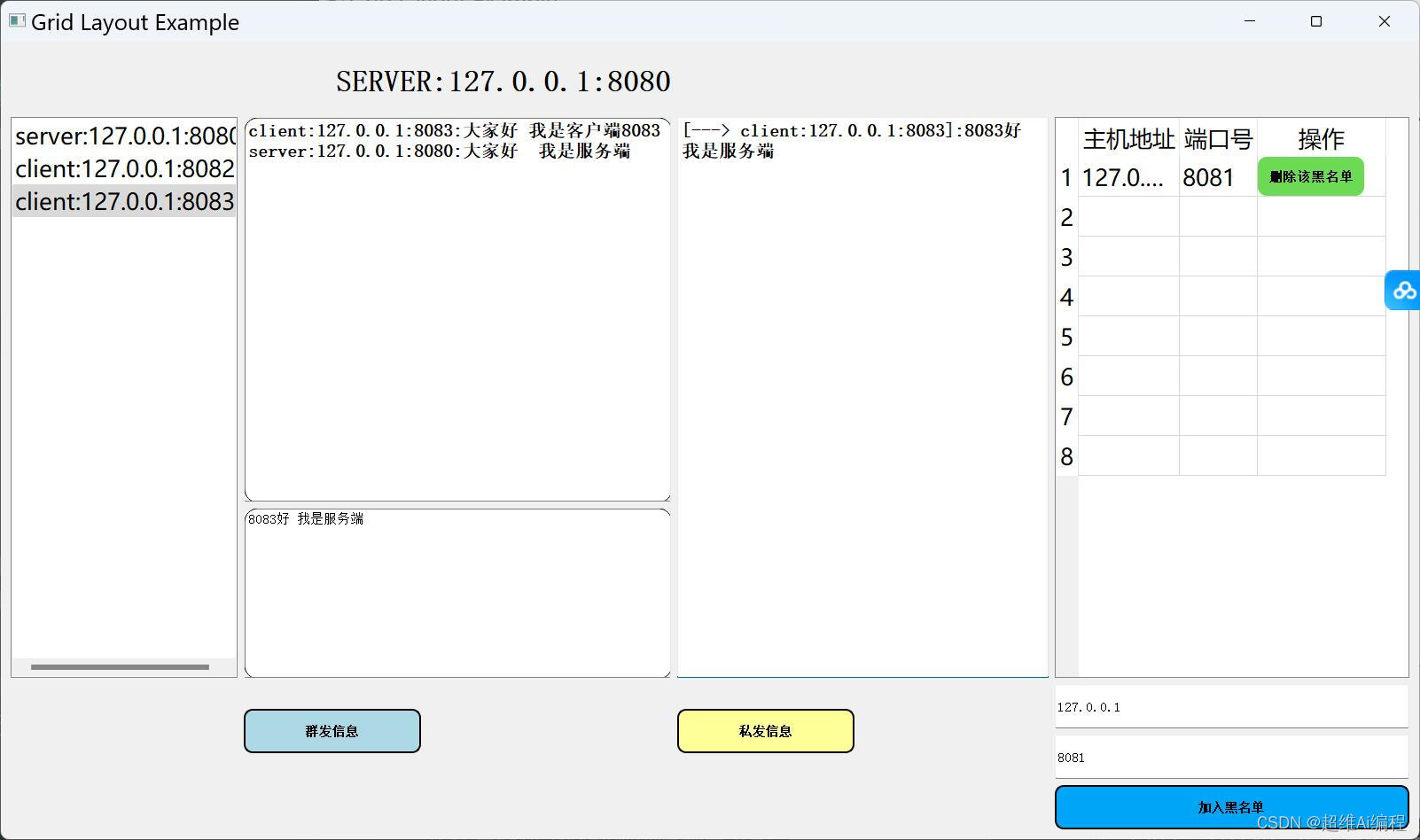
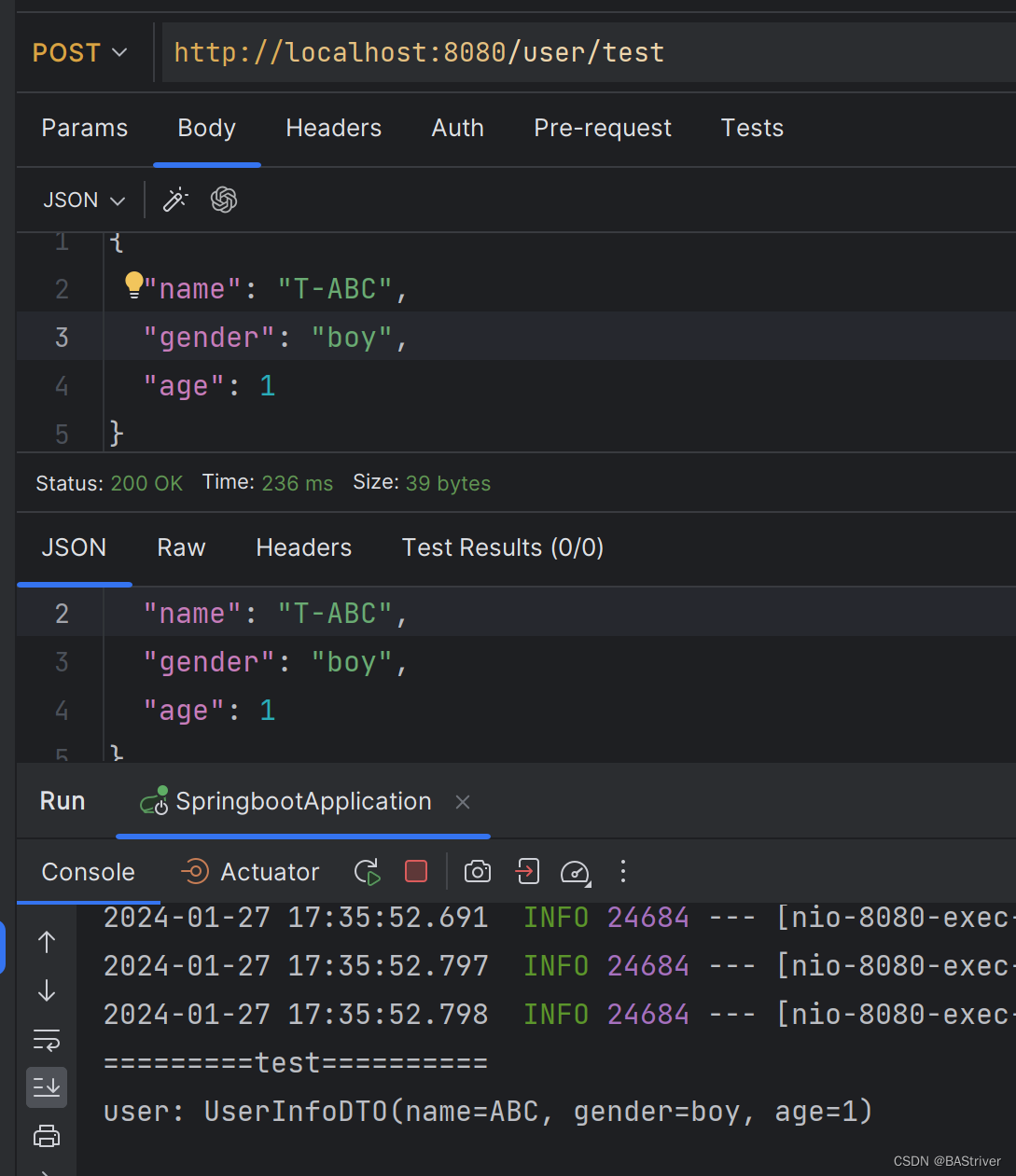
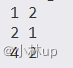
void test3() {
PTR p;
SL sl;
p = &sl;
initseqlist(p);
pushback(p, 5);//first init ---> size=4,capacity=4
pushback(p, 15);
pushback(p, 25);
pushback(p, 35);
pushback(p, 45);
printseqlist(p);
}这个时候来看一下打印结果:
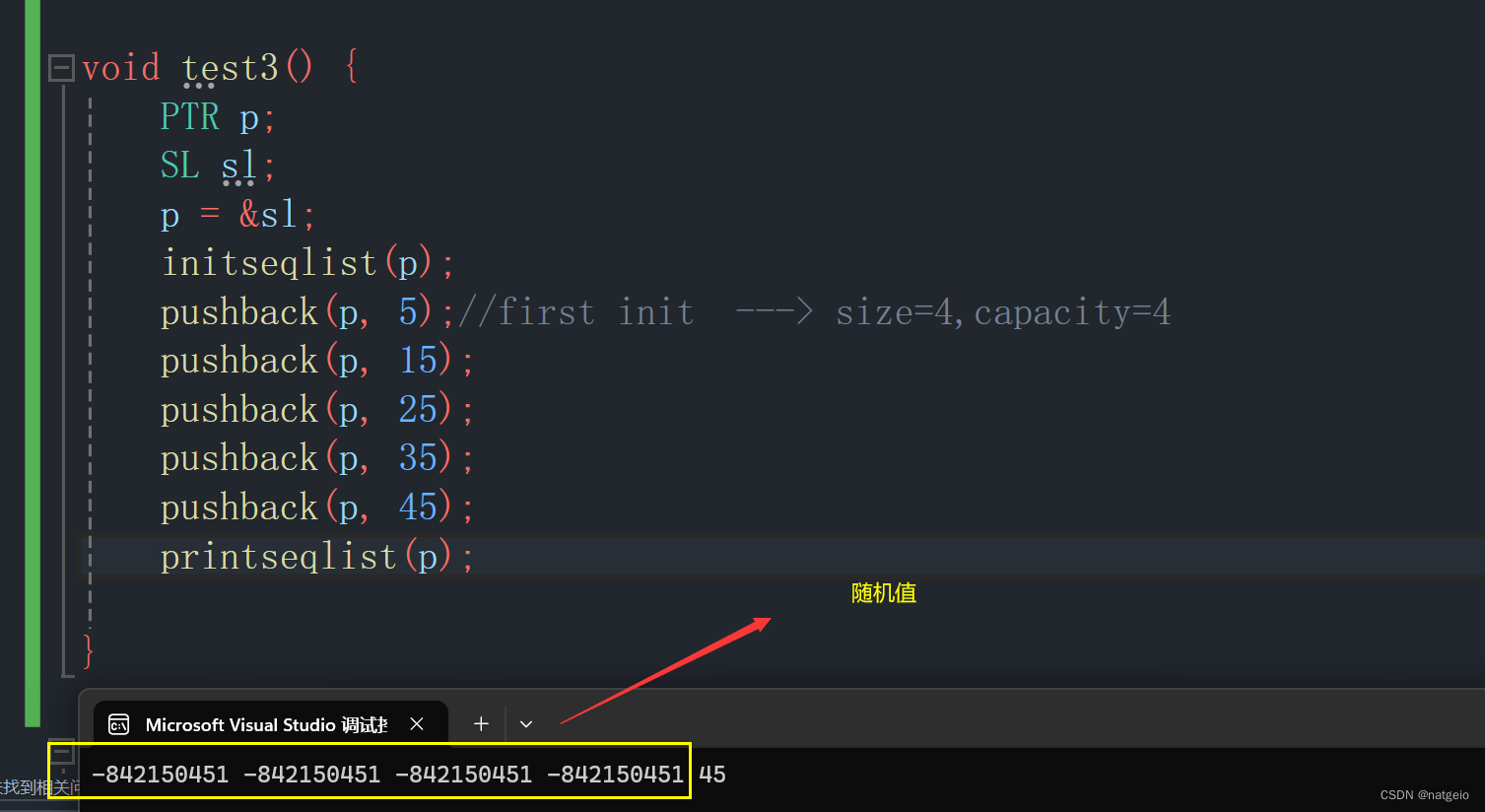
为什么会这样呢,这个时候我们就需要借助调试工具来找出问题所在
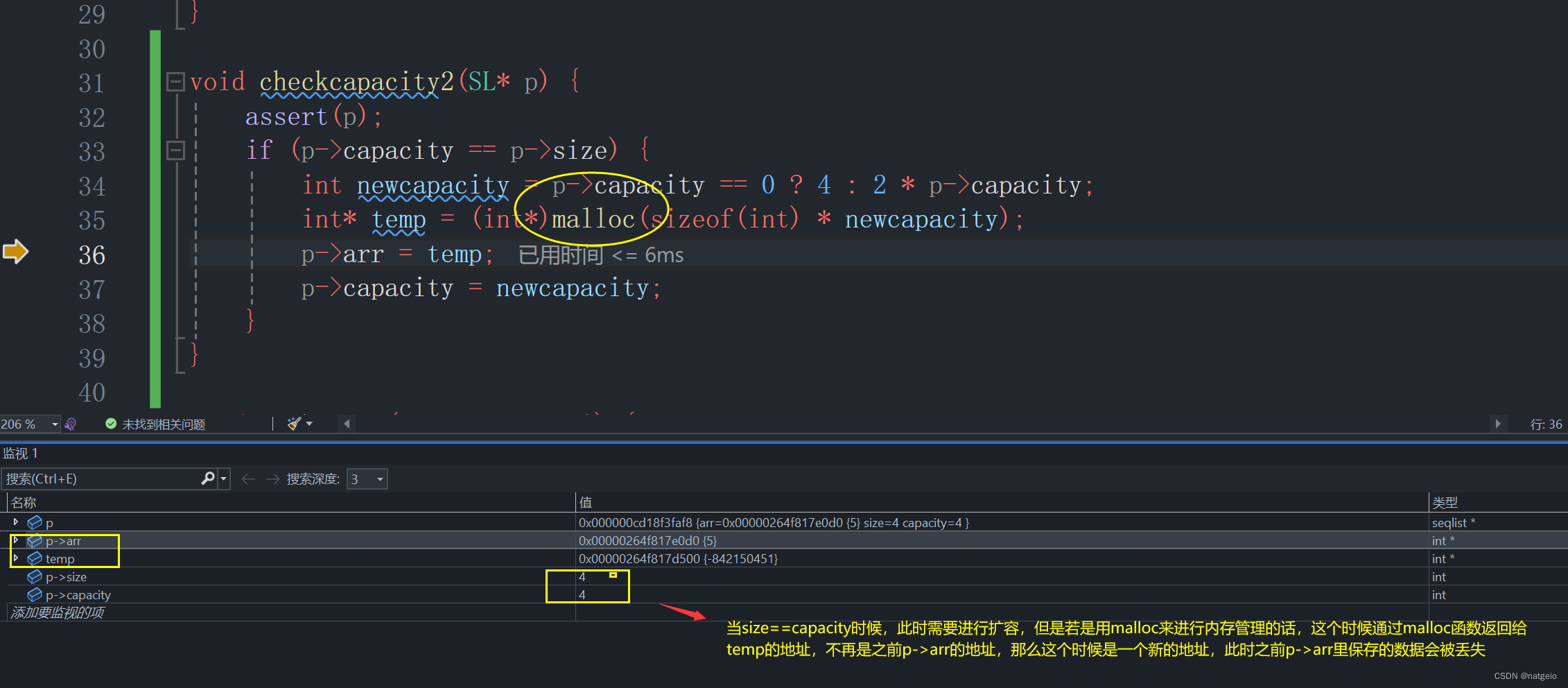
所以我们该处可以用realloc 函数 来进行动态内存管理:
void checkcapacity(SL* p) {
assert(p);
if (p->capacity == p->size) {
int newcapacity = p->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * p->capacity;
// if here use malloc,the origin data in this array might be missing
int* temp = (int*)realloc(p->arr,sizeof(int) * newcapacity);
p->arr = temp;
p->capacity = newcapacity;
}
}
3、顺序表插入数据:
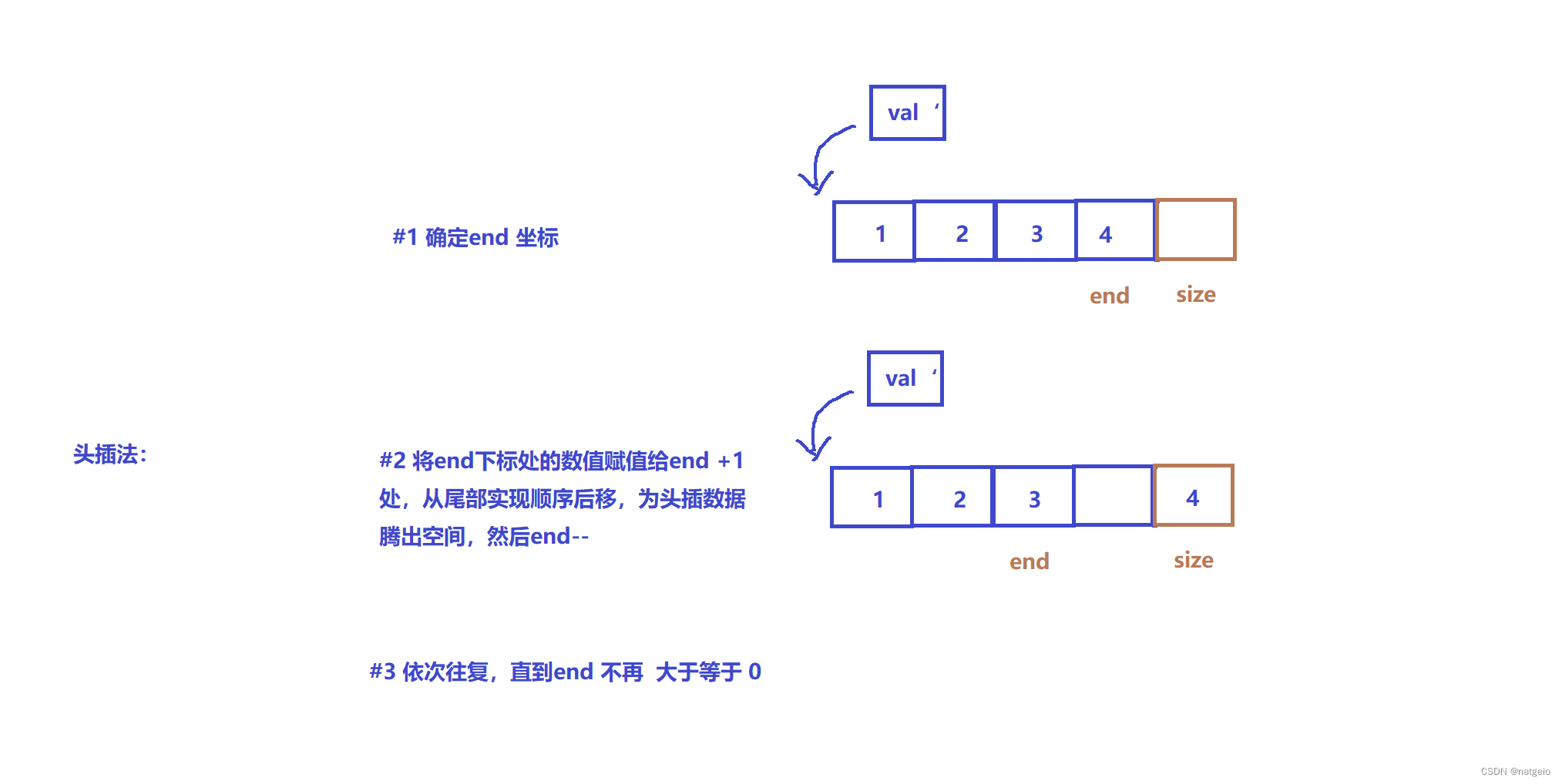
3.1头插:
void pushFront(SL* p, int val) {
assert(p);
checkcapacity(p);
int end = p->size - 1;
while (end >= 0) {
p->arr[end + 1] = p->arr[end];
end--;
}
p->arr[0 ] = val;
p->size++;
}
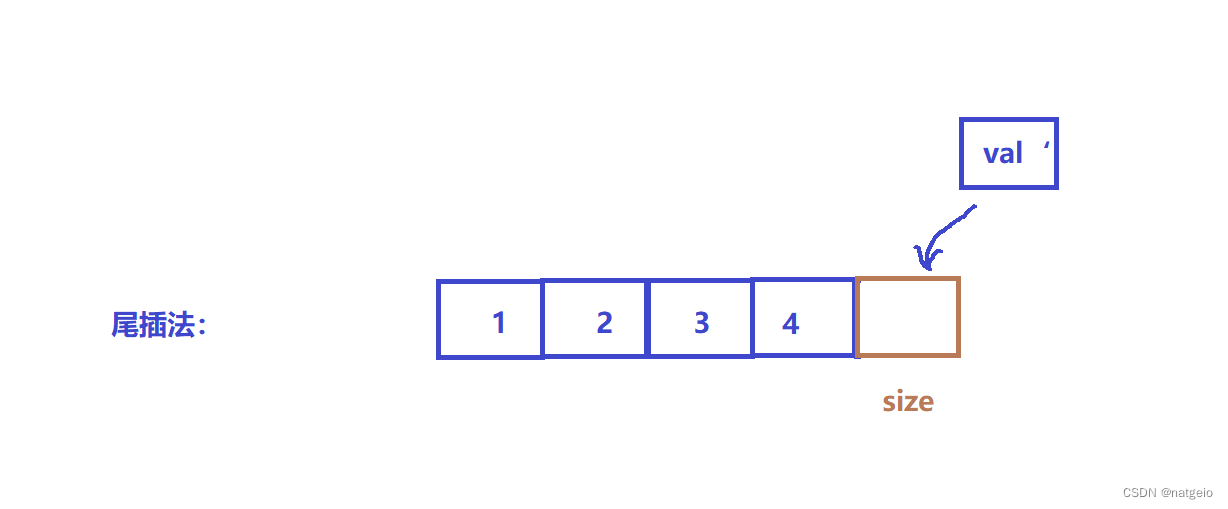
3.2尾插:
void pushback(SL* p,int val) {
//assert(p);
checkcapacity(p);
p->arr[p->size] = val;
p->size++;
}
4、顺序表删除数据:
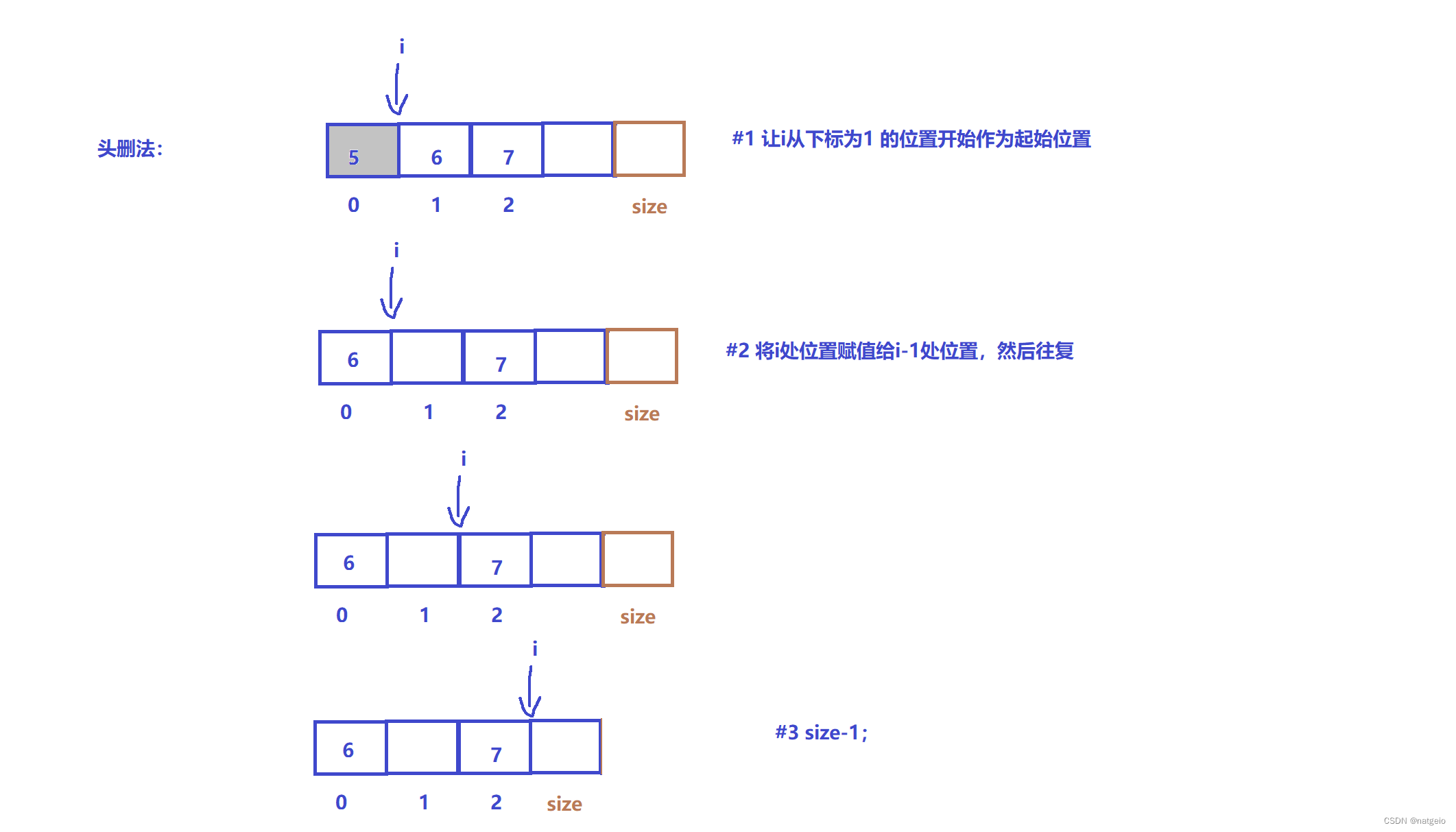
4.1头删
void popfront(SL* p) {
assert(p);
int n = p->arr[0];
// 可以起到记录作用
printf("将要被pop元素=%d\n", n);
for (int i = 1; i < p->size ; i++) {
p->arr[i - 1] = p->arr[i];
}
p->size--;
}
4.2尾删
5、任意位置实现插入功能:
void insertanyposition(SL* p, int pos, int val) {
assert(p);
assert(pos >= 0 && pos <= p->size);
int end = p->size - 1;
while (end>=pos) {
p->arr[end + 1] = p->arr[end];
end--;
}
p->arr[pos] = val;
p->size++;
}6、顺序表中实现查找功能:
int findDataPos(SL* p, int val) {
assert(p);
for (int i = 0; i < p->size; i++) {
if (p->arr[i] == val) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}