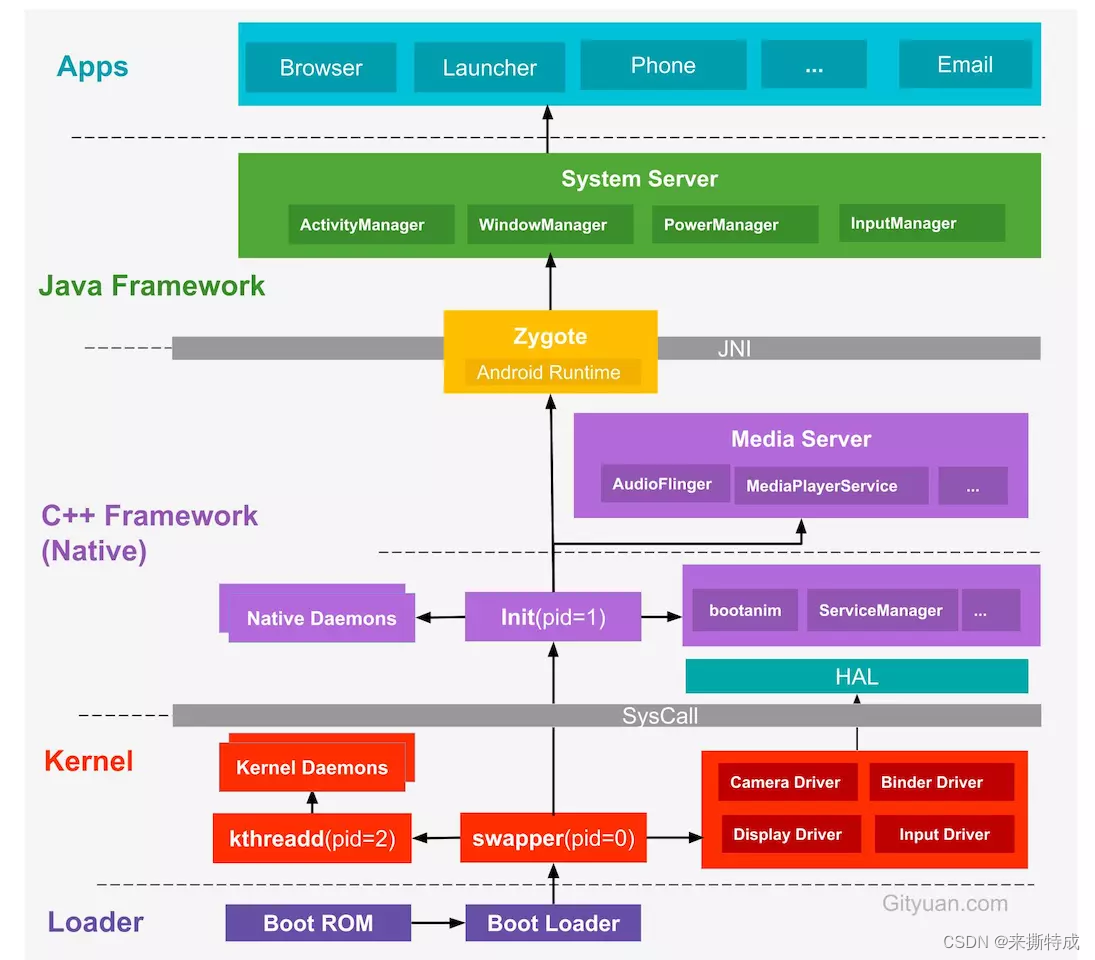
system_server 进程是 Zygote 进程 fork 出的第一个进程,它负责管理和启动整个 Framework 层,下面附上android系统启动流程图:
记得上一篇Zygote进程创建里面提到过,forckSystemServer创建system_server进程。
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/os/ZygoteInit.java 中代码如下:
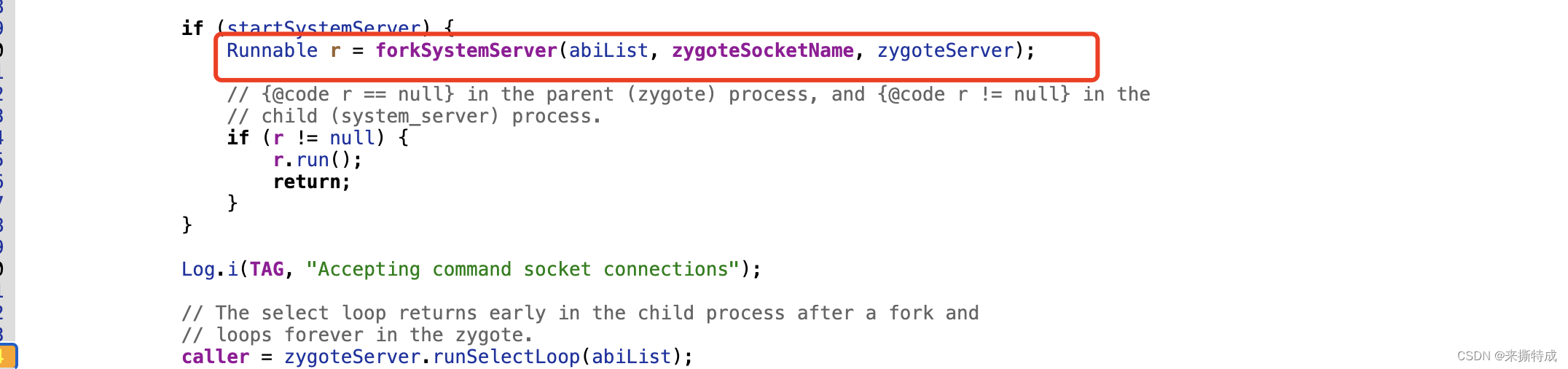
下面是forkSystemServer 里面的代码:
 Zygote.forkSystemServer 返回的是一个int型的pid,如果pid不等于0,代表的是在父进程中执行,即
Zygote.forkSystemServer 返回的是一个int型的pid,如果pid不等于0,代表的是在父进程中执行,即
Zygote进程,如果pid等于0,代表在子进程中执行。
最终执行handleSystemServerProcess,是在system_server进程中执行。
接下来看handleSystemServerProcess方法
/**
499 * Finish remaining work for the newly forked system server process.
500 */
501 private static Runnable handleSystemServerProcess(ZygoteArguments parsedArgs) {
502 // set umask to 0077 so new files and directories will default to owner-only permissions.
503 Os.umask(S_IRWXG | S_IRWXO);
504
505 if (parsedArgs.mNiceName != null) {
506 Process.setArgV0(parsedArgs.mNiceName);
507 }
508
509 final String systemServerClasspath = Os.getenv("SYSTEMSERVERCLASSPATH");
510 if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
511 performSystemServerDexOpt(systemServerClasspath);
512 // Capturing profiles is only supported for debug or eng builds since selinux normally
513 // prevents it.
514 if (shouldProfileSystemServer() && (Build.IS_USERDEBUG || Build.IS_ENG)) {
515 try {
516 Log.d(TAG, "Preparing system server profile");
517 prepareSystemServerProfile(systemServerClasspath);
518 } catch (Exception e) {
519 Log.wtf(TAG, "Failed to set up system server profile", e);
520 }
521 }
522 }
523
524 if (parsedArgs.mInvokeWith != null) {
525 String[] args = parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs;
526 // If we have a non-null system server class path, we'll have to duplicate the
527 // existing arguments and append the classpath to it. ART will handle the classpath
528 // correctly when we exec a new process.
529 if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
530 String[] amendedArgs = new String[args.length + 2];
531 amendedArgs[0] = "-cp";
532 amendedArgs[1] = systemServerClasspath;
533 System.arraycopy(args, 0, amendedArgs, 2, args.length);
534 args = amendedArgs;
535 }
536
537 WrapperInit.execApplication(parsedArgs.mInvokeWith,
538 parsedArgs.mNiceName, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
539 VMRuntime.getCurrentInstructionSet(), null, args);
540
541 throw new IllegalStateException("Unexpected return from WrapperInit.execApplication");
542 } else {
543 ClassLoader cl = null;
544 if (systemServerClasspath != null) {
545 cl = createPathClassLoader(systemServerClasspath, parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion);
546
547 Thread.currentThread().setContextClassLoader(cl);
548 }
549
550 /*
551 * Pass the remaining arguments to SystemServer.
552 */
553 return ZygoteInit.zygoteInit(parsedArgs.mTargetSdkVersion,
554 parsedArgs.mDisabledCompatChanges,
555 parsedArgs.mRemainingArgs, cl);
556 }
557
558 /* should never reach here */
559 }最终执行到ZygoteInit.zygoteInit方法,点进去看一下
/**
978 * The main function called when started through the zygote process. This could be unified with
979 * main(), if the native code in nativeFinishInit() were rationalized with Zygote startup.<p>
980 *
981 * Current recognized args:
982 * <ul>
983 * <li> <code> [--] <start class name> <args>
984 * </ul>
985 *
986 * @param targetSdkVersion target SDK version
987 * @param disabledCompatChanges set of disabled compat changes for the process (all others
988 * are enabled)
989 * @param argv arg strings
990 */
991 public static final Runnable zygoteInit(int targetSdkVersion, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
992 String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
993 if (RuntimeInit.DEBUG) {
994 Slog.d(RuntimeInit.TAG, "RuntimeInit: Starting application from zygote");
995 }
996
997 Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER, "ZygoteInit");
998 RuntimeInit.redirectLogStreams();
999
1000 RuntimeInit.commonInit();
1001 ZygoteInit.nativeZygoteInit();
1002 return RuntimeInit.applicationInit(targetSdkVersion, disabledCompatChanges, argv,
1003 classLoader);
1004 }再看看RuntimeInit.applicationInit方法
protected static Runnable applicationInit(int targetSdkVersion, long[] disabledCompatChanges,
405 String[] argv, ClassLoader classLoader) {
406 // If the application calls System.exit(), terminate the process
407 // immediately without running any shutdown hooks. It is not possible to
408 // shutdown an Android application gracefully. Among other things, the
409 // Android runtime shutdown hooks close the Binder driver, which can cause
410 // leftover running threads to crash before the process actually exits.
411 nativeSetExitWithoutCleanup(true);
412
413 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setTargetSdkVersion(targetSdkVersion);
414 VMRuntime.getRuntime().setDisabledCompatChanges(disabledCompatChanges);
415
416 final Arguments args = new Arguments(argv);
417
418 // The end of of the RuntimeInit event (see #zygoteInit).
419 Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_ACTIVITY_MANAGER);
420
421 // Remaining arguments are passed to the start class's static main
422 return findStaticMain(args.startClass, args.startArgs, classLoader);
423 }最终执行的是findStaticMain方法
/**
337 * Invokes a static "main(argv[]) method on class "className".
338 * Converts various failing exceptions into RuntimeExceptions, with
339 * the assumption that they will then cause the VM instance to exit.
340 *
341 * @param className Fully-qualified class name
342 * @param argv Argument vector for main()
343 * @param classLoader the classLoader to load {@className} with
344 */
345 protected static Runnable findStaticMain(String className, String[] argv,
346 ClassLoader classLoader) {
347 Class<?> cl;
348
349 try {
350 cl = Class.forName(className, true, classLoader);
351 } catch (ClassNotFoundException ex) {
352 throw new RuntimeException(
353 "Missing class when invoking static main " + className,
354 ex);
355 }
356
357 Method m;
358 try {
359 m = cl.getMethod("main", new Class[] { String[].class });
360 } catch (NoSuchMethodException ex) {
361 throw new RuntimeException(
362 "Missing static main on " + className, ex);
363 } catch (SecurityException ex) {
364 throw new RuntimeException(
365 "Problem getting static main on " + className, ex);
366 }
367
368 int modifiers = m.getModifiers();
369 if (! (Modifier.isStatic(modifiers) && Modifier.isPublic(modifiers))) {
370 throw new RuntimeException(
371 "Main method is not public and static on " + className);
372 }
373
374 /*
375 * This throw gets caught in ZygoteInit.main(), which responds
376 * by invoking the exception's run() method. This arrangement
377 * clears up all the stack frames that were required in setting
378 * up the process.
379 */
380 return new MethodAndArgsCaller(m, argv);
381 }再看看 MethodAndArgsCaller
/**
575 * Helper class which holds a method and arguments and can call them. This is used as part of
576 * a trampoline to get rid of the initial process setup stack frames.
577 */
578 static class MethodAndArgsCaller implements Runnable {
579 /** method to call */
580 private final Method mMethod;
581
582 /** argument array */
583 private final String[] mArgs;
584
585 public MethodAndArgsCaller(Method method, String[] args) {
586 mMethod = method;
587 mArgs = args;
588 }
589
590 public void run() {
591 try {
592 mMethod.invoke(null, new Object[] { mArgs });
593 } catch (IllegalAccessException ex) {
594 throw new RuntimeException(ex);
595 } catch (InvocationTargetException ex) {
596 Throwable cause = ex.getCause();
597 if (cause instanceof RuntimeException) {
598 throw (RuntimeException) cause;
599 } else if (cause instanceof Error) {
600 throw (Error) cause;
601 }
602 throw new RuntimeException(ex);
603 }
604 }
605 }
606 }这样一看就知道通过反射来调用方法的
最后回过头来看下顶部的代码图片

返回的Runnable对象,执行run, 执行system_server main 方法,然后return了。
接下来我们看SystemServer main 方法
/**
411 * The main entry point from zygote.
412 */
413 public static void main(String[] args) {
414 new SystemServer().run();
415 }run代码中大致分为11个步骤:
1.设定时间
//
450 // Default the timezone property to GMT if not set.
451 //
452 String timezoneProperty = SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.timezone");
453 if (timezoneProperty == null || timezoneProperty.isEmpty()) {
454 Slog.w(TAG, "Timezone not set; setting to GMT.");
455 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.timezone", "GMT");
456 }
457 2.设定语言
// If the system has "persist.sys.language" and friends set, replace them with
459 // "persist.sys.locale". Note that the default locale at this point is calculated
460 // using the "-Duser.locale" command line flag. That flag is usually populated by
461 // AndroidRuntime using the same set of system properties, but only the system_server
462 // and system apps are allowed to set them.
463 //
464 // NOTE: Most changes made here will need an equivalent change to
465 // core/jni/AndroidRuntime.cpp
466 if (!SystemProperties.get("persist.sys.language").isEmpty()) {
467 final String languageTag = Locale.getDefault().toLanguageTag();
468
469 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.locale", languageTag);
470 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.language", "");
471 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.country", "");
472 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.localevar", "");
473 }
474 3.虚拟机库文件路径
// In case the runtime switched since last boot (such as when
498 // the old runtime was removed in an OTA), set the system
499 // property so that it is in sync. We can't do this in
500 // libnativehelper's JniInvocation::Init code where we already
501 // had to fallback to a different runtime because it is
502 // running as root and we need to be the system user to set
503 // the property. http://b/11463182
504 SystemProperties.set("persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib.2", VMRuntime.getRuntime().vmLibrary());4.清除内存使用上限
// Mmmmmm... more memory!
507 VMRuntime.getRuntime().clearGrowthLimit();5.设定指纹使用
// Some devices rely on runtime fingerprint generation, so make sure
510 // we've defined it before booting further.
511 Build.ensureFingerprintProperty();6.设定环境变量访问用户条件
// Within the system server, it is an error to access Environment paths without
514 // explicitly specifying a user.
515 Environment.setUserRequired(true);7.设定binder服务永远运行在前台
// Ensure binder calls into the system always run at foreground priority.
525 BinderInternal.disableBackgroundScheduling(true);8.设定线程池最大线程数
527 // Increase the number of binder threads in system_server
528 BinderInternal.setMaxThreads(sMaxBinderThreads);9.启动各种服务
// Start services.
594 try {
595 t.traceBegin("StartServices");
596 startBootstrapServices(t);
597 startCoreServices(t);
598 startOtherServices(t);
599 } catch (Throwable ex) {
600 Slog.e("System", "******************************************");
601 Slog.e("System", "************ Failure starting system services", ex);
602 throw ex;
603 } finally {
604 t.traceEnd(); // StartServices
605 }
606
607 StrictMode.initVmDefaults(null);
608
609 if (!mRuntimeRestart && !isFirstBootOrUpgrade()) {
610 final long uptimeMillis = SystemClock.elapsedRealtime();
611 FrameworkStatsLog.write(FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME_REPORTED,
612 FrameworkStatsLog.BOOT_TIME_EVENT_ELAPSED_TIME__EVENT__SYSTEM_SERVER_READY,
613 uptimeMillis);
614 final long maxUptimeMillis = 60 * 1000;
615 if (uptimeMillis > maxUptimeMillis) {
616 Slog.wtf(SYSTEM_SERVER_TIMING_TAG,
617 "SystemServer init took too long. uptimeMillis=" + uptimeMillis);
618 }
619 }
620
621 // Diagnostic to ensure that the system is in a base healthy state. Done here as a common
622 // non-zygote process.
623 if (!VMRuntime.hasBootImageSpaces()) {
624 Slog.wtf(TAG, "Runtime is not running with a boot image!");
625 }
626 10.服务开启循环
// Loop forever.
628 Looper.loop();启动系统上下文
// Initialize the system context.
556 createSystemContext(); private void createSystemContext() {
696 ActivityThread activityThread = ActivityThread.systemMain();
697 mSystemContext = activityThread.getSystemContext();
698 mSystemContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
699
700 final Context systemUiContext = activityThread.getSystemUiContext();
701 systemUiContext.setTheme(DEFAULT_SYSTEM_THEME);
702 }创建SystemServiceManager
561 // Create the system service manager.
562 mSystemServiceManager = new SystemServiceManager(mSystemContext);
563 mSystemServiceManager.setStartInfo(mRuntimeRestart,
564 mRuntimeStartElapsedTime, mRuntimeStartUptime);
565 LocalServices.addService(SystemServiceManager.class, mSystemServiceManager);
566 // Prepare the thread pool for init tasks that can be parallelized
567 SystemServerInitThreadPool.start();




![[java基础揉碎]break跳出循环的标签使用方式(continue同理)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/904f3cb8484544368fedaf6981c95b47.png)