目录
- 104.二叉树的最大深度
- 题目描述
- 参考代码
- 111.二叉树的最小深度
- 题目描述
- 参考代码
- 222.完全二叉树的节点个数
- 题目描述
- 参考代码
104.二叉树的最大深度
题目描述
给定一个二叉树 root ,返回其最大深度。
二叉树的 最大深度 是指从根节点到最远叶子节点的最长路径上的节点数。
示例 1:
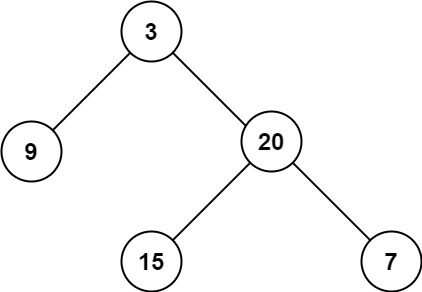
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:3
示例 2:
输入:root = [1,null,2]
输出:2
提示:
- 树中节点的数量在
[0, 104]区间内。 -100 <= Node.val <= 100
参考代码
class solution {
/**
* 递归法
*/
public int maxDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = maxDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = maxDepth(root.right);
return Math.max(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
111.二叉树的最小深度
题目描述
给定一个二叉树,找出其最小深度。
最小深度是从根节点到最近叶子节点的最短路径上的节点数量。
**说明:**叶子节点是指没有子节点的节点。
示例 1:
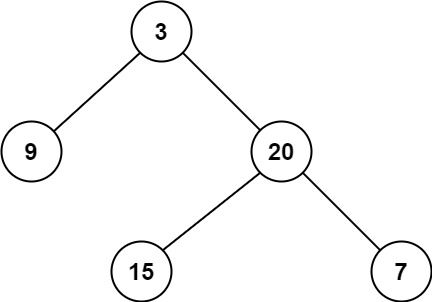
输入:root = [3,9,20,null,null,15,7]
输出:2
示例 2:
输入:root = [2,null,3,null,4,null,5,null,6]
输出:5
提示:
- 树中节点数的范围在
[0, 105]内 -1000 <= Node.val <= 1000
参考代码
class Solution {
/**
* 递归法,相比求MaxDepth要复杂点
* 因为最小深度是从根节点到最近**叶子节点**的最短路径上的节点数量
*/
public int minDepth(TreeNode root) {
if (root == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftDepth = minDepth(root.left);
int rightDepth = minDepth(root.right);
if (root.left == null) {
return rightDepth + 1;
}
if (root.right == null) {
return leftDepth + 1;
}
// 左右结点都不为null
return Math.min(leftDepth, rightDepth) + 1;
}
}
222.完全二叉树的节点个数
题目描述
给你一棵 完全二叉树 的根节点 root ,求出该树的节点个数。
完全二叉树 的定义如下:在完全二叉树中,除了最底层节点可能没填满外,其余每层节点数都达到最大值,并且最下面一层的节点都集中在该层最左边的若干位置。若最底层为第 h 层,则该层包含 1~ 2h 个节点。
示例 1:
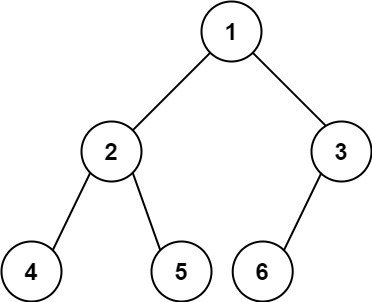
输入:root = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
输出:6
示例 2:
输入:root = []
输出:0
示例 3:
输入:root = [1]
输出:1
提示:
- 树中节点的数目范围是
[0, 5 * 104] 0 <= Node.val <= 5 * 104- 题目数据保证输入的树是 完全二叉树
参考代码
class Solution {
// 通用递归解法
public int countNodes(TreeNode root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}
Node root) {
if(root == null) {
return 0;
}
return countNodes(root.left) + countNodes(root.right) + 1;
}
}