写在前面
以下是微软官方对屏障类的介绍,System.Threading.Barrier 可用来作为实现并发同步操作的基本单元,让多个线程(参与者)分阶段并行处理目标算法。在达到代码中的屏障点之前,每个参与者将继续执行,屏障表示工作阶段的末尾;单个参与者到达屏障后将被阻止,直至所有参与者都已达到同一障碍。 所有参与者都已达到屏障后,你可以选择调用阶段后操作。 此阶段后操作可由单线程用于执行操作,而所有其他线程仍被阻止。执行此操作后,所有参与者将不受阻止,继续执行直到满足退出条件。
下面的程序用于统计两个线程使用随机算法重新随机选择字词,分别在同一阶段查找一半解决方案时所需的迭代次数(或阶段数)。在每个线程随机选择字词后,屏障后阶段操作会比较两个结果,以确定整个句子是否按正确的字词顺序呈现。
关键代码如下:
barrier.SignalAndWait()
设置了代码屏障点,代码运行到这里会等待所有参与的线程都执行完之前的代码。
代码实现
//#define TRACE
using System;
using System.Collections.Generic;
using System.Linq;
using System.Text;
using System.Threading;
using System.Threading.Tasks;
namespace BarrierSimple
{
class Program
{
static string[] words1 = new string[] { "brown", "jumps", "the", "fox", "quick" };
static string[] words2 = new string[] { "dog", "lazy", "the", "over" };
static string solution = "the quick brown fox jumps over the lazy dog.";
static bool success = false;
static Barrier barrier = new Barrier(2, (b) =>
{
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
for (int i = 0; i < words1.Length; i++)
{
sb.Append(words1[i]);
sb.Append(" ");
}
for (int i = 0; i < words2.Length; i++)
{
sb.Append(words2[i]);
if (i < words2.Length - 1)
sb.Append(" ");
}
sb.Append(".");
#if TRACE
System.Diagnostics.Trace.WriteLine(sb.ToString());
#endif
Console.CursorLeft = 0;
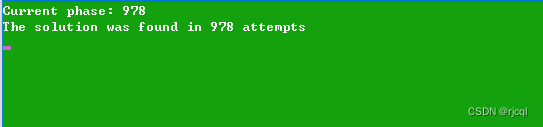
Console.Write("Current phase: {0}", barrier.CurrentPhaseNumber);
if (String.CompareOrdinal(solution, sb.ToString()) == 0)
{
success = true;
Console.WriteLine("\r\nThe solution was found in {0} attempts", barrier.CurrentPhaseNumber);
}
});
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Thread t1 = new Thread(() => Solve(words1));
Thread t2 = new Thread(() => Solve(words2));
t1.Start();
t2.Start();
// Keep the console window open.
Console.ReadLine();
}
// Use Knuth-Fisher-Yates shuffle to randomly reorder each array.
// For simplicity, we require that both wordArrays be solved in the same phase.
// Success of right or left side only is not stored and does not count.
static void Solve(string[] wordArray)
{
while (success == false)
{
Random random = new Random();
for (int i = wordArray.Length - 1; i > 0; i--)
{
int swapIndex = random.Next(i + 1);
string temp = wordArray[i];
wordArray[i] = wordArray[swapIndex];
wordArray[swapIndex] = temp;
}
// We need to stop here to examine results
// of all thread activity. This is done in the post-phase
// delegate that is defined in the Barrier constructor.
barrier.SignalAndWait();
}
}
}
}调用示例