webrtc线程类的实现集成了socket的收发,消息队列,值得研究,基于webrtc75版本。
主要类介绍
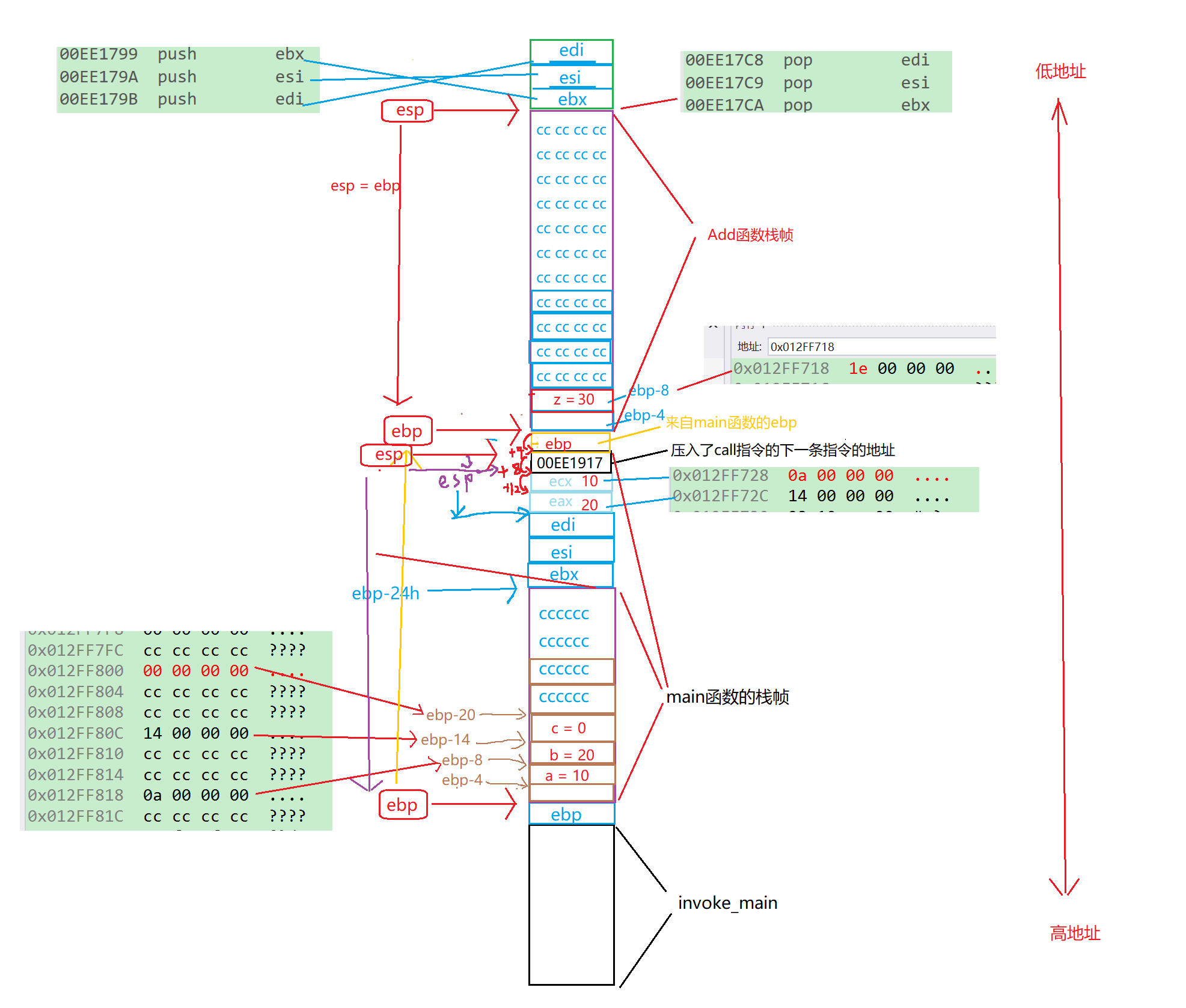
Thread类
虚线:继承 实线:调用 橙色:接口

- Thread继承MessageQueue
- Thread提供两个静态方法,分别用来创建带socket和不带socket的线程:
static std::unique_ptr<Thread> CreateWithSocketServer();
static std::unique_ptr<Thread> Create();调用Thread的Start方法时,会调用Thread::ProcessMessages方法。
bool Thread::ProcessMessages(int cmsLoop) {
// Using ProcessMessages with a custom clock for testing and a time greater
// than 0 doesn't work, since it's not guaranteed to advance the custom
// clock's time, and may get stuck in an infinite loop.
RTC_DCHECK(GetClockForTesting() == nullptr || cmsLoop == 0 ||
cmsLoop == kForever);
int64_t msEnd = (kForever == cmsLoop) ? 0 : TimeAfter(cmsLoop);
int cmsNext = cmsLoop;
while (true) {
#if defined(WEBRTC_MAC)
ScopedAutoReleasePool pool;
#endif
Message msg;
if (!Get(&msg, cmsNext))
return !IsQuitting();
Dispatch(&msg);
if (cmsLoop != kForever) {
cmsNext = static_cast<int>(TimeUntil(msEnd));
if (cmsNext < 0)
return true;
}
}
}- 不断调用MessageQueue::Get函数获取消息队列中的message。
- 获取message后,调用MessageQueue::Dispatch,分发消息。
- Get方法很关键,它获取消息队列中的message,如果MessageQueue有SocketServer对象,调用Wait方法,执行IO的读写操作。
- Linux中Wait实际调用的epoll wait方法,阻塞式获取IO事件,消息队列中如果没有消息,线程一直阻碍。
- PhysicalSocketServer中有一个信号量Signaler(一个pipe),也被epoll管理。当有message加入消息队列时(一个List),信号量发送1个字节的数据,触发epoll的读事件,让线程继续运行。
PhysicalSocketServer::PhysicalSocketServer() : fWait_(false) {
#if defined(WEBRTC_USE_EPOLL)
// Since Linux 2.6.8, the size argument is ignored, but must be greater than
// zero. Before that the size served as hint to the kernel for the amount of
// space to initially allocate in internal data structures.
epoll_fd_ = epoll_create(FD_SETSIZE);
if (epoll_fd_ == -1) {
// Not an error, will fall back to "select" below.
RTC_LOG_E(LS_WARNING, EN, errno) << "epoll_create";
epoll_fd_ = INVALID_SOCKET;
}
#endif
signal_wakeup_ = new Signaler(this, &fWait_);
#if defined(WEBRTC_WIN)
socket_ev_ = WSACreateEvent();
#endif
}
class EventDispatcher : public Dispatcher {
public:
EventDispatcher(PhysicalSocketServer* ss) : ss_(ss), fSignaled_(false) {
RTC_LOG_F(LS_WARNING)<<"EventDispatcher|"<<this;
if (pipe(afd_) < 0)
RTC_LOG(LERROR) << "pipe failed";
ss_->Add(this);
}
~EventDispatcher() override {
ss_->Remove(this);
close(afd_[0]);
close(afd_[1]);
}
virtual void Signal() {
CritScope cs(&crit_);
if (!fSignaled_) {
const uint8_t b[1] = {0};
const ssize_t res = write(afd_[1], b, sizeof(b));
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(1, res);
fSignaled_ = true;
}
}
uint32_t GetRequestedEvents() override { return DE_READ; }
void OnPreEvent(uint32_t ff) override {
// It is not possible to perfectly emulate an auto-resetting event with
// pipes. This simulates it by resetting before the event is handled.
CritScope cs(&crit_);
if (fSignaled_) {
uint8_t b[4]; // Allow for reading more than 1 byte, but expect 1.
const ssize_t res = read(afd_[0], b, sizeof(b));
RTC_DCHECK_EQ(1, res);
fSignaled_ = false;
}
}
void OnEvent(uint32_t ff, int err) override { RTC_NOTREACHED(); }
int GetDescriptor() override { return afd_[0]; }
bool IsDescriptorClosed() override { return false; }
private:
PhysicalSocketServer* ss_;
int afd_[2];
bool fSignaled_;
CriticalSection crit_;
};MessageQueue::Post方法也很重要,用于向消息队列中添加消息。
struct Message {
Message()
: phandler(nullptr), message_id(0), pdata(nullptr), ts_sensitive(0) {}
inline bool Match(MessageHandler* handler, uint32_t id) const {
return (handler == nullptr || handler == phandler) &&
(id == MQID_ANY || id == message_id);
}
Location posted_from;
MessageHandler* phandler;
uint32_t message_id;
MessageData* pdata;
int64_t ts_sensitive;
};
void MessageQueue::Post(const Location& posted_from,
MessageHandler* phandler,
uint32_t id,
MessageData* pdata,
bool time_sensitive) {
if (IsQuitting()) {
delete pdata;
return;
}
// Keep thread safe
// Add the message to the end of the queue
// Signal for the multiplexer to return
{
CritScope cs(&crit_);
Message msg;
msg.posted_from = posted_from;
msg.phandler = phandler;
msg.message_id = id;
msg.pdata = pdata;
if (time_sensitive) {
msg.ts_sensitive = TimeMillis() + kMaxMsgLatency;
}
msgq_.push_back(msg);
}
WakeUpSocketServer();
}
class MessageHandler {
public:
virtual ~MessageHandler();
virtual void OnMessage(Message* msg) = 0;
protected:
MessageHandler() {}
private:
RTC_DISALLOW_COPY_AND_ASSIGN(MessageHandler);
};MessageHandler是消息的回调接口,MessageData是消息的输入数据。线程取出消息,并调用MessageHandler的OnMessage方法。
【免费分享】音视频学习资料包、大厂面试题、技术视频和学习路线图,资料包括(C/C++,Linux,FFmpeg webRTC rtmp hls rtsp ffplay srs 等等)有需要的可以点击788280672加群免费领取~

小例子
客户端发数字1,服务端累加后返回给客户端。客户端收到数据后,加加,继续发送给服务端。如此反复循环。
#include <iostream>
#include "rtc_base/thread.h"
#include "rtc_base/async_invoker.h"
#include "rtc_base/event.h"
#include "rtc_base/null_socket_server.h"
#include "rtc_base/physical_socket_server.h"
#include "rtc_base/socket_address.h"
#include "rtc_base/third_party/sigslot/sigslot.h"
#include "rtc_base/async_udp_socket.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace rtc;
struct MyMessage : public MessageData {
explicit MyMessage(int v) : value(v) {}
int value;
};
class Client : public MessageHandler,public sigslot::has_slots<> {
public:
Client(AsyncUDPSocket* socket,Thread * thread) : socket_(socket),thread_(thread) {
// 用到了webrtc的sigslot,需要专门写篇文章。
// 简单理解:OnPacket注册为socket的数据读取回调。
socket_->SignalReadPacket.connect(this, &Client::OnPacket);
}
~Client() {
delete socket_;
}
// 消息队列中,消息触发后的回调。
void OnMessage(Message* pmsg) override {
MyMessage* msg = static_cast<MyMessage*>(pmsg->pdata);
PacketOptions opt;
socket_->Send(&msg->value, sizeof(msg->value),opt);
delete msg;
}
void OnPacket(AsyncPacketSocket* socket,
const char* buf,
size_t size,
const SocketAddress& remote_addr,
const int64_t& packet_time_us) {
uint32_t data = reinterpret_cast<const uint32_t*>(buf)[0];
cout << "---Recv server data:"<<data<<endl;
data++;
// 收到服务端的消息,累加后,继续发送给服务端
thread_->PostDelayed(RTC_FROM_HERE, 2000, this, 0,new MyMessage(data));
}
private:
AsyncUDPSocket* socket_;
Thread * thread_;
};
class Server : public MessageHandler,public sigslot::has_slots<> {
public:
Server(AsyncUDPSocket* socket,Thread * thread) : socket_(socket),thread_(thread) {
socket_->SignalReadPacket.connect(this, &Server::OnPacket);
}
~Server() {
delete socket_;
}
void OnMessage(Message* pmsg) override {
MyMessage* msg = static_cast<MyMessage*>(pmsg->pdata);
PacketOptions opt;
socket_->SendTo(&msg->value, sizeof(msg->value),remote_addr_,opt);
delete msg;
}
void OnPacket(AsyncPacketSocket* socket,
const char* buf,
size_t size,
const SocketAddress& remote_addr,
const int64_t& packet_time_us) {
remote_addr_=remote_addr;
uint32_t data = reinterpret_cast<const uint32_t*>(buf)[0];
cout << "---Recv client data:"<<data<<"|"<<remote_addr_.ToString()<<endl;
data++;
// 收到客户端的消息,累加后,继续发送给客户端
thread_->PostDelayed(RTC_FROM_HERE, 2000, this, 0,new MyMessage(data));
}
private:
AsyncUDPSocket* socket_;
Thread * thread_;
SocketAddress remote_addr_;
};
int main(){
// 客户端
SocketAddress addr1("0.0.0.0", 7000);
std::unique_ptr<Thread> th1=Thread::CreateWithSocketServer();
AsyncSocket* sock1 = th1->socketserver()->CreateAsyncSocket(addr1.family(), SOCK_DGRAM);
AsyncUDPSocket * clientSock=AsyncUDPSocket::Create(sock1, addr1);
Client client(clientSock,th1.get());
// 服务端
SocketAddress addr2("0.0.0.0", 7001);
std::unique_ptr<Thread> th2=Thread::CreateWithSocketServer();
AsyncSocket* sock2 = th2->socketserver()->CreateAsyncSocket(addr2.family(), SOCK_DGRAM);
AsyncUDPSocket * serverSock=AsyncUDPSocket::Create(sock2, addr2);
Server server(serverSock,th2.get());
sock1->Connect(serverSock->GetLocalAddress());
th1->Start();
th2->Start();
// 触发终端发数据,向线程的消息队列添加Message
th1->PostDelayed(RTC_FROM_HERE, 1000, &client, 0, new MyMessage(1));
// 主线程,无限循环,避免程序退出
Thread::Current()->ProcessMessages(-1);
return 0;
}#include <iostream>
#include "rtc_base/thread.h"
#include "rtc_base/async_invoker.h"
#include "rtc_base/event.h"
#include "rtc_base/null_socket_server.h"
#include "rtc_base/physical_socket_server.h"
#include "rtc_base/socket_address.h"
#include "rtc_base/third_party/sigslot/sigslot.h"
#include "rtc_base/async_udp_socket.h"
using namespace std;
using namespace rtc;
enum {
MSG_ACTION_A = 0,
MSG_ACTION_B,
MSG_ACTION_C,
};
struct MyMessage : public MessageData {
explicit MyMessage(int v) : value(v) {}
int value;
};
class MyHandler : public MessageHandler {
public:
MyHandler(){}
~MyHandler(){}
void OnMessage(Message* msg) override {
switch (msg->message_id) {
case MSG_ACTION_A: {
MyMessage * param = static_cast<MyMessage*>(msg->pdata);
cout << "---Action A | "<<param->value<<endl;
delete param;
break;
}
case MSG_ACTION_B: {
MyMessage * param = static_cast<MyMessage*>(msg->pdata);
cout << "---Action B | "<<param->value<<endl;
delete param;
break;
}
case MSG_ACTION_C: {
MyMessage * param = static_cast<MyMessage*>(msg->pdata);
cout << "---Action C | "<<param->value<<endl;
delete param;
break;
}
default:
cout << "Not implemented" << endl;
break;
}
}
void Func1(int a){
cout << "----a:"<<a<<endl;
}
};
int main(){
std::unique_ptr<Thread> th1=Thread::Create();
th1->Start();
MyHandler handler;
// 往消息队列Add消息,不阻塞主线程
th1->Post(RTC_FROM_HERE, &handler, MSG_ACTION_A, new MyMessage(1));
th1->Post(RTC_FROM_HERE, &handler, MSG_ACTION_B, new MyMessage(2));
// Add消息,会阻塞主线程,一般不调用这个方法
th1->Send(RTC_FROM_HERE,&handler,MSG_ACTION_C,new MyMessage(4));
th1->Send(RTC_FROM_HERE,&handler,MSG_ACTION_C,new MyMessage(5));
th1->Send(RTC_FROM_HERE,&handler,MSG_ACTION_C,new MyMessage(6));
// Thread提供了Invoke和PostTask模板函数,一个用于同步,一个用于异步
// 阻塞主线程,同步调用
// 让某个方法在th1中运行
th1->Invoke<void>(RTC_FROM_HERE,[](){
cout << "--lambda func" <<endl;
});
// 异步调用,采用Bind方式,也可以是lambda函数
th1->PostTask(RTC_FROM_HERE,Bind(&MyHandler::Func1,&handler,90));
// 主线程,无限循环,避免程序退出
Thread::Current()->ProcessMessages(-1);
return 0;
}ProcessThread类
这种线程在webrtc modules中使用,例如PacerThread、ModuleProcessThread就用的这种线程。

- 可以注册多个Module到ProcessThread中。
- ProccessThread实际调用的PlatformThread,Platform Thread为对系统层的thread的封装。
class ProcessThread {
public:
virtual ~ProcessThread();
static std::unique_ptr<ProcessThread> Create(const char* thread_name);
// Starts the worker thread. Must be called from the construction thread.
virtual void Start() = 0;
// Stops the worker thread. Must be called from the construction thread.
virtual void Stop() = 0;
// Wakes the thread up to give a module a chance to do processing right
// away. This causes the worker thread to wake up and requery the specified
// module for when it should be called back. (Typically the module should
// return 0 from TimeUntilNextProcess on the worker thread at that point).
// Can be called on any thread.
virtual void WakeUp(Module* module) = 0;
// Queues a task object to run on the worker thread. Ownership of the
// task object is transferred to the ProcessThread and the object will
// either be deleted after running on the worker thread, or on the
// construction thread of the ProcessThread instance, if the task did not
// get a chance to run (e.g. posting the task while shutting down or when
// the thread never runs).
virtual void PostTask(std::unique_ptr<QueuedTask> task) = 0;
// Adds a module that will start to receive callbacks on the worker thread.
// Can be called from any thread.
virtual void RegisterModule(Module* module, const rtc::Location& from) = 0;
// Removes a previously registered module.
// Can be called from any thread.
virtual void DeRegisterModule(Module* module) = 0;
};
class Module {
public:
// Returns the number of milliseconds until the module wants a worker
// thread to call Process.
// This method is called on the same worker thread as Process will
// be called on.
// TODO(tommi): Almost all implementations of this function, need to know
// the current tick count. Consider passing it as an argument. It could
// also improve the accuracy of when the next callback occurs since the
// thread that calls Process() will also have it's tick count reference
// which might not match with what the implementations use.
virtual int64_t TimeUntilNextProcess() = 0;
// Process any pending tasks such as timeouts.
// Called on a worker thread.
virtual void Process() = 0;
// This method is called when the module is attached to a *running* process
// thread or detached from one. In the case of detaching, |process_thread|
// will be nullptr.
//
// This method will be called in the following cases:
//
// * Non-null process_thread:
// * ProcessThread::RegisterModule() is called while the thread is running.
// * ProcessThread::Start() is called and RegisterModule has previously
// been called. The thread will be started immediately after notifying
// all modules.
//
// * Null process_thread:
// * ProcessThread::DeRegisterModule() is called while the thread is
// running.
// * ProcessThread::Stop() was called and the thread has been stopped.
//
// NOTE: This method is not called from the worker thread itself, but from
// the thread that registers/deregisters the module or calls Start/Stop.
virtual void ProcessThreadAttached(ProcessThread* process_thread) {}
protected:
virtual ~Module() {}
};- Module的实现类需要实现TimeUntilNextProcess,Process接口。代表线程每隔多少毫秒调用一次Process接口。
- ProccessThread的PostTask方法,代表向当前线程添加任务。
核心的两个方法如下
// static
bool ProcessThreadImpl::Run(void* obj) {
return static_cast<ProcessThreadImpl*>(obj)->Process();
}
bool ProcessThreadImpl::Process() {
TRACE_EVENT1("webrtc", "ProcessThreadImpl", "name", thread_name_);
int64_t now = rtc::TimeMillis();
int64_t next_checkpoint = now + (1000 * 60);
{
rtc::CritScope lock(&lock_);
if (stop_)
return false;
for (ModuleCallback& m : modules_) {
// TODO(tommi): Would be good to measure the time TimeUntilNextProcess
// takes and dcheck if it takes too long (e.g. >=10ms). Ideally this
// operation should not require taking a lock, so querying all modules
// should run in a matter of nanoseconds.
if (m.next_callback == 0)
m.next_callback = GetNextCallbackTime(m.module, now);
if (m.next_callback <= now ||
m.next_callback == kCallProcessImmediately) {
{
TRACE_EVENT2("webrtc", "ModuleProcess", "function",
m.location.function_name(), "file",
m.location.file_and_line());
m.module->Process();
}
// Use a new 'now' reference to calculate when the next callback
// should occur. We'll continue to use 'now' above for the baseline
// of calculating how long we should wait, to reduce variance.
int64_t new_now = rtc::TimeMillis();
m.next_callback = GetNextCallbackTime(m.module, new_now);
}
if (m.next_callback < next_checkpoint)
next_checkpoint = m.next_callback;
}
while (!queue_.empty()) {
QueuedTask* task = queue_.front();
queue_.pop();
lock_.Leave();
task->Run();
delete task;
lock_.Enter();
}
}
int64_t time_to_wait = next_checkpoint - rtc::TimeMillis();
if (time_to_wait > 0)
wake_up_.Wait(static_cast<int>(time_to_wait));
return true;
}原文链接 webrtc线程代码研究 - 掘金