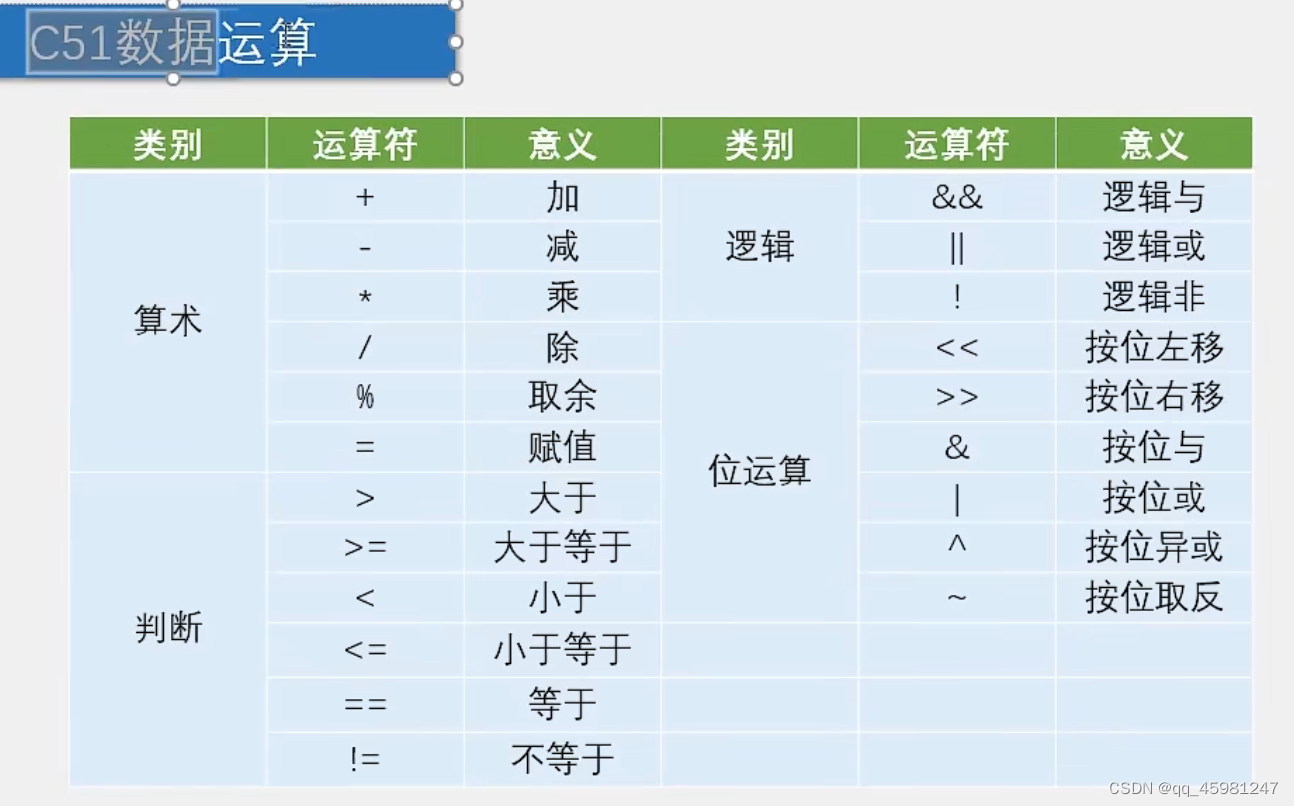
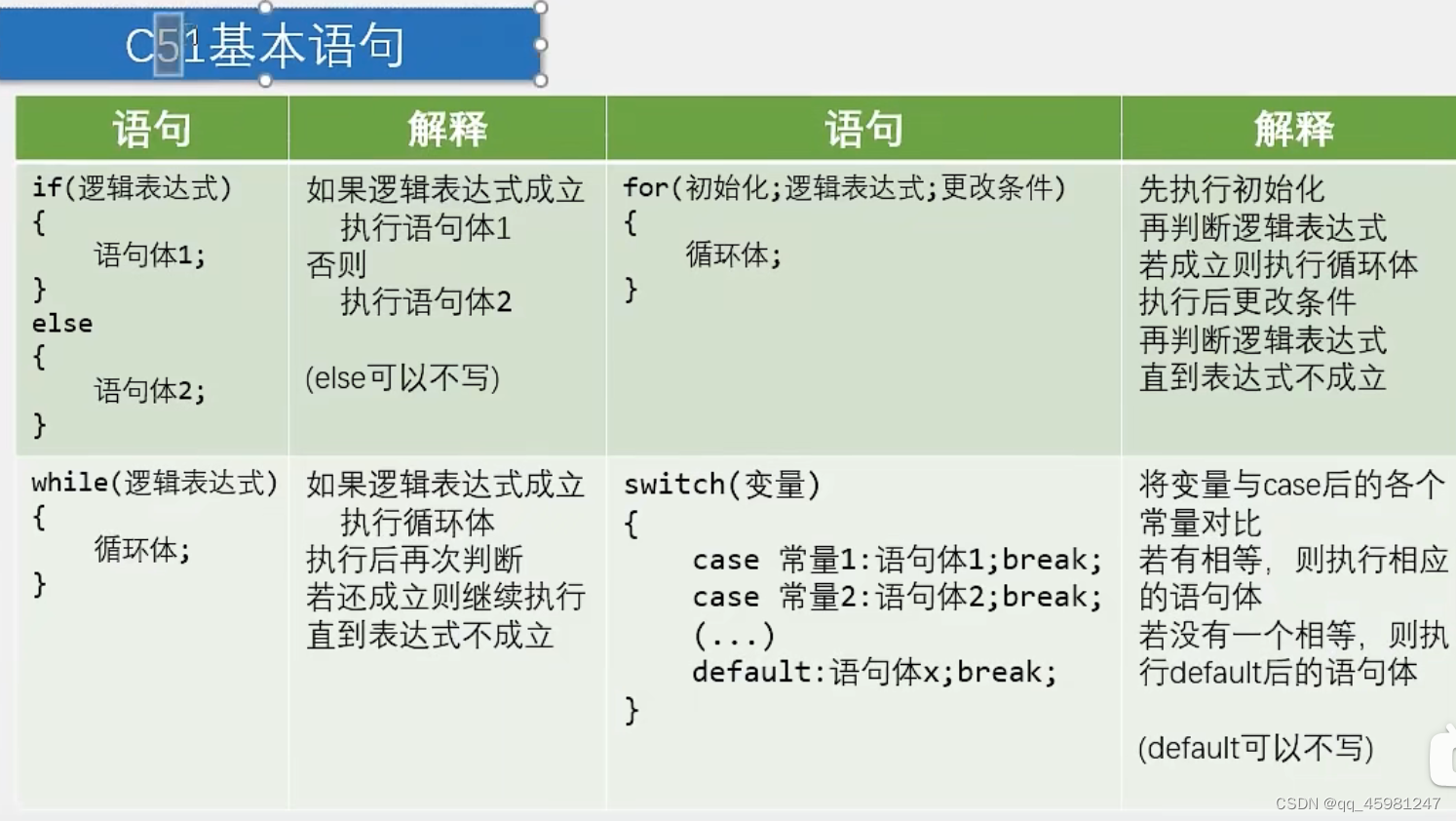
目录
单片机介绍
点亮一个LED
流水灯参考代码
点亮流水LEDplus版本
独立按键
独立按键控制LED亮灭
静态数码管
静态数码管显示
动态数码管显示
模块化编程
调试工具
矩阵键盘
矩阵键盘显示数据
矩阵键盘密码锁
学习B站江协科技课程笔记。
安装keil,下载大佬简介内的应用,注意注册机是keygen那个文件,解压前先关闭防火墙。
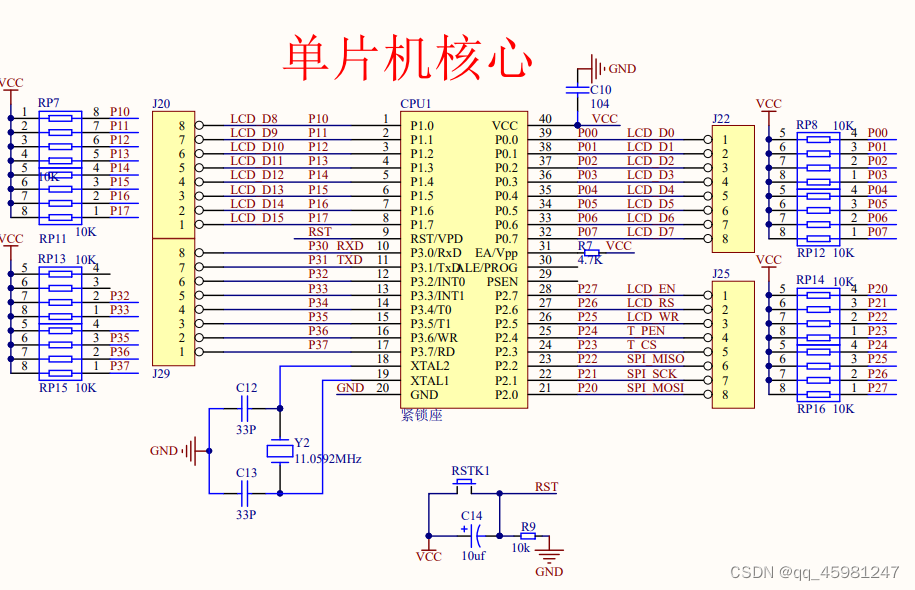
单片机介绍
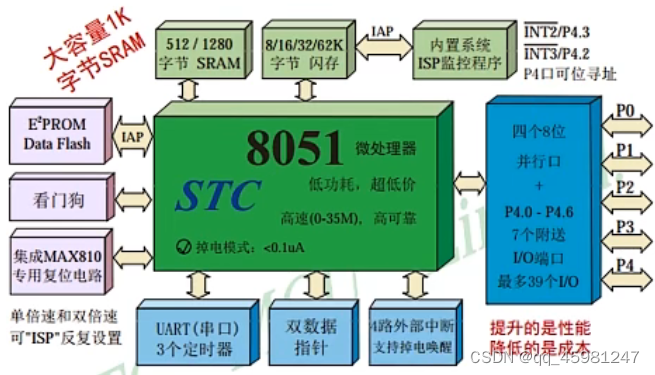
单片机,Micro Controller Unit,简称MCU
内部集成了CPU、ARM、ROM、定时器、中断系统、通讯接口等一系列电脑的常用硬件功能
单片机的任务是信息采集(依靠传感器)、处理(依靠CPU)和硬件设备(例如电机、LED等)的控制
单片机跟计算机相比,单片机算是一个袖珍版计算机,一个芯片就能构成完整的计算机系统。但性能上,与计算机相差甚远,但单片机成本低,体积小,结构简单,在生活和工业控制领域大有所用
同时,学习使用单片机是了解计算机原理与结构的最佳选择
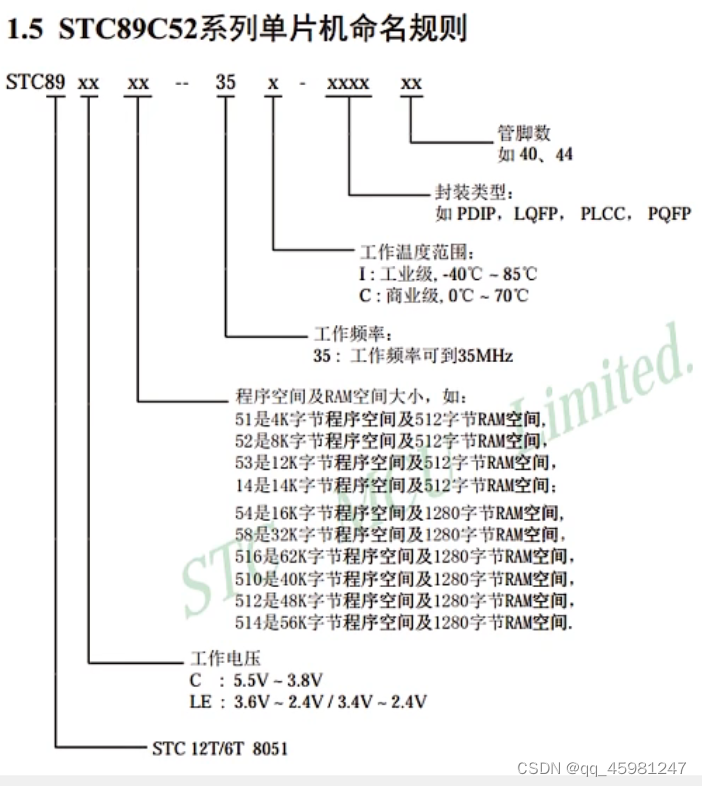
STC89C52单片机
所属系列:51单片机系列
公司:STC公司
位数:8位
RAM:512字节
ROM:8k(flash)
工作频率:12MHz(本开发板使用)
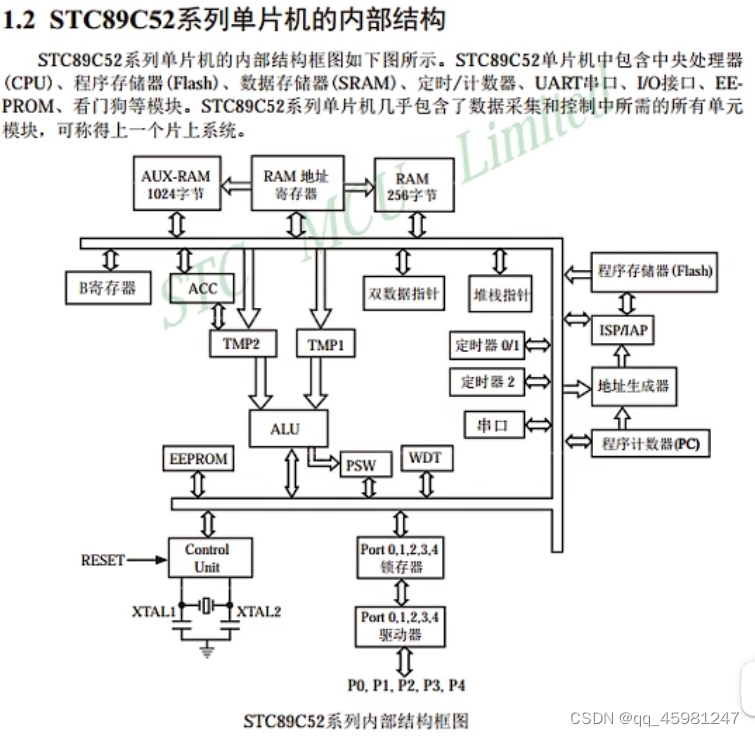
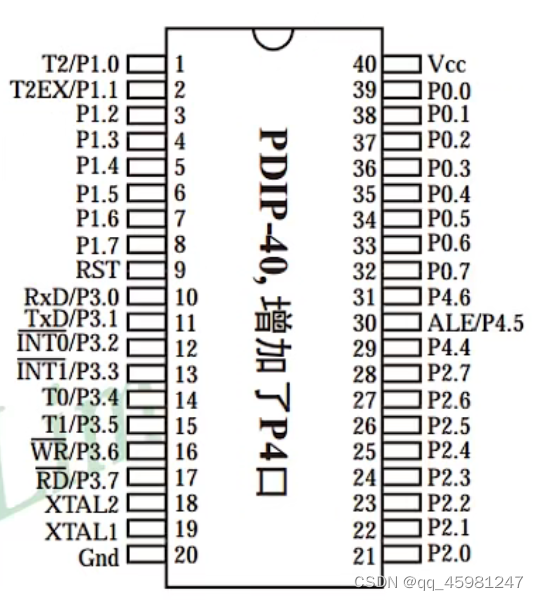
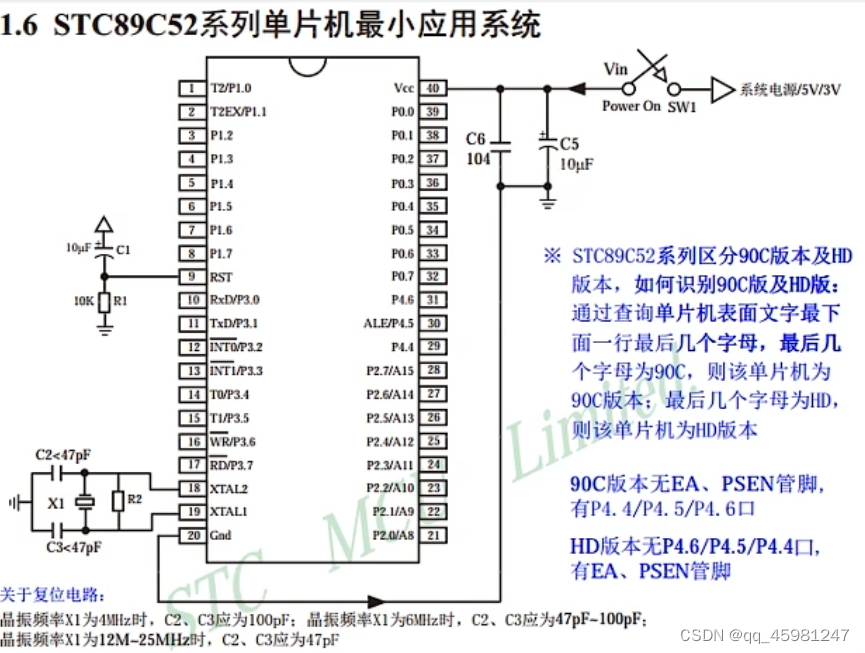

LED介绍
中文名:发光二极管
外文名:Light Emitting Diode
简称:LED
用途:照明、广告灯、指引灯、屏幕
keil中新建文件选择CPU:Atmel ->at89c52

本想使用proteus进行模拟实验,技术力不太足够。只好浅浅投资了
点亮一个LED
先进行编程

注意:P2 端口大写,为什么是P2
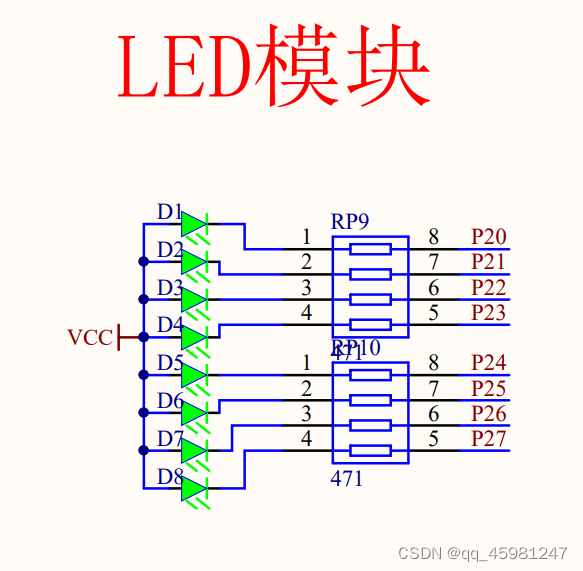
P21到P27都由P2.X进行控制,为什么亮的位置置零,设置低电平才会有电流流过,要用16进制数进行设置,0x...。烧录时注意单片机型号在上面有写,打开生成的.hex文件,点击下载/编程。然后重启单片机。右下角显示

keil编辑新项目:
1.创建项目
2.选择芯片类型
3.添加主函数
4.编入程序
延时函数:
void Delay500ms() //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j, k;
_nop_();//¿ÕÓï¾ä
i = 4;
j = 205;
k = 187;
do
{
do
{
while (--k);
} while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
使其能够进行亮灭控制,注意加入 INTRINS.H 头函数,以及每写一句记得加 ;
流水灯参考代码
#include <REGX52.H>
#include <INTRINS.H>
void Delay500ms() //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j, k;
_nop_();
i = 4;
j = 205;
k = 187;
do
{
do
{
while (--k);
} while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
void main(){
while(1){
P2 = 0xFE;//1111 1110
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xFD;//1111 1101
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xFB;//1111 1011
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xF7;//1111 0111
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xEF;//1110 1111
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xDF;//1101 1111
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0xBF;//1011 1111
Delay500ms();
P2 = 0x7F;//0111 1111
Delay500ms();
}
}点亮流水LEDplus版本
#include <REGX52.H>
void Delay1ms(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
while (xms) {
unsigned char i, j;
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms --;
}
}
void main(){
while(1){
P2 = 0xFE;//1111 1110
Delay1ms(500);
P2 = 0xFD;//1111 1101
Delay1ms(500);
P2 = 0xFB;//1111 1011
Delay1ms(500);
P2 = 0xF7;//1111 0111
Delay1ms(500);
P2 = 0xEF;//1110 1111
Delay1ms(500);
P2 = 0xDF;//1101 1111
Delay1ms(500);
P2 = 0xBF;//1011 1111
Delay1ms(500);
P2 = 0x7F;//0111 1111
Delay1ms(500);
}
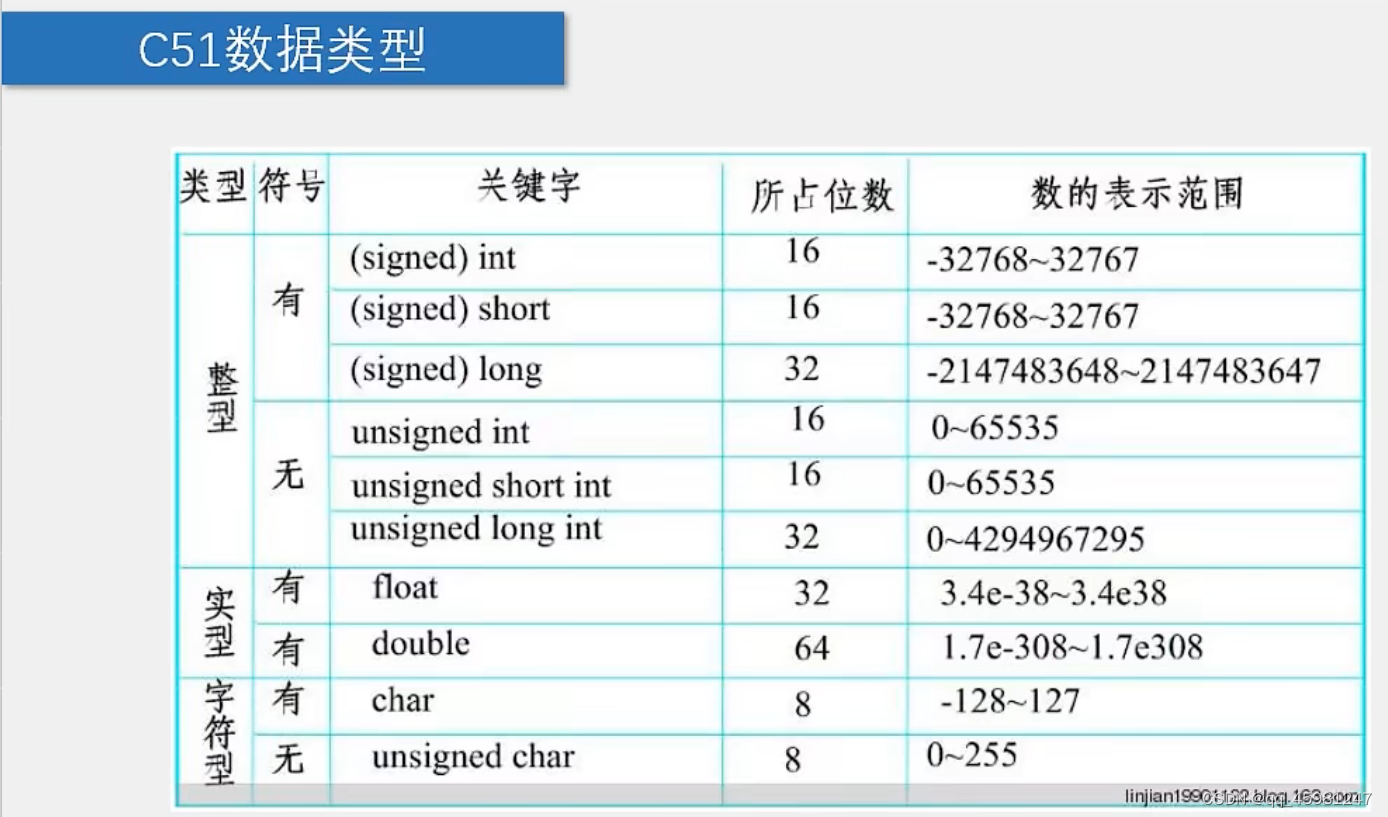
}
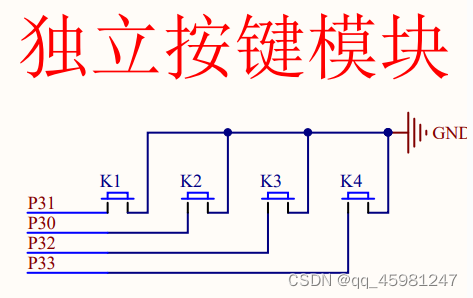
独立按键
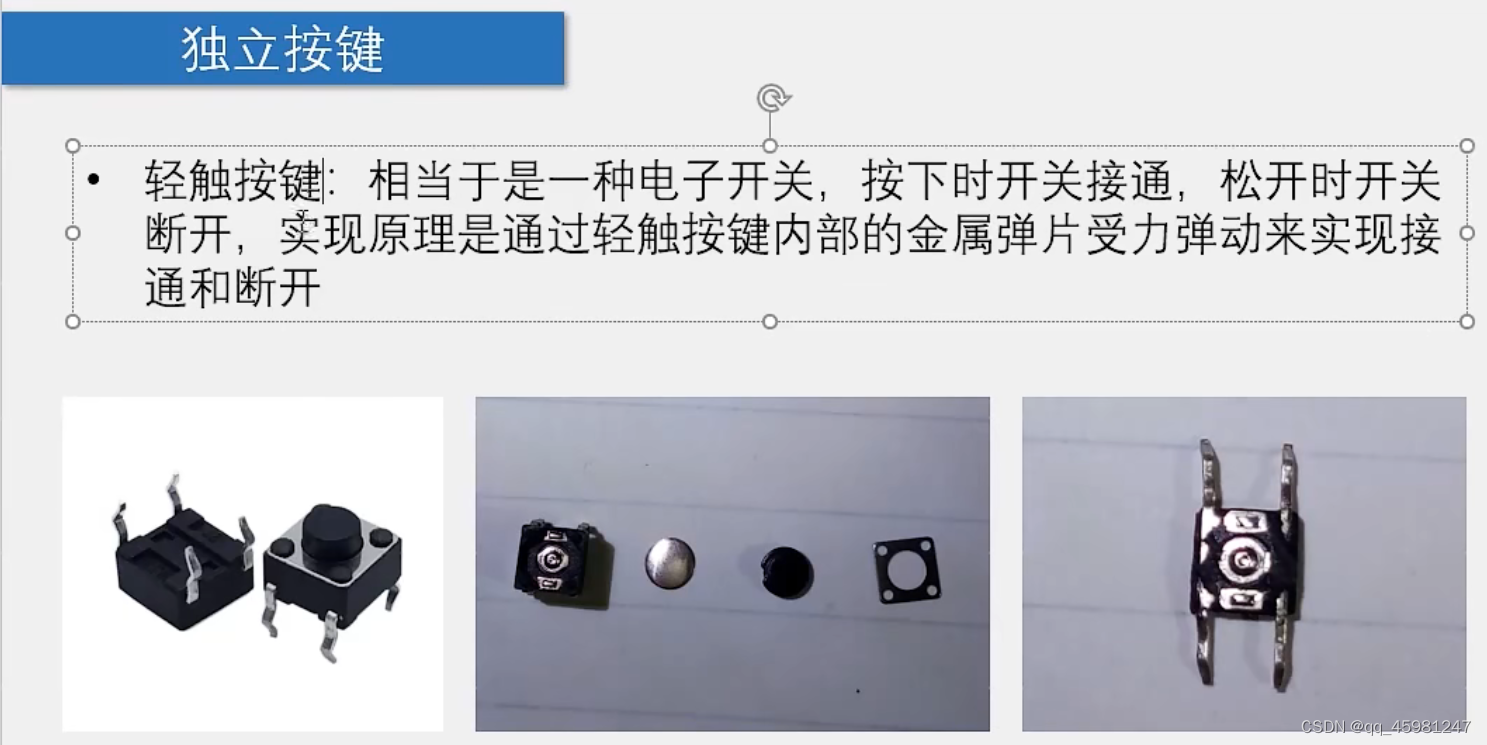
独立按键控制LED亮灭
#include <REGX52.H>
void main(){
//P2 = 0xFE;//1111 1110操作八位寄存器给八位
P2_0 = 0;//操作一位寄存器给一位赋值即可,控制其亮
P2_0 = 1;//控制其灭
while(1){
if(P3_1 == 0){
P2_0 = 0;
}else{
P2_0 = 1;
}
}
}为什么是P3_1
独立按键控制LED状态
#include <REGX52.H>
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms){
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
xms--;
}
}
void main(){
while(1){
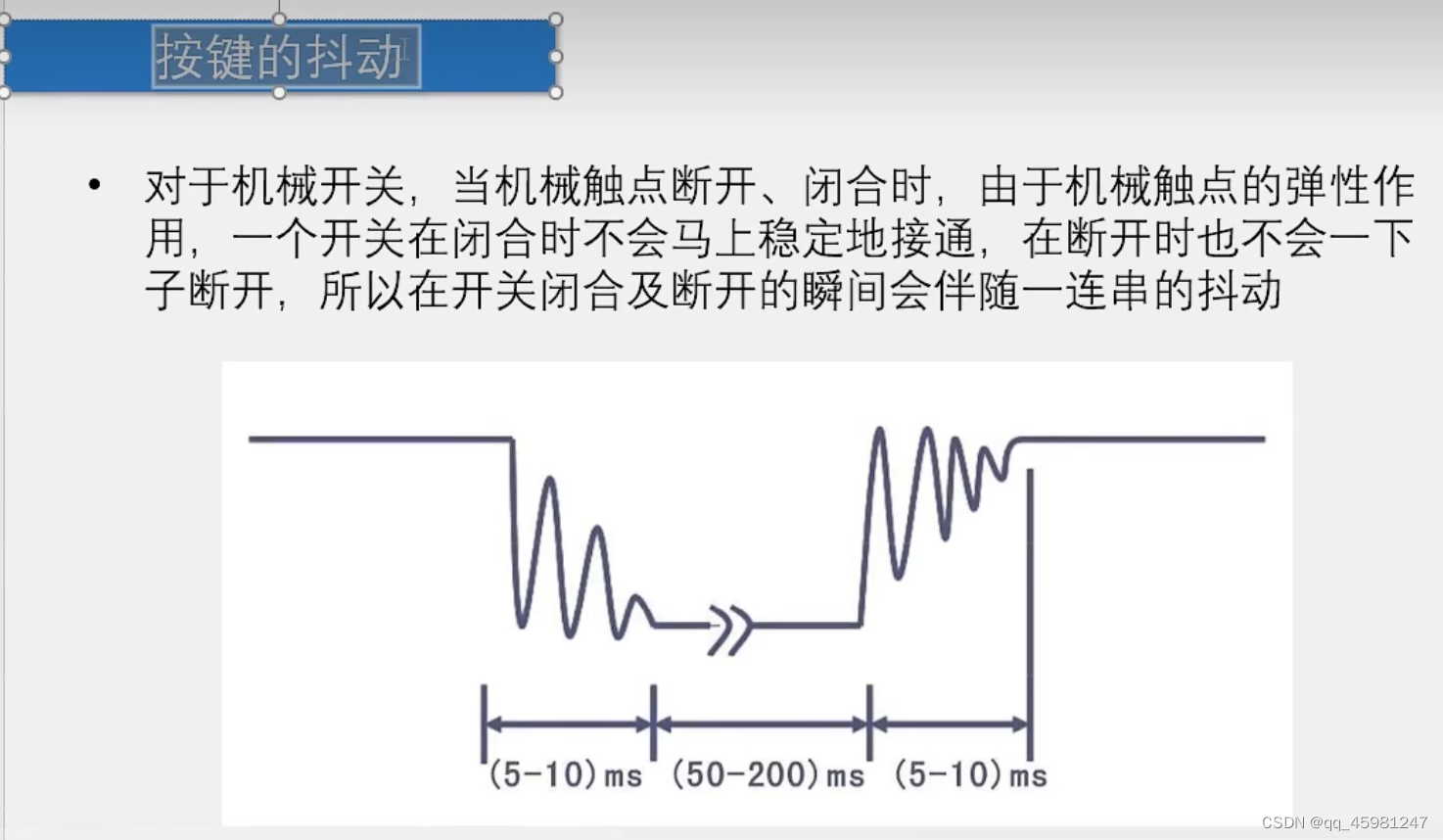
//按下过后弹起才变化电平
if(P3_1 == 0){//按下按键
Delay(20);//除抖,这段时间都是低电平
while(P3_1 == 0);//再次判断,这时是低电平,是否是持续按下的
//如果是真的是就什么都不做。等待弹起
Delay(20);//除抖,这段时间变为高电平
//按下并弹起后引起灯灭灯亮
P2_0 = ~P2_0;
}
}
}独立按键控制二进制输出
#include <REGX52.H>
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms--){
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
}
void main(){
unsigned char LEDNum = 0;
while(1){
if(P3_1 == 0){
Delay(20);
while(P3_1 == 0);
Delay(20);
LEDNum ++;//
P2 = ~LEDNum;//按位取反
}
}
}多个按键实现移位
#include <REGX52.H>
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms--){
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
}
unsigned char LEDNum;
void main(){
P2 =~0x01;
while (1){
if ( P3_1 == 0 ){
Delay(20);
while ( P3_1 == 0 )
Delay(20);
LEDNum ++ ;
if( LEDNum >= 8 )
LEDNum = 0;
P2 = ~( 0x01 << LEDNum );
}
if ( P3_0 == 0 ){
Delay(20);
while ( P3_0 == 0 )
Delay(20);
if(LEDNum == 0){
LEDNum = 7 ;
}else{
LEDNum --;
}
P2 = ~( 0x01 << LEDNum );
}
}
}对固定值进行位移时,选择同一方向。
静态数码管

公用引脚
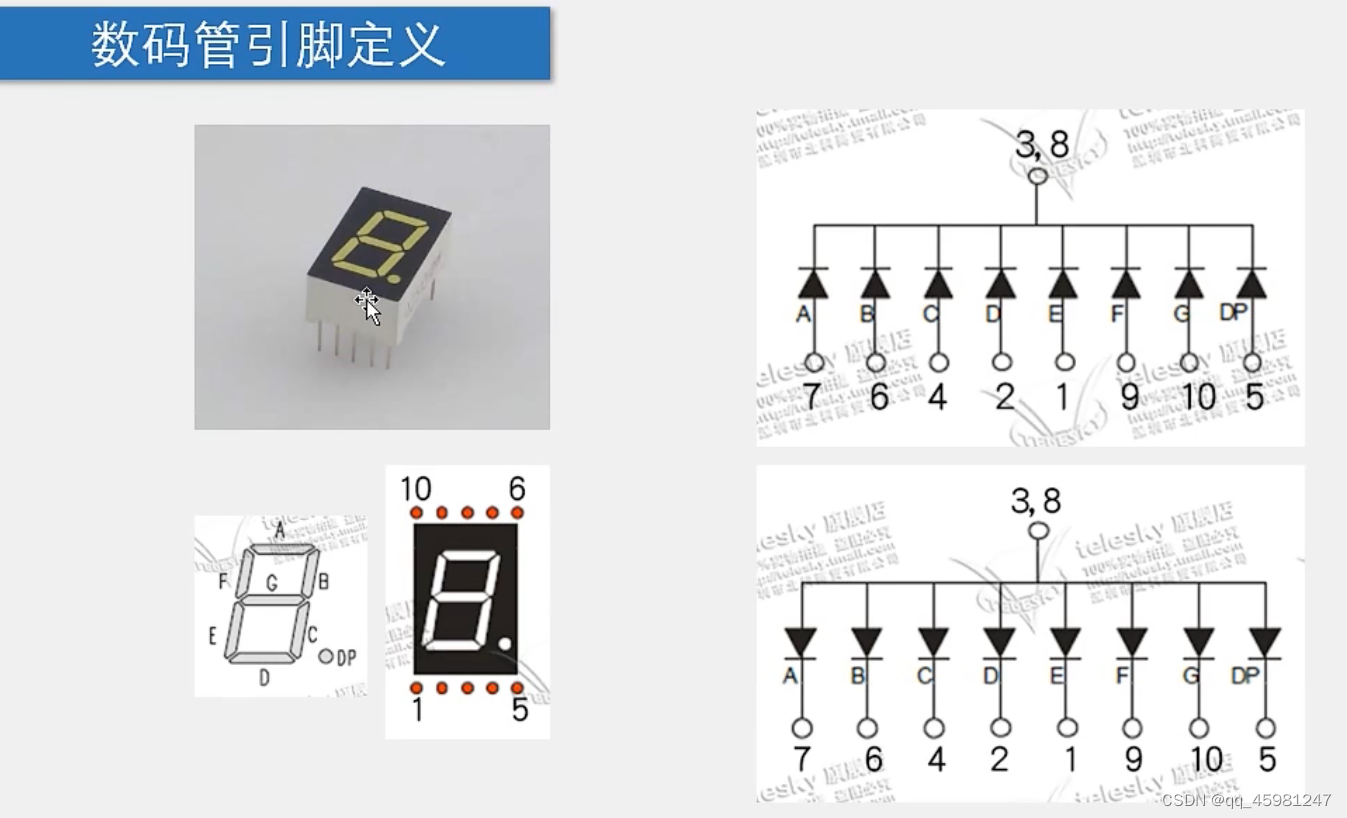
共阴极(上)与共阳极连接(下),想选中该数码管就要赋值0,反之1,共阴极要想亮就设置高电平(为公共的地方是接地的,需要高电平流过),共阳极要想亮就设置低电平(公共的地方是接电的,需要低电平流过)
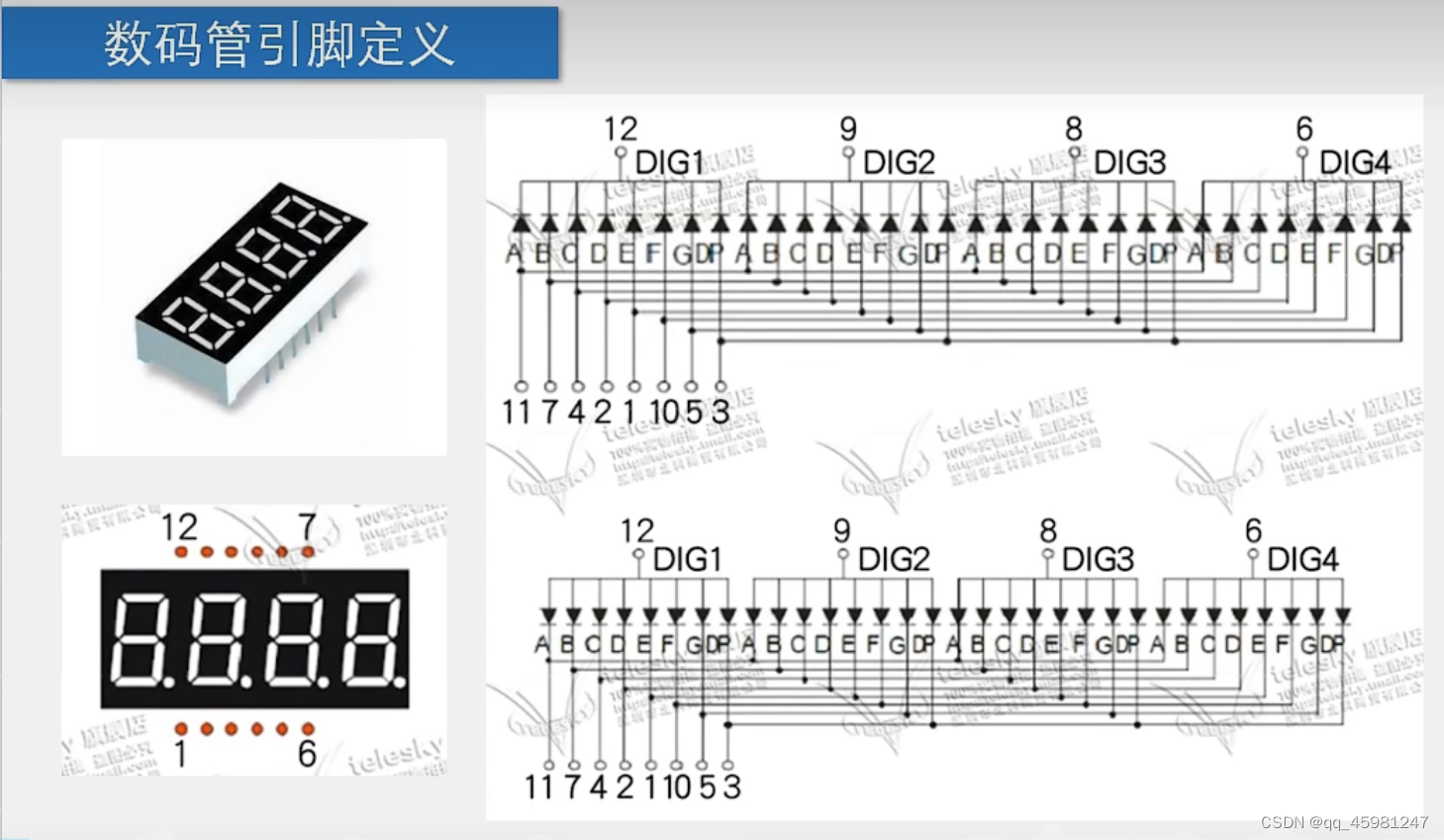
共阴极(上)与共阳极(下)连接方式。与上同理
静态数码管显示
电容单位,进率为1000
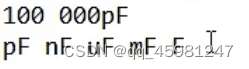


输出静态数字
例如选择第三个数码管显示6;
#include <REGX52.H>
void main(){
P2_4 = 1;//101
P2_3 = 0;
P2_2 = 1;
P0 = 0x7D;
while(1){
}
}
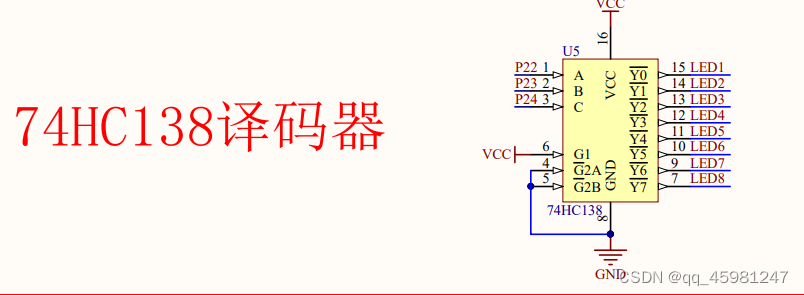

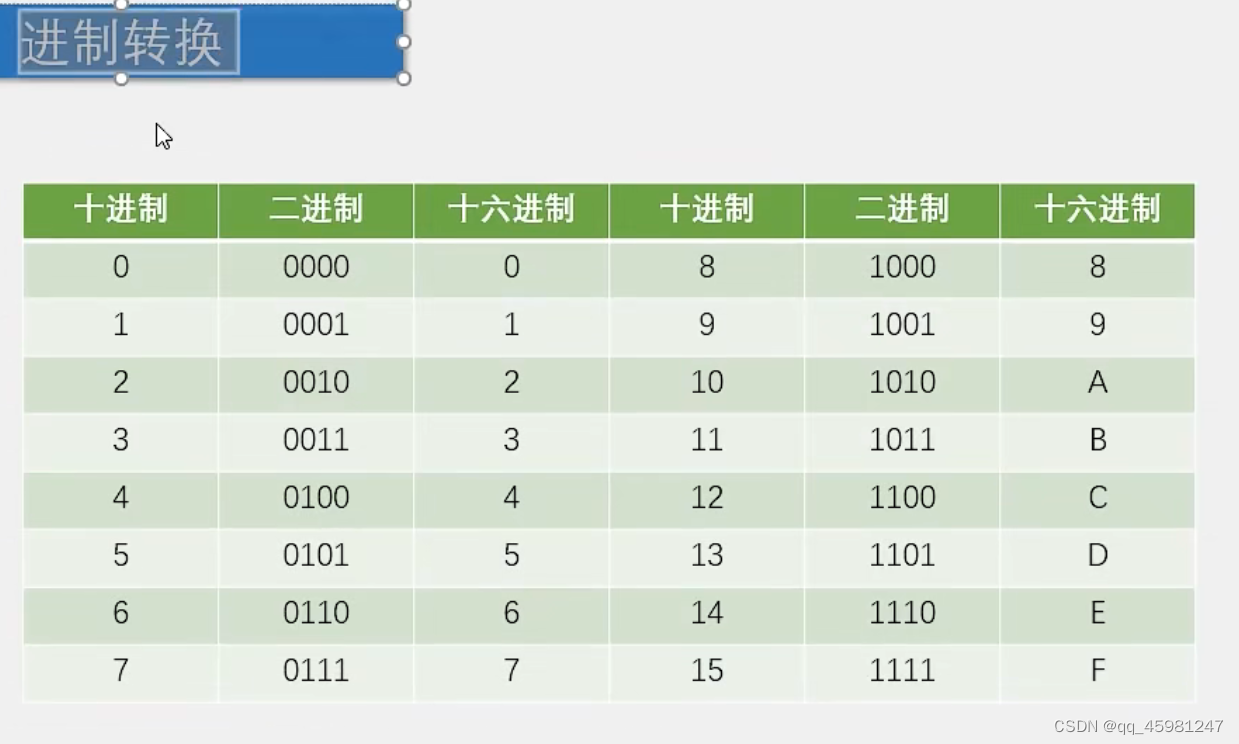
其中为什么是P2_2~P2_4进行赋值,因为数码管连接译码器,由译码器输入高低电平进行显示,这里赋值是为了选择第几个led亮,从左往右的第三个代表着LED6,而LED6需要Y5进行输入,需要三位二进制数代表5,从而使其被选择,即101,此时LED6已被选中,6需要acdefg灯管亮,又因为是共阴极,故1才代表亮,从上至下写出应为 1011 1110,最后一个代表dp而从左边输入到右边需要从下往上进行输入故需要倒置为 0111 1101转化为十六进制为 0x7D

就如6的来历,段码表也是这样推出来的。
将显示的位置以及显示的数字抽象为一个函数。
#include <REGX52.H>
unsigned char NixieTable [] = {0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,
0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x6F};
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number){
switch(Location){
case 1:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 2:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;
case 3:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 4:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;
case 5:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 6:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;
case 7:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 8:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;
}
P0 = NixieTable[Number];
}
void main(){
Nixie(7,2);
while(1){
}
}
动态数码管显示
消影

#include <REGX52.H>
unsigned char NixieTable [] = {0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,
0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x6F};
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms--){
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
}
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number){
switch(Location){
case 1:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 2:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;
case 3:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 4:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;
case 5:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 6:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;
case 7:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 8:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;
}
P0 = NixieTable[Number];
Delay(1);//消影操作
P0 = 0x00;
}
void main(){
while(1){
Nixie(1,1);
//Delay(1);
Nixie(2,2);
//Delay(1);
Nixie(3,3);
//Delay(1);
}
}
模块化编程




模块化编程需要注意:
1.使用ifndef 以及 define 尽量将被定义的变量进行大写。
2. .c文件放置函数体以及被调用的头文件, .h文件放置函数声明以及预编译语句
3.函数声明句末记得添加 ;
将Delay函数变为一个模块
Delay.h中
#ifndef __DELAY_H__
#define __DELAY_H__
void Delay(unsigned int xms);
#endifDelay.c中
void Delay(unsigned int xms) //@12.000MHz
{
unsigned char i, j;
while(xms--){
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
}将晶体管显示也转变为一个模块
Nixie.h中
#ifndef __NIXIE_H__
#def __NIXIE_H__
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number);
#endifNixie.c中
#include <REGX52.H>
#include "Delay.h"
unsigned char NixieTable [] = {0x3F,0x06,0x5B,0x4F,0x66,
0x6D,0x7D,0x07,0x7F,0x6F};
void Nixie(unsigned char Location,Number){
switch(Location){
case 1:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 2:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;
case 3:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 4:
P2_4 = 1;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;
case 5:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 6:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 1;P2_2 = 0;break;
case 7:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 1;break;
case 8:
P2_4 = 0;P2_3 = 0;P2_2 = 0;break;
}
P0 = NixieTable[Number];
Delay(1);
P0 = 0x00;
}在需要的地方进行引用头文件以及调用函数即可。
调试工具

加入LCD1602调试头文件以及c语言文件
LCD1602.h
#ifndef __LCD1602_H__
#define __LCD1602_H__
//用户调用函数:
void LCD_Init();
void LCD_ShowChar(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char Char);
void LCD_ShowString(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char *String);
void LCD_ShowNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length);
void LCD_ShowSignedNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,int Number,unsigned char Length);
void LCD_ShowHexNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length);
void LCD_ShowBinNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length);
#endif
LCD1602.c
#include <REGX52.H>
//引脚配置:
sbit LCD_RS=P2^6;
sbit LCD_RW=P2^5;
sbit LCD_EN=P2^7;
#define LCD_DataPort P0
//函数定义:
/**
* @brief LCD1602延时函数,12MHz调用可延时1ms
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_Delay()
{
unsigned char i, j;
i = 2;
j = 239;
do
{
while (--j);
} while (--i);
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602写命令
* @param Command 要写入的命令
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_WriteCommand(unsigned char Command)
{
LCD_RS=0;
LCD_RW=0;
LCD_DataPort=Command;
LCD_EN=1;
LCD_Delay();
LCD_EN=0;
LCD_Delay();
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602写数据
* @param Data 要写入的数据
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_WriteData(unsigned char Data)
{
LCD_RS=1;
LCD_RW=0;
LCD_DataPort=Data;
LCD_EN=1;
LCD_Delay();
LCD_EN=0;
LCD_Delay();
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602设置光标位置
* @param Line 行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 列位置,范围:1~16
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_SetCursor(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column)
{
if(Line==1)
{
LCD_WriteCommand(0x80|(Column-1));
}
else if(Line==2)
{
LCD_WriteCommand(0x80|(Column-1+0x40));
}
}
/**
* @brief LCD1602初始化函数
* @param 无
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_Init()
{
LCD_WriteCommand(0x38);//八位数据接口,两行显示,5*7点阵
LCD_WriteCommand(0x0c);//显示开,光标关,闪烁关
LCD_WriteCommand(0x06);//数据读写操作后,光标自动加一,画面不动
LCD_WriteCommand(0x01);//光标复位,清屏
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置上显示一个字符
* @param Line 行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Char 要显示的字符
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowChar(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char Char)
{
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
LCD_WriteData(Char);
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始显示所给字符串
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param String 要显示的字符串
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowString(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,char *String)
{
unsigned char i;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=0;String[i]!='\0';i++)
{
LCD_WriteData(String[i]);
}
}
/**
* @brief 返回值=X的Y次方
*/
int LCD_Pow(int X,int Y)
{
unsigned char i;
int Result=1;
for(i=0;i<Y;i++)
{
Result*=X;
}
return Result;
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:0~65535
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~5
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
LCD_WriteData(Number/LCD_Pow(10,i-1)%10+'0');
}
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始以有符号十进制显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:-32768~32767
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~5
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowSignedNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i;
unsigned int Number1;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
if(Number>=0)
{
LCD_WriteData('+');
Number1=Number;
}
else
{
LCD_WriteData('-');
Number1=-Number;
}
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
LCD_WriteData(Number1/LCD_Pow(10,i-1)%10+'0');
}
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始以十六进制显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:0~0xFFFF
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~4
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowHexNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i,SingleNumber;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
SingleNumber=Number/LCD_Pow(16,i-1)%16;
if(SingleNumber<10)
{
LCD_WriteData(SingleNumber+'0');
}
else
{
LCD_WriteData(SingleNumber-10+'A');
}
}
}
/**
* @brief 在LCD1602指定位置开始以二进制显示所给数字
* @param Line 起始行位置,范围:1~2
* @param Column 起始列位置,范围:1~16
* @param Number 要显示的数字,范围:0~1111 1111 1111 1111
* @param Length 要显示数字的长度,范围:1~16
* @retval 无
*/
void LCD_ShowBinNum(unsigned char Line,unsigned char Column,unsigned int Number,unsigned char Length)
{
unsigned char i;
LCD_SetCursor(Line,Column);
for(i=Length;i>0;i--)
{
LCD_WriteData(Number/LCD_Pow(2,i-1)%2+'0');
}
}
主函数中进行调用
#include <REGX52.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "Delay.h"
int Res = 0;
void main(){
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowChar(1,1,'A');
LCD_ShowString(1,3,"Hello");
LCD_ShowNum(1,9,123,3);//位数不够显示会高位补零,位数多余显示位,
//会显示从后开始数的几位
LCD_ShowSignedNum(1,13,-65,2);//显示位数不算符号位
LCD_ShowHexNum(2,1,0xA8,2);
LCD_ShowBinNum(2,4,0xAA,8);
while(1){
Res++;
Delay(1000);
LCD_ShowNum(2,13,Res,3);
}
}细节:LCD1602需要插紧,有时对比度也有影响,看着没有显示出来,其实已经显示出来了
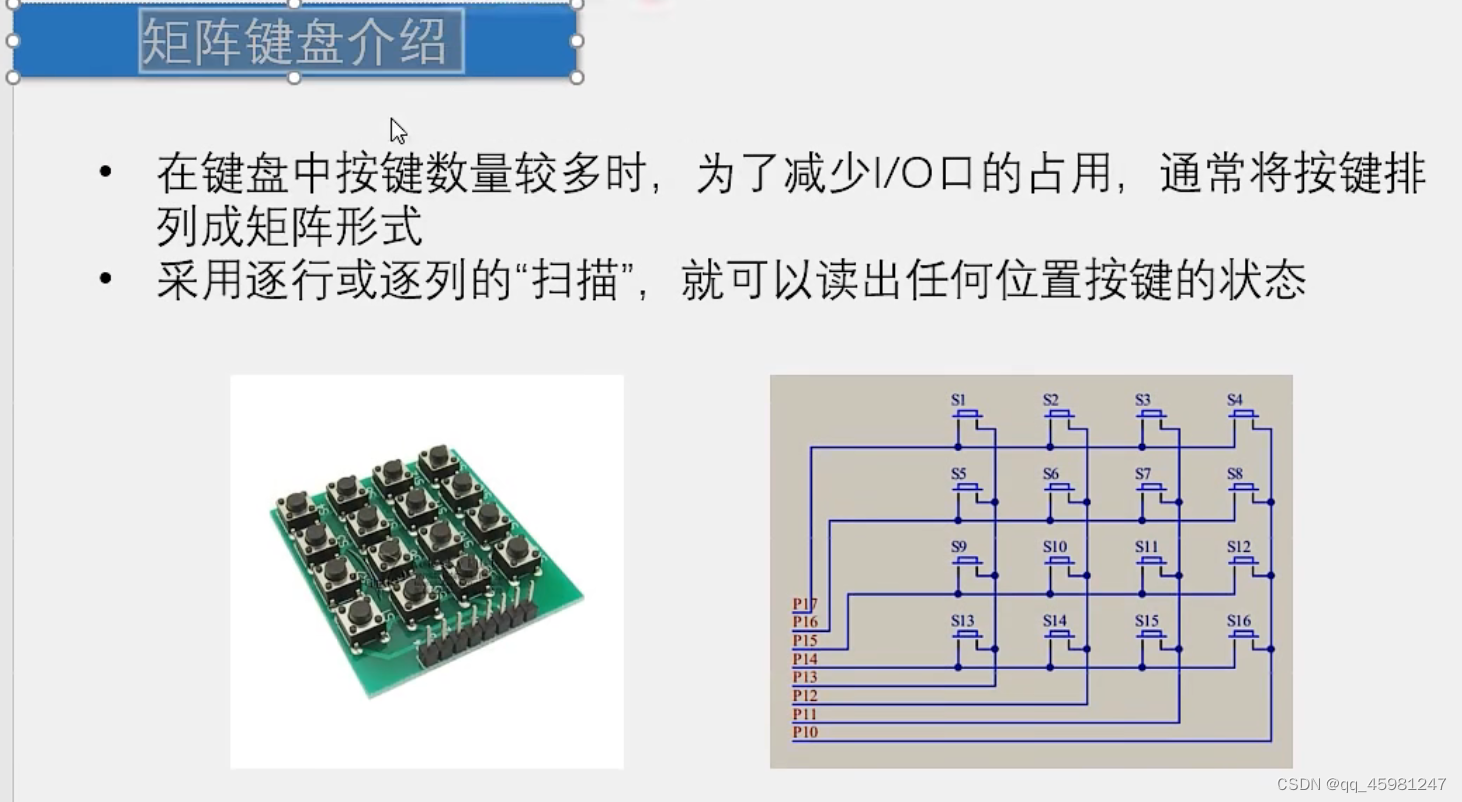
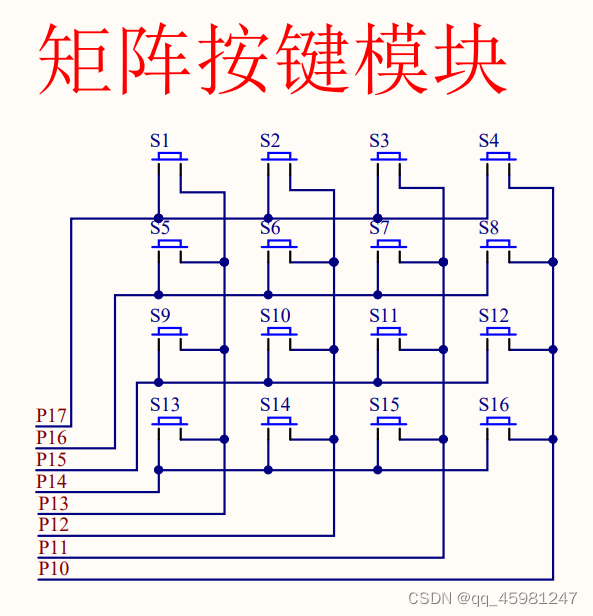
矩阵键盘

矩阵键盘显示数据
MatrixKey.h
#ifndef __MATRIXKEY__H__
#define __MATRIXKEY__H__
unsigned char MatrixKey();
#endifMatrixKey.c
#include <REGX52.H>
#include "Delay.h"
/**
* @brief 矩阵键盘读取按键键码
* @param 无
* @retval KeyNum 按下按键的键码值
* 如果按键按下不放,则程序会停留在此函数,
* 松手一瞬间,返回按键码,没有按键按下时,返回0
*/
unsigned char MatrixKey(){
unsigned char KeyNum = 0;
P1 = 0xff;//将按键全部置于高电平
P1_3 = 0;//选中第一列
if( P1_7 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_7 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 1;}//s1的检测
if( P1_6 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_6 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 5;}//s5的检测
if( P1_5 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_5 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 9;}//s9的检测
if( P1_4 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_4 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 13;}//s13的检测
P1 = 0xff;//将按键全部置于高电平
P1_2 = 0;//选中第二列
if( P1_7 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_7 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 2;}//s2的检测
if( P1_6 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_6 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 6;}//s6的检测
if( P1_5 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_5 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 10;}//s10的检测
if( P1_4 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_4 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 14;}//s14的检测
P1 = 0xff;//将按键全部置于高电平
P1_1 = 0;//选中第三列
if( P1_7 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_7 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 3;}//s3的检测
if( P1_6 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_6 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 7;}//s7的检测
if( P1_5 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_5 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 11;}//s11的检测
if( P1_4 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_4 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 15;}//s15的检测
P1 = 0xff;//将按键全部置于高电平
P1_0 = 0;//选中第四列
if( P1_7 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_7 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 4;}//s4的检测
if( P1_6 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_6 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 8;}//s8的检测
if( P1_5 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_5 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 12;}//s12的检测
if( P1_4 == 0 ){ Delay(20); while( P1_4 == 0) Delay(20); KeyNum = 16;}//s16的检测
return KeyNum;
}主函数调用
#include <REGX52.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "Delay.h"
#include "MatrixKey.h"
unsigned char KeyNum ;
void main(){
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"MatrixKey:");//打印
while(1){
KeyNum = MatrixKey();
if( KeyNum ) {//延迟刷新
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,KeyNum,2);
}
}
}矩阵键盘密码锁
主函数内容
#include <REGX52.H>
#include "LCD1602.h"
#include "Delay.h"
#include "MatrixKey.h"
unsigned char KeyNum ;
unsigned int Password,Count;
void main(){
LCD_Init();
LCD_ShowString(1,1,"Password:");//打印
while(1){
KeyNum = MatrixKey();
if( KeyNum ) {//延迟刷新
if( KeyNum <= 10){//如果s1-s10按键按下,输入密码
if(Count < 4){//控制只能输入四个数
Password *= 10;//密码左移一位
Password += KeyNum % 10;//获取一位密码并加到密码中
Count ++;//计次加一
}
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4);//刷新显示
}
if( KeyNum == 11){//如果s11被按下,进行确认操作
if( Password == 2345){//进行密码比对,2345为正确密码
LCD_ShowString(1,14,"OK ");//显示ok
Password = 0;//密码清零
Count = 0;//计次清零
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4);//刷新显示
}else{//否则
LCD_ShowString(1,14,"ERR");//显示ERR
Password = 0;//密码清零
Count = 0;//计次清零
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4);//刷新显示
}
}
if( KeyNum == 12){//如果s12被按下,进行取消操作
LCD_ShowString(1,14," ");//显示空
Password = 0;//密码清零
Count = 0;//计次清零
LCD_ShowNum(2,1,Password,4);//刷新显示
}
}
}
}