文章目录
- 网站中的消息功能如何实现?
- 什么是WebSocket?
- http与websocket的区别
- http
- websocket
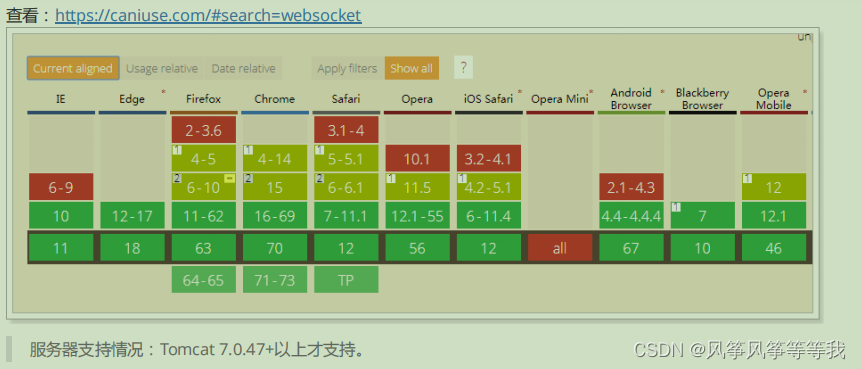
- 浏览器支持情况
- 快速入门
- 创建itcast-websocket工程
- websocket的相关注解说明
- 实现websocket服务
- 测试
- 编写js客户端
- SpringBoot整合WebSocket
- 导入依赖
- 编写WebSocketHandler
- 编写配置类
- 编写启动类
- 测试
- websocket拦截器
网站中的消息功能如何实现?
思考:像这样的消息功能怎么实现? 如果网页不刷新,服务端有新消息如何推送到浏览器?
解决方案,采用轮询的方式。即:通过js不断的请求服务器,查看是否有新数据,如果有,就获取到新数据。
这种解决方法是否存在问题呢?
当然是有的,如果服务端一直没有新的数据,那么js也是需要一直的轮询查询数据,这就是一种资源的浪费。
那么,有没有更好的解决方案? 有!那就是采用WebSocket技术来解决。
什么是WebSocket?
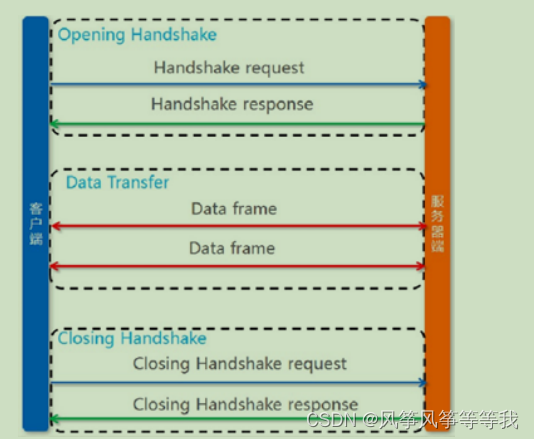
WebSocket 是HTML5一种新的协议。它实现了浏览器与服务器全双工通信(full-duplex)。一开始的握手需要借助HTTP请求完成。 WebSocket是真正实现了全双工通信的服务器向客户端推的互联网技术。 它是一种在单个TCP连接上进行全双工通讯协议。Websocket通信协议与2011年倍IETF定为标准RFC 6455,Websocket API被W3C定为标准。
全双工和单工的区别?
- 全双工(Full Duplex)是通讯传输的一个术语。通信允许数据在两个方向上同时传输,它在能力上相当于两个单工通信方式的结合。全双工指可以同时(瞬时)进行信号的双向传输(A→B且B→A)。指A→B的同时B→A,是瞬时同步的。
- 单工、半双工(Half Duplex),所谓半双工就是指一个时间段内只有一个动作发生,举个简单例子,一条窄窄的马路,同时只能有一辆车通过,当目前有两辆车对开,这种情况下就只能一辆先过,等到头儿后另一辆再开,这个例子就形象的说明了半双工的原理。早期的对讲机、以及早期集线器等设备都是基于半双工的产品。随着技术的不断进步,半双工会逐渐退出历史舞台。
http与websocket的区别
http
http协议是短连接,因为请求之后,都会关闭连接,下次重新请求数据,需要再次打开链接。
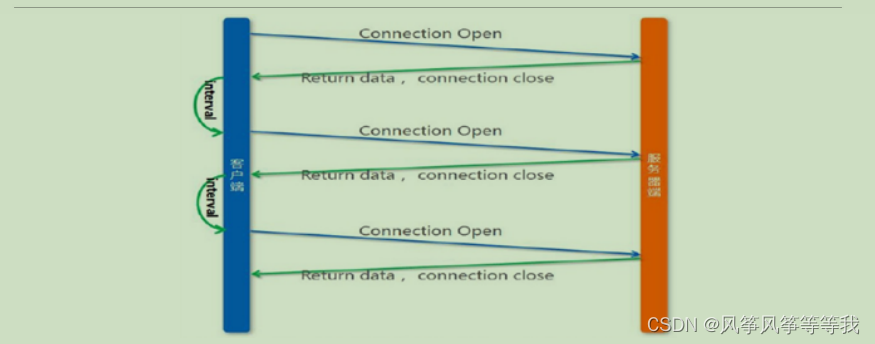
websocket
WebSocket协议是一种长链接,只需要通过一次请求来初始化链接,然后所有的请求和响应都是通过这个TCP链接进行通讯。
浏览器支持情况
快速入门
创建itcast-websocket工程
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>cn.itcast.websocket</groupId>
<artifactId>itcast-websocket</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>javax</groupId>
<artifactId>javaee-api</artifactId>
<version>7.0</version>
<scope>provided</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- java编译插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!-- 配置Tomcat插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<port>8082</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
websocket的相关注解说明
@ServerEndpoint(“/websocket/{uid}”)
申明这是一个websocket服务
需要指定访问该服务的地址,在地址中可以指定参数,需要通过{}进行占位
@OnOpen
用法:public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam(“uid”) String uid) throws
IOException{}
该方法将在建立连接后执行,会传入session对象,就是客户端与服务端建立的长连接通道
通过@PathParam获取url申明中的参数
@OnClose
用法:public void onClose() {}
该方法是在连接关闭后执行
@OnMessage
用法:public void onMessage(String message, Session session) throws IOException {}
该方法用于接收客户端发来的消息
message:发来的消息数据
session:会话对象(也是通道)
发送消息到客户端
用法:session.getBasicRemote().sendText(“你好”);
通过session进行发送。
实现websocket服务
package cn.itcast.websocket;
import javax.websocket.*;
import javax.websocket.server.PathParam;
import javax.websocket.server.ServerEndpoint;
import java.io.IOException;
@ServerEndpoint("/websocket/{uid}")
public class MyWebSocket {
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(Session session, @PathParam("uid") String uid) throws IOException {
// 连接成功
session.getBasicRemote().sendText(uid + ",你好,欢迎连接WebSocket!");
}
@OnClose
public void onClose() {
System.out.println(this + "关闭连接");
}
@OnMessage
public void onMessage(String message, Session session) throws IOException {
System.out.println("接收到消息:" + message);
session.getBasicRemote().sendText("消息已收到.");
}
@OnError
public void onError(Session session, Throwable error) {
System.out.println("发生错误");
error.printStackTrace();
}
}
编写完成后,无需进额外的配置,直接启动tomcat即可。
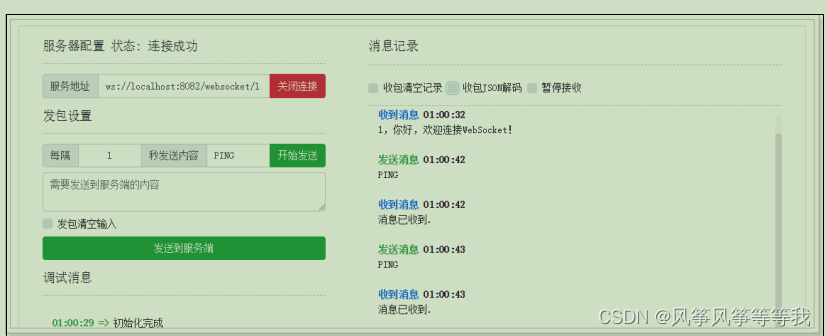
测试
可以通过安装chrome插件或者通过在线工具进行测试:
chrome插件,Simple WebSocket Client:
https://chrome.google.com/webstore/detail/simple-websocket-client/pfdhoblngboilpfeibdedpjgfnlcodoo
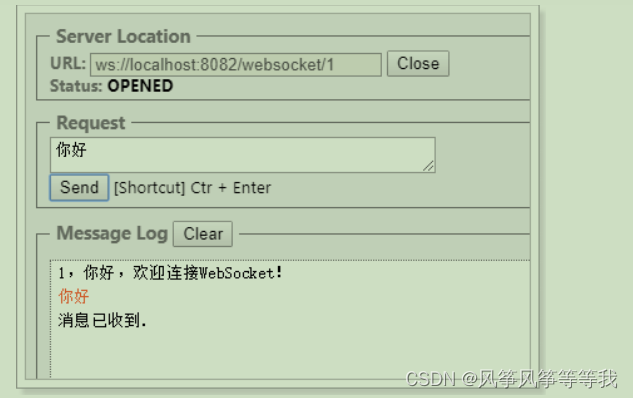
在线工具:https://wstool.js.org/
编写js客户端
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<script>
const socket = new WebSocket("ws://localhost:8082/websocket/1");
socket.onopen = (ws) =>{
console.log("建立连接!", ws);
}
socket.onmessage = (ws) =>{
console.log("接收到消息 >> ",ws.data);
}
socket.onclose = (ws) =>{
console.log("连接已断开!", ws);
}
socket.onerror = (ws) => {
console.log("发送错误!", ws);
}
// 2秒后向服务端发送消息
setTimeout(()=>{
socket.send("发送一条消息试试");
},2000);
// 5秒后断开连接
setTimeout(()=>{
socket.close();
},5000);
</script>
</body>
</html>
测试:
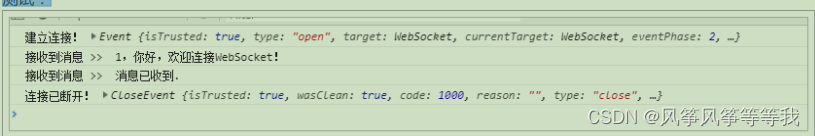
SpringBoot整合WebSocket
Spring对WebSocket做了支持,下面我们看下在springboot中如何使用。
导入依赖
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0
http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<!--spring boot的支持-->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.0.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<groupId>cn.itcast.websocket</groupId>
<artifactId>itcast-websocket</artifactId>
<version>1.0-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<!--<dependency>-->
<!--<groupId>javax</groupId>-->
<!--<artifactId>javaee-api</artifactId>-->
<!--<version>7.0</version>-->
<!--<scope>provided</scope>-->
<!--</dependency>-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-websocket</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<plugins>
<!-- java编译插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2</version>
<configuration>
<source>1.8</source>
<target>1.8</target>
<encoding>UTF-8</encoding>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!-- 配置Tomcat插件 -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.tomcat.maven</groupId>
<artifactId>tomcat7-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>2.2</version>
<configuration>
<port>8082</port>
<path>/</path>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>
编写WebSocketHandler
在Spring中,处理消息的具体业务逻辑需要实现WebSocketHandler接口。
package cn.itcast.websocket.spring;
import org.springframework.web.socket.CloseStatus;
import org.springframework.web.socket.TextMessage;
import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketSession;
import org.springframework.web.socket.handler.TextWebSocketHandler;
import java.io.IOException;
public class MyHandler extends TextWebSocketHandler {
@Override
public void handleTextMessage(WebSocketSession session, TextMessage message) throws IOException {
System.out.println("获取到消息 >> " + message.getPayload());
session.sendMessage(new TextMessage("消息已收到"));
if(message.getPayload().equals("10")){
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
session.sendMessage(new TextMessage("消息 -> " + i));
try {
Thread.sleep(100);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
@Override
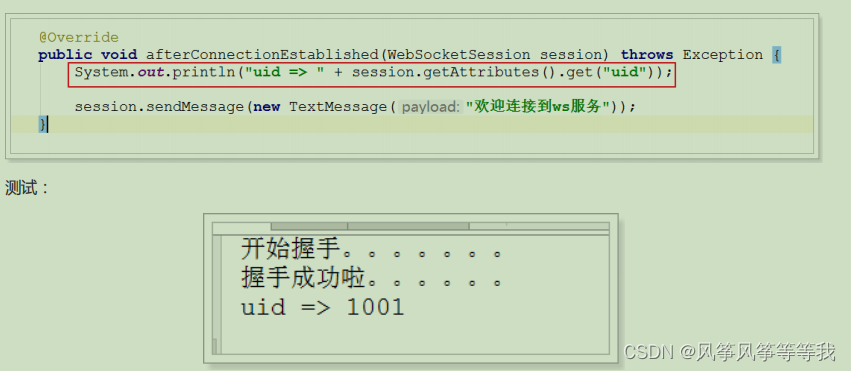
public void afterConnectionEstablished(WebSocketSession session) throws Exception {
session.sendMessage(new TextMessage("欢迎连接到ws服务"));
}
@Override
public void afterConnectionClosed(WebSocketSession session, CloseStatus status) throws Exception {
System.out.println("断开连接!");
}
}
编写配置类
package cn.itcast.websocket.spring;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketHandler;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.EnableWebSocket;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketHandlerRegistry;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSocket
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketConfigurer {
@Override
public void registerWebSocketHandlers(WebSocketHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addHandler(myHandler(), "/ws").setAllowedOrigins("*");
}
@Bean
public WebSocketHandler myHandler() {
return new MyHandler();
}
}
编写启动类
package cn.itcast.websocket;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
测试
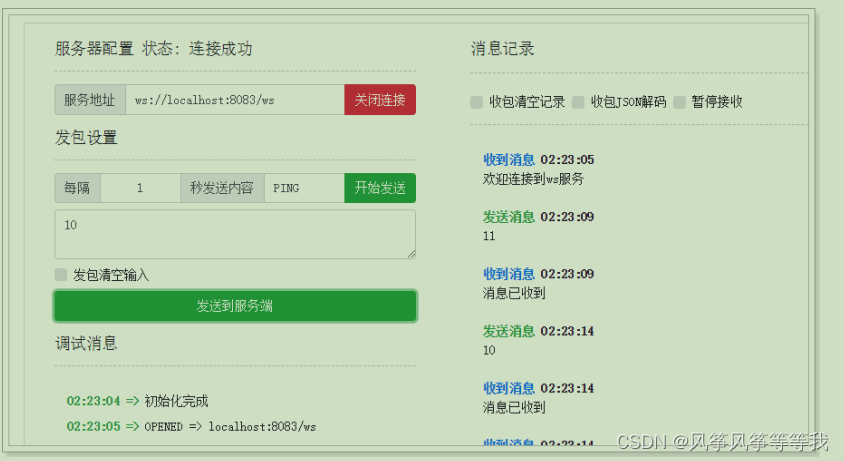
websocket拦截器
在Spring中提供了websocket拦截器,可以在建立连接之前写些业务逻辑,比如校验登录等
package cn.itcast.websocket.spring;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpRequest;
import org.springframework.http.server.ServerHttpResponse;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketHandler;
import org.springframework.web.socket.server.HandshakeInterceptor;
import java.util.Map;
@Component
public class MyHandshakeInterceptor implements HandshakeInterceptor {
/**
* 握手之前,若返回false,则不建立链接
*
* @param request
* @param response
* @param wsHandler
* @param attributes
* @return
* @throws Exception
*/
@Override
public boolean beforeHandshake(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response, WebSocketHandler wsHandler, Map<String, Object> attributes) throws
Exception {
//将用户id放入socket处理器的会话(WebSocketSession)中
attributes.put("uid", 1001);
System.out.println("开始握手。。。。。。。");
return true;
}
@Override
public void afterHandshake(ServerHttpRequest request, ServerHttpResponse response, WebSocketHandler wsHandler, Exception exception) {
System.out.println("握手成功啦。。。。。。");
}
}
将拦截器添加到websocket服务中:
package cn.itcast.websocket.spring;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
import org.springframework.web.socket.WebSocketHandler;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.EnableWebSocket;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketConfigurer;
import org.springframework.web.socket.config.annotation.WebSocketHandlerRegistry;
@Configuration
@EnableWebSocket
public class WebSocketConfig implements WebSocketConfigurer {
@Autowired
private MyHandshakeInterceptor myHandshakeInterceptor;
@Override
public void registerWebSocketHandlers(WebSocketHandlerRegistry registry) {
registry.addHandler(myHandler(), "/ws")
.setAllowedOrigins("*").addInterceptors(this.myHandshakeInterceptor);
}
@Bean
public WebSocketHandler myHandler() {
return new MyHandler();
}
}
获取uid: