文章目录
- 前言
- 一步步安装免费版
- 主要模块介绍
- 1. depot point
- 2. customer point
- 3. links
- 4. vehicle type
- VRPTW 算例
- 数据说明
- 模型建立
- 输出求解状态及结果
前言
VRPSolverEasy 是用于车辆路径问题(VRP)的最先进的分支切割和定价算法求解器1,它的一大特点是,即使没有运筹学背景的用户,也可以直观地通过Python接口定义出VRP问题,无需知道模型是如何建立为 MIP 问题以及底层进行的线性处理,只需要通过配置好的方法,向模型中添加高度抽象的VehicleType、Point(衍生出depot、customer)、links 即可。
VRPSolver将VRP问题进行了高度抽象,尽管较大程度方便使用,但代价是限制了VRPSolver只能建模常见的标准的VRP变体问题,例如:
- 车辆带容量限制;
- 客户点带时间窗;
- 车辆不同质;
- 多depot发车;
- 客户点指定车辆资质;
- 时间依赖…
VRPSolver的内核是分支切割定价算法,其高效性在于对可行解最优界(下界)的优化上,而在初始可行解的寻找方面效率较低,因此由外部启发式求解器获得非常好的初始解(上界)时,VRPSolver的求解性能可以得到改善。
目前的VRPSolver仍然是proof-of-concept的代码,容易出现问题,因此建议仅用于研究、教学、测试等非生产环境。
一步步安装免费版
VRPSolverEasy有两种安装模式,一种是免费版本,直接安装VRPSolverEasy库(内嵌了COIN-OR CLP线性规划求解器),以及下载Bapcod发行版即可。另一种是学术版本,该版本使用了商业CPLEX MIP求解器,由于CPLEX可以免费用于学术目的,因此这个版本下的VRPSolverEasy也被称为学术版,该版本提高了求解性能,并提供了内置的基于MIP的启发式算法,对寻找可行的初始解非常有用。
这里我们仅介绍安装免费版的 VRPSolverEasy,操作系统默认为Windows。(学术版的安装请参考 官方文档)
(1)确认python版本及更新pip
VRPSolverEasy库要求python版本不小于 3.6,因此在开始安装前,先确认好python的版本,并建议更新 pip 库:
python -m pip install --upgrade pip
(2)安装VRPSolverEasy库
VRPSolverEasy库的安装可以直接用pip安装:
python -m pip install VRPSolverEasy
(3)安装Bapcod依赖的环境
由于内嵌的 CLP 仅是线性规划求解器,要用 B&C&P 求解MIP问题,还需安装Bapcod,由于Bapcod的底层是C++,因此要用Python接口使用,就还需下载能对该库进行编译和管理的工具CMake,该工具的官网下载地址为:Download CMake,具体的安装细节可以参考:Windows 安装CMake。在cmd控制台输入 cmake --version 即可查看CMake的版本。
接着还需安装 Bapcod 依赖的python库:
- Boost库版本1.76
pip install boost - LEMON 库版本 1.3.1
pip install lemon
(4)申请Bapcod并替换相应文件
尽管Bapcod是免费开源的库,但是需要学术机构的电子邮箱才能下载Bapcod的源码,在 BaPCod官方网站 填写相应信息并回车进行申请。系统会自动验证该邮箱,并向该邮箱发送下载链接。
解压下载的文件,例如为 bapcod-v0.82.5,找到该文件夹下的 VRPSolverEasy 文件夹,复制该文件夹下的 Windows 文件夹到 VRPSolverEasy 库下面的 lib 文件夹中替换 Windows 即可。
主要模块介绍
关于主要模块的介绍我们截取翻译自VRPSolverEasy的技术报告1。
导入VRPSolverEasy库,并通过以下命令创建模型。
import VRPSolverEasy
model = VRPSolverEasy.Model()
VRPSolverEasy库模型由四组实体对象定义:depot points、customer points、links、vehicle types。
1. depot point
depot 可以通过如下命令添加
model.add_depot(id=<id>, name='', service_time=0.0, tw_begin=0.0, tw_end=0.0)
添加 depot 方法的参数说明如下:

2. customer point
customer 可以通过如下命令添加:
model.add_customer(id=<id>, id_customer=<id>, name ='', demand=0, penalty=0.0, service_time=0.0, tw_begin=0.0, tw_end=0.0, incompatible_vehicles=[])
添加 customer 方法的参数说明如下:
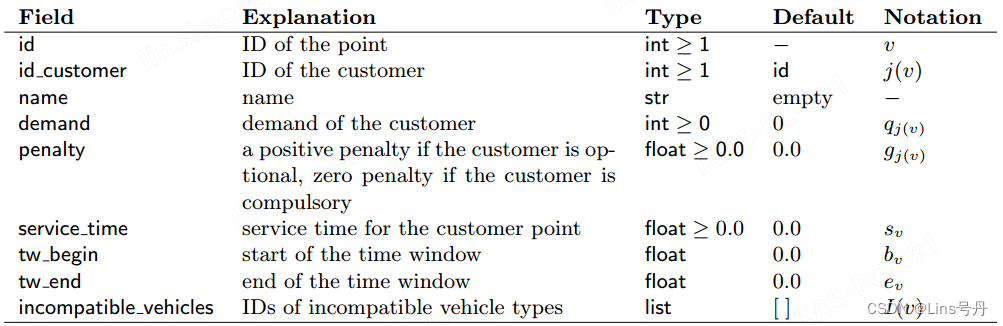
不论是 depot point 还是 customer point,都应该有一个唯一的点 id,且每个 customer 都与一个或多个点相关联,其中 id 与 id_customer 可以不同。
对于一些特殊的问题,例如同一个客户点具有不同的时间窗,且每个时间窗所兼容的车辆可能不同,常见于时间依赖的VRPTW问题,这类问题中,客户点可能会被多辆车访问(同时或者有时间前后约束),这时候为了避免与子环路消除约束相冲突,往往会创建虚拟点,在这里,如果我们要创建 customer point 的额外点,可以通过以下命令添加:
model.add_point(id=<id>, id_customer=<id>, name ='', demand=0, penalty=0.0, service_time=0.0, tw_begin=0.0, tw_end=0.0, incompatible_vehicles=[])
3. links
link 可以通过如下命令添加:
model.add_link(start_point_id=<id>, end_point_id=<id>, name='', is_directed=False, distance=0.0, time=0.0, fixed_cost=0.0)
添加 link 方法的参数说明如下:

每一条 link 代表有向图G当中的一条弧,如果 is_directed=True,则说明该弧具有方向,只能从 start_point_id 到 end_point_id 方向;如果 is_directed=False,则说明该弧是双向的(若不设置该参数默认为双向的)。
4. vehicle type
vehicle type 可以通过如下命令添加:
model.add_vehicle_type(id=<id>, start_point_id=-1, end_point_id=-1, name='', capacity=0, fixed_cost=0.0, var_cost_dist=0.0, var_cost_time=0.0, max_number=1, tw_begin=0.0, tw_end=0.0)
添加 vehicle type 方法的参数说明如下:
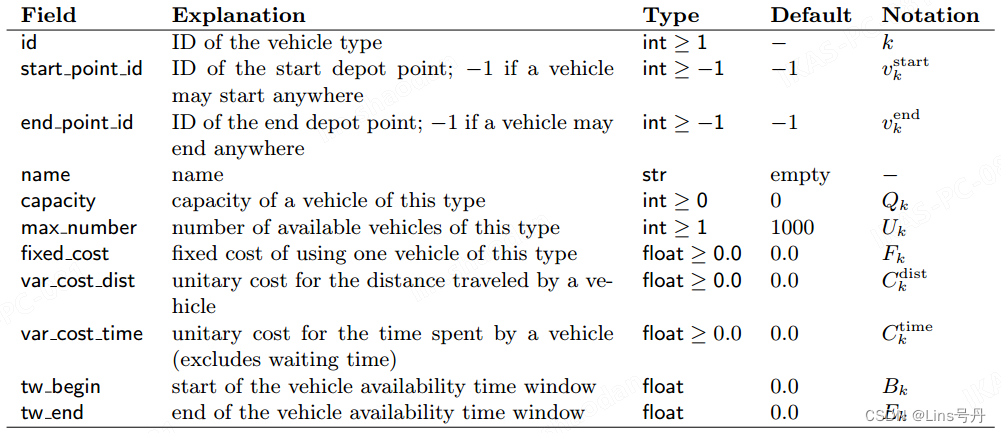
当车辆的开始点和结束点都为 -1 时,说明该车辆可以在任意节点处出发,和返回任意节点处。
VRPTW 算例
数据说明
如下设置 7 个节点,以第 1 个节点 Wisconsin, USA 为 depot point,其余节点为 customer point,除了 depot 其余节点都有大于0需求量,车辆的时间窗为
[
0
,
5000
]
[0, 5000]
[0,5000],每辆车单位距离成本为 10,节点与节点之间的距离通过欧式距离公式计算 compute_euclidean_distance。
import VRPSolverEasy as vrpse
import math
def compute_euclidean_distance(x_i, x_j, y_i, y_j):
"""compute the euclidean distance between 2 points from graph"""
return round(math.sqrt((x_i - x_j)**2 + (y_i - y_j)**2), 3)
# Data
cost_per_distance = 10
begin_time = 0
end_time = 5000
nb_point = 7
# Map with names and coordinates
coordinates = {"Wisconsin, USA": (44.50, -89.50), # depot
"West Virginia, USA": (39.000000, -80.500000),
"Vermont, USA": (44.000000, -72.699997),
"Texas, the USA": (31.000000, -100.000000),
"South Dakota, the US": (44.500000, -100.000000),
"Rhode Island, the US": (41.742325, -71.742332),
"Oregon, the US": (44.000000, -120.500000)
}
# Demands of points
demands = [0, 500, 300, 600, 658, 741, 436]
模型建立
依次建立求解车辆路径网络流问题的要素:车辆、节点、弧。要素的参数值可以自定义配置。
# Initialisation
model = vrpse.Model()
# Add vehicle type
model.add_vehicle_type(
id=1,
start_point_id=0,
end_point_id=0,
name="VEH1",
capacity=1100,
max_number=6,
var_cost_dist=cost_per_distance,
tw_end=5000)
# Add depot
model.add_depot(id=0, name="D1", tw_begin=0, tw_end=5000)
coordinates_keys = list(coordinates.keys())
# Add customers
for i in range(1, nb_point):
model.add_customer(
id=i,
name=coordinates_keys[i],
demand=demands[i],
tw_begin=begin_time,
tw_end=end_time)
# Add links
coordinates_values = list(coordinates.values())
for i in range(0, 7):
for j in range(i + 1, 7):
dist = compute_euclidean_distance(coordinates_values[i][0],
coordinates_values[j][0],
coordinates_values[i][1],
coordinates_values[j][1])
model.add_link(
start_point_id=i,
end_point_id=j,
distance=dist,
time=dist)
输出求解状态及结果
当建立模型后,通过以下命令即可实现求解,求解的结果都会保存在 model 的属性当中。
# solve model
model.solve()
打印模型信息可以通过以下命令,默认将模型信息保存在 instance.json 文件中。
model.export()
通过 model.status 可以返回模型的求解状态码:
| 状态码 | 说明 |
|---|---|
| 0 | 找到一个解并证明了最优性 |
| 1 | 求解过程被时间限制打断,但找到了优于截断值的解 |
| 2 | 求解器证明不存在由于截断值的解 |
| 3 | 求解过程被时间限制打断,且没找到由于截断值的解 |
判断求解状态码是一种输出结果的前置判断,在该库中也可以用 model.solution.is_defined() 进行判断,后者表示找到了可行解,且解的信息会保存到模型的属性当中:
if model.solution.is_defined():
# 打印解的目标值及方案的全部信息
print(model.solution)
# 仅打印路线方案
print(model.solution.routes)
# 仅打印目标值
print(model.solution.value)
# 打印解的求解时间和上下界信息等
print(model.statistics)
打印解的目标值及方案的全部信息如下:
Solution cost : 1479.6800000008684
Route for vehicle 1:
ID : 0 --> 2 --> 5 --> 0
Name : D1 --> Vermont, USA --> Rhode Island, the US --> D1
End time : 0.0 --> 16.807 --> 19.259 --> 37.230000000000004
Load : 0.0 --> 300.0 --> 1041.0 --> 1041.0
Total cost : 372.29999999999995
Route for vehicle 1:
ID : 0 --> 1 --> 3 --> 0
Name : D1 --> West Virginia, USA --> Texas, the USA --> D1
End time : 0.0 --> 10.548 --> 31.625 --> 48.728
Load : 0.0 --> 500.0 --> 1100.0 --> 1100.0
Total cost : 487.2800000000001
Route for vehicle 1:
ID : 0 --> 4 --> 6 --> 0
Name : D1 --> South Dakota, the US --> Oregon, the US --> D1
End time : 0.0 --> 10.5 --> 31.006 --> 62.010000000000005
Load : 0.0 --> 658.0 --> 1094.0 --> 1094.0
Total cost : 620.1
N. Errami, E. Queiroga, R. Sadykov, E. Uchoa. “VRPSolverEasy: a Python library for the exact solution of a rich vehicle routing problem”, Technical report HAL-04057985, 2023. ↩︎ ↩︎