参考知识:
- 什么是链表
- Optional有什么用
题目:
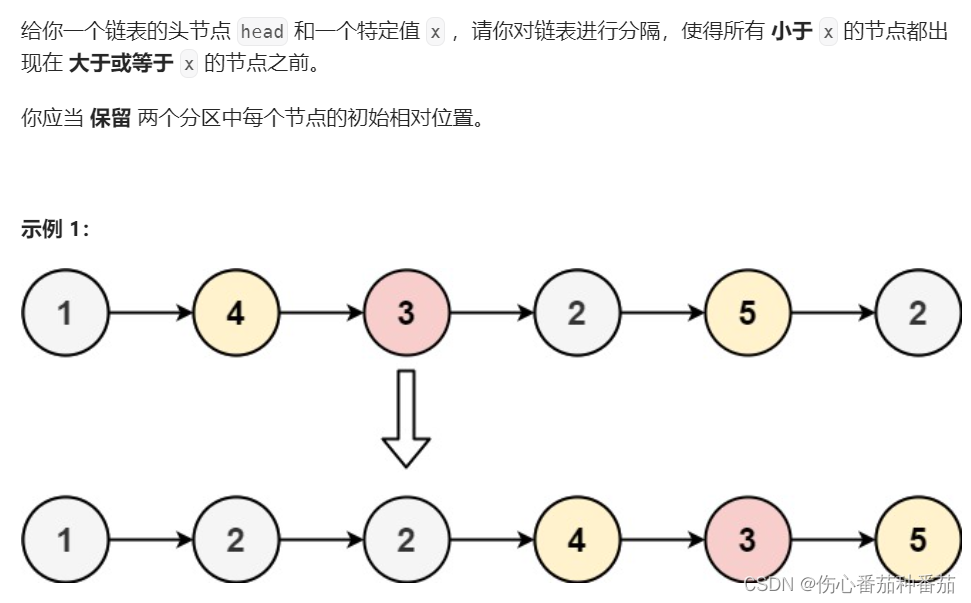
题目来源:力扣
代码:
from typing import Optional
class ListNode:
''' 链表结点的数据类型 '''
def __init__(self, val=0,next=None):
self.val = val
self.next = next
def convert_to_linked_list(lst):
''' 将list转换为单链表 '''
if not lst:
return None
head = ListNode(lst[0]) # list第一个元素作为head结点
i = head
for i in range(1, len(lst)):
new_node = ListNode(lst[i]) # 元素结点化
i.next = new_node # 追加新node
i = i.next # 结点标志位移到下一结点
return head #返回head结点
class Solution:
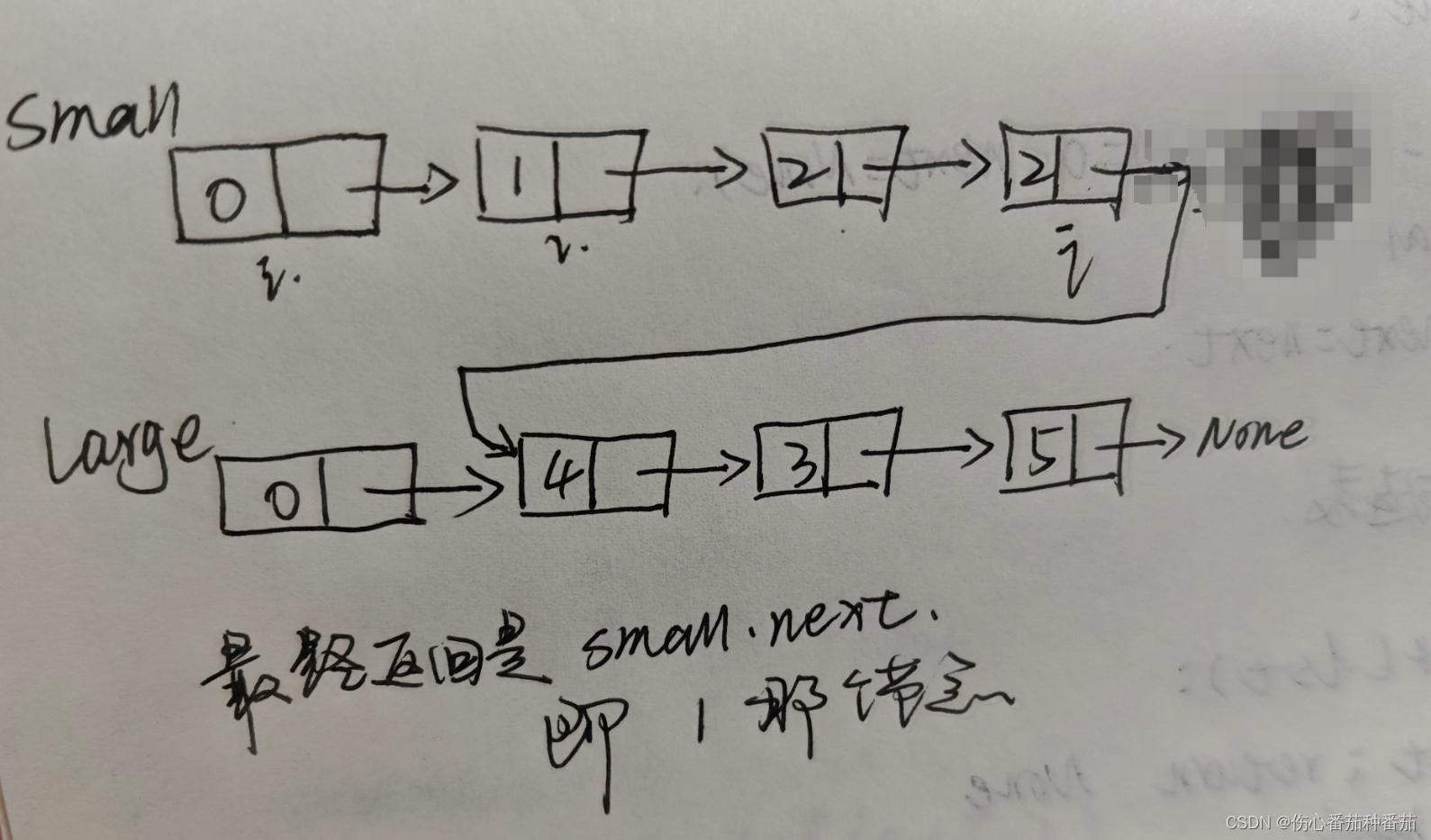
''' 小于x的元素在x左边,大于x的元素在x右边,保持相对位置不变 '''
def partition(self, head: Optional[ListNode], x: int) -> Optional[ListNode]:
small, large = ListNode(0), ListNode(0) #声明2个链表
i, j = small, large # 两个链表的结点标志位
while head:
if head.val < x: # <x 的放在small链表
i.next = head
i = i.next
else: # >=x 的放在large链表
j.next = head
j = j.next
head = head.next # 比较完当前head后,比较下一个
i.next = large.next # 连接2个链表,i结点 即 large链表的第二个结点
j.next = None # 尾结点指向None
return small.next
def run(self,lst,x):
''' 以list形式输出最终结果 '''
res=[]
head = self.partition(head=convert_to_linked_list(lst),x=x)
while head:
res.append(head.val)
head=head.next
return res
if __name__ == '__main__':
lst=[1,4,3,2,5,2]
s=Solution()
print(s.run(lst,x=3))