目录
- 前言
- 1. @JsonFormat注解
- 2. @DateTimeFormat注解
- 3. Demo
- 3.1 无注解
- 3.2 有注解
- 4. 拓展
前言
下文中涉及MybatisPlus的逻辑删除的知识,可看我之前这篇文章:详细讲解MybatisPlus实现逻辑删除
对应的Navicat设置数据库最新时间可看我这篇文章:Navicat 设置时间默认值(当前最新时间)
为了使 @JsonFormat 生效,项目必须引入 Jackson 库的相关依赖:
(如果是springboot项目,可不用配置,本身spring-boot-start-web依赖已包含)
<!-- JSON工具类 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>com.fasterxml.jackson.core</groupId>
<artifactId>jackson-databind</artifactId>
<version>2.12.6</version>
</dependency>
摘要:
-
注解
@JsonFormat主要是后端到前端的时间格式的转换 -
注解
@DateTimeFormat主要是前端到后端的时间格式的转换
1. @JsonFormat注解
@JsonFormat 是 Jackson 库中的注解,用于在序列化和反序列化过程中控制日期和时间的格式。
该注解提供了一种自定义日期和时间格式的方式,以确保在 JSON 数据和 Java 对象之间正确地进行转换。
以下是 @JsonFormat 注解的一些主要概念和功能:
-
pattern(模式): 通过 pattern 属性,您可以指定日期和时间的格式。
例如,如果要将日期格式设置为"yyyy-MM-dd",可以使用@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") -
timezone(时区): 使用 timezone 属性可以指定日期和时间的时区。这对于确保正确地处理跨时区的日期数据很重要。 -
locale(区域设置): 通过 locale 属性,您可以指定用于格式化的区域设置,以便支持不同的语言和地区。 -
shape(形状): shape 属性定义了序列化后的日期表示形式。例如,您可以将日期表示为字符串或时间戳。 -
with(特定类型的格式): 使用 with 属性,您可以为不同的 Java 类型指定不同的格式。这对于处理不同类型的日期数据非常有用。
下面是一个简单的 Java 类示例,演示如何使用 @JsonFormat 注解:
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonFormat;
import java.util.Date;
public class MyObject {
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", timezone = "GMT+00:00")
private Date myDate;
// 其他属性和方法
public Date getMyDate() {
return myDate;
}
public void setMyDate(Date myDate) {
this.myDate = myDate;
}
}
在这个例子中,myDate 属性使用了 @JsonFormat 注解,指定了日期的格式和时区。
当这个对象被序列化成 JSON 或者从 JSON 反序列化时,将使用指定的格式来处理日期数据。
2. @DateTimeFormat注解
@DateTimeFormat 是 Spring 框架中用于处理日期和时间格式的注解。
它通常与 @RequestMapping、@RequestParam 等注解一起使用,以指定接收或发送日期时间参数时的格式。
以下是 @DateTimeFormat 注解的一些主要概念和功能:
-
pattern(模式): 通过 pattern 属性,您可以指定日期和时间的格式。
与@JsonFormat不同,@DateTimeFormat是专门为 Spring 框架设计的,用于在 Web 请求中处理日期参数。 -
iso(ISO标准格式): 使用 iso 属性可以指定使用 ISO 标准的日期时间格式。
例如,@DateTimeFormat(iso = ISO.DATE)表示日期部分采用标准日期格式。 -
style(样式): style 属性定义了预定义的日期和时间格式。
有三种样式可用:DEFAULT、SHORT、MEDIUM、LONG、FULL。这些样式在不同的地区设置下有不同的显示效果。 -
lenient(宽松解析): lenient 属性用于指定是否宽松解析日期。
如果设置为 true,则在解析日期时会尽量接受不严格符合格式的输入。 -
patternResolver(模式解析器): patternResolver 属性允许您指定自定义的模式解析器,以便更灵活地处理日期时间格式。
下面是一个简单的 Spring MVC 控制器示例,演示如何使用 @DateTimeFormat 注解:
import org.springframework.format.annotation.DateTimeFormat;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
import java.util.Date;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/date")
public class DateController {
@RequestMapping("/processDate")
public String processDate(@RequestParam("myDate") @DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd") Date myDate) {
// 处理日期逻辑
return "Received date: " + myDate;
}
}
processDate 方法接收一个名为 myDate 的参数,并使用 @DateTimeFormat 注解指定了日期的格式。
当请求中包含名为 myDate 的参数时,Spring 将自动将参数解析为 Date 类型,并应用指定的格式。
3. Demo
为了做好例子的前提,需要配置好数据库以及代码信息。
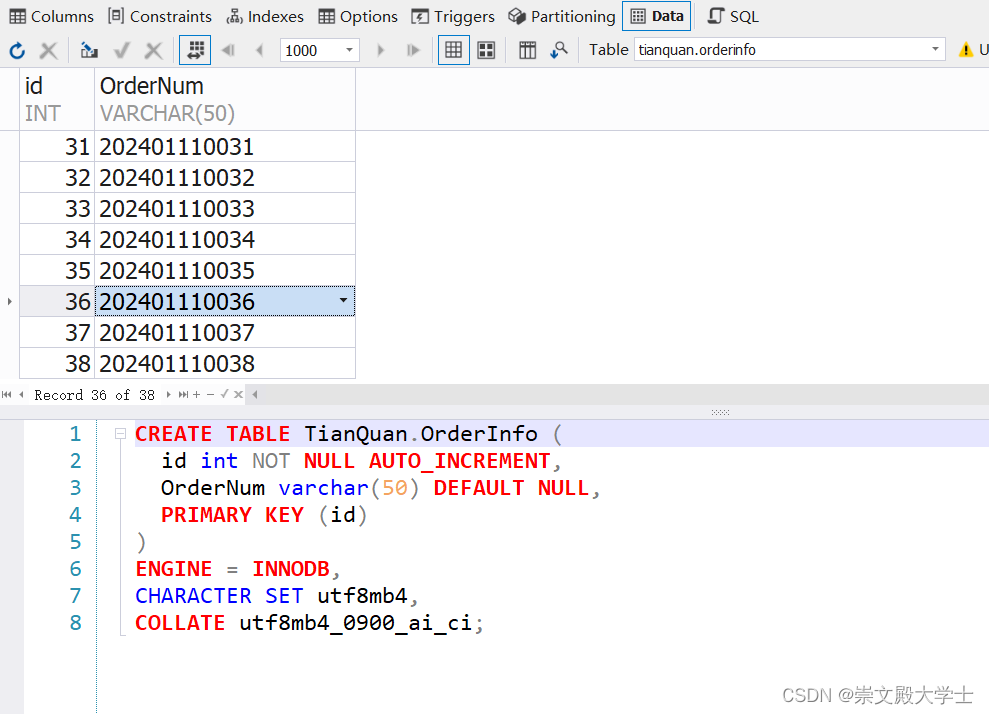
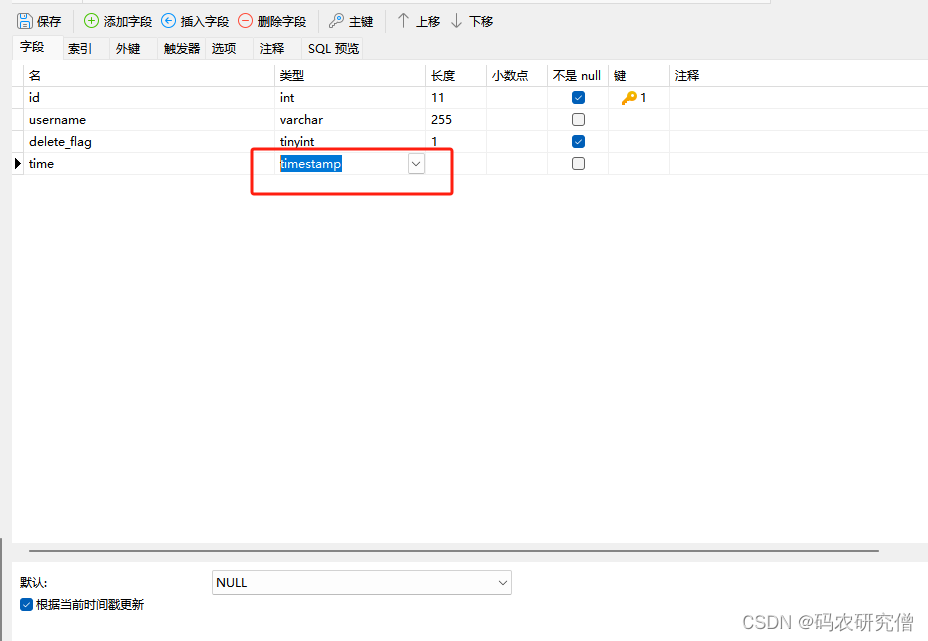
数据库相应的信息如下:
数据库类型为datetime或者timestamp,根据时间戳更新:
代码信息主要如下:(实体类)
@Data
@AllArgsConstructor
@NoArgsConstructor
@TableName("test_student")
public class student{
@TableId(value = "id", type = IdType.AUTO)
private int id;
private String username;
// 其他字段...
private Date time;
@TableLogic
private Integer deleteFlag;
}
service类:
public interface StudentService extends IService<student> {
// 这里可以自定义一些业务方法
}
实现类:
@Service
public class StrudentServiceimpl extends ServiceImpl<StudentMapper, student> implements StudentService {
// 这里可以实现自定义的业务方法
}
Mapper类:
@Mapper
public interface StudentMapper extends BaseMapper<student> {
// 这里可以自定义一些查询方法
}
3.1 无注解
对应的实体类在Date中没有相关的注解:private Date time;
对应没有注解的时候,测试类输出结果如下:time=Thu Jan 11 21:02:06 CST 2024
3.2 有注解
这两者的注解一般联合使用
@DateTimeFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss")
@JsonFormat(pattern = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss", timezone="GMT+8")
private Date time;
一般系统都是前后交互
对此总结如下:
-
注解
@JsonFormat主要是后端到前端的时间格式的转换 -
注解
@DateTimeFormat主要是前端到后端的时间格式的转换
4. 拓展
常用的配置如下:
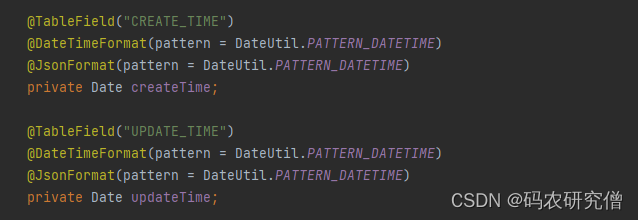
对应的时间配置可以使用该类进行拓展:
//
// Source code recreated from a .class file by IntelliJ IDEA
// (powered by FernFlower decompiler)
//
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.Instant;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.Period;
import java.time.ZoneId;
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.time.temporal.Temporal;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAccessor;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAmount;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalQuery;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
import java.util.GregorianCalendar;
import java.util.TimeZone;
import org.springframework.util.Assert;
public class DateUtil {
public static final String PATTERN_DATETIME = "yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss";
public static final String PATTERN_DATETIME_MINI = "yyyyMMddHHmmss";
public static final String PATTERN_DATE = "yyyy-MM-dd";
public static final String PATTERN_TIME = "HH:mm:ss";
public static final ConcurrentDateFormat DATETIME_FORMAT = ConcurrentDateFormat.of("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static final ConcurrentDateFormat DATETIME_MINI_FORMAT = ConcurrentDateFormat.of("yyyyMMddHHmmss");
public static final ConcurrentDateFormat DATE_FORMAT = ConcurrentDateFormat.of("yyyy-MM-dd");
public static final ConcurrentDateFormat TIME_FORMAT = ConcurrentDateFormat.of("HH:mm:ss");
public static final DateTimeFormatter DATETIME_FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
public static final DateTimeFormatter DATETIME_MINI_FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyyMMddHHmmss");
public static final DateTimeFormatter DATE_FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd");
public static final DateTimeFormatter TIME_FORMATTER = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("HH:mm:ss");
public DateUtil() {
}
public static Date now() {
return new Date();
}
public static Date plusYears(Date date, int yearsToAdd) {
return set(date, 1, yearsToAdd);
}
public static Date plusMonths(Date date, int monthsToAdd) {
return set(date, 2, monthsToAdd);
}
public static Date plusWeeks(Date date, int weeksToAdd) {
return plus(date, Period.ofWeeks(weeksToAdd));
}
public static Date plusDays(Date date, long daysToAdd) {
return plus(date, Duration.ofDays(daysToAdd));
}
public static Date plusHours(Date date, long hoursToAdd) {
return plus(date, Duration.ofHours(hoursToAdd));
}
public static Date plusMinutes(Date date, long minutesToAdd) {
return plus(date, Duration.ofMinutes(minutesToAdd));
}
public static Date plusSeconds(Date date, long secondsToAdd) {
return plus(date, Duration.ofSeconds(secondsToAdd));
}
public static Date plusMillis(Date date, long millisToAdd) {
return plus(date, Duration.ofMillis(millisToAdd));
}
public static Date plusNanos(Date date, long nanosToAdd) {
return plus(date, Duration.ofNanos(nanosToAdd));
}
public static Date plus(Date date, TemporalAmount amount) {
Instant instant = date.toInstant();
return Date.from(instant.plus(amount));
}
public static Date minusYears(Date date, int years) {
return set(date, 1, -years);
}
public static Date minusMonths(Date date, int months) {
return set(date, 2, -months);
}
public static Date minusWeeks(Date date, int weeks) {
return minus(date, Period.ofWeeks(weeks));
}
public static Date minusDays(Date date, long days) {
return minus(date, Duration.ofDays(days));
}
public static Date minusHours(Date date, long hours) {
return minus(date, Duration.ofHours(hours));
}
public static Date minusMinutes(Date date, long minutes) {
return minus(date, Duration.ofMinutes(minutes));
}
public static Date minusSeconds(Date date, long seconds) {
return minus(date, Duration.ofSeconds(seconds));
}
public static Date minusMillis(Date date, long millis) {
return minus(date, Duration.ofMillis(millis));
}
public static Date minusNanos(Date date, long nanos) {
return minus(date, Duration.ofNanos(nanos));
}
public static Date minus(Date date, TemporalAmount amount) {
Instant instant = date.toInstant();
return Date.from(instant.minus(amount));
}
private static Date set(Date date, int calendarField, int amount) {
Assert.notNull(date, "The date must not be null");
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.setLenient(false);
c.setTime(date);
c.add(calendarField, amount);
return c.getTime();
}
public static String formatDateTime(Date date) {
return DATETIME_FORMAT.format(date);
}
public static String formatDateTimeMini(Date date) {
return DATETIME_MINI_FORMAT.format(date);
}
public static String formatDate(Date date) {
return DATE_FORMAT.format(date);
}
public static String formatTime(Date date) {
return TIME_FORMAT.format(date);
}
public static String format(Date date, String pattern) {
return ConcurrentDateFormat.of(pattern).format(date);
}
public static String formatDateTime(TemporalAccessor temporal) {
return DATETIME_FORMATTER.format(temporal);
}
public static String formatDateTimeMini(TemporalAccessor temporal) {
return DATETIME_MINI_FORMATTER.format(temporal);
}
public static String formatDate(TemporalAccessor temporal) {
return DATE_FORMATTER.format(temporal);
}
public static String formatTime(TemporalAccessor temporal) {
return TIME_FORMATTER.format(temporal);
}
public static String format(TemporalAccessor temporal, String pattern) {
return DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(pattern).format(temporal);
}
public static Date parse(String dateStr, String pattern) {
ConcurrentDateFormat format = ConcurrentDateFormat.of(pattern);
try {
return format.parse(dateStr);
} catch (ParseException var4) {
throw Exceptions.unchecked(var4);
}
}
public static Date parse(String dateStr, ConcurrentDateFormat format) {
try {
return format.parse(dateStr);
} catch (ParseException var3) {
throw Exceptions.unchecked(var3);
}
}
public static <T> T parse(String dateStr, String pattern, TemporalQuery<T> query) {
return DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern(pattern).parse(dateStr, query);
}
public static Instant toInstant(LocalDateTime dateTime) {
return dateTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant();
}
public static LocalDateTime toDateTime(Instant instant) {
return LocalDateTime.ofInstant(instant, ZoneId.systemDefault());
}
public static Date toDate(LocalDateTime dateTime) {
return Date.from(toInstant(dateTime));
}
public static Date toDate(final LocalDate localDate) {
return Date.from(localDate.atStartOfDay(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant());
}
public static Calendar toCalendar(final LocalDateTime localDateTime) {
return GregorianCalendar.from(ZonedDateTime.of(localDateTime, ZoneId.systemDefault()));
}
public static long toMilliseconds(final LocalDateTime localDateTime) {
return localDateTime.atZone(ZoneId.systemDefault()).toInstant().toEpochMilli();
}
public static long toMilliseconds(LocalDate localDate) {
return toMilliseconds(localDate.atStartOfDay());
}
public static LocalDateTime fromCalendar(final Calendar calendar) {
TimeZone tz = calendar.getTimeZone();
ZoneId zid = tz == null ? ZoneId.systemDefault() : tz.toZoneId();
return LocalDateTime.ofInstant(calendar.toInstant(), zid);
}
public static LocalDateTime fromInstant(final Instant instant) {
return LocalDateTime.ofInstant(instant, ZoneId.systemDefault());
}
public static LocalDateTime fromDate(final Date date) {
return LocalDateTime.ofInstant(date.toInstant(), ZoneId.systemDefault());
}
public static LocalDateTime fromMilliseconds(final long milliseconds) {
return LocalDateTime.ofInstant(Instant.ofEpochMilli(milliseconds), ZoneId.systemDefault());
}
public static Duration between(Temporal startInclusive, Temporal endExclusive) {
return Duration.between(startInclusive, endExclusive);
}
public static Period between(LocalDate startDate, LocalDate endDate) {
return Period.between(startDate, endDate);
}
public static Duration between(Date startDate, Date endDate) {
return Duration.between(startDate.toInstant(), endDate.toInstant());
}
public static String secondToTime(Long second) {
if (second != null && second != 0L) {
long days = second / 86400L;
second = second % 86400L;
long hours = second / 3600L;
second = second % 3600L;
long minutes = second / 60L;
second = second % 60L;
return days > 0L ? StringUtil.format("{}天{}小时{}分{}秒", new Object[]{days, hours, minutes, second}) : StringUtil.format("{}小时{}分{}秒", new Object[]{hours, minutes, second});
} else {
return "";
}
}
public static String today() {
return format(new Date(), "yyyyMMdd");
}
public static String time() {
return format(new Date(), "yyyyMMddHHmmss");
}
public static Integer hour() {
return NumberUtil.toInt(format(new Date(), "HH"));
}
}