文章目录
- 0 前言
- 1 技术介绍
- 1.1 技术概括
- 1.2 目前表情识别实现技术
- 2 实现效果
- 3 深度学习表情识别实现过程
- 3.1 网络架构
- 3.2 数据
- 3.3 实现流程
- 3.4 部分实现代码
- 4 最后
0 前言
🔥 优质竞赛项目系列,今天要分享的是
基于深度学习的人脸表情识别
该项目较为新颖,适合作为竞赛课题方向,学长非常推荐!
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate
1 技术介绍
1.1 技术概括
面部表情识别技术源于1971年心理学家Ekman和Friesen的一项研究,他们提出人类主要有六种基本情感,每种情感以唯一的表情来反映当时的心理活动,这六种情感分别是愤怒(anger)、高兴(happiness)、悲伤
(sadness)、惊讶(surprise)、厌恶(disgust)和恐惧(fear)。
尽管人类的情感维度和表情复杂度远不是数字6可以量化的,但总体而言,这6种也差不多够描述了。

1.2 目前表情识别实现技术

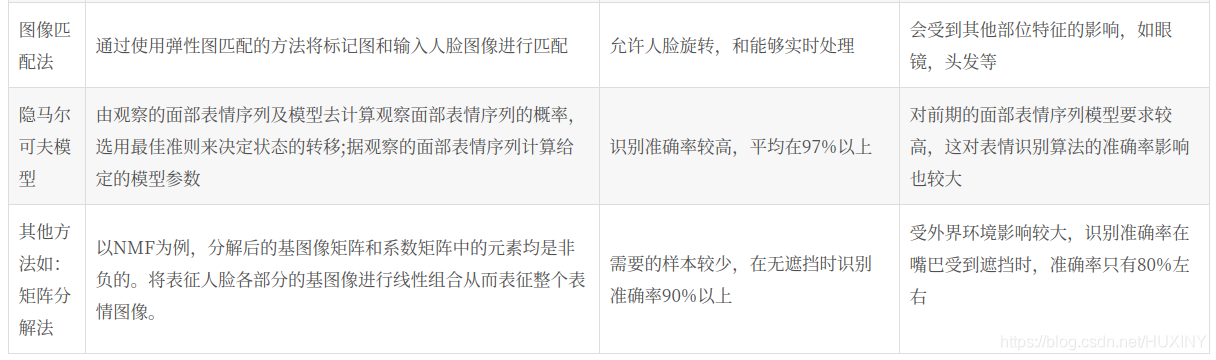
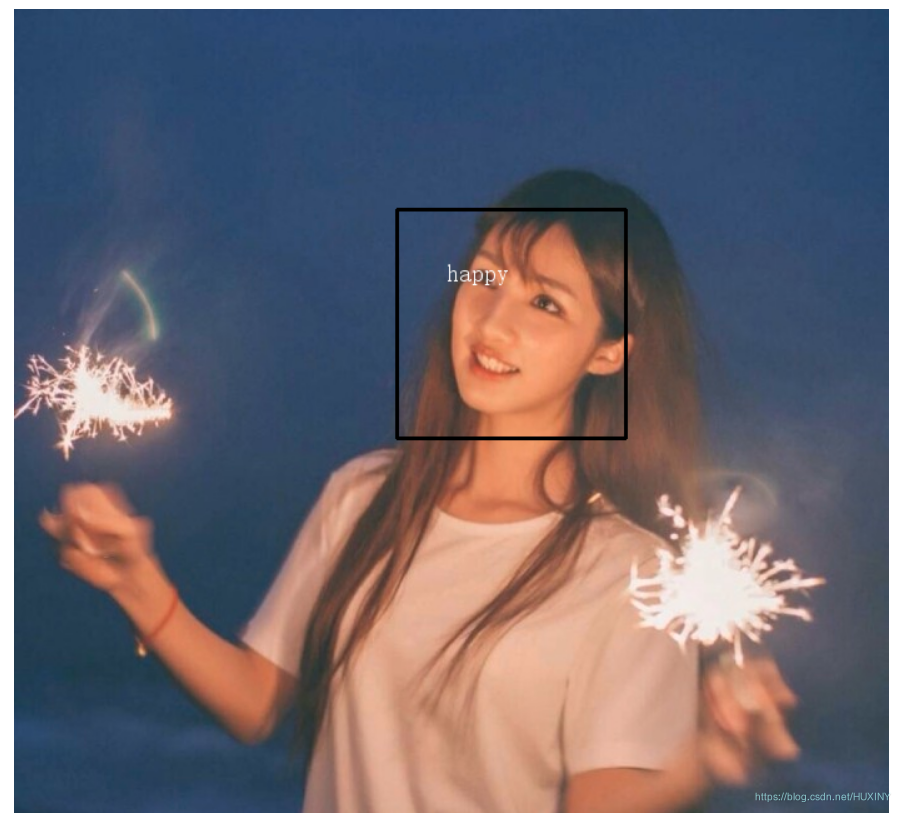
2 实现效果
废话不多说,先上实现效果


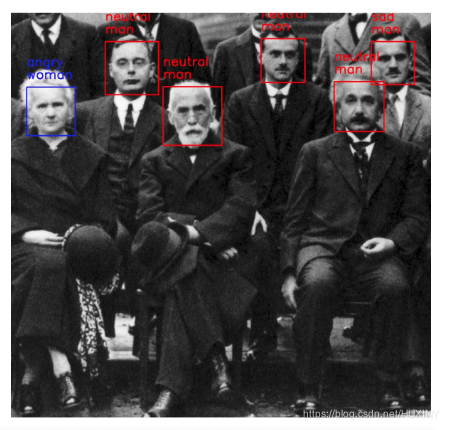
3 深度学习表情识别实现过程
3.1 网络架构
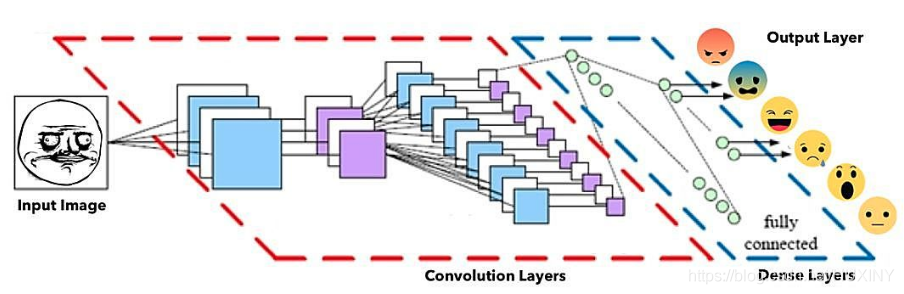
面部表情识别CNN架构(改编自 埃因霍芬理工大学PARsE结构图)
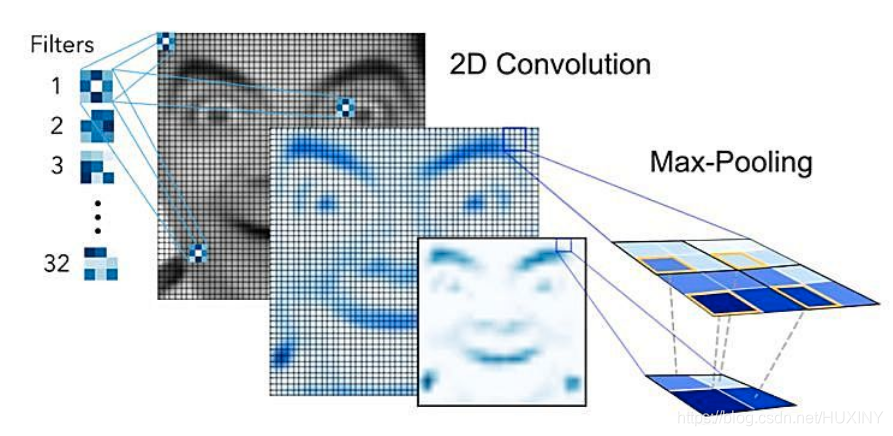
其中,通过卷积操作来创建特征映射,将卷积核挨个与图像进行卷积,从而创建一组要素图,并在其后通过池化(pooling)操作来降维。
3.2 数据
主要来源于kaggle比赛,下载地址。
有七种表情类别: (0=Angry, 1=Disgust, 2=Fear, 3=Happy, 4=Sad, 5=Surprise, 6=Neutral).
数据是48x48 灰度图,格式比较奇葩。
第一列是情绪分类,第二列是图像的numpy,第三列是train or test。

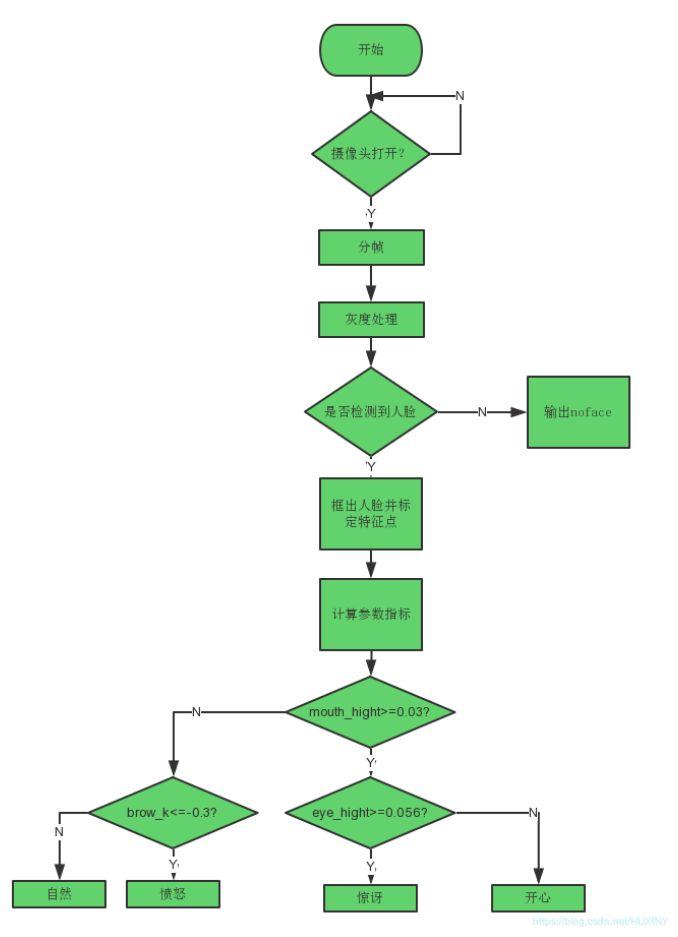
3.3 实现流程
3.4 部分实现代码
import cv2
import sys
import json
import numpy as np
from keras.models import model_from_json
emotions = ['angry', 'fear', 'happy', 'sad', 'surprise', 'neutral']
cascPath = sys.argv[1]
faceCascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(cascPath)
noseCascade = cv2.CascadeClassifier(cascPath)
# load json and create model arch
json_file = open('model.json','r')
loaded_model_json = json_file.read()
json_file.close()
model = model_from_json(loaded_model_json)
# load weights into new model
model.load_weights('model.h5')
# overlay meme face
def overlay_memeface(probs):
if max(probs) > 0.8:
emotion = emotions[np.argmax(probs)]
return 'meme_faces/{}-{}.png'.format(emotion, emotion)
else:
index1, index2 = np.argsort(probs)[::-1][:2]
emotion1 = emotions[index1]
emotion2 = emotions[index2]
return 'meme_faces/{}-{}.png'.format(emotion1, emotion2)
def predict_emotion(face_image_gray): # a single cropped face
resized_img = cv2.resize(face_image_gray, (48,48), interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
# cv2.imwrite(str(index)+'.png', resized_img)
image = resized_img.reshape(1, 1, 48, 48)
list_of_list = model.predict(image, batch_size=1, verbose=1)
angry, fear, happy, sad, surprise, neutral = [prob for lst in list_of_list for prob in lst]
return [angry, fear, happy, sad, surprise, neutral]
video_capture = cv2.VideoCapture(0)
while True:
# Capture frame-by-frame
ret, frame = video_capture.read()
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(frame, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY,1)
faces = faceCascade.detectMultiScale(
img_gray,
scaleFactor=1.1,
minNeighbors=5,
minSize=(30, 30),
flags=cv2.cv.CV_HAAR_SCALE_IMAGE
)
# Draw a rectangle around the faces
for (x, y, w, h) in faces:
face_image_gray = img_gray[y:y+h, x:x+w]
filename = overlay_memeface(predict_emotion(face_image_gray))
print filename
meme = cv2.imread(filename,-1)
# meme = (meme/256).astype('uint8')
try:
meme.shape[2]
except:
meme = meme.reshape(meme.shape[0], meme.shape[1], 1)
# print meme.dtype
# print meme.shape
orig_mask = meme[:,:,3]
# print orig_mask.shape
# memegray = cv2.cvtColor(orig_mask, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
ret1, orig_mask = cv2.threshold(orig_mask, 10, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
orig_mask_inv = cv2.bitwise_not(orig_mask)
meme = meme[:,:,0:3]
origMustacheHeight, origMustacheWidth = meme.shape[:2]
roi_gray = img_gray[y:y+h, x:x+w]
roi_color = frame[y:y+h, x:x+w]
# Detect a nose within the region bounded by each face (the ROI)
nose = noseCascade.detectMultiScale(roi_gray)
for (nx,ny,nw,nh) in nose:
# Un-comment the next line for debug (draw box around the nose)
#cv2.rectangle(roi_color,(nx,ny),(nx+nw,ny+nh),(255,0,0),2)
# The mustache should be three times the width of the nose
mustacheWidth = 20 * nw
mustacheHeight = mustacheWidth * origMustacheHeight / origMustacheWidth
# Center the mustache on the bottom of the nose
x1 = nx - (mustacheWidth/4)
x2 = nx + nw + (mustacheWidth/4)
y1 = ny + nh - (mustacheHeight/2)
y2 = ny + nh + (mustacheHeight/2)
# Check for clipping
if x1 < 0:
x1 = 0
if y1 < 0:
y1 = 0
if x2 > w:
x2 = w
if y2 > h:
y2 = h
# Re-calculate the width and height of the mustache image
mustacheWidth = (x2 - x1)
mustacheHeight = (y2 - y1)
# Re-size the original image and the masks to the mustache sizes
# calcualted above
mustache = cv2.resize(meme, (mustacheWidth,mustacheHeight), interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
mask = cv2.resize(orig_mask, (mustacheWidth,mustacheHeight), interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
mask_inv = cv2.resize(orig_mask_inv, (mustacheWidth,mustacheHeight), interpolation = cv2.INTER_AREA)
# take ROI for mustache from background equal to size of mustache image
roi = roi_color[y1:y2, x1:x2]
# roi_bg contains the original image only where the mustache is not
# in the region that is the size of the mustache.
roi_bg = cv2.bitwise_and(roi,roi,mask = mask_inv)
# roi_fg contains the image of the mustache only where the mustache is
roi_fg = cv2.bitwise_and(mustache,mustache,mask = mask)
# join the roi_bg and roi_fg
dst = cv2.add(roi_bg,roi_fg)
# place the joined image, saved to dst back over the original image
roi_color[y1:y2, x1:x2] = dst
break
# cv2.rectangle(frame, (x, y), (x+w, y+h), (0, 255, 0), 2)
# angry, fear, happy, sad, surprise, neutral = predict_emotion(face_image_gray)
# text1 = 'Angry: {} Fear: {} Happy: {}'.format(angry, fear, happy)
# text2 = ' Sad: {} Surprise: {} Neutral: {}'.format(sad, surprise, neutral)
#
# cv2.putText(frame, text1, (50, 50), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, (255, 0, 0), 3)
# cv2.putText(frame, text2, (50, 150), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 2, (255, 0, 0), 3)
# Display the resulting frame
cv2.imshow('Video', frame)
if cv2.waitKey(1) & 0xFF == ord('q'):
break
# When everything is done, release the capture
video_capture.release()
cv2.destroyAllWindows()
4 最后
🧿 更多资料, 项目分享:
https://gitee.com/dancheng-senior/postgraduate