第一章:整数
面试题1:整数除法
题目
输入两个int型整数,求它们除法的商,要求不得使用乘号’*‘、除号’/‘以及求余符号’%'。当发生溢出时返回最大的整数值。假设除数不为0。例如,输入15和2,输出15/2的结果,即7。
参考代码
public int divide(int dividend, int divisor) {
if (dividend == 0x80000000 && divisor == -1){
return Integer.MAX_VALUE;
}
int negative = 2;
if (dividend > 0) {
negative--;
dividend = -dividend;
}
if (divisor > 0) {
negative--;
divisor = -divisor;
}
int result = divideCore(dividend, divisor);
return negative == 1 ? -result : result;
}
private int divideCore(int dividend, int divisor) {
int result = 0;
while (dividend <= divisor) {
int value = divisor;
int quotient = 1;
while (value >= 0xc0000000 && dividend <= value + value) {
quotient += quotient;
value += value;
}
result += quotient;
dividend -= value;
}
return result;
}
面试题2:二进制加法
题目
输入两个表示二进制的字符串,请计算它们的和,并以二进制字符串的形式输出。例如输入的二进制字符串分别是"11"和"10",则输出"101"。
参考代码
public String addBinary(String a, String b) {
StringBuilder result = new StringBuilder();
int i = a.length() - 1;
int j = b.length() - 1;
int carry = 0;
while (i >= 0 || j >= 0) {
int digitA = i >= 0 ? a.charAt(i--) - '0' : 0;
int digitB = j >= 0 ? b.charAt(j--) - '0' : 0;
int sum = digitA + digitB + carry;
carry = sum >= 2 ? 1 : 0;
sum = sum >= 2 ? sum - 2 : sum;
result.append(sum);
}
if (carry == 1) {
result.append(1);
}
return result.reverse().toString();
}
面试题3:前n个数字二进制中1的个数
题目
输入一个非负数n,请计算0到n之间每个数字的二进制表示中1的个数,并输出一个数组。例如,输入n为4,由于0、1、2、3、4的二进制表示的1的个数分别为0、1、1、2、1,因此输出数组[0, 1, 1, 2, 1]。
参考代码
解法一
public int[] countBits(int num) {
int[] result = new int[num + 1];
for (int i = 0; i <= num; ++i) {
int count = 0;
int j = i;
while (j != 0) {
result[i]++;
j = j & (j - 1);
}
}
return result;
}
解法二
public int[] countBits(int num) {
int[] result = new int[num + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= num; ++i) {
result[i] = result[i & (i - 1)] + 1;
}
return result;
}
解法三
public int[] countBits(int num) {
int[] result = new int[num + 1];
for (int i = 1; i <= num; ++i) {
result[i] = result[i >> 1] + (i & 1);
}
return result;
}
面试题4:只出现一次的数字
题目
输入一个整数数组,数组中除一个数字只出现一次之外其他数字都出现三次。请找出那个唯一只出现一次的数字。例如,如果输入的数组为[0, 1, 0, 1, 0, 1, 100],则只出现一次的数字时100。
参考代码
public int singleNumber(int[] nums) {
int[] bitSums = new int[32];
for (int num : nums) {
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
bitSums[i] += (num >> (31 - i)) & 1;
}
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 32; i++) {
result = (result << 1) + bitSums[i] % 3;
}
return result;
}
面试题5:单词长度的最大乘积
题目
输入一个字符串数组words,请计算当两个字符串words[i]和words[j]不包含相同字符时它们长度的乘积的最大值。如果没有不包含相同字符的一对字符串,那么返回0。假设字符串中只包含英语的小写字母。例如,输入的字符串数组words为["abcw", "foo", "bar", "fxyz","abcdef"],数组中的字符串"bar"与"foo"没有相同的字符,它们长度的乘积为9。“abcw"与” fxyz "也没有相同的字符,它们长度的乘积是16,这是不含相同字符的一对字符串的长度乘积的最大值。
参考代码
public int maxProduct(String[] words) {
boolean[][] flags = new boolean[words.length][26];
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
for(char c: words[i].toCharArray()) {
flags[i][c - 'a'] = true;
}
}
int result = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < words.length; i++) {
for (int j = i + 1; j < words.length; j++) {
int k = 0;
for (; k < 26; k++) {
if (flags[i][k] && flags[j][k]) {
break;
}
}
if (k == 26) {
int prod = words[i].length() * words[j].length();
result = Math.max(result, prod);
}
}
}
return result;
}
第二章:数组
面试题6:排序数组中两个数字之和
题目
输入一个递增排序的数组和一个值k,请问如何在数组中找出两个和为k的数字并返回它们的下标?假设数组中存在且只存在一对符合条件的数字,同时一个数字不能使用两次。例如输入数组[1, 2, 4, 6, 10],k的值为8,数组中的数字2和6的和为8,它们的下标分别为1和3。
参考代码
public int[] twoSum(int[] numbers, int target) {
int i = 0;
int j = numbers.length - 1;
while (i < j && numbers[i] + numbers[j] != target) {
if (numbers[i] + numbers[j] < target) {
i++;
} else {
j--;
}
}
return new int[] {
i, j};
}
面试题7:数组中和为0的三个数字
题目
输入一个数组,如何找出数组中所有和为0的三个数字的三元组?注意返回值中不得包含重复的三元组。例如在数组中[-1, 0, 1, 2, -1, -4]中有两个三元组的和为0,它们分别是[-1, 0, 1]和[-1, -1, 2]。
参考代码
public List<List<Integer>> threeSum(int[] nums) {
List<List<Integer>> result = new LinkedList<List<Integer>>();
if (nums.length >= 3) {
Arrays.sort(nums);
int i = 0;
while(i < nums.length - 2) {
twoSum(nums, i, result);
int temp = nums[i];
while(i < nums.length && nums[i] == temp) {
++i;
}
}
}
return result;
}
private void twoSum(int[] nums, int i, List<List<Integer>> result) {
int j = i + 1;
int k = nums.length - 1;
while (j < k) {
if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] == 0) {
result.add(Arrays.asList(nums[i], nums[j], nums[k]));
int temp = nums[j];
while (nums[j] == temp && j < k) {
++j;
}
} else if (nums[i] + nums[j] + nums[k] < 0) {
++j;
} else {
--k;
}
}
}
面试题8:和大于等于k的最短子数组
题目
输入一个正整数组成的数组和一个正整数k,请问数组中和大于或等于k的连续子数组的最短长度是多少?如果不存在所有数字之和大于k的子数组,则返回0。例如输入数组[5, 1, 4, 3],k的值为7,和大于或等于7的最短连续子数组是[4, 3],因此输出它的长度2。
参考代码
public int minSubArrayLen(int k, int[] nums) {
int left = 0;
int sum = 0;
int minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
for (int right = 0; right < nums.length; right++) {
sum += nums[right];
while (left <= right && sum >= k) {
minLength = Math.min(minLength, right - left + 1);
sum -= nums[left++];
}
}
return minLength == Integer.MAX_VALUE ? 0 : minLength;
}
面试题9:乘积小于k的子数组
题目
输入一个由正整数组成的数组和一个正整数k,请问数组中有多少个数字乘积小于k的连续子数组?例如输入数组[10, 5, 2, 6],k的值为100,有8个子数组的所有数字的乘积小于100,它们分别是[10]、[5]、[2]、[6]、[10, 5]、[5, 2]、[2, 6]和[5, 2, 6]。
参考代码
public int numSubarrayProductLessThanK(int[] nums, int k) {
long product = 1;
int left = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int right = 0; right < nums.length; ++right) {
product *= nums[right];
while (left <= right && product >= k) {
product /= nums[left];
left++;
}
count += right >= left ? right - left + 1 : 0;
}
return count;
}
面试题10:和为k的子数组
题目:输入一个整数数组和一个整数k,请问数组中有多少个数字之和等于k的连续子数组?例如输入数组[1, 1, 1],k的值为2,有2个连续子数组之和等于2。
参考代码
public int subarraySum(int[] nums, int k) {
Map<Integer, Integer> sumToCount = new HashMap<>();
sumToCount.put(0, 1);
int sum = 0;
int count = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
sum += num;
count += sumToCount.getOrDefault(sum - k, 0);
sumToCount.put(sum, sumToCount.getOrDefault(sum, 0) + 1);
}
return count;
}
面试题11:0和1个数相同的子数组
题目
输入一个只包含0和1的数组,请问如何求最长0和1的个数相同的连续子数组的长度?例如在数组[0, 1, 0]中有两个子数组包含相同个数的0和1,分别是[0, 1]和[1, 0],它们的长度都是2,因此输出2。
参考代码
public int findMaxLength(int[] nums) {
Map<Integer, Integer> sumToIndex = new HashMap();
sumToIndex.put(0, -1);
int sum = 0;
int maxLength = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
sum += nums[i] == 0 ? -1 : 1;
if (sumToIndex.containsKey(sum)) {
maxLength = Math.max(maxLength, i - sumToIndex.get(sum));
} else {
sumToIndex.put(sum, i);
}
}
return maxLength;
}
面试题12:左右两边子数组的和相等
题目
输入一个整数数组,如果一个数字左边的子数组数字之和等于右边的子数组数字之和,请返回该数字的下标。如果存在多个这样的数字,则返回最左边一个的下标。如果不存在这样的数字,则返回-1。例如在数组1, 7, 3, 6, 2, 9]中,下标为3的数字(值为6)左边三个数字1、7、3和右边两个数字2和9的和相等,都是11,因此正确的输出值是3。
参考代码
public int pivotIndex(int[] nums) {
int total = 0;
for (int num : nums) {
total += num;
}
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < nums.length; ++i) {
sum += nums[i];
if (sum - nums[i] == total - sum) {
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
面试题13:二维子矩阵的和
题目
输入一个二维矩阵,如何计算给定左上角坐标和右下角坐标的子矩阵数字之和?对同一个二维矩阵,计算子矩阵数字之和的函数可能输入不同的坐标而被反复调用多次。例如输入图2.1中的二维矩阵,以及左上角坐标为(2, 1)和右下角坐标为(4, 3),该函数输出8。

图2.1:在一个5×5的二维数组中左上角坐标为(2, 1)、右下角坐标为(4, 3)的子矩阵(有灰色背景部分)的和等于8。
参考代码
class NumMatrix {
private int[][] sums;
public NumMatrix(int[][] matrix) {
if (matrix.length == 0 || matrix[0].length == 0) {
return;
}
sums = new int[matrix.length + 1][matrix[0].length + 1];
for (int i = 0; i < matrix.length; ++i) {
int rowSum = 0;
for (int j = 0; j < matrix[0].length; ++j) {
rowSum += matrix[i][j];
sums[i + 1][j + 1] = sums[i][j + 1] + rowSum;
}
}
}
public int sumRegion(int row1, int col1, int row2, int col2) {
return sums[row2 + 1][col2 + 1] - sums[row1][col2 + 1]
- sums[row2 + 1][col1] + sums[row1][col1];
}
}
第三章:字符串
面试题14:字符串中的变位词
题目
输入两个字符串s1和s2,如何判断s2中是否包含s1的某个变位词?如果s2中包含s1的某个变位词,则s1至少有一个变位词是s2的子字符串。假设两个输入字符串中只包含英语小写字母。例如输入字符串s1为"ab",s2为"dgcaf",由于s2中包含s1的变位词"ba",因此输出是true。如果输入字符串s1为"ac",s2为"dcgaf",输出为false。
参考代码
public boolean checkInclusion(String s1, String s2) {
if (s2.length() >= s1.length()) {
int[] counts = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < s1.length(); ++i) {
counts[s1.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
counts[s2.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
}
if (areAllZero(counts)) {
return true;
}
for (int i = s1.length(); i < s2.length(); ++i) {
counts[s2.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
counts[s2.charAt(i - s1.length()) - 'a']++;
if (areAllZero(counts)) {
return true;
}
}
}
return false;
}
private boolean areAllZero(int[] counts) {
for (int count : counts) {
if (count != 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
面试题15:字符串中的所有变位词
题目
输入两个字符串s1和s2,如何找出s2的所有变位词在s1中的起始下标?假设两个输入字符串中只包含英语小写字母。例如输入字符串s1为"cbadabacg",s2为"abc",s2有两个变位词"cba"和"bac"是s1中的字符串,输出它们在s1中的起始下标0和5。
参考代码
public List<Integer> findAnagrams(String s1, String s2) {
List<Integer> indices = new LinkedList<>();
if (s1.length() >= s2.length()) {
int[] counts = new int[26];
for (int i = 0; i < s2.length(); ++i) {
counts[s2.charAt(i) - 'a']++;
counts[s1.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
}
if (areAllZero(counts)) {
indices.add(0);
}
for (int i = s2.length(); i < s1.length(); ++i) {
counts[s1.charAt(i) - 'a']--;
counts[s1.charAt(i - s2.length()) - 'a']++;
if (areAllZero(counts)) {
indices.add(i - s2.length() + 1);
}
}
}
return indices;
}
private boolean areAllZero(int[] counts) {
for (int count : counts) {
if (count != 0) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
面试题16:不含重复字符的最长子字符串
题目
输入一个字符串,求该字符串中不含重复字符的最长连续子字符串的长度。例如,输入字符串"babcca",它最长的不含重复字符串的子字符串是"abc",长度为3。
参考代码
解法一
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int[] counts = new int[256];
int longest = s.length() > 0 ? 1 : 0;
for (int i = 0, j = -1; i < s.length(); ++i) {
counts[s.charAt(i)]++;
while (hasGreaterThan1(counts)) {
++j;
counts[s.charAt(j)]--;
}
longest = Math.max(i - j, longest);
}
return longest;
}
private boolean hasGreaterThan1(int[] counts) {
for (int count : counts) {
if (count > 1) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
解法二
public int lengthOfLongestSubstring(String s) {
int[] counts = new int[256];
int longest = s.length() > 0 ? 1 : 0;
int countDup = 0;
for (int i = 0, j = -1; i < s.length(); ++i) {
counts[s.charAt(i)]++;
if (counts[s.charAt(i)] == 2) {
countDup++;
}
while (countDup > 0) {
++j;
counts[s.charAt(j)]--;
if (counts[s.charAt(j)] == 1) {
countDup--;
}
}
longest = Math.max(i - j, longest);
}
return longest;
}
面试题17:含有所有字符的最短字符串
题目
输入两个字符串s和t,请找出s中包含t的所有字符的最短子字符串。例如输入s为字符串"ADDBANCAD",t为字符串"ABC",则s中包含字符’A’、‘B’、'C’的最短子字符串是"BANC"。如果不存在符合条件的子字符串,返回空字符串""。如果存在多个符合条件的子字符串,返回任意一个。
参考代码
public String minWindow(String s, String t) {
HashMap<Character, Integer> charToCount = new HashMap<>();
for (char ch : t.toCharArray()) {
charToCount.put(ch, charToCount.getOrDefault(ch, 0) + 1);
}
int count = charToCount.size();
int start = 0, end = 0, minStart = 0, minEnd = 0;
int minLength = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
while (end < s.length() || (count == 0 && end == s.length())) {
if (count > 0) {
char endCh = s.charAt(end);
if (charToCount.containsKey(endCh)) {
charToCount.put(endCh, charToCount.get(endCh) - 1);
if (charToCount.get(endCh) == 0) {
count--;
}
}
end++;
} else {
if (end - start < minLength) {
minLength = end - start;
minStart = start;
minEnd = end;
}
char startCh = s.charAt(start);
if (charToCount.containsKey(startCh)) {
charToCount.put(startCh, charToCount.get(startCh) + 1);
if (charToCount.get(startCh) == 1) {
count++;
}
}
start++;
}
}
return minLength < Integer.MAX_VALUE
? s.substring(minStart, minEnd)
: "";
}
面试题18:有效的回文
题目
给定一个字符串,请判断它是不是一个回文字符串。我们只需要考虑字母或者数字字符,并忽略大小写。例如,"A man, a plan, a canal: Panama"是一个回文字符串,而"race a car"不是。
参考代码
public boolean isPalindrome(String s) {
int i = 0;
int j = s.length() - 1;
while (i < j) {
char ch1 = s.charAt(i);
char ch2 = s.charAt(j);
if (!Character.isLetterOrDigit(ch1)) {
i++;
} else if (!Character.isLetterOrDigit(ch2)) {
j--;
} else {
ch1 = Character.toLowerCase(ch1);
ch2 = Character.toLowerCase(ch2);
if (ch1 != ch2) {
return false;
}
i++;
j--;
}
}
return true;
}
面试题19:最多删除一个字符得到回文
题目
给定一个字符串,请判断如果最多从字符串中删除一个字符能不能得到一个回文字符串。例如,如果输入字符串"abca",由于删除字符’b’或者’c’就能得到一个回文字符串,因此输出为true。
参考代码
public boolean validPalindrome(String s) {
int start = 0;
int end = s.length() - 1;
for (; start < s.length() / 2; ++start, --end) {
if (s.charAt(start) != s.charAt(end)) {
break;
}
}
return start == s.length() / 2
|| isPalindrome(s, start, end - 1)
|| isPalindrome(s, start + 1, end);
}
private boolean isPalindrome(String s, int start, int end) {
while (start < end) {
if (s.charAt(start) != s.charAt(end)) {
break;
}
start++;
end--;
}
return start >= end;
}
面试题20:回文子字符串的个数
题目
给定一个字符串,请问字符串里有多少回文连续子字符串?例如,字符串里"abc"有3个回文字符串,分别为"a"、“b”、“c”;而字符串"aaa"里有6个回文子字符串,分别为"a"、“a”、“a”、“aa”、“aa"和"aaa”。
参考代码
public int countSubstrings(String s) {
if (s == null || s.length() == 0) {
return 0;
}
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); ++i) {
count += countPalindrome(s, i, i);
count += countPalindrome(s, i, i + 1);
}
return count;
}
private int countPalindrome(String s, int start, int end) {
int count = 0;
while (start >= 0 && end < s.length()
&& s.charAt(start) == s.charAt(end)) {
count++;
start--;
end++;
}
return count;
}
第四章:链表
面试题21:删除倒数第k个结点
题目
给你一个链表,请问如何删除链表中的倒数第k个结点?假设链表中结点的总数为n,那么1≤k≤n。要求只能遍历链表一次。
例如输入图4.1中(a)的链表,删除倒数第2个结点之后的链表如图4.1中(b)所示。

图4.1:从链表中删除倒数第2个结点。(a)一个包含6个结点的链表。(b)删除倒数第2个结点(值为5的结点)之后的链表。
参考代码
public ListNode removeNthFromEnd(ListNode head, int n) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode front = head, back = dummy;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
front = front.next;
}
while (front != null) {
front = front.next;
back = back.next;
}
back.next = back.next.next;
return dummy.next;
}
面试题22:链表中环的入口结点
题目
一个链表中包含环,如何找出环的入口结点?从链表的头结点开始沿着next指针进入环的第一个结点为环的入口结点。例如,在图4.3的链表中,环的入口结点是结点3。

图4.3:结点3是链表中环的入口结点
参考代码
public ListNode detectCycle(ListNode head) {
ListNode inLoop = getNodeInLoop(head);
if (inLoop == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode node = head;
while (node != inLoop) {
node = node.next;
inLoop = inLoop.next;
}
return node;
}
private ListNode getNodeInLoop(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
ListNode slow = head.next;
ListNode fast = slow.next;
while (slow != null && fast != null) {
if (slow == fast)
return slow;
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast != null)
fast = fast.next;
}
return null;
}
面试题23:两个链表的第一个重合结点
题目
输入两个单向链表,请问如何找出它们的第一个重合结点。例如图4.5中的两个链表的第一个重合的结点的值是4。
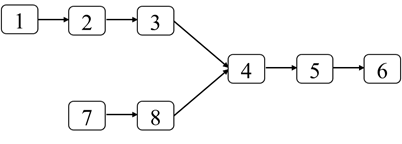
图4.5:两个部分重合的链表,它们的第一个重合的结点的值是4。
参考代码
public ListNode getIntersectionNode(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) {
int count1 = countList(headA);
int count2 = countList(headB);
int delta = Math.abs(count1 - count2);
ListNode longer = count1 > count2 ? headA : headB;
ListNode shorter = count1 > count2 ? headB : headA;
ListNode node1 = longer;
for (int i = 0; i < delta; ++i) {
node1 = node1.next;
}
ListNode node2 = shorter;
while (node1 != node2) {
node2 = node2.next;
node1 = node1.next;
}
return node1;
}
private int countList(ListNode head) {
int count = 0;
while (head != null) {
count++;
head = head.next;
}
return count;
}
面试题24:反转链表
题目
定义一个函数,输入一个链表的头结点,反转该链表并输出反转后链表的头结点。例如,把图4.8(a)中的链表反转之后得到的链表如图4.8(b)所示。
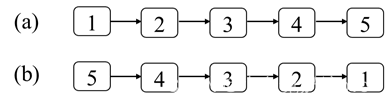
图4.8:反转一个链表。(a)一个含有5个结点的链表。(b)反转之后的链表。
参考代码
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return prev;
}
面试题25:链表中的数字相加
题目
给你两个表示非负整数的单向链表,请问如何实现这两个整数的相加并且把和仍然用单向链表表示?链表中的每个结点表示整数十进制的一位,并且头结点对应整数的最高位数而尾结点对应整数的个位数。例如在图4.10(a)和(b)中的两个链表分别表示整数123和531,它们的和为654,对应的链表尾图4.10的(c)所示。

图4.10:链表中数字以及它们的和。(a)表示整数123的链表。(b)表示整数531的链表。(c)表示123与531的和654的链表。
参考代码
public ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
head1 = reverseList(head1);
head2 = reverseList(head2);
ListNode reversedHead = addReversed(head1, head2);
return reverseList(reversedHead);
}
private ListNode addReversed(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
ListNode sumNode = dummy;
int carry = 0;
while (head1 != null || head2 != null) {
int sum = (head1 == null ? 0 : head1.val)
+ (head2 == null ? 0 : head2.val) + carry;
carry = sum >= 10 ? 1 : 0;
sum = sum >= 10 ? sum - 10 : sum;
ListNode newNode = new ListNode(sum);
sumNode.next = newNode;
sumNode = sumNode.next;
head1 = head1 == null ? null : head1.next;
head2 = head2 == null ? null : head2.next;
}
if (carry > 0) {
sumNode.next = new ListNode(carry);
}
return dummy.next;
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode reversedHead = null;
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
if (next == null)
reversedHead = cur;
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return reversedHead;
}
面试题26:重排链表
题目
给你一个链表,链表中结点的顺序是L0→ L1→ L2→…→ Ln-1→ Ln,请问如何重排链表使得结点的顺序变成L0→ Ln→ L1→ Ln-1→ L2→ Ln-2→…?例如输入图4.12(a)中的链表,重排之后的链表如图4.12(b)所示。
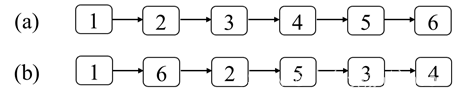
图4.12:重排链表。(a)一个含有6个结点的链表。(b)重排之后的链表。
参考代码
public void reorderList(ListNode head) {
ListNode dummy = new ListNode(0);
dummy.next = head;
ListNode fast = dummy;
ListNode slow = dummy;
while (fast != null && fast.next != null) {
slow = slow.next;
fast = fast.next;
if (fast.next != null) {
fast = fast.next;
}
}
ListNode temp = slow.next;
slow.next = null;
link(head, reverseList(temp), dummy);
}
private void link(ListNode node1, ListNode node2, ListNode head) {
ListNode prev = head;
while (node1 != null && node2 != null) {
ListNode temp = node1.next;
prev.next = node1;
node1.next = node2;
prev = node2;
node1 = temp;
node2 = node2.next;
}
if (node1 != null) {
prev.next = node1;
}
}
private ListNode reverseList(ListNode first) {
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = first;
ListNode head = null;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
cur.next = prev;
if (next == null) {
head = cur;
}
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return head;
}
面试题27:回文链表
题目
如何判断一个链表是不是回文?要求解法的时间复杂度是O(n),另外不得使用超过O(1)的辅助空间。如果一个链表是回文,那么链表中结点序列从前往后看和从后往前看是相同的。例如,图4.13中的链表的结点序列从前往后看和从后往前看都是1、2、3、3、2、1,因此这是一个回文链表。
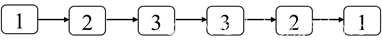
图4.13:一个回文链表。
参考代码
public boolean isPalindrome(ListNode head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return true;
}
ListNode slow = head;
ListNode fast = head.next;
while (fast.next != null && fast.next.next != null) {
fast = fast.next.next;
slow = slow.next;
}
ListNode secondHalf = slow.next;
if (fast.next != null) {
secondHalf = slow.next.next;
}
slow.next = null;
return equals(secondHalf, reverseList(head));
}
public ListNode reverseList(ListNode head) {
ListNode reversedHead = null;
ListNode prev = null;
ListNode cur = head;
while (cur != null) {
ListNode next = cur.next;
if (next == null) {
reversedHead = cur;
}
cur.next = prev;
prev = cur;
cur = next;
}
return reversedHead;
}
面试题28:展平多级双向链表
题目
在一个多级双向链表中节点除了有两个指针分别指向前后两个节点之外,还有一个指针指向它的子链表,并且子链表也是一个双向链表,它的节点也有指向子链表的指针。请将这样的多级双向链表展平成普通的双向链表,即所有节点都没有子链表。例如图4.14(a)是一个多级双向链表,它展平之后如图4.14(b)所示。

图4.14:展平多级双向链表。(a)一个多级双向链表。(b)展平之后的双向链表。
参考代码
public Node flatten(Node head) {
flattenGetTail(head);
return head;
}
private Node flattenGetTail(Node head) {
Node node = head;
Node tail = null;
while (node != null) {
Node next = node.next;
if (node.child != null) {
Node child = node.child;
Node childTail = flattenGetTail(node.child);
node.child = null;
node.next = child;
child.prev = node;
childTail.next = next;