15721这一章没什么好说的,不再贴课程内容了。codegen和simd在工业界一般只会选一种实现。比如phothon之前用codegen,然后改成了向量化引擎。一般gen的都是weld IR/LLVM IR/当前语言,gen成C++的也要检查是不是有本地预编译版本,要不没法用。因为clickhouse没有codegen,这节课就拿我比较熟悉的spark的tungsten来当例子,tungsten会gen成scala,然后拿janino动态编译。
tungsten主要有两个特色:一个是codegen,另一个是in-heap memory的管理。本文顺便把它的内存管理也分析一下。在jvm堆内自由分配内存,不被free,不受gc影响,还是挺有意思的。
WASG
手写代码的生成过程分为两个步骤:
- 从父节点到子节点,递归调用 doProduce,生成框架
- 从子节点到父节点,递归调用 doConsume,向框架填充每一个操作符的运算逻辑
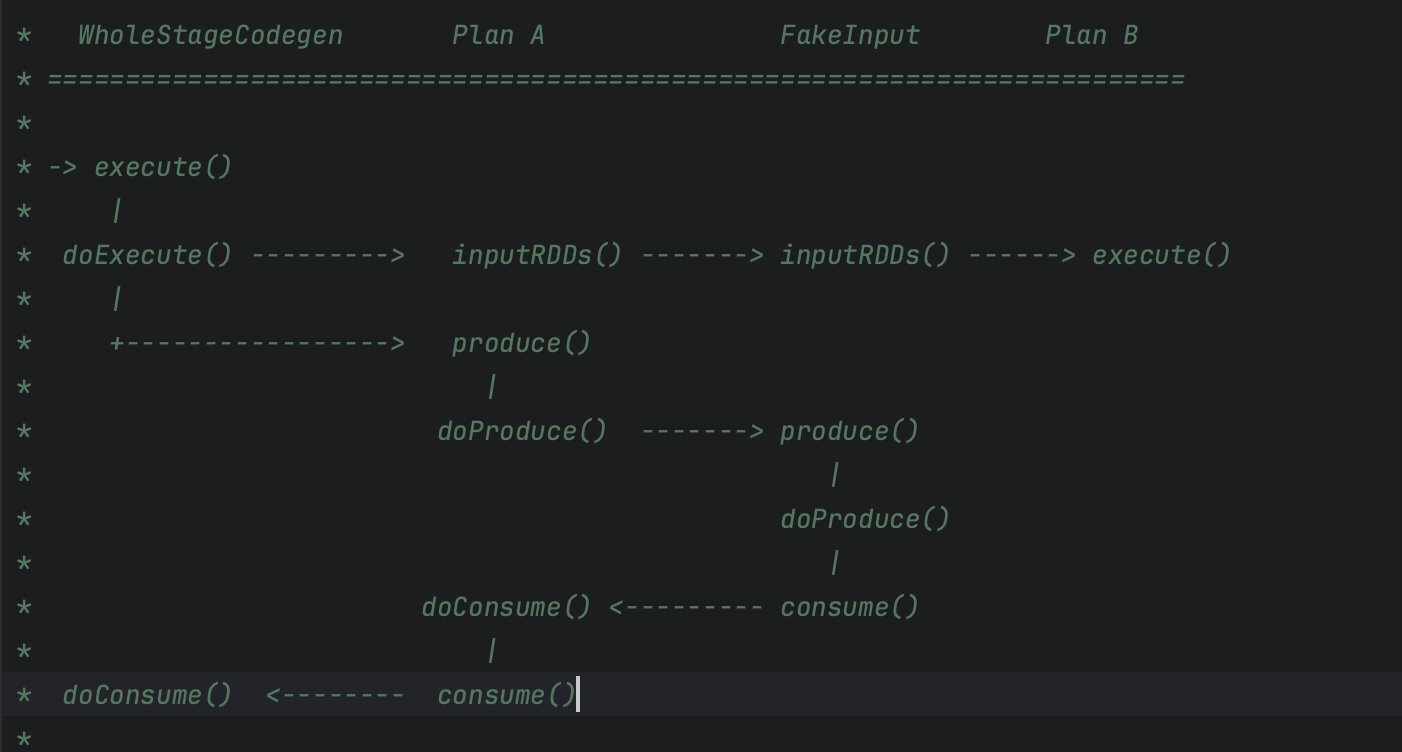
首先,在 Stage 顶端节点也就是 Project 之上,添加 WholeStageCodeGen 节点。WholeStageCodeGen 节点通过调用 doExecute 来触发整个代码生成过程的计算。doExecute 会递归调用子节点的 doProduce 函数,直到遇到 Shuffle Boundary 为止。这里,Shuffle Boundary 指的是 Shuffle 边界,要么是数据源,要么是上一个 Stage 的输出。在叶子节点(也就是 Scan)调用的 doProduce 函数会先把手写代码的框架生成出来。
override def doExecute(): RDD[InternalRow] = {
// 下面这一行将会调用子类的produce完成上述过程。
val (ctx, cleanedSource) = doCodeGen()
// try to compile and fallback if it failed
// 调用janino完成动态编译过程
val (_, compiledCodeStats) = try {
CodeGenerator.compile(cleanedSource)
} catch {
case NonFatal(_) if !Utils.isTesting && conf.codegenFallback =>
// We should already saw the error message
logWarning(s"Whole-stage codegen disabled for plan (id=$codegenStageId):\n $treeString")
return child.execute()
}
// Check if compiled code has a too large function
if (compiledCodeStats.maxMethodCodeSize > conf.hugeMethodLimit) {
logInfo(s"Found too long generated codes and JIT optimization might not work: " +
s"the bytecode size (${compiledCodeStats.maxMethodCodeSize}) is above the limit " +
s"${conf.hugeMethodLimit}, and the whole-stage codegen was disabled " +
s"for this plan (id=$codegenStageId). To avoid this, you can raise the limit " +
s"`${SQLConf.WHOLESTAGE_HUGE_METHOD_LIMIT.key}`:\n$treeString")
return child.execute()
}
val references = ctx.references.toArray
val durationMs = longMetric("pipelineTime")
// Even though rdds is an RDD[InternalRow] it may actually be an RDD[ColumnarBatch] with
// type erasure hiding that. This allows for the input to a code gen stage to be columnar,
// but the output must be rows.
val rdds = child.asInstanceOf[CodegenSupport].inputRDDs()
assert(rdds.size <= 2, "Up to two input RDDs can be supported")
if (rdds.length == 1) {
rdds.head.mapPartitionsWithIndex { (index, iter) =>
val (clazz, _) = CodeGenerator.compile(cleanedSource)
val buffer = clazz.generate(references).asInstanceOf[BufferedRowIterator]
buffer.init(index, Array(iter))
new Iterator[InternalRow] {
override def hasNext: Boolean = {
val v = buffer.hasNext
if (!v) durationMs += buffer.durationMs()
v
}
override def next: InternalRow = buffer.next()
}
}
} else {
// Right now, we support up to two input RDDs.
rdds.head.zipPartitions(rdds(1)) { (leftIter, rightIter) =>
Iterator((leftIter, rightIter))
// a small hack to obtain the correct partition index
}.mapPartitionsWithIndex { (index, zippedIter) =>
val (leftIter, rightIter) = zippedIter.next()
val (clazz, _) = CodeGenerator.compile(cleanedSource)
val buffer = clazz.generate(references).asInstanceOf[BufferedRowIterator]
buffer.init(index, Array(leftIter, rightIter))
new Iterator[InternalRow] {
override def hasNext: Boolean = {
val v = buffer.hasNext
if (!v) durationMs += buffer.durationMs()
v
}
override def next: InternalRow = buffer.next()
}
}
}
}
def doCodeGen(): (CodegenContext, CodeAndComment) = {
val startTime = System.nanoTime()
val ctx = new CodegenContext
val code = child.asInstanceOf[CodegenSupport].produce(ctx, this)
// main next function.
ctx.addNewFunction("processNext",
s"""
protected void processNext() throws java.io.IOException {
${code.trim}
}
""", inlineToOuterClass = true)
val className = generatedClassName()
val source = s"""
public Object generate(Object[] references) {
return new $className(references);
}
${ctx.registerComment(
s"""Codegened pipeline for stage (id=$codegenStageId)
|${this.treeString.trim}""".stripMargin,
"wsc_codegenPipeline")}
${ctx.registerComment(s"codegenStageId=$codegenStageId", "wsc_codegenStageId", true)}
final class $className extends ${classOf[BufferedRowIterator].getName} {
private Object[] references;
private scala.collection.Iterator[] inputs;
${ctx.declareMutableStates()}
public $className(Object[] references) {
this.references = references;
}
public void init(int index, scala.collection.Iterator[] inputs) {
partitionIndex = index;
this.inputs = inputs;
${ctx.initMutableStates()}
${ctx.initPartition()}
}
${ctx.emitExtraCode()}
${ctx.declareAddedFunctions()}
}
""".trim
// try to compile, helpful for debug
val cleanedSource = CodeFormatter.stripOverlappingComments(
new CodeAndComment(CodeFormatter.stripExtraNewLines(source), ctx.getPlaceHolderToComments()))
val duration = System.nanoTime() - startTime
WholeStageCodegenExec.increaseCodeGenTime(duration)
logDebug(s"\n${CodeFormatter.format(cleanedSource)}")
(ctx, cleanedSource)
}
然后,Scan 中的 doProduce 会反向递归调用每个父节点的 doConsume 函数。不同操作符在执行 doConsume 函数的过程中,会把关系表达式转化成 Java 代码,然后把这份代码像做“完形填空”一样,嵌入到刚刚的代码框架里。
doConsume代码不太好理解,我们以filter为例:
override def doConsume(ctx: CodegenContext, input: Seq[ExprCode], row: ExprCode): String = {
val numOutput = metricTerm(ctx, "numOutputRows")
val predicateCode = generatePredicateCode(
ctx, child.output, input, output, notNullPreds, otherPreds, notNullAttributes)
// Reset the isNull to false for the not-null columns, then the followed operators could
// generate better code (remove dead branches).
val resultVars = input.zipWithIndex.map { case (ev, i) =>
if (notNullAttributes.contains(child.output(i).exprId)) {
ev.isNull = FalseLiteral
}
ev
}
// Note: wrap in "do { } while(false);", so the generated checks can jump out with "continue;"
s"""
|do {
| $predicateCode
| $numOutput.add(1);
| ${consume(ctx, resultVars)}
|} while(false);
""".stripMargin
}
protected def generatePredicateCode(
ctx: CodegenContext,
inputAttrs: Seq[Attribute],
inputExprCode: Seq[ExprCode],
outputAttrs: Seq[Attribute],
notNullPreds: Seq[Expression],
otherPreds: Seq[Expression],
nonNullAttrExprIds: Seq[ExprId]): String = {
/**
* Generates code for `c`, using `in` for input attributes and `attrs` for nullability.
*/
def genPredicate(c: Expression, in: Seq[ExprCode], attrs: Seq[Attribute]): String = {
val bound = BindReferences.bindReference(c, attrs)
val evaluated = evaluateRequiredVariables(inputAttrs, in, c.references)
// Generate the code for the predicate.
val ev = ExpressionCanonicalizer.execute(bound).genCode(ctx)
val nullCheck = if (bound.nullable) {
s"${ev.isNull} || "
} else {
s""
}
s"""
|$evaluated
|${ev.code}
|if (${nullCheck}!${ev.value}) continue;
""".stripMargin
}
// To generate the predicates we will follow this algorithm.
// For each predicate that is not IsNotNull, we will generate them one by one loading attributes
// as necessary. For each of both attributes, if there is an IsNotNull predicate we will
// generate that check *before* the predicate. After all of these predicates, we will generate
// the remaining IsNotNull checks that were not part of other predicates.
// This has the property of not doing redundant IsNotNull checks and taking better advantage of
// short-circuiting, not loading attributes until they are needed.
// This is very perf sensitive.
// TODO: revisit this. We can consider reordering predicates as well.
val generatedIsNotNullChecks = new Array[Boolean](notNullPreds.length)
val extraIsNotNullAttrs = mutable.Set[Attribute]()
val generated = otherPreds.map { c =>
val nullChecks = c.references.map { r =>
val idx = notNullPreds.indexWhere { n => n.asInstanceOf[IsNotNull].child.semanticEquals(r)}
if (idx != -1 && !generatedIsNotNullChecks(idx)) {
generatedIsNotNullChecks(idx) = true
// Use the child's output. The nullability is what the child produced.
genPredicate(notNullPreds(idx), inputExprCode, inputAttrs)
} else if (nonNullAttrExprIds.contains(r.exprId) && !extraIsNotNullAttrs.contains(r)) {
extraIsNotNullAttrs += r
genPredicate(IsNotNull(r), inputExprCode, inputAttrs)
} else {
""
}
}.mkString("\n").trim
// Here we use *this* operator's output with this output's nullability since we already
// enforced them with the IsNotNull checks above.
s"""
|$nullChecks
|${genPredicate(c, inputExprCode, outputAttrs)}
""".stripMargin.trim
}.mkString("\n")
val nullChecks = notNullPreds.zipWithIndex.map { case (c, idx) =>
if (!generatedIsNotNullChecks(idx)) {
genPredicate(c, inputExprCode, inputAttrs)
} else {
""
}
}.mkString("\n")
s"""
|$generated
|$nullChecks
""".stripMargin
}
}
这个地方先裁剪再判断,首先对涉及到谓词的is not null生成判断,之后进行裁剪,然后对裁剪后的列没有覆盖到is not null的再做一次is not null。这里的性能比较关键。
对于以下sql:
SELECT department, AVG(salary) AS avg_salary
FROM employee
GROUP BY department
HAVING AVG(salary) > 60000
生成效果如下:
generated:
boolean filter_value_2 = !hashAgg_isNull_11;
if (!filter_value_2) continue;
boolean filter_value_3 = false;
filter_value_3 = org.apache.spark.sql.catalyst.util.SQLOrderingUtil.compareDoubles(hashAgg_value_11, 60000.0D) > 0;
if (!filter_value_3) continue;
如果加上一句where salary IS NOT NULL,那么在hashAgg之前,还会插入一段null的判断:
boolean rdd_isNull_3 = rdd_row_0.isNullAt(3);
double rdd_value_3 = rdd_isNull_3 ?
-1.0 : (rdd_row_0.getDouble(3));
boolean filter_value_2 = !rdd_isNull_3;
if (!filter_value_2) continue;
内存管理
tungsten memory management

这里的idea很简单,重构对象模型但是不改变gc逻辑,于是tungsten抽象出了page table,来存放大量java native object,page table地址还是由jvm进行管理,拿到地址后在jvm堆内查找。
spark-core
在看spark-unsafe中的tungsten分配器之前, 我们先看下spark-core中的内存管理模块,
我们可以看到MemoryManager中的分配器已经默认换成了tungsten
/**
* Allocates memory for use by Unsafe/Tungsten code.
*/
private[memory] final val tungstenMemoryAllocator: MemoryAllocator = {
tungstenMemoryMode match {
case MemoryMode.ON_HEAP => MemoryAllocator.HEAP
case MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP => MemoryAllocator.UNSAFE
}
}
MemoryManager就是用来管理Execution和Storage之间内存分配的类。
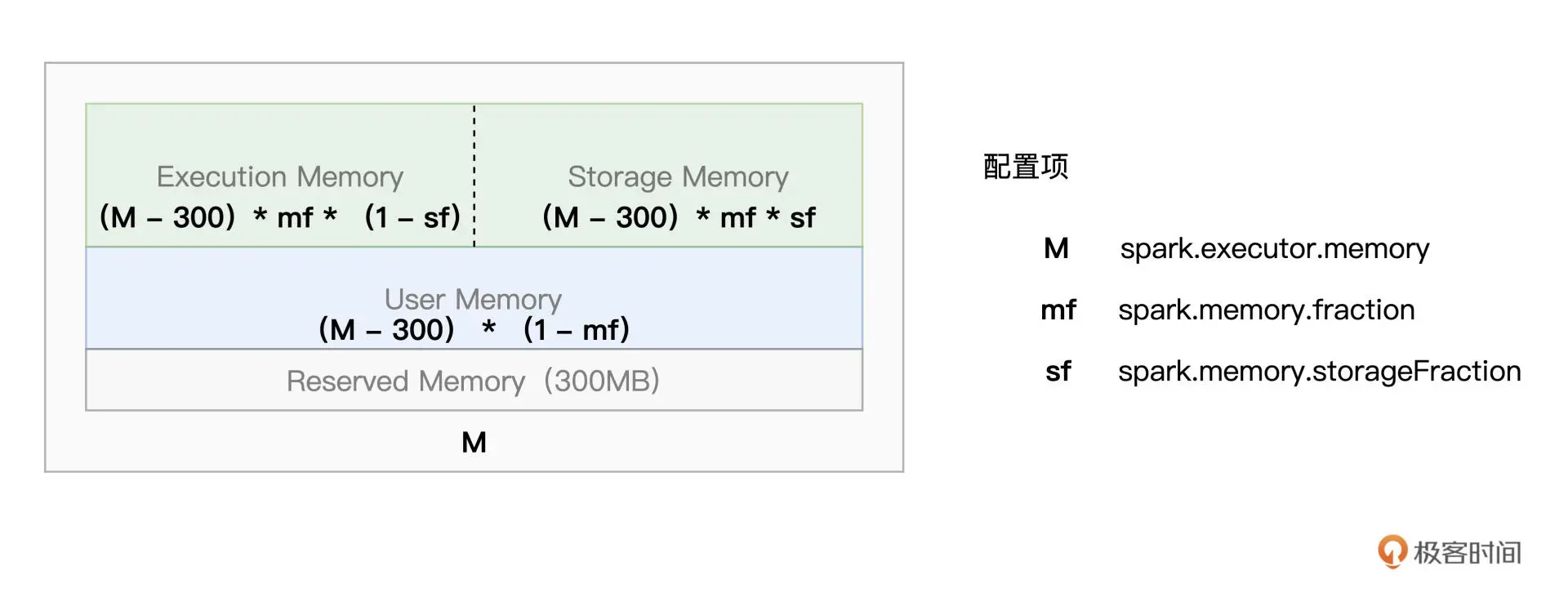
Execution和Storage都有堆内和堆外内存,使用内存池的方式由MemoryManager进行管理。
@GuardedBy("this")
protected val onHeapStorageMemoryPool = new StorageMemoryPool(this, MemoryMode.ON_HEAP)
@GuardedBy("this")
protected val offHeapStorageMemoryPool = new StorageMemoryPool(this, MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP)
@GuardedBy("this")
protected val onHeapExecutionMemoryPool = new ExecutionMemoryPool(this, MemoryMode.ON_HEAP)
@GuardedBy("this")
protected val offHeapExecutionMemoryPool = new ExecutionMemoryPool(this, MemoryMode.OFF_HEAP)
对于tungsten的实际调用在TaskMMemoryManager中:
// 调用ExecutorMemoryManager进行内存分配,分配得到一个内存页,将其添加到
// page table中,用于内存地址映射
/**
* Allocate a block of memory that will be tracked in the MemoryManager's page table; this is
* intended for allocating large blocks of memory that will be shared between operators.
*/
public MemoryBlock allocatePage(long size) {
if (size > MAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException(
"Cannot allocate a page with more than " + MAXIMUM_PAGE_SIZE_BYTES + " bytes");
}
final int pageNumber;
synchronized (this) {
// allocatedPages是一个bitmap
// PAGE_TABLE_SIZE是两个内存页 8KB
pageNumber = allocatedPages.nextClearBit(0);
if (pageNumber >= PAGE_TABLE_SIZE) {
throw new IllegalStateException(
"Have already allocated a maximum of " + PAGE_TABLE_SIZE + " pages");
}
allocatedPages.set(pageNumber);
}
try {
page = memoryManager.tungstenMemoryAllocator().allocate(acquired);
} catch (OutOfMemoryError e) {
// 继续清理直到满足需要
logger.warn("Failed to allocate a page ({} bytes), try again.", acquired);
// there is no enough memory actually, it means the actual free memory is smaller than
// MemoryManager thought, we should keep the acquired memory.
synchronized (this) {
acquiredButNotUsed += acquired;
allocatedPages.clear(pageNumber);
}
// this could trigger spilling to free some pages.
return allocatePage(size, consumer);
}
page.pageNumber = pageNumber;
pageTable[pageNumber] = page;
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Allocate page number {} ({} bytes)", pageNumber, size);
}
return page;
}
给定分配到的内存页和页内的偏移,生成一个64bits的逻辑地址
/**
* Given a memory page and offset within that page, encode this address into a 64-bit long.
* This address will remain valid as long as the corresponding page has not been freed.
*
* @param page a data page allocated by {@link TaskMemoryManager#allocate(long)}.
* @param offsetInPage an offset in this page which incorporates the base offset. In other words,
* this should be the value that you would pass as the base offset into an
* UNSAFE call (e.g. page.baseOffset() + something).
* @return an encoded page address.
*/
public long encodePageNumberAndOffset(MemoryBlock page, long offsetInPage) {
if (!inHeap) {
// In off-heap mode, an offset is an absolute address that may require a full 64 bits to
// encode. Due to our page size limitation, though, we can convert this into an offset that's
// relative to the page's base offset; this relative offset will fit in 51 bits.
offsetInPage -= page.getBaseOffset();
}
return encodePageNumberAndOffset(page.pageNumber, offsetInPage);
}
高13bits是page number,低位为页内偏移
@VisibleForTesting
public static long encodePageNumberAndOffset(int pageNumber, long offsetInPage) {
assert (pageNumber != -1) : "encodePageNumberAndOffset called with invalid page";
return (((long) pageNumber) << OFFSET_BITS) | (offsetInPage & MASK_LONG_LOWER_51_BITS);
}
给定逻辑地址,获取page number
@VisibleForTesting
public static int decodePageNumber(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) {
return (int) ((pagePlusOffsetAddress & MASK_LONG_UPPER_13_BITS) >>> OFFSET_BITS);
}
给定逻辑地址,获取页内偏移
private static long decodeOffset(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) {
return (pagePlusOffsetAddress & MASK_LONG_LOWER_51_BITS);
}
给定地址,获取内存页
/**
* Get the page associated with an address encoded by
* {@link TaskMemoryManager#encodePageNumberAndOffset(MemoryBlock, long)}
*/
public Object getPage(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) {
if (inHeap) {
final int pageNumber = decodePageNumber(pagePlusOffsetAddress);
assert (pageNumber >= 0 && pageNumber < PAGE_TABLE_SIZE);
final MemoryBlock page = pageTable[pageNumber];
assert (page != null);
assert (page.getBaseObject() != null);
return page.getBaseObject();
} else {
return null;
}
}
给定地址获取页内偏移
/**
* Get the offset associated with an address encoded by
* {@link TaskMemoryManager#encodePageNumberAndOffset(MemoryBlock, long)}
*/
public long getOffsetInPage(long pagePlusOffsetAddress) {
final long offsetInPage = decodeOffset(pagePlusOffsetAddress);
if (inHeap) {
return offsetInPage;
} else {
// In off-heap mode, an offset is an absolute address. In encodePageNumberAndOffset, we
// converted the absolute address into a relative address. Here, we invert that operation:
final int pageNumber = decodePageNumber(pagePlusOffsetAddress);
assert (pageNumber >= 0 && pageNumber < PAGE_TABLE_SIZE);
final MemoryBlock page = pageTable[pageNumber];
assert (page != null);
return page.getBaseOffset() + offsetInPage;
}
}
spark-storage
spark-storage中类的关系比较复杂,不在这里展开,列一下几个重要类:
- BlockId:
表示 Spark 中数据块的唯一标识符。
依赖关系:通常作为其他存储相关类的参数或属性,例如 BlockManager。
- BlockInfo:
包含有关数据块的元数据信息。
依赖关系:依赖于 BlockId,并且可以与 BlockManager 一起使用。
- BlockManager:
负责管理分布式数据块的存储和检索。
依赖关系:依赖于 BlockId、BlockInfo 等类,与 DiskStore、MemoryStore 等一起协同工作。
- BlockManagerMaster:
管理集群中所有 BlockManager 的主节点。
依赖关系:依赖于 BlockManager,与 BlockManagerId 等协同工作。
- BlockManagerId:
表示 BlockManager 的唯一标识符。
依赖关系:通常作为 BlockManagerMaster 的参数,用于标识不同的 BlockManager。
- BlockManagerMasterEndpoint:
BlockManagerMaster 与其他节点通信的端点。
依赖关系:依赖于 BlockManagerMaster,与 RpcEndpoint 等一起使用。
- DiskBlockManager:
BlockManager 的一个实现,负责将数据块持久化到磁盘。
依赖关系:依赖于 BlockManager 和 DiskStore,与 DiskStore 等一起工作。
- MemoryStore:
BlockManager 中负责将数据块存储在内存中的组件。
依赖关系:依赖于 BlockManager 和 MemoryManager,与 MemoryManager 等协同工作。
- DiskStore:
BlockManager 中负责将数据块持久化到磁盘的组件。
依赖关系:依赖于 BlockManager 和 DiskBlockManager。
- MemoryManager:
负责管理内存的组件,与 MemoryStore 等协同工作。
依赖关系:通常与 MemoryStore 和 BlockManager 一起使用。
- ShuffleBlockId:
用于表示与Shuffle相关的数据块的标识符。
依赖关系:依赖于 BlockId。
spark-unsafe
HeapMemoryAllocator实现了堆内存的实际分配
@GuardedBy("this")
private final Map<Long, LinkedList<WeakReference<long[]>>> bufferPoolsBySize = new HashMap<>();
private static final int POOLING_THRESHOLD_BYTES = 1024 * 1024;
/**
* Returns true if allocations of the given size should go through the pooling mechanism and
* false otherwise.
*/
private boolean shouldPool(long size) {
// Very small allocations are less likely to benefit from pooling.
return size >= POOLING_THRESHOLD_BYTES;
}
这里使用一个弱引用的Long数组对于1M以上的回收内存进行资源池化,弱引用为了避免长时间未使用的数组一直保留在缓冲池中,消耗内存资源。
这也是spark内存使用不稳定的原因之一:弱引用对象的回收仍然是jvm控制的,没办法做到立即回收。
@Override
public MemoryBlock allocate(long size) throws OutOfMemoryError {
int numWords = (int) ((size + 7) / 8);
long alignedSize = numWords * 8L;
assert (alignedSize >= size);
if (shouldPool(alignedSize)) {
synchronized (this) {
final LinkedList<WeakReference<long[]>> pool = bufferPoolsBySize.get(alignedSize);
if (pool != null) {
while (!pool.isEmpty()) {
final WeakReference<long[]> arrayReference = pool.pop();
final long[] array = arrayReference.get();
if (array != null) {
assert (array.length * 8L >= size);
MemoryBlock memory = new MemoryBlock(array, Platform.LONG_ARRAY_OFFSET, size);
if (MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_ENABLED) {
memory.fill(MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_CLEAN_VALUE);
}
return memory;
}
}
bufferPoolsBySize.remove(alignedSize);
}
}
}
long[] array = new long[numWords];
MemoryBlock memory = new MemoryBlock(array, Platform.LONG_ARRAY_OFFSET, size);
if (MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_ENABLED) {
memory.fill(MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_CLEAN_VALUE);
}
return memory;
}
free的时候如果大于1M,则池化,否则清空引用
@Override
public void free(MemoryBlock memory) {
assert (memory.obj != null) :
"baseObject was null; are you trying to use the on-heap allocator to free off-heap memory?";
assert (memory.pageNumber != MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_ALLOCATOR_PAGE_NUMBER) :
"page has already been freed";
assert ((memory.pageNumber == MemoryBlock.NO_PAGE_NUMBER)
|| (memory.pageNumber == MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_TMM_PAGE_NUMBER)) :
"TMM-allocated pages must first be freed via TMM.freePage(), not directly in allocator " +
"free()";
final long size = memory.size();
if (MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_ENABLED) {
memory.fill(MemoryAllocator.MEMORY_DEBUG_FILL_FREED_VALUE);
}
// Mark the page as freed (so we can detect double-frees).
memory.pageNumber = MemoryBlock.FREED_IN_ALLOCATOR_PAGE_NUMBER;
// As an additional layer of defense against use-after-free bugs, we mutate the
// MemoryBlock to null out its reference to the long[] array.
long[] array = (long[]) memory.obj;
memory.setObjAndOffset(null, 0);
long alignedSize = ((size + 7) / 8) * 8;
if (shouldPool(alignedSize)) {
synchronized (this) {
LinkedList<WeakReference<long[]>> pool =
bufferPoolsBySize.computeIfAbsent(alignedSize, k -> new LinkedList<>());
pool.add(new WeakReference<>(array));
}
}
}









![[C#]winform利用seetaface6实现C#人脸检测活体检测口罩检测年龄预测性别判断眼睛状态检测](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/55f3328baf324a65a90b14bc61671c13.jpeg)