简介
残差连接是一种非常重要的网络结构创新,最早被广泛应用于ResNet(Residual Neural Network)模型中,由何凯明等人在2015年的论文"Deep Residual Learning for Image Recognition"中提出。
核心思想
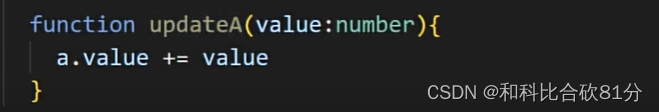
通过引入“shortcut connections”或者叫做捷径,直接将输入信息跳过若干层传到后面较深的层,然后将这个信息与经过多层非线性变换后的输出进行相加。这样做可以有效缓解随着网络深度增加而出现的梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题,使得训练更深的神经网络成为可能,并且能够显著提升模型的性能。
结构
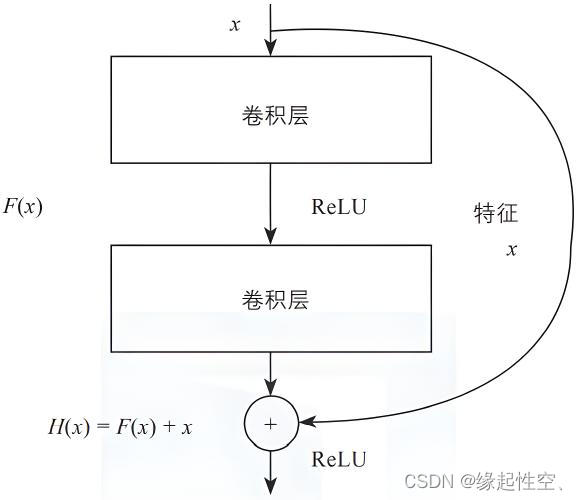
示例
Keras实现残差结构
import keras
from keras.layers import Dense, Add
from keras.models import Model
# 定义一个包含两个全连接层的模型
input_layer = keras.Input(shape=(10,)) # 创建一个输入层,形状为(10,)
#添加一个全连接层,输出维度为32,激活函数为ReLU
x = Dense(32, activation='relu')(input_layer)
#添加一个全连接层,输出维度为64,激活函数为ReLU
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
#添加一个全连接层,输出维度为64,激活函数为ReLU,用于残差连接
residual = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
#将原始输入与残差相加,得到最终输出
output_layer = Add()([x, residual])
#使用输入层和输出层创建模型
model = Model(inputs=input_layer, outputs=output_layer) #
#使用Adam优化器和均方误差损失函数编译模型
model.compile(optimizer='adam', loss='mse')
#打印模型的结构信息,包括每一层的名称、输出维度等
model.summary()模型结构
Model: "model"
__________________________________________________________________________________________________
Layer (type) Output Shape Param # Connected to
==================================================================================================
input_1 (InputLayer) [(None, 10)] 0 []
dense (Dense) (None, 32) 352 ['input_1[0][0]']
dense_1 (Dense) (None, 64) 2112 ['dense[0][0]']
dense_2 (Dense) (None, 64) 4160 ['dense_1[0][0]']
add (Add) (None, 64) 0 ['dense_1[0][0]',
'dense_2[0][0]']
==================================================================================================
Total params: 6624 (25.88 KB)
Trainable params: 6624 (25.88 KB)
Non-trainable params: 0 (0.00 Byte)