常用API
- 1 Math类
- 2 system类
- 3 Object类
- 3.1 概述
- 3.2 常用方法
- 3.3 常见面试题
- 4 Objects类
- 5 BigDecimal类
- 5.1 构造方法
- 5.2 常用方法
- 6 时间日期类
- 6.1 Date类
- 6.2 SimpleDateFormat类
- 6.3 JDK8新增日期类
1 Math类
Math 包含执行基本数字运算的方法
Math中方法的调用方式:Math类的构造方法被private修饰,但内部的方法都是静态的,则可以通过类名.方法名 进行调用
Math类的常用方法
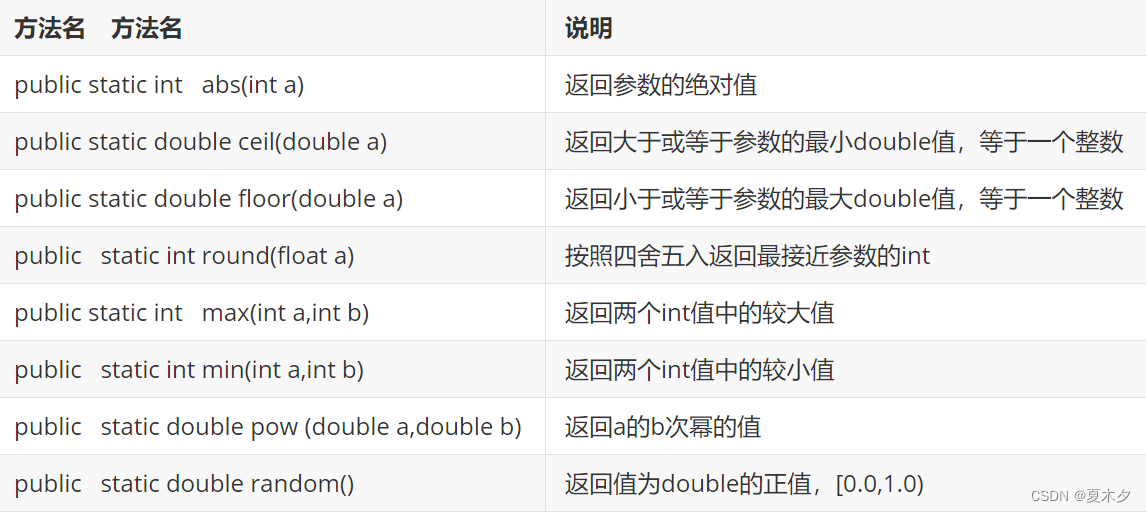
Math.PI代表近似的圆周率常量(double)
Math.E代表自然对数的底数e(double)
public static void main(String[] args) {
int abs = Math.abs(-10);
System.out.println(abs); // 10
double ceil = Math.ceil(10.9);
System.out.println(ceil); // 11.0
double floor = Math.floor(10.9);
System.out.println(floor); // 10.0
long round = Math.round(10.5);
System.out.println(round); // 11
int max = Math.max(12, 13);
System.out.println(max); // 13
int min = Math.min(12, 13);
System.out.println(min); // 12
double pow = Math.pow(3, 2);
System.out.println(pow); // 9.0
double random = Math.random();
System.out.println(random); // 返回[0.0,1.0)之间的随机数
System.out.println(Math.E); // 2.718281828459045
System.out.println(Math.PI); // 3.141592653589793
}
2 system类
不能实例化,其构造方法被private修饰
System类的常用方法
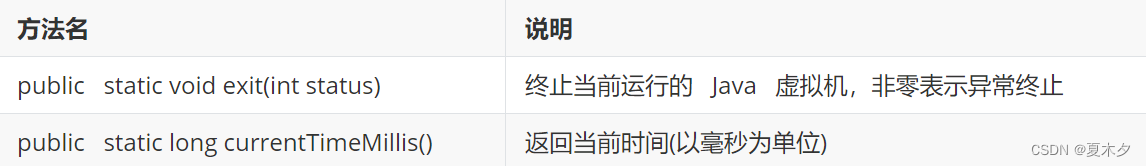
arraycopy(数据源数组, 起始索引, 目的地数组, 起始索引, 拷贝个数):拷贝数组
public class SystemDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// System.exit(0); //终止当前运行的 Java 虚拟机,非零表示异常终止
// long start = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取当前时间
// //System.out.println(l);
// for (int i = 0; i < 10000; i++) {
// System.out.println(i);
// }
// long end = System.currentTimeMillis();//获取当前时间
// System.out.println(end - start);//472,得到的就是这个for循环运行的时间.
// arraycopy(数据源数组, 起始索引, 目的地数组, 起始索引, 拷贝个数) 数组copy
int [] arr1 = {1,2,3,4,5};
int [] arr2 = new int[10];
//需求:我要把arr1中的数据拷贝到arr2中.
System.arraycopy(arr1,0,arr2,0,arr1.length);
for (int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) {
System.out.println(arr2[i]);
}
3 Object类
3.1 概述
每个类都可以将Object类作为父类,所有类都直接或间接的继承自该类
Object类的构造方法:public Objecct()
回想面向对象中,为什么说子类的构造方法默认访问的是父类的无参构造方法?
因为它们的顶级父类只有无参构造方法
3.2 常用方法
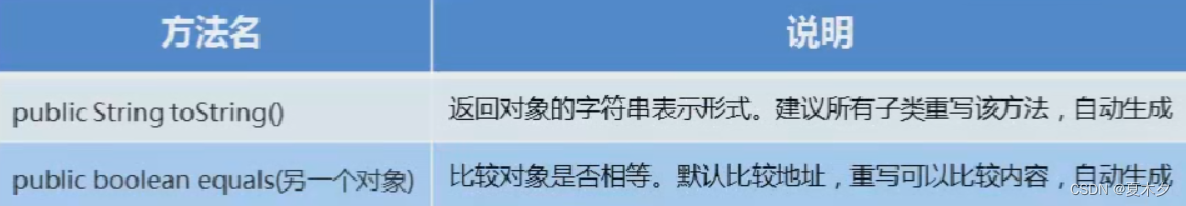
- toString()方法
class Student extends Object {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
public class ObjectDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s = new Student();
s.setName("林青霞");
s.setAge(30);
System.out.println(s);
System.out.println(s.toString());
}
}
结论:
- 直接打印一个对象就是打印这个对象的toString方法的返回值
- object类的toString方法得到的是对象的地址值,我们一般会对toString方法进行重写
- equals()方法
Student类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
/*
重写equals方法的方式:
1. alt + insert 选择equals() and hashCode(),IntelliJ Default,一路next,finish即可
2. 在类的空白区域,右键 -> Generate -> 选择equals() and hashCode(),后面的同上。
*/
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student = (Student) o;
if (age != student.age) return false;
return name != null ? name.equals(student.name) : student.name == null;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("zhangsan",23);
Student s2 = new Student("zhangsan",23);
// == 比较的是地址值
System.out.println(s1 == s2);//false
//Object类中的equals方法,底层也是用==号比较地址值。重写equals()方法可以比较内容,也即是对象的属性值,此时System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));的值为true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2));//false
}
}
3.3 常见面试题
public class InterviewTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "abc";
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder("abc");
//1.此时调用的是String类中的equals方法.
//保证参数也是字符串,否则不会比较属性值而直接返回false
System.out.println(s1.equals(sb)); // false
//StringBuilder类中是没有重写equals方法,用的就是Object类中的.
System.out.println(sb.equals(s1)); // false
}
}
4 Objects类
Objects类的常用方法
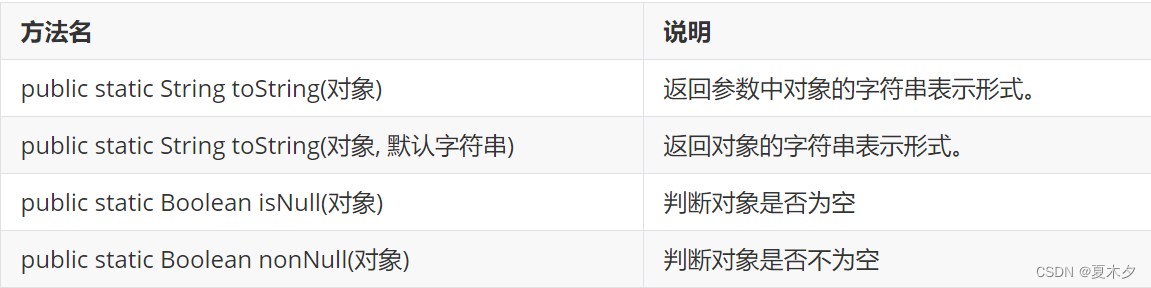
使用示例:
学生类
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public int getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(int age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
//System.out.println("看看我执行了吗?");
return "Student{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age=" + age +
'}';
}
}
测试类
import java.util.Objects;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student("小罗同学", 50);
String result1 = Objects.toString(s1);
System.out.println(result1); // Student{name='小罗同学', age=50}
System.out.println(s1); // Student{name='小罗同学', age=50}
// Student s2 = new Student("小花同学",23);
Student s2 = null;
// 返回对象的字符串表示形式。如果对象为空,那么返回第二个参数.
String result2 = Objects.toString(s2, "随便写一个");
System.out.println(result2); // 随便写一个
// Student s3 = null;
Student s3 = new Student();
boolean result3 = Objects.isNull(s3);
System.out.println(result3); // false
//Student s4 = new Student();
Student s4 = null;
boolean result4 = Objects.nonNull(s4);
System.out.println(result4); // false
}
}
5 BigDecimal类
作用:可以用来进行精确计算
5.1 构造方法
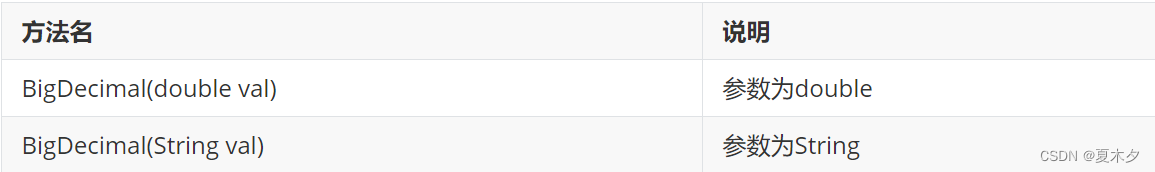
import java.math.BigDecimal;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal(10.0); // 如果是整数则自动去掉小数点
// 如果是字符串则自动去掉双引号,而且字符串里面只能是数字
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("0.3");
BigDecimal bd3 = new BigDecimal("300.0");
System.out.println(bd1);// 10
System.out.println(bd2);// 0.3
System.out.println(bd3);// 300.0
}
}
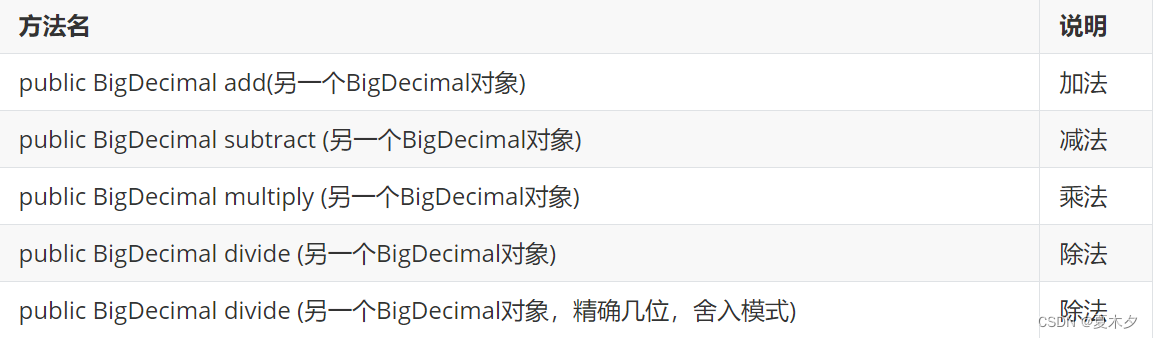
5.2 常用方法
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
/* 会报错,因为【字符串构造方法是精确计算】,而 10.0/3.0 的结果是无限循环小数,永远计算不完
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("10.0");
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("3.0");
BigDecimal divide = bd1.divide(bd2);
System.out.println(divide);
*/
BigDecimal bd1 = new BigDecimal("0.3");
BigDecimal bd2 = new BigDecimal("4"); //0.075
// BigDecimal divide = bd1.divide(bd2);
// System.out.println(divide);
//参数一:表示参数运算的另一个对象
//参数二:表示小数点后精确到多少位
//参数三:舍入模式
//进一法 BigDecimal.ROUND_UP
//去尾法 BigDecimal.ROUND_FLOOR
//四舍五入 BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP
BigDecimal divide = bd1.divide(bd2, 2, BigDecimal.ROUND_HALF_UP);
System.out.println(divide);
}
}
注意:
- 创建BigDecimal的对象,构造方法建议使用参数类型为字符串的
- 四则运算中的除法,如果除不尽请使用divide的三个参数的方法
6 时间日期类
计算机中的时间原点为:1970年1月1日 00:00:00,中国的标准时间为北京时间,北京位于东八区,需要在世界标准时间的基础上+8。
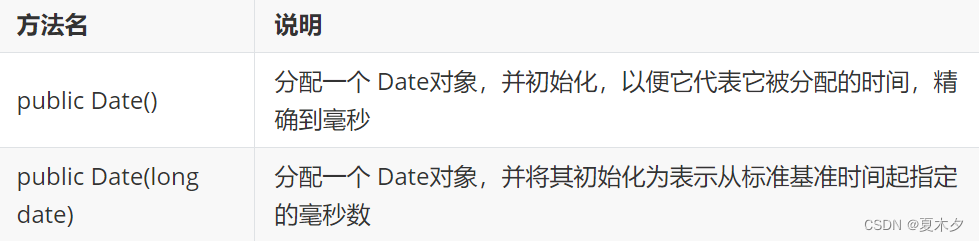
6.1 Date类
Date 代表了一个特定的时间,精确到毫秒
- 构造方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
//那么这个时间就表示电脑中的当前时间。
Date date1 = new Date();
System.out.println(date1);
//从计算机的时间原点开始,过了指定毫秒的那个时间。
Date date2 = new Date(0L);
System.out.println(date2);//Thu Jan 01 08:00:00 CST 1970
//从时间原点开始,过了0毫秒。
//因为我们是在中国,我们是在东八区需要+8小时。
//1970年1月1日 上午的9点
Date date3 = new Date(3600L * 1000); //
System.out.println(date3);
}
- 常用方法

public static void main(String[] args) {
//method1();
//method2();
}
private static void method2() {
Date date1 = new Date();
date1.setTime(0L);
System.out.println(date1);
}
private static void method1() {
//把当前时间封装成一个date对象
Date date1 = new Date();
//获取这个date对象的毫秒值 --- 获取当前时间的毫秒值
long time = date1.getTime();
System.out.println(time);
long time2 = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println(time2);
}
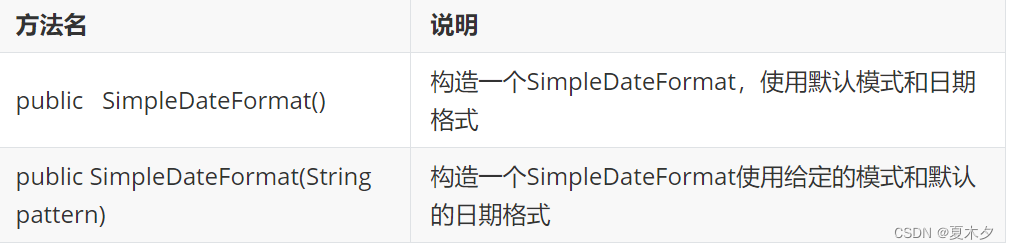
6.2 SimpleDateFormat类
SimpleDateFormat是一个具体的类,用于以区域设置敏感的方式 格式化 和 解析 日期。
常用的模式字母以及对应关系如下:
- y —— 年
- M —— 月
- d —— 日
- H —— 时
- m —— 分
- s —— 秒
举例:
- 2022-11-27 14:09:39 —— yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss
- 2022年11月27日 14:09:39 —— yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss
- 构造方法
2. 常用方法
- 格式化(从Date到String)
public final String format(Date date):将日期格式化成日期/时间字符串
- 解析(从String到Date)
public Date parse(String source):从给定字符串的开始解析文本以生成日期
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
//当前时间的Date对象
Date date1 = new Date();
//创建了一个日期格式。
SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss"); // 2022年11月27日 14:51:51
// SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日"); // 2022年11月27日
// SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd"); // 2022-11-27
// SimpleDateFormat sdf1 = new SimpleDateFormat(); // 22-11-27 下午2:51
String result1 = sdf1.format(date1);
System.out.println(result1);
String s = "2022-01-01";
// SimpleDateFormat参数的格式必须和字符串一致
//SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
SimpleDateFormat sdf2 = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd");
Date date2 = sdf2.parse(s);
System.out.println(date2); // Sat Jan 01 00:00:00 CST 2022
}
- 案例
秒杀开始时间是2020年11月11日 00:00:00,结束时间是2020年11月11日 00:10:00,用户小贾下单时间是2020年11月11日 00:03:47,用户小皮下单时间是2020年11月11日 00:10:11,判断用户有没有成功参与秒杀活动。
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
//1.判断两位同学的下单时间是否在范围之内就可以了。
//2.要把每一个时间都换算成毫秒值。
String start = "2020年11月11日 0:0:0";
String end = "2020年11月11日 0:10:0";
String jia = "2020年11月11日 0:03:47";
String pi = "2020年11月11日 0:10:11";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
long startTime = sdf.parse(start).getTime();
long endTime = sdf.parse(end).getTime();
// System.out.println(startTime);
// System.out.println(endTime);
long jiaTime = sdf.parse(jia).getTime();
long piTime = sdf.parse(pi).getTime();
if(jiaTime >= startTime && jiaTime <= endTime){
System.out.println("小贾同学参加上了秒杀活动");
}else{
System.out.println("小贾同学没有参加上秒杀活动");
}
System.out.println("------------------------");
if(piTime >= startTime && piTime <= endTime){
System.out.println("小皮同学参加上了秒杀活动");
}else{
System.out.println("小皮同学没有参加上秒杀活动");
}
}
6.3 JDK8新增日期类
- LocalDate 表示日期(年月日)
- LocalTime 表示时间(时分秒)
- LocalDateTime 表示时间+ 日期 (年月日时分秒)
- JDK8的体验
定义一个时间,String start = "2022年11月27日 00:00:00";,将这个时间+1天,再按照原来的格式进行输出。
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import java.util.Date;
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
oldMethod();
jdkMethod();
}
private static void jdkMethod() {
String s = "2022年11月27日 00:00:00";
DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.parse(s, pattern);
LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.plusDays(1);
String time = newLocalDateTime.format(pattern);
System.out.println(time); // 2022年11月28日 00:00:00
}
private static void oldMethod() throws ParseException {
String s = "2022年11月27日 00:00:00";
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
Date date = sdf.parse(s);
long dateTime = date.getTime();
dateTime = dateTime+(3600*1000*24);
String newtime = sdf.format(dateTime);
System.out.println(newtime); // 2022年11月28日 00:00:00
}
}
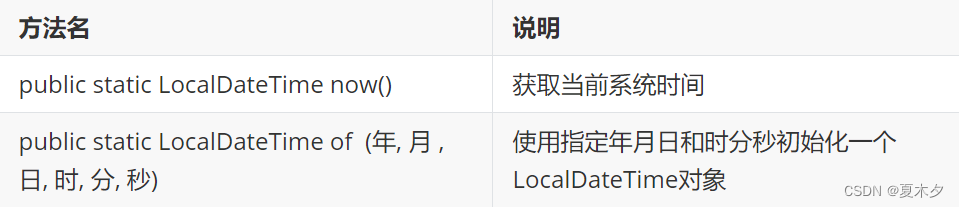
- LocalDateTime构造方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now); // 2022-11-27T20:35:04.898
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 11, 11, 11);
System.out.println(localDateTime); // 2020-11-11T11:11:11
}
- LocalDateTime获取方法
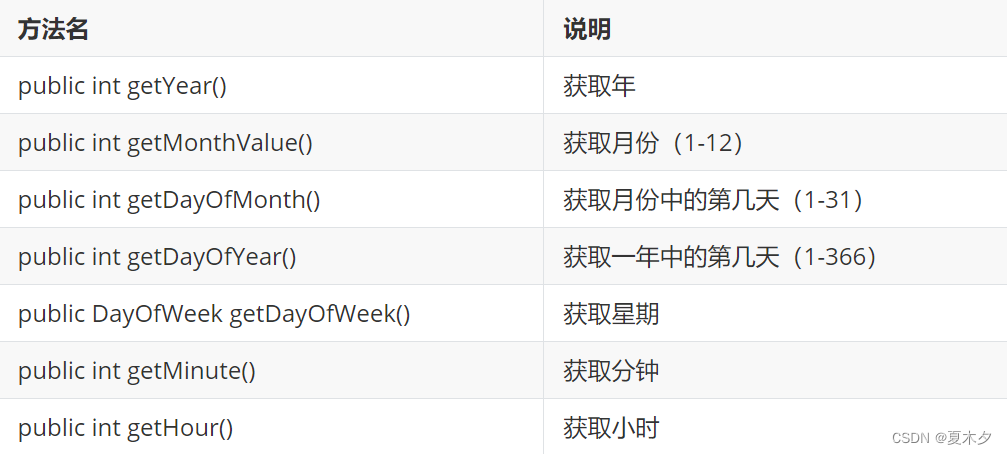
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 11, 11, 20);
int year = localDateTime.getYear();
System.out.println("年为" +year); // 年为2020
int month = localDateTime.getMonthValue();
System.out.println("月份为" + month); // 月份为11
Month month1 = localDateTime.getMonth();
System.out.println(month1); // 输出英文的月份:NOVEMBER
int day = localDateTime.getDayOfMonth();
System.out.println("日期为" + day); // 日期为11
int dayOfYear = localDateTime.getDayOfYear();
System.out.println("这是一年中的第" + dayOfYear + "天"); // 这是一年中的第316天
DayOfWeek dayOfWeek = localDateTime.getDayOfWeek();
System.out.println("星期为" + dayOfWeek); // 星期为WEDNESDAY
int minute = localDateTime.getMinute();
System.out.println("分钟为" + minute); // 分钟为11
int hour = localDateTime.getHour();
System.out.println("小时为" + hour); // 小时为11
}
- LocalDateTime转换方法
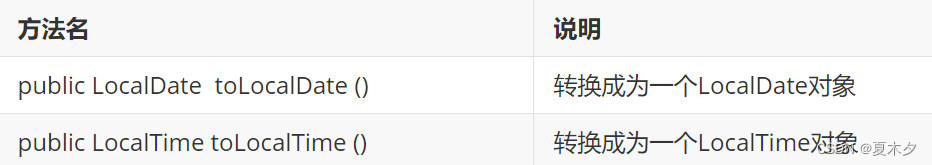
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 12, 12, 8, 10, 12);
LocalDate localDate = localDateTime.toLocalDate();
System.out.println(localDate); // 2020-12-12
LocalTime localTime = localDateTime.toLocalTime();
System.out.println(localTime); // 08:10:12
}
- LocalDateTime格式化和解析
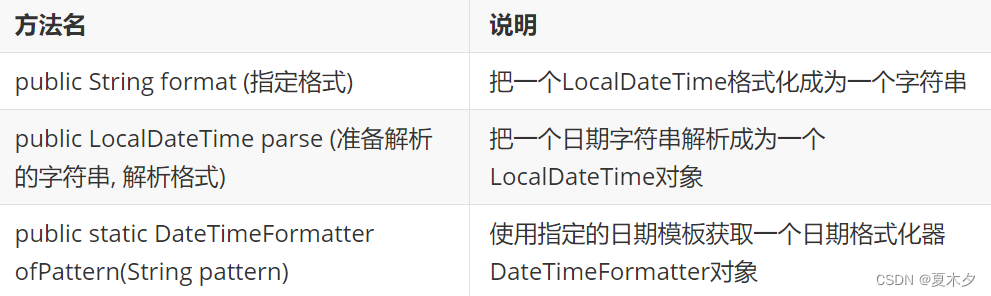
public static void main(String[] args) {
method1(); // 解析时间格式字符串
method2(); // 指定时间格式
}
private static void method2() {
String s = "2020年11月12日 13:14:15";
DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse(s, pattern);
System.out.println(parse); // 2020-11-12T13:14:15
}
private static void method1() {
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 12, 13, 14, 15);
System.out.println(localDateTime); // 2020-11-12T13:14:15
DateTimeFormatter pattern = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy年MM月dd日 HH:mm:ss");
String s = localDateTime.format(pattern);
System.out.println(s); // 2020年11月12日 13:14:15
}
- LocalDateTime增加或者减少时间的方法
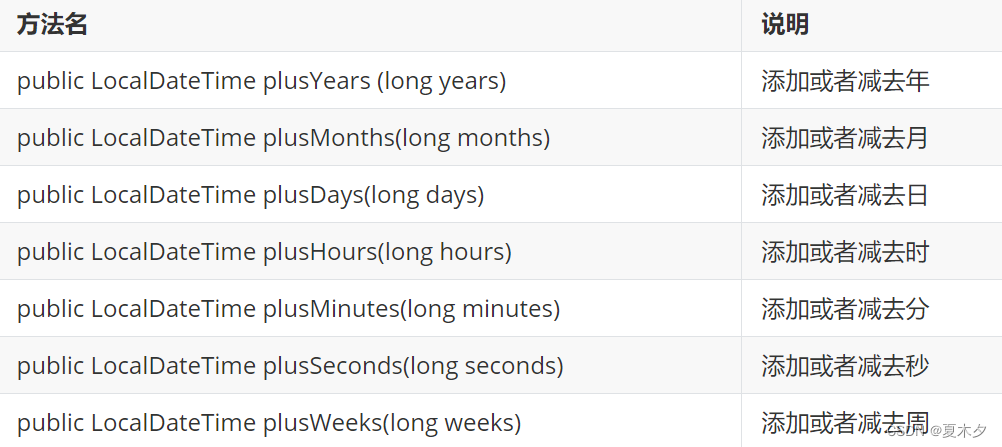
注意:
- 方法返回一个新的LocalDateTime对象,返回值就是修改之后的结果
- 参数可正可负
- 参数为正,就是往后加
- 参数为负,就是往前减
public static void main(String[] args) {
//public LocalDateTime plusYears (long years) 添加或者减去年
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 13, 14, 15);
//LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.plusYears(1);
//System.out.println(newLocalDateTime);
LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.plusYears(-1);
System.out.println(newLocalDateTime);
}
LocalDateTime减少或者增加时间的方法(参数规则与plus相反 )
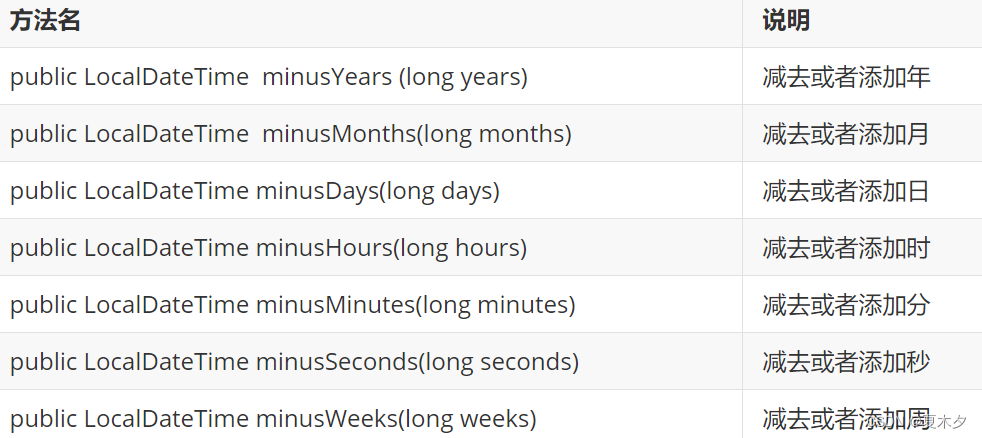
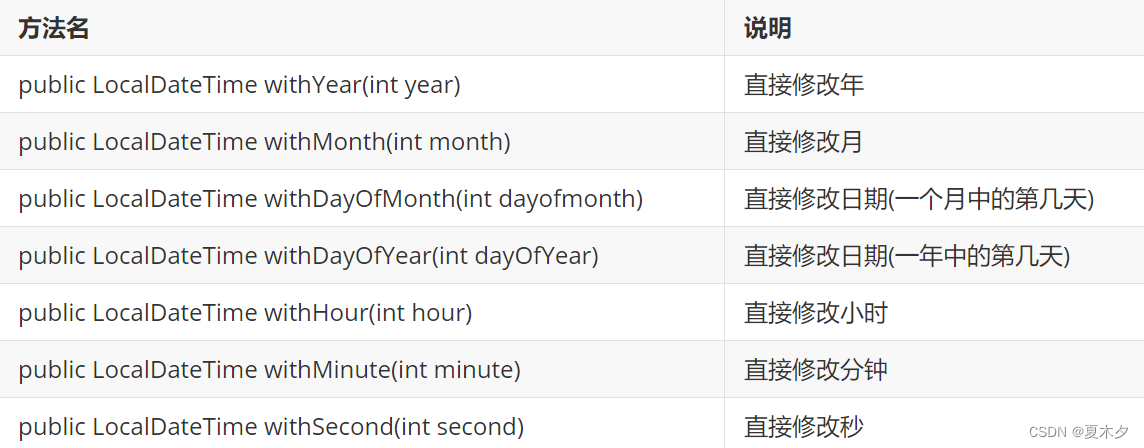
- LocalDateTime修改方法
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 11, 11, 13, 14, 15);
LocalDateTime newLocalDateTime = localDateTime.withYear(2048);
System.out.println(newLocalDateTime); // 2048-11-11T13:14:15
}
注意修改的范围
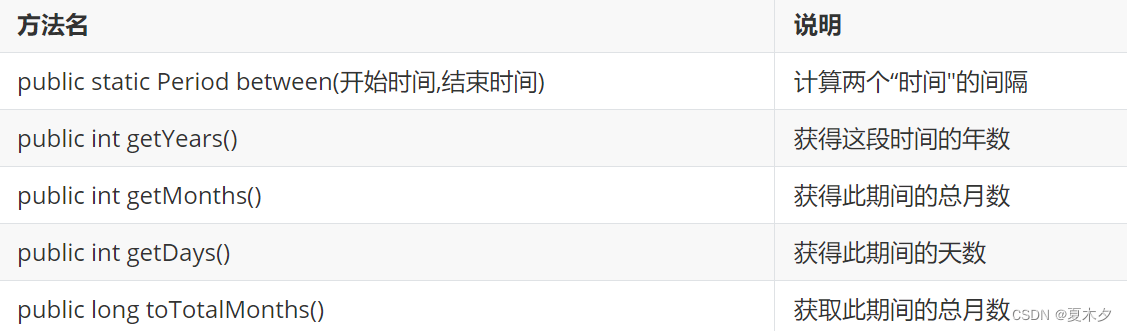
- 获取日期时间间隔的方法
period
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2020, 1, 1);
LocalDate localDate2 = LocalDate.of(2048, 12, 12);
Period period = Period.between(localDate1, localDate2);
System.out.println(period);//P28Y11M11D
System.out.println(period.getYears());//28
System.out.println(period.getMonths());//11
System.out.println(period.getDays());//11
System.out.println(period.toTotalMonths());//347
}
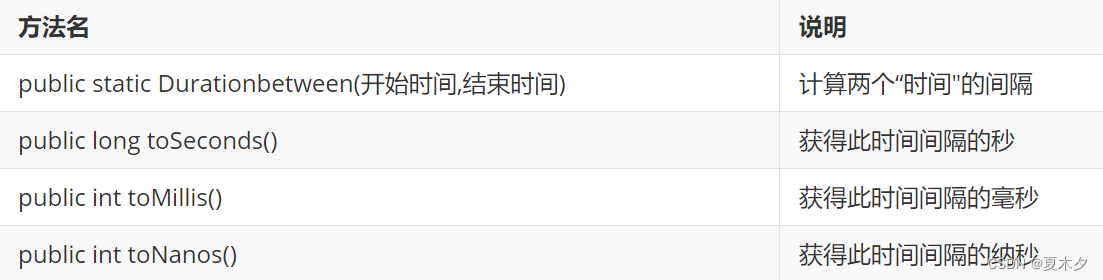
duration
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 1, 1, 13, 14, 15);
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = LocalDateTime.of(2020, 1, 2, 11, 12, 13);
Duration duration = Duration.between(localDateTime1, localDateTime2);
System.out.println(duration);//PT21H57M58S
System.out.println(duration.toSeconds());//79078
System.out.println(duration.toMillis());//79078000
System.out.println(duration.toNanos());//79078000000000
}