IO与网络编程
- 3 输入输出流IO
- 3.1 基础定义
- 3.2 IO框架
- 3.3 读取字节输入流-InputStream
- 3.3.1 InputStream.read
- 3.3.2 FileInputStream类说明
- 3.4读取字符输入流Reader
- 3.4.1 Reader.read
- 3.4.2 FileReader类说明
- 3.5 字节输出流OutputStream
- 3.5.1 OutputStream.write
- 3.5.2 FileOutputStream类说明
- 3.6字符输出流Writer
- 3.6.1 Writer.write
- 3.6.2 FileWriter类说明
- 3.7 BufferedInputStream类说明
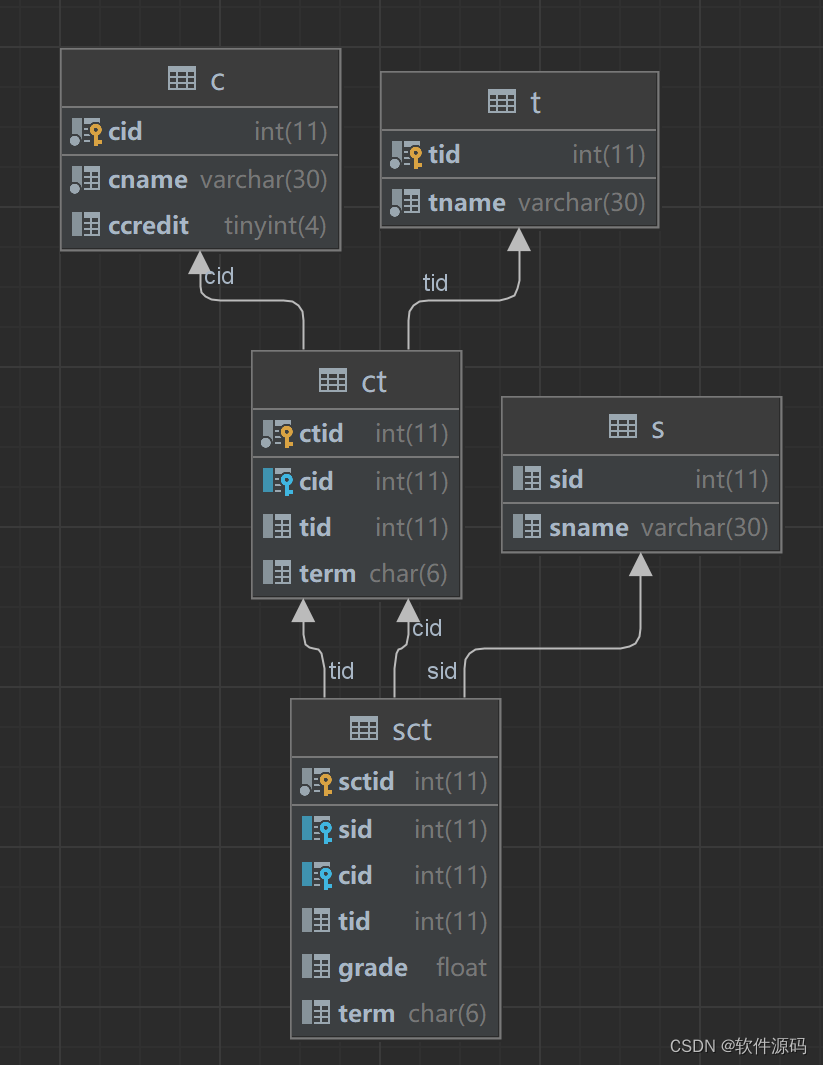
3 输入输出流IO
3.1 基础定义
java的输入输出流是比较难懂的地方,什么是java.io?
I/O 是指Input/Output,即输入和输出。
Input指从外部读入数据到内存,例如,把文件从磁盘读取到内存,从网络读取数据到内存等等。
Output指把数据从内存输出到外部,例如,把数据从内存写入到文件,把数据从内存输出到网络等等。
Java程序在执行的时候,是在内存进行的,外部的数据需要读写到内存才能处理;而在内存中的数据是随着程序结束就消失的,有时候我们也需要把数据输出到外部文件。Java中,是通过流 处理IO的,这种处理模式称为 IO流,IO流是一种顺序读写数据的模式。
你可以想象它是一根水管,数据就像水一样, 起点—终点 可互相流动。
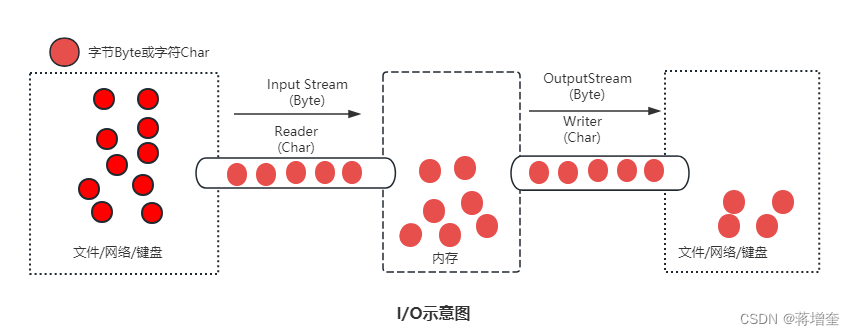
-
源头
从文件、网络、管道,我们称之为目标源 -
输入/输出
从目标源读取到内容,我们叫输入,用InputStream或者Reader相关子类来处理。
从内存输出到目标源,我们称之为输出,用OutputStream或者Writer相关子类来处理 -
传递介质
我们想要把目标源转化成Byte或者Char才能传输,Byte用InputStream/OutputStream来操作,Char用Reader/Writer来操作。
一般情况,视频、音频、图片等,用byte来传递;文字类的用Char来传递方便一些
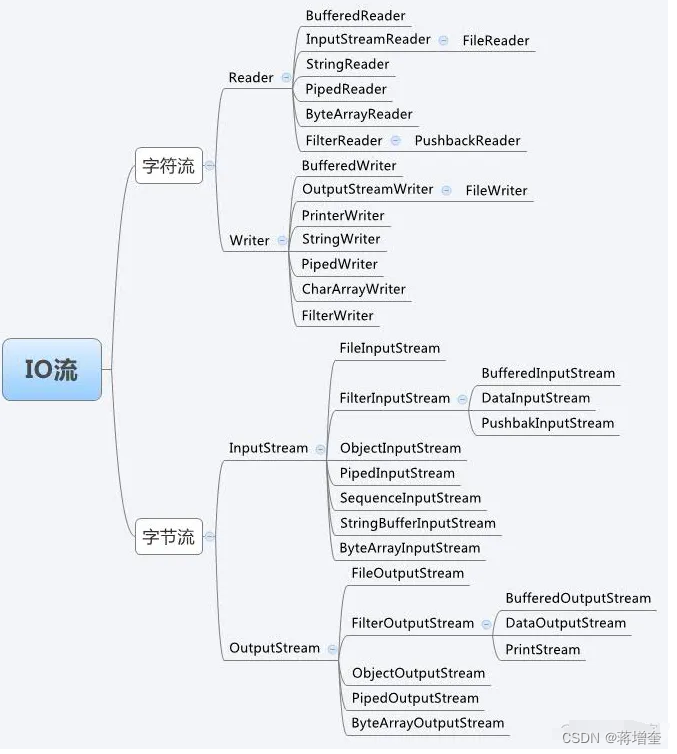
3.2 IO框架
1.4大框架类
| 类型 | 字节流 | 字符流 |
|---|---|---|
| 输入流 | InputStream | Reader |
| 输出流 | OutputStream | Writer |
3.3 读取字节输入流-InputStream
InputStream 这个抽象类是表示输入字节流的所有类的超类(父类)。
3.3.1 InputStream.read
InputStream 中的三个基本的读方法:
- int read() :
读取一个字节数据,并返回读到的数据,如果返回 -1,表示读到了输入流的末尾。 - int read(byte[] b) :
将数据读入一个字节数组,同时返回实际读取的字节数。如果返回-1,表示读到了输入流的末尾。 - int read(byte[] b, int off, int len) :
将数据读入一个字节数组,同时返回实际读取的字节数。如果返回 -1,表示读到了输入流的末尾。off 指定在数组 b 中存放数据的起始偏移位置;len 指定读取的最大字节数。
InputStream子类
ByteArrayInputStream
FileInputStream
FilterInputStream
PushbackInputStream
DataInputStream
BufferedInputStream
LineNumberInputStream
ObjectInputStream
PipedInputStream
SequenceInputStream
StringBufferInputStream
其中最重要的是FileInputStream、BufferedInputStream
3.3.2 FileInputStream类说明
FileInputStream是文件字节输入流,就是对文件数据以字节的方式来处理,如音乐、视频、图片等。
//1.一个一个和字节读入
@Test
public void t2() throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis=new FileInputStream("d:\\x.txt");
int dataByte=0;
//1.一个一个和字节读入,如果返回-1,表示读取到末尾
while((dataByte=fis.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)dataByte);
}
fis.close();
}
//以字节数组读入
@Test
public void t3() throws IOException {
File file=new File("d:\\x.txt");
InputStream fis=new FileInputStream(file);
int byte_len=0;
byte[]bytes=new byte[8];
//一个字节数组的读出数据,放置到bytes数组李,高效
while((byte_len=fis.read(bytes))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(bytes));
// for (int i = 0; i < byte_len; i++) {
// System.out.print((char) bytes[i]);
// }
}
}
//一次性读入
@Test
public void t4() throws IOException {
File file=new File("d:\\a.txt");
InputStream fis=new FileInputStream(file);
//把流里面左右内容转化为字节,jdk1.9以上提供
byte[]bytes = fis.readAllBytes();
System.out.println(new String(bytes));
//或者用以下方法
/**
int iAvail = fis.available(); //总的字节数
int byte_len=0;
byte[]bytes2=new byte[iAvail];
//一个字节数组的读出数据,放置到bytes数组李,高效
while((byte_len=fis.read(bytes2))!=-1){
System.out.println(new String(bytes2));
}
**/
}
注意:
英文一般占用1个字节,中文占用3个字节,直接用FileInputStream操作字符形式的文件,容易出现乱码,所以视频、音频、图片这些非字符型的流处理才直接使用FileInputStream
3.4读取字符输入流Reader
我们程序很多时候是操作字符型的输入流,如果用字节inputStream来读取,其是以字节byte形式,容易出现乱码,用Reader操作的是字符流,是字符,不会出现乱码
3.4.1 Reader.read
两则都是通过read方法来读取,一个是直接,一个是字符。
| 类 | 读取方法说明 |
|---|---|
| InputStream | int read();//读取一个字节,返回的是字节,本身是一个整数 int read(byte[] bs) //把流内容读取到字节数组bs里 |
| Reader | int read();//读取的是一个字符char,返回这个字符对应的整数 int read(char[] chs) //把流的内容读取到一字符数组里 |
3.4.2 FileReader类说明
我们这个例子是以Reader->InputStreamReader->FileReader为例子
@Test
public void t5() throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\x.txt");
Reader reader=new FileReader(file);
//一个一个字符读取,注意read返回的是一个整数,用char可以转化为对应的char
//在java中,char可以用整数表示
int ch;
while((ch=reader.read())!=-1){
System.out.print((char)ch);
}
reader.close();
}
@Test
public void t6() throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\x.txt");
Reader reader=new FileReader(file);
//读取一个字符数组,高效
int len=-1;
char[] ch=new char[10];
//这里字符数组的大写可以任意定义,也可以定义全部大小
//ch=new char[(int)file.length()]; //这个写法是long->int,如果文字内容太大,可能造成丢失
while((len=reader.read(ch))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(ch));
}
//或者这样写
while((len=reader.read(ch,0,10))!=-1){
System.out.print(new String(ch));
}
reader.close();
}
3.5 字节输出流OutputStream
3.5.1 OutputStream.write
OutputStream最重要的方法就是write
OutputStream源码
/**
b就是字节值
如果读完流后返回-1
*/
public abstract void write(int b) throws IOException;
/**
字节数组
如果读完流后返回-1
*/
public void write(byte b[]) throws IOException {
write(b, 0, b.length);
}
/**
字节数组
如果读完流后返回-1
*/
public void write(byte b[], int off, int len) throws IOException {
Objects.checkFromIndexSize(off, len, b.length);
// len == 0 condition implicitly handled by loop bounds
for (int i = 0 ; i < len ; i++) {
write(b[off + i]);
}
}
3.5.2 FileOutputStream类说明
OutputStream->FileOutputStream,FileOutputStream是处理文件流的类
@Test
public void t7() throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\jj.txt");
//把字符串写入
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(file);
String str="我热你温\n你个蛤蟆皮";
os.write(str.getBytes());
os.close();
}
//文件复制
@Test
public void t8() throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\a.txt");
File target = new File("d:\\jb.txt");
InputStream is=new FileInputStream(file);
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(target);
int len=-1;
byte[] bs=new byte[10];
while((len=is.read(bs))!=-1){
os.write(bs);
}
System.out.println("copy ok");
is.close();
os.close();
}
@Test
public void t9() throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\a.txt");
File target = new File("d:\\jb.txt");
InputStream is=new FileInputStream(file);
OutputStream os=new FileOutputStream(target);
int c=-1;
while((c=is.read())!=-1){
os.write(c);
}
System.out.println("copy ok");
is.close();
os.close();
}
3.6字符输出流Writer
OutputStream一般用于视频、音频、图片等非字符类的资源流,如果是文字类型,用Writer最方便
3.6.1 Writer.write
和OutputStream一致,其最重要的方法就是write方法
Writer源码:
/**
输入一个char字符对应的整数
*/
public void write(int c) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
if (writeBuffer == null){
writeBuffer = new char[WRITE_BUFFER_SIZE];
}
writeBuffer[0] = (char) c;
write(writeBuffer, 0, 1);
}
}
/**
输入char数组
*/
public void write(char cbuf[]) throws IOException {
write(cbuf, 0, cbuf.length);
}
/**
字符串
*/
public void write(String str) throws IOException {
write(str, 0, str.length());
}
/**
字符串
*/
public void write(String str, int off, int len) throws IOException {
synchronized (lock) {
.....
}
}
3.6.2 FileWriter类说明
代码说明
@Test
public void t10() throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\x.txt");
String str="宇宙第一胎神,四川蛤蟆皮";
Writer writer=new FileWriter(file);
writer.write(str);
writer.close();
}
@Test
public void t11() throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\a.txt");
File target = new File("d:\\jb2.txt");
Reader rd=new FileReader(file);
Writer wt=new FileWriter(target);
int c=-1;
//读取字符
while((c=rd.read())!=-1){
wt.write(c);
}
System.out.println("copy ok");
rd.close();
wt.close();
}
@Test
public void t12() throws IOException {
File file = new File("d:\\a.txt");
File target = new File("d:\\jb3.txt");
Reader rd=new FileReader(file);
Writer wt=new FileWriter(target);
int len=-1;
char[] cs=new char[20];
//读取字符
while((len=rd.read(cs))!=-1){
wt.write(cs);
}
System.out.println("copy ok");
rd.close();
wt.close();
}
3.7 BufferedInputStream类说明
使用方式基本和FileInputStream一致。
BufferedInputStream有一个内部缓冲区数组,一次性读取较多的字节缓存起来,默认读取defaultBufferSize = 8192,作用于读文件时可以提高性能。


![[2024区块链开发入门指引] - 比特币运行原理](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/679a4160ce14887093a56d47d4e30d01.jpeg#pic_center)