在大家的日常python程序的编写过程中,都会有自己解决某个问题的解决办法,或者是在程序的调试过程中,用来帮助调试的程序公式。小编通过几十万行代码的总结处理,总结出了22个python万用公式,可以帮助大家解决在日常的python编程中遇到的大多数问题,一起来看看吧
前言
在大家的日常python程序的编写过程中,都会有自己解决某个问题的解决办法,或者是在程序的调试过程中,用来帮助调试的程序公式。
小编通过几十万行代码的总结处理,总结出了22个python万用公式,可以帮助大家解决在日常的python编程中遇到的大多数问题,一起来看看吧。
1、一次性进行多个数值的输入
对于数值的输入问题,是很多笔试题目中经常遇到的问题,一次性输入多个参数值 ,可以节省时间和代码量,为后面的程序编写节省时间。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | # 确定数值的输入时
num1,num2 = map(int,input().split())
print("num1:",num1)
print("num2:",num2)
# 不确定数值的输入时
list1 = list(map(int,input().split()))
print("list1:",list1)
|
运行结果

2、同时获取索引和数值
在进行数值的迭代时,可以利用enumerate的内置函数来获取可迭代对象数值的同时,得到数值的索引,并利用索引对数值进行操作。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | list2 = [1,2,3,4,5,6]
for k, v in enumerate(list2):
if k % 2 == 0:
print("v**2:",v**2)
else:
print("v:",v)
|
运行结果

3、对象内存占用量
通过下图的程序,可以进行对象的内存占用量查询。
| 1 2 3 | from sys import getsizeof
num = 1
print(getsizeof(num))
|
运行结果
4、对象内存地址的查询
通过内置函数id(),可以进行不同变量的内存地址的查询
| 1 2 3 4 | num1 = 20
str1 = "hello world"
print(id(num1))
print(id(str1))
|
运行结果

5、检查列表、字符串是否有相同的元素
不同的字符串,可以有相同的字母组成,同样,列表也可以有相同的元素组成,通过下述的程序,可以判断不同字符串或者是列表是否有相同的元素。
| 1 2 3 4 5 | def CheckStr(gen1,gen2):
return sorted(gen1) == sorted(gen2)
print(CheckStr("python","python"))
print(CheckStr([1,2,3],[3,2,1]))
|
运行结果

6、合并字典
当处理json数据或者是数据库中的内容时,会用到字典的合并,有时候还会遇到具有相同键值的字典,可以通过下图程序中的两种方法进行解决。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 | dict1 = {"name":['Jame','Alice'],"num":["212019","312016"]}
dict2 = {"sex":["M","F"]}
# 方法1
finaldict = {**dict1,**dict2}
print(finaldict)
# 方法2
finaldict = dict1.copy()
finaldict.update(dict2)
print(finaldict)
|
运行结果

7、检查文件是否存在
在程序运行中,会遇到保存一些图片、文字的情况,这个时候就需要利用程序来判断某个文件或者文件夹是否存在。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 | import os
def CheckFile():
print("文件夹存在:",os.path.exists("data"))
if not os.path.exists("data"):
os.mkdir("data")
CheckFile()
|
运行结果

8、对列表元素进行操作
通过Python语言的内联for循环的方式,实现对于列表中的所有元素的操作。
| 1 2 3 | list8 = range(1,8)
list_squares = [i**2 for i in list8]
print(list_squares)
|
运行结果

9、将两个列表转换为字典
将两个列表转换为字典,常见的情况是一个列表作为键,另一个列表作为值来构造字典。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | list1 = ['James','Alice','Hoton']
list2 = [88,86,91]
# 方法1 利用zip内置函数
dict1 = dict(zip(list1,list2))
# 方法2 去除dict的隐式转换
dict2 = {key:value for key,value in zip(list1,list2)}
# 方法3 利用for循环
dict3 = {}
for k, v in zip(list1,list2):
if k not in dict3.keys():
dict3[k] = v
print("dict1:",dict1)
print("dict2:",dict2)
print("dict3:",dict3)
|
运行结果

10、字符串列表的排序
当大家需要对一个字符串列表进行排序时,可以利用下图中的程序进行排序。
| 1 2 3 | list1 = ['James','Alice','Hoton','Cris']
print(sorted(list1,key=lambda x:x.lower()[0])) # 按照字符串的第一个字母排序
print(sorted(list1,key=lambda x:x.lower()[-1])) # 按照字符串的最后一个字母排序
|
运行结果

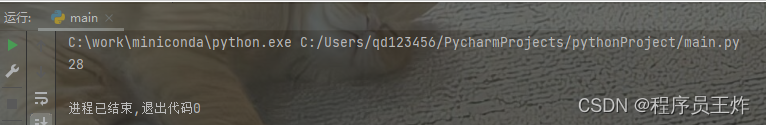
11、利用if和else对列表进行处理
利用if和else的操作,可以基于某些条件过滤数据,如下图所示。
| 1 2 | list11 = list(range(1,20))
print("偶数平方:",[i**2 if i % 2 == 0 else i for i in list11])
|
运行结果
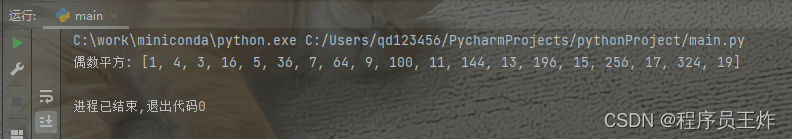
12、合并两个列表
对于两个列表的合并,可以通过花式的列表合并来将两个列表组合成一个新的列表。
| 1 2 3 4 5 | list1 = ["1","2","3","4"]
list2 = ["one","two","three","four"]
new_list = [x + y for x,y in zip(list1,list2)]
print("逐元素相加:",new_list)
|
运行结果
13、对字典列表进行排序
当有字典组成的列表时,可以按照字典的键值对列表进行排序。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | dict1 = [
{"name":"James",
"num":25},
{"name":"Alice",
"num":39},
{"name":"Hoton",
"num":35}
]
# 方法1 利用字典的sort函数
dict1.sort(key=lambda item:item["num"])
print(dict1)
# 方法2 利用sorted函数
dict1 = sorted(dict1,key=lambda item:item["num"])
print(dict1)
|
14、计算程序执行的时间
对于程序计算时间 的计算,可以帮助大家对于程序或者算法的性能有更好的了解。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | from time import sleep
def funcl():
for i in range(10000000):
a = i
sleep(2)
# 方法1
from datetime import datetime
start = datetime.now()
funcl()
print("程序执行所用的时间为:",datetime.now()-start)
# 方法2
import time
start_time = time.time()
funcl()
print("程序执行所用的时间为:",time.time()-start_time)
|
15、检查是否包含子字符串
对于子字符串的检查是Python日常应用中经常遇到的一个问题,当一个字符串中包含某些关键子字符串时,将这些字符串进行打印。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 | str_list = ["小圆爱python","hello world","小圆爱python","kaka小圆"]
keywords = 'python'
for strs in str_list:
if keywords in strs:
print(strs)
|
16、格式化字符串
对于Python的输入,逻辑和输出。这三个部分在编写代码时都需要某种格式,Python提供了多种格式化字符串的方法,以便获得更好和易于阅读的输出。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | name = "爱坤"
num = 100
# 方法1 字符串相加
print("我的名字是"+name+",我的成绩是"+str(num)+"。")
# 方法2 Python3 中的F-strings
print(f"我的名字是{name},我的成绩是{num}。")
# 方法3 join函数
print(''.join(["我的名字是",name,",我的成绩是",str(num),"。"]))
# 方法4 操作字符处理
print("我的名字是%s,我的成绩是%d。" % (name,num))
# 方法5 format(python2.7以上的版本)
print("我的名字是{},我的成绩是{}。".format(name,num))
|
17、错误捕捉
在Python语言中,提供了使用try,except和finally块处理异常报错的方法
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 | # 错误1 扣除为0
try:
num1 = 10
num2 = 0
print(num1 / num2)
except ZeroDivisionError :
print("除数不能为0")
print("=================")
# 错误2 找不到文件
try:
with open("data.txt",'r') as fr:
print(fr.readlines())
except IOError:
print("该文件不存在")
finally:
print("程序执行结束")
|
18、列表元素频率统计
对于列表等可迭代对象中的元素进行频次的统计,也是一项非常常见的问题。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | list1 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,3,3,4,5,2,3,2]
# 方法1 利用for循环统计
frequ_dict = {}
for i in list1:
if i in frequ_dict.keys():
frequ_dict[i] += 1
else:
frequ_dict[i] = 1
print(frequ_dict)
# 方法2 李彤Counter类
from collections import Counter
Counter = Counter(list1)
print(Counter.most_common())
|
19、简易计算器制作
下图的程序中,不需要if-else的操作,即可制作一个简易的计算器。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 | from operator import add, sub, truediv, mul
operation = {
"+" : add,
"-" : sub,
"/" : truediv,
"*" : mul,
"**" : pow
}
print(operation['+'](2,3))
print(operation['*'](2,3))
print(operation['**'](2,3))
print(operation['/'](10,3))
|
20、链式函数调用
通过一行程序,可以调用多个不同的函数,进行计算。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 | def add(x,y):
return x + y
def sub(x,y):
return x - y
x,y = 2,3
print((sub if x > y else add)(x,y))
# 通过条件判断执行的函数
|
21、两个数值交换
Python中的交换,不仅仅可以直接通过a,b = b,a的方式进行数值的交换,而且还可以进行列表等可迭代对象的交换。
| 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 | x, y = 2, 3
print("交换前:x={}, y={}".format(x, y))
x, y = y, x
print("交换后:x={}, y={}".format(x, y))
x, y = [2, 3], [4,5]
print("交换前: x={}, y={}".format(x, y))
x, y = y, x
print("交换后:x={}, y={}".format(x, y))
|
22、检查是否有重复元素
对于检查列表中是否有重复的元素,可以通过将列表转换为set来快速检查。
| 1 2 3 4 | list1 = [1,2,3,4,2,4,5]
list2 = [1,2,3,4,5,6,7]
print("list1有重复元素:",len(list1) != len(set(list1)))
print("list2有重复元素:",len(list2) != len(set(list2)))
|
到此这篇关于22个Python的万用公式分享的文章就介绍到这了
300+Python经典编程案例
50G+学习视频教程
100+Python初阶、中阶、高阶电子书籍
点击拿去