1、入门
1.1、环境要求
- JDK:Java17+(Spring6要求JDK最低版本是Java17)
- Maven:3.6+
- Spring:6.1.2
1.2、构建模块
(1)构建父模块spring6
在idea中,依次单击 File -> New -> Project -> New Project,创建Maven项目giser-java-spring6,引入依赖坐标
<packaging>pom</packaging>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring.version>6.1.1</spring.version>
<junit.version>5.10.1</junit.version>
</properties>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.springframework/spring-context -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.junit.jupiter/junit-jupiter-api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<finalName>giser-java-spring6</finalName>
<pluginManagement>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<target>17</target>
<source>17</source>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-source-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>attach-sources</id>
<phase>verify</phase>
<goals>
<goal>jar-no-fork</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</pluginManagement>
</build>
(2)构建子模块giser-java-spring6-01
引入依赖坐标
<packaging>war</packaging>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.junit.jupiter</groupId>
<artifactId>junit-jupiter-api</artifactId>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>giser-java-spring6-01</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.8.1</version>
<configuration>
<target>17</target>
<source>17</source>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-source-plugin</artifactId>
<version>3.2.1</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<id>attach-sources</id>
<phase>verify</phase>
<goals>
<goal>jar-no-fork</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
1.3、程序开发
1.3.1、创建java类
package com.giser.spring6;
/**
* @author giserDev
* @description
* @date 2023-12-26 23:46:49
*/
public class HelloWorld {
public void sayHello(){
System.out.println("hello world!");
}
}
1.3.2、创建配置文件
在resources目录创建一个 Spring 配置文件 beans.xml(New-XML Configuration File - Spring Config)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd">
<!--
向Spring容器中注册bean信息
id: 注册的bean的id,作为bean的唯一标识
class: 注册bean的类全路径,用户创建bean对象
-->
<bean id="helloWorld" class="com.giser.spring6.HelloWorld"></bean>
</beans>
1.3.3、创建测试类测试
package com.giser.spring6;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.context.ApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.support.ClassPathXmlApplicationContext;
/**
* @author giserDev
* @description
* @date 2023-12-26 23:50:45
*/
public class HelloWordTest {
@Test
public void testSpringBean() {
// 读取配置信息
ApplicationContext applicationContext = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
// 根据bean的类型获取bean,此时要求此类型的bean只能存在一个,否则会抛异常
// HelloWorld bean = applicationContext.getBean(HelloWorld.class);
HelloWorld bean = applicationContext.getBean("helloWorld", HelloWorld.class);
bean.sayHello();
}
}
1.3.4、运行测试程序
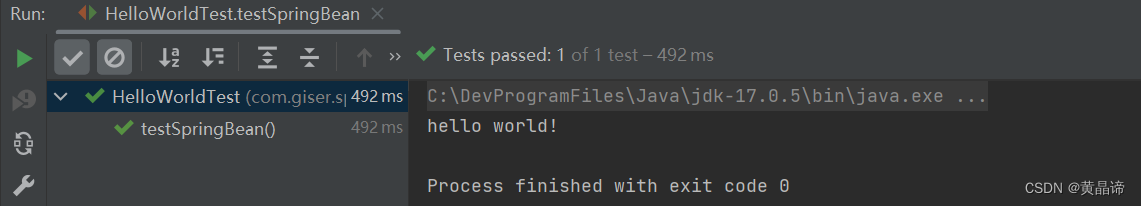
1.4、程序分析
-
- 底层是怎么创建对象的,是通过反射机制调用无参数构造方法吗?
在HelloWorld类中添加无参构造方法,如下:
public HelloWorld(){
System.out.println("constructor execute...");
}
执行结果:
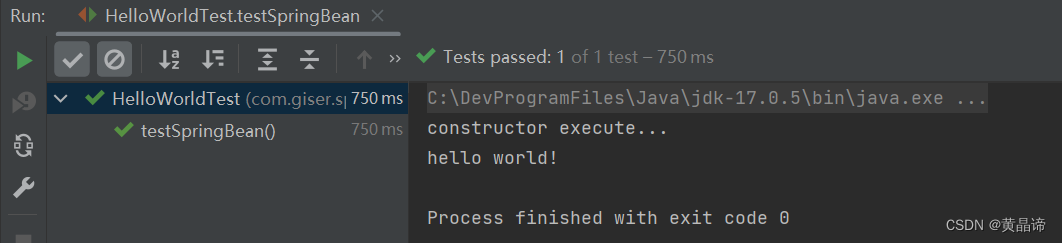
测试得知:创建对象时确实调用了无参数构造方法。
-
- Spring是如何创建对象的呢?原理是什么?
// dom4j解析beans.xml文件,从中获取class属性值,类的全类名
// 通过反射机制调用无参数构造方法创建对象
Class clazz = Class.forName("com.giser.spring6.HelloWorld");
//Object obj = clazz.newInstance();
Object object = clazz.getDeclaredConstructor().newInstance();
-
- 把创建好的对象存储到一个什么样的数据结构当中了呢?
bean对象最终存储在spring容器中,在spring源码底层就是一个map集合,存储bean的map在DefaultListableBeanFactory类中:
private final Map<String, BeanDefinition> beanDefinitionMap = new ConcurrentHashMap<>(256);
Spring容器加载到Bean类时 , 会把这个类的描述信息, 以包名加类名的方式存到beanDefinitionMap 中,
Map<String,BeanDefinition> , 其中 String是Key , 默认是类名首字母小写 , BeanDefinition , 存的是类的定义(描述信息) , 我们通常叫BeanDefinition接口为 : bean的定义对象。
1.5、启用Log4j2日志框架
1.5.1、Log4j2日志概述
在项目开发中,日志十分的重要,不管是记录运行情况还是定位线上问题,都离不开对日志的分析。日志记录了系统行为的时间、地点、状态等相关信息,能够帮助我们了解并监控系统状态,在发生错误或者接近某种危险状态时能够及时提醒我们处理,同时在系统产生问题时,能够帮助我们快速的定位、诊断并解决问题。
Apache Log4j2是一个开源的日志记录组件,使用非常的广泛。在工程中以易用方便代替了 System.out 等打印语句,它是JAVA下最流行的日志输入工具。
Log4j2主要由几个重要的组件构成:
(1)日志信息的优先级,日志信息的优先级从高到低有TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR < FATAL
TRACE:追踪,是最低的日志级别,相当于追踪程序的执行
DEBUG:调试,一般在开发中,都将其设置为最低的日志级别
INFO:信息,输出重要的信息,使用较多
WARN:警告,输出警告的信息
ERROR:错误,输出错误信息
FATAL:严重错误
这些级别分别用来指定这条日志信息的重要程度;级别高的会自动屏蔽级别低的日志,也就是说,设置了WARN的日志,则INFO、DEBUG的日志级别的日志不会显示
(2)日志信息的输出目的地,日志信息的输出目的地指定了日志将打印到控制台还是文件中;
(3)日志信息的输出格式,而输出格式则控制了日志信息的显示内容。
1.5.2、引入Log4j2依赖
在giser-java-spring6中添加以下依赖
<!--log4j2的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
<version>${log4j.version}</version>
</dependency>
在giser-java-spring6-01中添加以下依赖
<!--log4j2的依赖-->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-core</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.logging.log4j</groupId>
<artifactId>log4j-slf4j2-impl</artifactId>
</dependency>
1.5.3、加入日志配置文件
在类的根路径下提供log4j2.xml配置文件(文件名固定为:log4j2.xml,文件必须放到类根路径下。)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<loggers>
<!--
level指定日志级别,从低到高的优先级:
TRACE < DEBUG < INFO < WARN < ERROR < FATAL
trace:追踪,是最低的日志级别,相当于追踪程序的执行
debug:调试,一般在开发中,都将其设置为最低的日志级别
info:信息,输出重要的信息,使用较多
warn:警告,输出警告的信息
error:错误,输出错误信息
fatal:严重错误
-->
<root level="DEBUG">
<appender-ref ref="spring6log"/>
<appender-ref ref="RollingFile"/>
<appender-ref ref="log"/>
</root>
</loggers>
<appenders>
<!--输出日志信息到控制台-->
<console name="spring6log" target="SYSTEM_OUT">
<!--控制日志输出的格式-->
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss SSS} [%t] %-3level %logger{1024} - %msg%n"/>
</console>
<!--文件会打印出所有信息,这个log每次运行程序会自动清空,由append属性决定,适合临时测试用-->
<File name="log" fileName="d:/spring6_log/test.log" append="false">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{HH:mm:ss.SSS} %-5level %class{36} %L %M - %msg%xEx%n"/>
</File>
<!-- 这个会打印出所有的信息,
每次大小超过size,
则这size大小的日志会自动存入按年份-月份建立的文件夹下面并进行压缩,
作为存档-->
<RollingFile name="RollingFile" fileName="d:/spring6_log/app.log"
filePattern="log/$${date:yyyy-MM}/app-%d{MM-dd-yyyy}-%i.log.gz">
<PatternLayout pattern="%d{yyyy-MM-dd 'at' HH:mm:ss z} %-5level %class{36} %L %M - %msg%xEx%n"/>
<SizeBasedTriggeringPolicy size="50MB"/>
<!-- DefaultRolloverStrategy属性如不设置,
则默认为最多同一文件夹下7个文件,这里设置了20 -->
<DefaultRolloverStrategy max="20"/>
</RollingFile>
</appenders>
</configuration>
1.5.4、测试
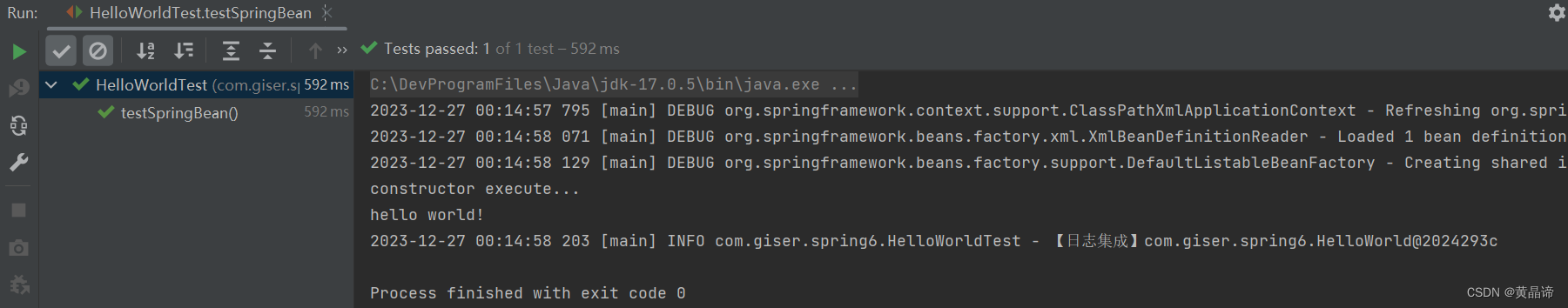
运行原测试程序
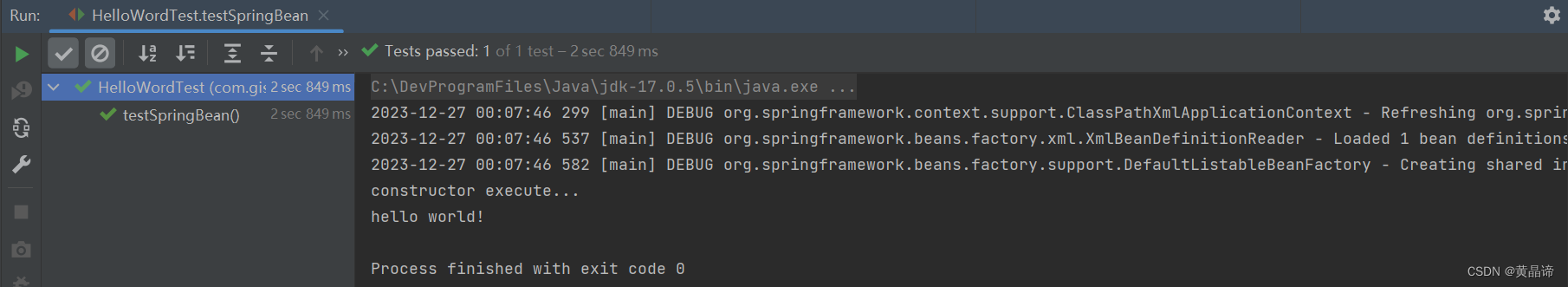
运行原测试程序,多了spring打印日志
1.5.5、使用日志
public class HelloWorldTest {
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(HelloWorldTest.class);
@Test
public void testHelloWorld(){
ApplicationContext ac = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml");
HelloWorld helloworld = (HelloWorld) ac.getBean("helloWorld");
helloworld.sayHello();
logger.info("执行成功");
}
}
控制台: