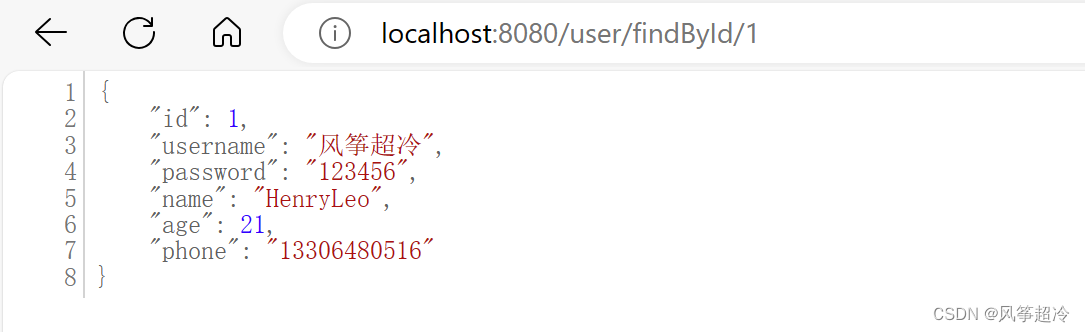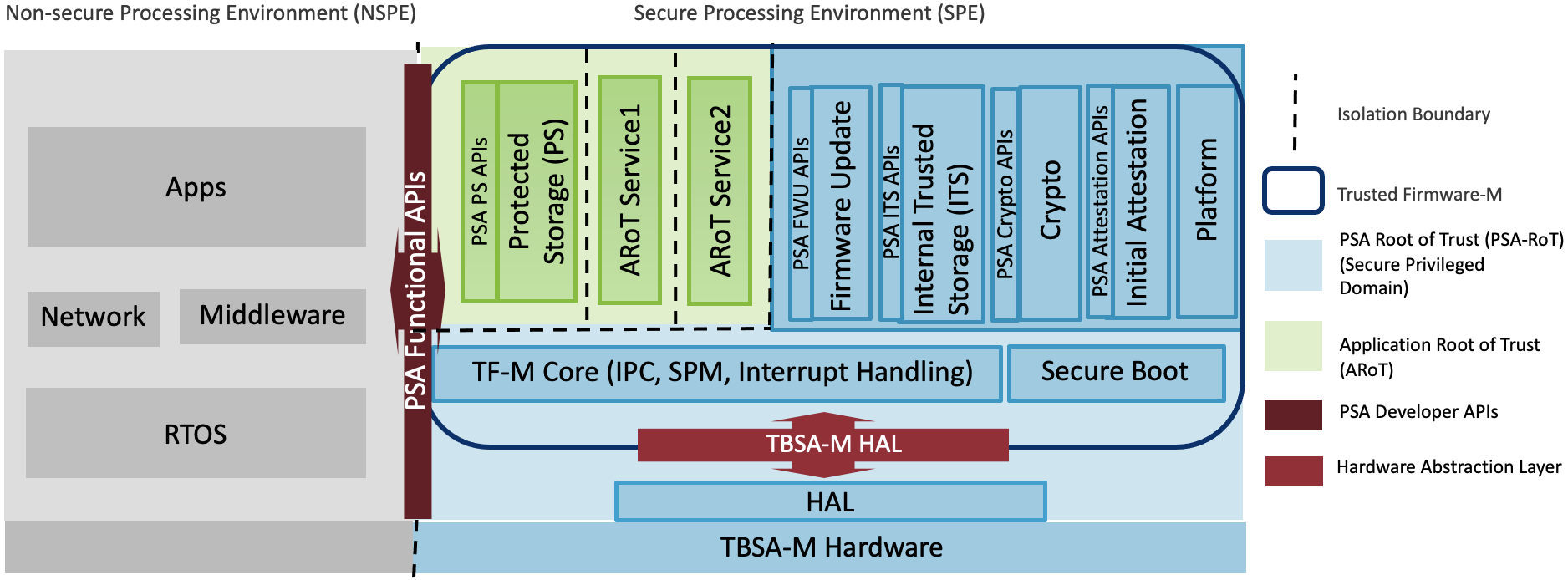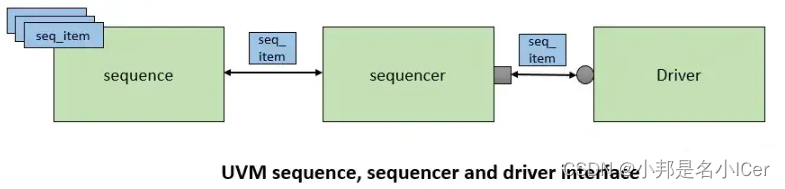
我们分别讨论了sequece_item、sequence、sequencer和driver。在本节中,我们将讨论他们如何相互talk,sequencer如何给driver提供从sequence里的sequence item。在开始阅读本节之前,请确保您了解sequencer和driver中使用的所有方法。(参考:UVM seqeuencer和UVM driver ).
1 Sequencer-Driver Connections

sequencer和driver使用双向TLM接口相互通信,以传输REQ和RSP序列项。
driver的uvm_seq_iem_pull _port和相应的sequencer的uvm_seq_item_pull_export连接。这个TLM接口提供了一个工具,可以使用实现的API检索REQ item并返回RSP项。
注:
- uvm_seq_item_pull_port和uvm_secq_itemp_pull_export都是带有REQ和RSP sequence item的参数化类。
- driver和sequencer之间的TLM连接是一对一的。这意味着没有多个sequencer连接到单个driver,也没有多个driver连接到单个sequencer。
connections:driver和sequence在UVM agent的connect_phase中连接。
<driver_inst>.seq_item_port.connect(<sequencer_inst>.seq_item_export);seq_item_port和seq_iem_export分别是uvm_seq_itemp_pull_port和uvm_sseq_tem_pull_export的实例句柄(instance handle)。
2 Sequence-Driver-Sequencer communication Approaches
基于sequence和driver可用的各种方法,进一步解释所有组合。
方法A:Using get_next_item and item_done methods in the driver
方法B:Using get and put methods in driver
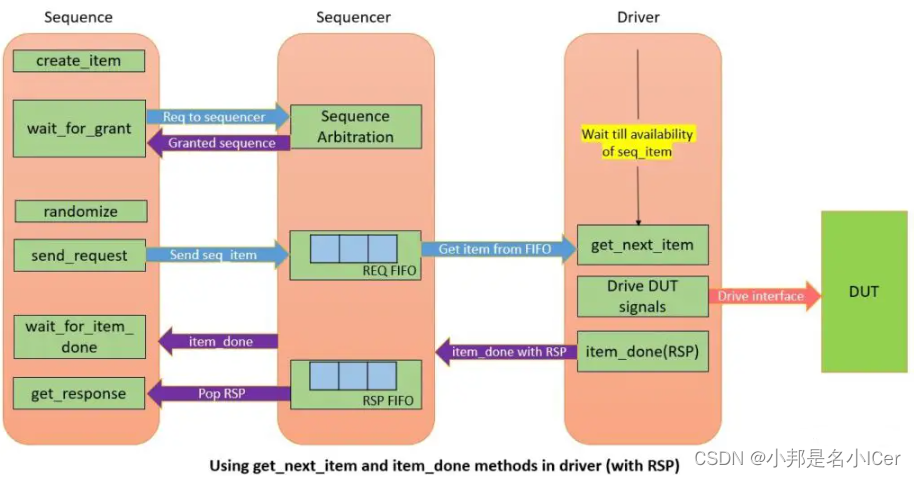
2.1 A. Using get_next_item and item_done methods in the driver
2.1.1 Without RSP packet
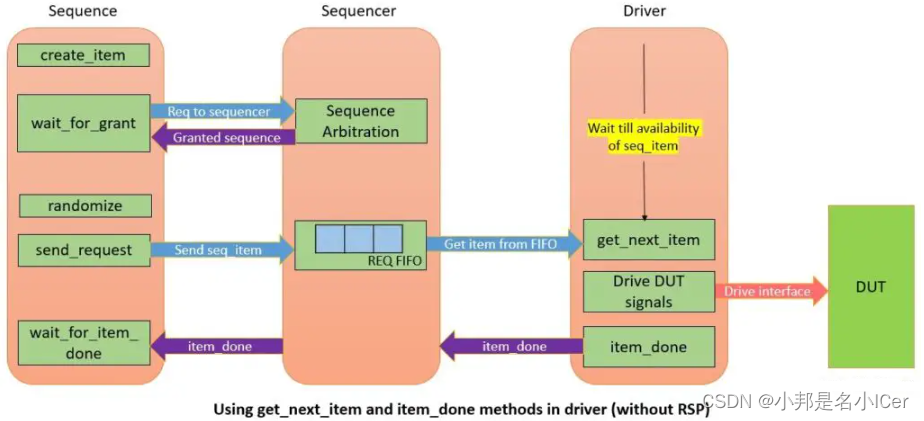
- 创建一个sequence item,并使用create_item函数在工厂中注册。
- wait_for_grant向sequencer发出请求,并等待sequencer的授权。当sequencer授予sequence时返回。
- 对sequence item进行随机化,并使用send_request将其发送到sequencer。wait_for_grant和send_request方法之间不能有任何仿真时间延迟。sequencer在REQ FIFO的帮助下将sequence item转发给driver。这将取消阻止get_next_item()调用,driver将接收序列sequence item。
- 来自sequence的wait_for_item_done()调用被阻止,直到driver响应。
- 同时,driver使用virtual interface句柄将sequence item驱动到DUT。完成后,将调用item_done方法。这将从sequence中取消阻止wait_for_item_done方法。
- 如果必须从driver向sequence发送响应,则使用RSP项作为参数调用item_done(RSP)。RSP项目通过sequencer在RSP FIFO的帮助下与sequence通信。调用get_response方法以获取响应很重要。如果DUT没有发送RSP项目,则此步骤是可选的,不是必需的。
// Driver Code
class driver extends uvm_driver#(seq_item);
`uvm_component_utils(driver)
function new(string name = "driver", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
endfunction
task run_phase (uvm_phase phase);
forever begin
seq_item_port.get_next_item(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "After get_next_item call", UVM_LOW);
#50; // Driving delay. Assuming time taken to drive RTL signals
seq_item_port.item_done();
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "After item_done call", UVM_LOW);
end
endtask
endclass
// Sequence Code
class base_seq extends uvm_sequence #(seq_item);
seq_item req;
`uvm_object_utils(base_seq)
function new (string name = "base_seq");
super.new(name);
endfunction
task body();
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "Base seq: Inside Body", UVM_LOW);
//req = seq_item::type_id::create("req");
// or
$cast(req, create_item(seq_item::get_type(), m_sequencer, "req"));
wait_for_grant();
assert(req.randomize());
send_request(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "Before wait_for_item_done", UVM_LOW);
wait_for_item_done();
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "After wait_for_item_done", UVM_LOW);
endtask
endclassOutput:
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(21) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] Base seq: Inside Body
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(28) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] Before wait_for_item_done
UVM_INFO driver.sv(15) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.drv [driver] After get_next_item call
UVM_INFO driver.sv(19) @ 50: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.drv [driver] After item_done call
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(30) @ 50: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] After wait_for_item_done2.1.2 With RSP packet
// Driver Code
class driver extends uvm_driver#(seq_item);
`uvm_component_utils(driver)
function new(string name = "driver", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
endfunction
task run_phase (uvm_phase phase);
forever begin
seq_item_port.get_next_item(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "After get_next_item call", UVM_LOW);
#50; // Driving delay. Assuming time taken to drive RTL signals
req.rsp_b = 1;
seq_item_port.item_done(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "After item_done call", UVM_LOW);
end
endtask
endclass
// Sequence Code
class base_seq extends uvm_sequence #(seq_item);
seq_item req;
`uvm_object_utils(base_seq)
function new (string name = "base_seq");
super.new(name);
endfunction
task body();
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "Base seq: Inside Body", UVM_LOW);
//req = seq_item::type_id::create("req");
// or
$cast(req, create_item(seq_item::get_type(), m_sequencer, "req"));
wait_for_grant();
assert(req.randomize());
send_request(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "Before wait_for_item_done", UVM_LOW);
wait_for_item_done();
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "After wait_for_item_done", UVM_LOW);
get_response(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), $sformatf("After get_response: rsp_b = %0d", req.rsp_b), UVM_LOW);
endtask
endclassOutput:
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(21) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] Base seq: Inside Body
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(28) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] Before wait_for_item_done
UVM_INFO driver.sv(15) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.drv [driver] After get_next_item call
UVM_INFO driver.sv(20) @ 50: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.drv [driver] After item_done call
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(30) @ 50: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] After wait_for_item_done
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(32) @ 50: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] After get_response: rsp_b = 12.2 B. Using get and put methods in driver
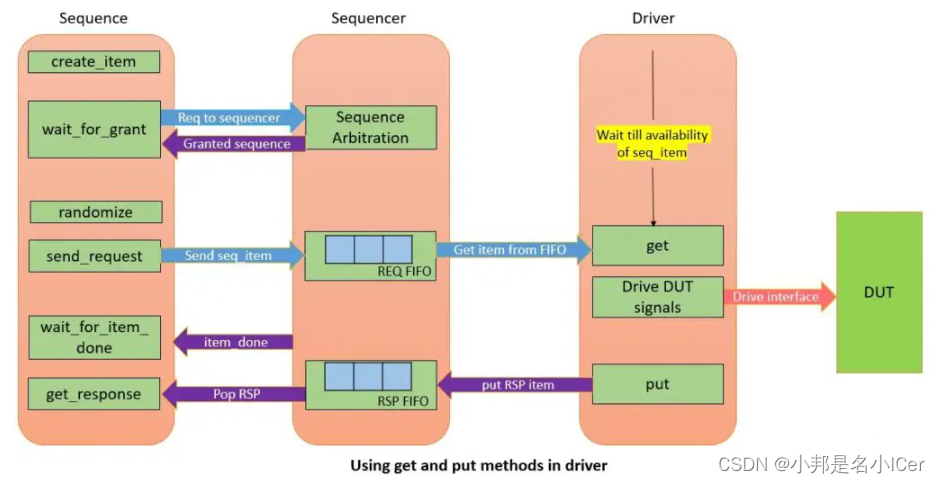
- Create a sequence item and register in the factory using the create_item function call.
- The wait_for_grant issues the request to the sequencer and wait for the grant from the sequencer. It returns when the sequencer has granted the sequence.
- Randomize the sequence item and send it to the sequencer using send_request call. There should not be any simulation time delay between wait_for_grant and send_request method call. The sequencer forwards the sequence item to the driver with the help of REQ FIFO. This unblocks the get() call and the driver receives the sequence item.
- The wait_for_item_done() call from the sequence gets blocked until the driver calls the get method.
- Once the get method is called, the wait_for_item_done() call from sequence gets unblocked immediately without caring about driving the virtual interface.
- The get_response call is necessary to call that completes the communication. The get_response method is blocked until the driver calls put(RSP).
- In the meantime, the driver drives the sequence item to the DUT using a virtual interface handle. Once it is completed, the put(RSP) method is called. This unblocks the get_response method from the sequence. The RSP item is communicated to the sequence by a sequencer with help of RSP FIFO.
// Driver Code
class driver extends uvm_driver#(seq_item);
`uvm_component_utils(driver)
function new(string name = "driver", uvm_component parent = null);
super.new(name, parent);
endfunction
function void build_phase(uvm_phase phase);
super.build_phase(phase);
endfunction
task run_phase (uvm_phase phase);
forever begin
seq_item_port.get(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "After get call", UVM_LOW);
#50; // Driving delay. Assuming time taken to drive RTL signals
req.rsp_b = 1;
seq_item_port.put(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "After put call", UVM_LOW);
end
endtask
endclass
// Sequence Code
class base_seq extends uvm_sequence #(seq_item);
seq_item req;
`uvm_object_utils(base_seq)
function new (string name = "base_seq");
super.new(name);
endfunction
task body();
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "Base seq: Inside Body", UVM_LOW);
//req = seq_item::type_id::create("req");
// or
$cast(req, create_item(seq_item::get_type(), m_sequencer, "req"));
wait_for_grant();
assert(req.randomize());
send_request(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "Before wait_for_item_done call", UVM_LOW);
wait_for_item_done();
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), "After wait_for_item_done call", UVM_LOW);
get_response(req);
`uvm_info(get_type_name(), $sformatf("After get_response: rsp_b = %0d", req.rsp_b), UVM_LOW);
endtask
endclassOutput:
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(21) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] Base seq: Inside Body
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(28) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] Before wait_for_item_done call
UVM_INFO driver.sv(15) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.drv [driver] After get call
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(30) @ 0: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] After wait_for_item_done call
UVM_INFO driver.sv(20) @ 50: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.drv [driver] After put call
UVM_INFO testbench.sv(32) @ 50: uvm_test_top.env_o.agt.seqr@@bseq [base_seq] After get_response: rsp_b = 1