论文地址:Run, Don't Walk: Chasing Higher FLOPS for Faster Neural Networks
代码地址:https://github.com/jierunchen/fasternet
该论文主要提出了PConv,通过优化FLOPS提出了快速推理模型FasterNet。
在设计神经网络结构的时候,大部分注意力都会放在降低FLOPs( floating-point opera-
tions)上,有的时候FLOPs降低了,并不意味了推理速度加快了,这主要是因为没考虑到FLOPS(floating-point operations per second)。针对该问题,作者提出了PConv( partial convolution),通过提高FLOPS来加快推理速度。
一、引言
非常多的实时推理模型都将重点放在降低FLOPs上,比如:MobileNet,ShuffleNet,GhostNet等等。虽然这些网络都降低了FLOPs,但是他们没有考虑到FLOPS,所以推理速度仍有优化空间,推理的延时计算公式如下:

由上式可以看出,要想加快推理速度,不仅可以从FLOPs入手,也可以优化FLOPS。作者在多个模型上做了实验,发现很多模型的FLOPS低于ResNet50。于是作者提出了PConv,通过提高FLOPS来加快推理速度。

二、PConv
为了提高FLOPS,作者提出了PConv,其结构如下图:

部分通道数经过卷积运算,其他通道不进行运算。再看了几眼。。。。这个和GhostConv好像呀。。。。
网络整体结构如下:

三、模型性能
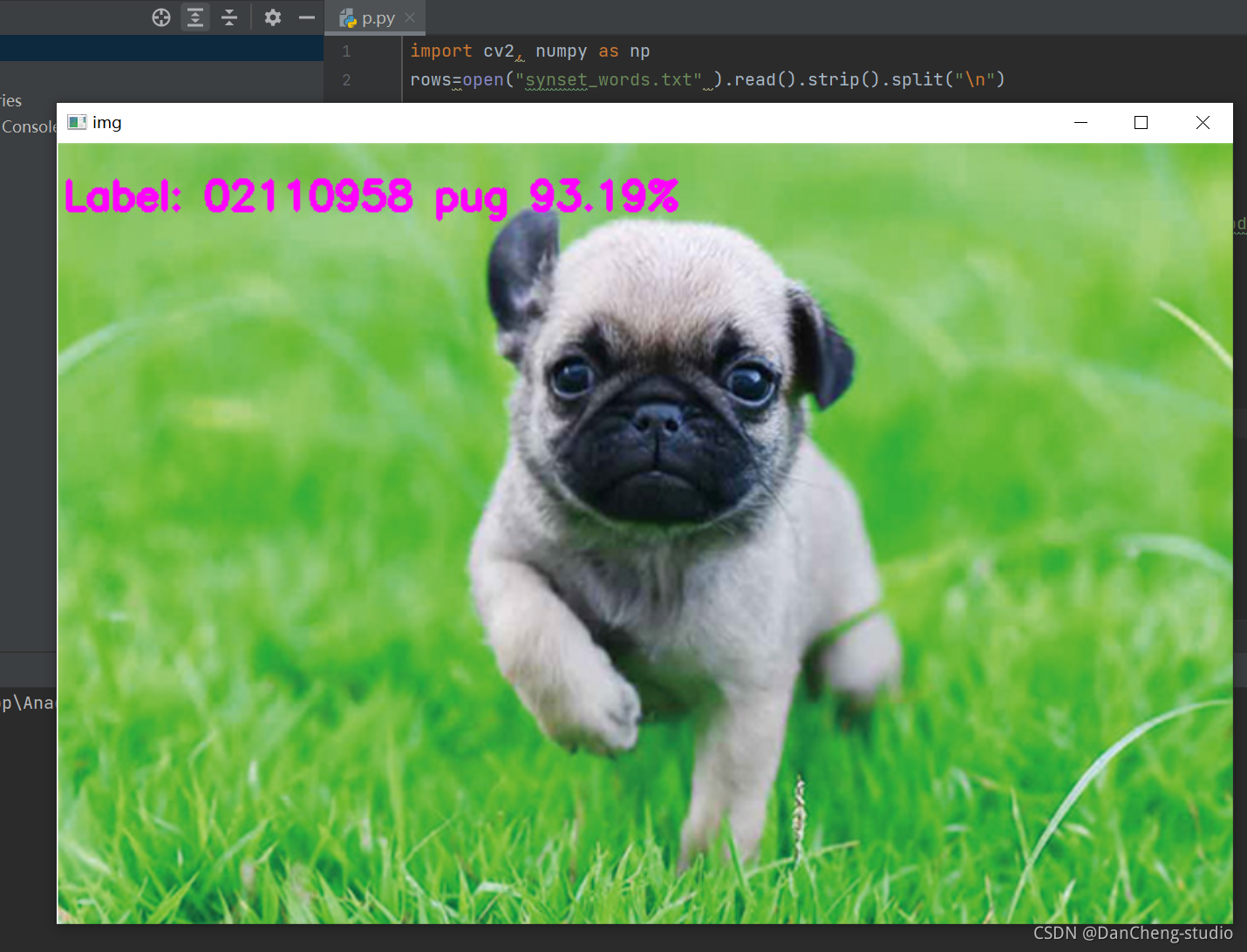
FasterNet在ImageNet-1K上的表现如下:

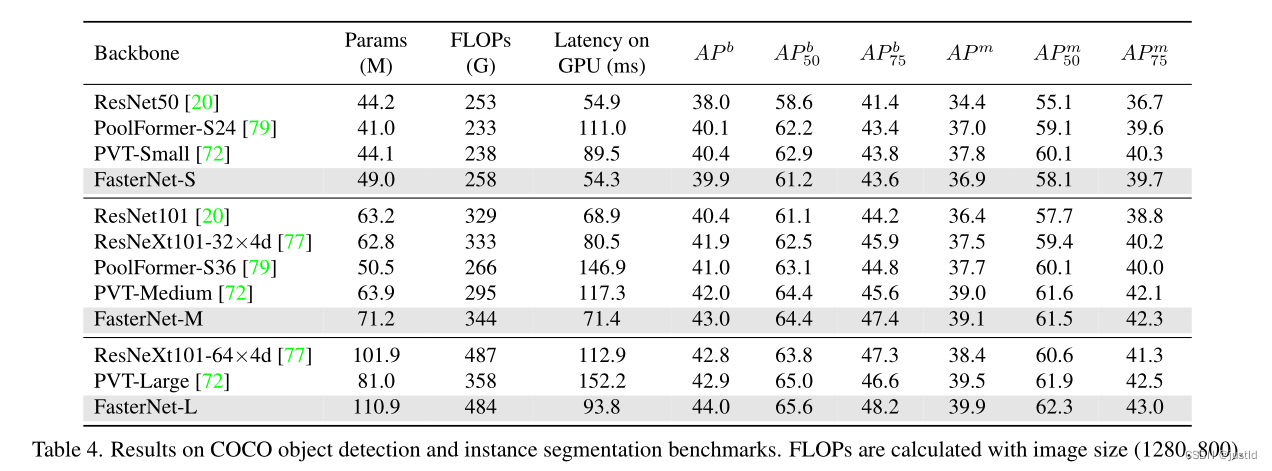
在coco数据集上的表现如下:
四、代码
给出PConv的代码,也是非常简单:
# Copyright (c) Microsoft Corporation.
# Licensed under the MIT License.
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
from timm.models.layers import DropPath, to_2tuple, trunc_normal_
from functools import partial
from typing import List
from torch import Tensor
import copy
import os
try:
from mmdet.models.builder import BACKBONES as det_BACKBONES
from mmdet.utils import get_root_logger
from mmcv.runner import _load_checkpoint
has_mmdet = True
except ImportError:
print("If for detection, please install mmdetection first")
has_mmdet = False
class Partial_conv3(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, dim, n_div, forward):
super().__init__()
self.dim_conv3 = dim // n_div
self.dim_untouched = dim - self.dim_conv3
self.partial_conv3 = nn.Conv2d(self.dim_conv3, self.dim_conv3, 3, 1, 1, bias=False)
if forward == 'slicing':
self.forward = self.forward_slicing
elif forward == 'split_cat':
self.forward = self.forward_split_cat
else:
raise NotImplementedError
def forward_slicing(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
# only for inference
x = x.clone() # !!! Keep the original input intact for the residual connection later
x[:, :self.dim_conv3, :, :] = self.partial_conv3(x[:, :self.dim_conv3, :, :])
return x
def forward_split_cat(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
# for training/inference
x1, x2 = torch.split(x, [self.dim_conv3, self.dim_untouched], dim=1)
x1 = self.partial_conv3(x1)
x = torch.cat((x1, x2), 1)
return x
class MLPBlock(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dim,
n_div,
mlp_ratio,
drop_path,
layer_scale_init_value,
act_layer,
norm_layer,
pconv_fw_type
):
super().__init__()
self.dim = dim
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.drop_path = DropPath(drop_path) if drop_path > 0. else nn.Identity()
self.n_div = n_div
mlp_hidden_dim = int(dim * mlp_ratio)
mlp_layer: List[nn.Module] = [
nn.Conv2d(dim, mlp_hidden_dim, 1, bias=False),
norm_layer(mlp_hidden_dim),
act_layer(),
nn.Conv2d(mlp_hidden_dim, dim, 1, bias=False)
]
self.mlp = nn.Sequential(*mlp_layer)
self.spatial_mixing = Partial_conv3(
dim,
n_div,
pconv_fw_type
)
if layer_scale_init_value > 0:
self.layer_scale = nn.Parameter(layer_scale_init_value * torch.ones((dim)), requires_grad=True)
self.forward = self.forward_layer_scale
else:
self.forward = self.forward
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
shortcut = x
x = self.spatial_mixing(x)
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(self.mlp(x))
return x
def forward_layer_scale(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
shortcut = x
x = self.spatial_mixing(x)
x = shortcut + self.drop_path(
self.layer_scale.unsqueeze(-1).unsqueeze(-1) * self.mlp(x))
return x
class BasicStage(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
dim,
depth,
n_div,
mlp_ratio,
drop_path,
layer_scale_init_value,
norm_layer,
act_layer,
pconv_fw_type
):
super().__init__()
blocks_list = [
MLPBlock(
dim=dim,
n_div=n_div,
mlp_ratio=mlp_ratio,
drop_path=drop_path[i],
layer_scale_init_value=layer_scale_init_value,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
pconv_fw_type=pconv_fw_type
)
for i in range(depth)
]
self.blocks = nn.Sequential(*blocks_list)
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.blocks(x)
return x
class PatchEmbed(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, patch_size, patch_stride, in_chans, embed_dim, norm_layer):
super().__init__()
self.proj = nn.Conv2d(in_chans, embed_dim, kernel_size=patch_size, stride=patch_stride, bias=False)
if norm_layer is not None:
self.norm = norm_layer(embed_dim)
else:
self.norm = nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.norm(self.proj(x))
return x
class PatchMerging(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, patch_size2, patch_stride2, dim, norm_layer):
super().__init__()
self.reduction = nn.Conv2d(dim, 2 * dim, kernel_size=patch_size2, stride=patch_stride2, bias=False)
if norm_layer is not None:
self.norm = norm_layer(2 * dim)
else:
self.norm = nn.Identity()
def forward(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
x = self.norm(self.reduction(x))
return x
class FasterNet(nn.Module):
def __init__(self,
in_chans=3,
num_classes=1000,
embed_dim=96,
depths=(1, 2, 8, 2),
mlp_ratio=2.,
n_div=4,
patch_size=4,
patch_stride=4,
patch_size2=2, # for subsequent layers
patch_stride2=2,
patch_norm=True,
feature_dim=1280,
drop_path_rate=0.1,
layer_scale_init_value=0,
norm_layer='BN',
act_layer='RELU',
fork_feat=False,
init_cfg=None,
pretrained=None,
pconv_fw_type='split_cat',
**kwargs):
super().__init__()
if norm_layer == 'BN':
norm_layer = nn.BatchNorm2d
else:
raise NotImplementedError
if act_layer == 'GELU':
act_layer = nn.GELU
elif act_layer == 'RELU':
act_layer = partial(nn.ReLU, inplace=True)
else:
raise NotImplementedError
if not fork_feat:
self.num_classes = num_classes
self.num_stages = len(depths)
self.embed_dim = embed_dim
self.patch_norm = patch_norm
self.num_features = int(embed_dim * 2 ** (self.num_stages - 1))
self.mlp_ratio = mlp_ratio
self.depths = depths
# split image into non-overlapping patches
self.patch_embed = PatchEmbed(
patch_size=patch_size,
patch_stride=patch_stride,
in_chans=in_chans,
embed_dim=embed_dim,
norm_layer=norm_layer if self.patch_norm else None
)
# stochastic depth decay rule
dpr = [x.item()
for x in torch.linspace(0, drop_path_rate, sum(depths))]
# build layers
stages_list = []
for i_stage in range(self.num_stages):
stage = BasicStage(dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_stage),
n_div=n_div,
depth=depths[i_stage],
mlp_ratio=self.mlp_ratio,
drop_path=dpr[sum(depths[:i_stage]):sum(depths[:i_stage + 1])],
layer_scale_init_value=layer_scale_init_value,
norm_layer=norm_layer,
act_layer=act_layer,
pconv_fw_type=pconv_fw_type
)
stages_list.append(stage)
# patch merging layer
if i_stage < self.num_stages - 1:
stages_list.append(
PatchMerging(patch_size2=patch_size2,
patch_stride2=patch_stride2,
dim=int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_stage),
norm_layer=norm_layer)
)
self.stages = nn.Sequential(*stages_list)
self.fork_feat = fork_feat
if self.fork_feat:
self.forward = self.forward_det
# add a norm layer for each output
self.out_indices = [0, 2, 4, 6]
for i_emb, i_layer in enumerate(self.out_indices):
if i_emb == 0 and os.environ.get('FORK_LAST3', None):
raise NotImplementedError
else:
layer = norm_layer(int(embed_dim * 2 ** i_emb))
layer_name = f'norm{i_layer}'
self.add_module(layer_name, layer)
else:
self.forward = self.forward_cls
# Classifier head
self.avgpool_pre_head = nn.Sequential(
nn.AdaptiveAvgPool2d(1),
nn.Conv2d(self.num_features, feature_dim, 1, bias=False),
act_layer()
)
self.head = nn.Linear(feature_dim, num_classes) \
if num_classes > 0 else nn.Identity()
self.apply(self.cls_init_weights)
self.init_cfg = copy.deepcopy(init_cfg)
if self.fork_feat and (self.init_cfg is not None or pretrained is not None):
self.init_weights()
def cls_init_weights(self, m):
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if isinstance(m, nn.Linear) and m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, (nn.Conv1d, nn.Conv2d)):
trunc_normal_(m.weight, std=.02)
if m.bias is not None:
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
elif isinstance(m, (nn.LayerNorm, nn.GroupNorm)):
nn.init.constant_(m.bias, 0)
nn.init.constant_(m.weight, 1.0)
# init for mmdetection by loading imagenet pre-trained weights
def init_weights(self, pretrained=None):
logger = get_root_logger()
if self.init_cfg is None and pretrained is None:
logger.warn(f'No pre-trained weights for '
f'{self.__class__.__name__}, '
f'training start from scratch')
pass
else:
assert 'checkpoint' in self.init_cfg, f'Only support ' \
f'specify `Pretrained` in ' \
f'`init_cfg` in ' \
f'{self.__class__.__name__} '
if self.init_cfg is not None:
ckpt_path = self.init_cfg['checkpoint']
elif pretrained is not None:
ckpt_path = pretrained
ckpt = _load_checkpoint(
ckpt_path, logger=logger, map_location='cpu')
if 'state_dict' in ckpt:
_state_dict = ckpt['state_dict']
elif 'model' in ckpt:
_state_dict = ckpt['model']
else:
_state_dict = ckpt
state_dict = _state_dict
missing_keys, unexpected_keys = \
self.load_state_dict(state_dict, False)
# show for debug
print('missing_keys: ', missing_keys)
print('unexpected_keys: ', unexpected_keys)
def forward_cls(self, x):
# output only the features of last layer for image classification
x = self.patch_embed(x)
x = self.stages(x)
x = self.avgpool_pre_head(x) # B C 1 1
x = torch.flatten(x, 1)
x = self.head(x)
return x
def forward_det(self, x: Tensor) -> Tensor:
# output the features of four stages for dense prediction
x = self.patch_embed(x)
outs = []
for idx, stage in enumerate(self.stages):
x = stage(x)
if self.fork_feat and idx in self.out_indices:
norm_layer = getattr(self, f'norm{idx}')
x_out = norm_layer(x)
outs.append(x_out)
return outs
![[Angular] 笔记 10:服务与依赖注入](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/c5f4e7938b7a48cd999fdb21660c4127.png)