AspectJ是一个面向切面的框架,扩展了Java语言。有一个专门的编译器用来生成遵守Java字节编码规范的Class文件。Spring的AOP底层也是用了这个框架。
AOP可以拦截指定的方法并对方法增强,而且无需侵入到业务代码中,使业务与非业务处理逻辑分离。
| join point 连接点 | 是在程序中已经定义好的点。 |
| pointcuts 切点 | 挑选这些连接点及取值。动态影响程序流程。 |
| advice 通知/处理 | 对连接点进行增强的部分,动态影响程序流程。 |
| inter-type declarations 类系间声明 | 允许程序员修改程序的静态关系,即程序的类的成员和类之间的关系。 |
| aspects 切面 | 封装上面这些结构。 |
表 AspectJ中的相关概念
1 idea 运行AspectJ
1,下载并安装AspectJ编译器。下载连接。

图 Mac系统下安装AspectJ编译器
2,在idea中安装AspectJ及AOP Pointcut Language插件。

图 idea 中安装相关插件
3,在项目中,编译器配置选择AJC。

图 Java编译器配置
4,添加AspectJ依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjrt</artifactId>
<version>1.9.6</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.aspectj</groupId>
<artifactId>aspectjweaver</artifactId>
<version>1.9.5</version>
</dependency>5,创建Aspect文件,Aspect的大致语法和Java一样。(如果在点击new时没有发现Aspect选项,则选择“File”类型,并把后缀改为.aj。)

图 点击new时可创建的文件类型部分截图
2 pointcuts
切点是用来挑选连接点的。
call(void article.service.ShopService.showGoods(String)):表示service包下的ShopService类,方法名为showGoods,有一个String类型参数,返回值为void方法的切点。
切点还可以使用逻辑运算符(&&,||及!)及通配符表示:
before():call(void article.service.ShopService.showGoods(String)) || call(void article..say*(..)) {
System.out.println("这是一个通知");
}表示service包下的ShopService类,方法名为showGoods,有一个String类型参数,返回值为void的方法或者是article包下,方法名以say开头,返回值为void的方法的切点。
2.1 命名切点
命名切点格式为:pointcut 切点名():切点表达式
public aspect ShopAspect {
pointcut shopPointcut(): call(void article.service.ShopService.showGoods(String)) || call(void article..say*(..));
before():shopPointcut() {
System.out.println("这是一个通知");
}
}2.2 引入与织入
引入,introduction,向现有的类添加新的方法或者属性。
织入,weaving,把切面应用到目标对象并创建新的代理对象的过程。切面在指定的连接点被织入到目标对象中。

图 切面的目标对象类的反编译代码
2.3 获取程序流中的所有连接点 cflow
cflow获取特定连接点之后在程序控制流程内遇到的所有连接点。(每行代码编译后的字节码都属于连接点)
cflowbelow与cflow用法是一样的,唯一的区别是cflowbelow不包括初始连接点。
public aspect SimpleAspect {
before():cflowbelow(call(* article.flow.AObject.methodA())) && !within(SimpleAspect) {
System.out.println("连接");
}
}
public class AObject {
public static void methodA() {
System.out.println("hello");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AObject.methodA();
}
}
//运行结果
//连接A
//连接A
//连接A
//hello3 Advice
通知是增强指定连接点(目标方法)的代码片段。
| before() | 在目标方法调用之前执行。 |
| after() | 在目标方法返回或异常后调用。 |
| after() returning: | 在目标方法返回后调用。 |
| after() throwing: | 在目标方法异常后调用。 |
| around | 会将这个目标方法封装起来。 |
表 通知的5种位置
public aspect AdviceAspect {
after() throwing: call(void article.service.AdviceService.methodThrowing(..)) {
System.out.println("methodThrowing通知");
}
}
public class AdviceService {
public void methodThrowing() {
System.out.println("开始执行方法");
throw new RuntimeException();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AdviceService adviceService = new AdviceService();
adviceService.methodThrowing();
}
}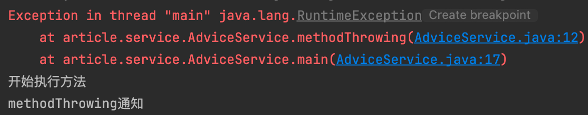
图 运行结果
3.1 从切点中获取上下文信息
通知可以从切点那获取并使用连接点的方法参数和目标对象等上下文信息。
public aspect ContextAspect {
after(ContextService contextService, String argName, int argNum): call(String article.service.ContextService.contextInfo(String,int))
&& args(argName,argNum) && target(contextService){
System.out.println("织入:argName:" + argName + ";argNum:" + argNum);
System.out.println(contextService);
}
}
public class ContextService {
public String contextInfo(String name, int num){
System.out.println("hello:" + name + "," + num);
return "temp";
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ContextService contextService = new ContextService();
contextService.contextInfo("word",999);
}
}使用命名切点时,如果需要在通知中获取上下文,则需要在命名切点调用时指出这些参数名。
public aspect ContextAspect {
pointcut argPoint(ContextService contextService, String argName, int argNum): call(String article.service.ContextService.contextInfo(String,int))
&& args(argName,argNum) && target(contextService);
after(ContextService contextService, String argName, int argNum): argPoint(contextService,argName,argNum){
System.out.println("织入:argName:" + argName + ";argNum:" + argNum);
System.out.println(contextService);
}
}4 类型间声明
AspectJ可以静态改变类的结构(新增方法、成员变量及构造函数),也可以更改类之间的继承关系。
需求:对于已经写好的Shop类,我们希望通过AspectJ增加记录访客信息及对每位客户到店进行提醒的功能。
public aspect ShopAspect {
public List<String> Shop.visitInfos = new ArrayList();
public static void addInfo(Shop shop,String info) {
shop.visitInfos.add(info);
}
before(Shop shop,String customName,String gender):call(void article.entity.Shop.visit(String,String)) && args(customName,gender) && target(shop){
System.out.println("欢迎光临:" + customName);
String info = "姓名:" + customName + ";性别:" + gender + ";到访时间:" + new Date();
addInfo(shop,info);
}
after(Shop shop): call(void article.entity.Shop.summary()) && target(shop){
System.out.println(shop.visitInfos);
}
}
public class Shop {
public void visit(String customName,String gender) {
System.out.println(customName + "进入店铺");
}
public void summary() {
System.out.println("店铺一天总结。");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws InterruptedException {
Shop shop = new Shop();
shop.visit("黄先生","男");
Thread.sleep(1000*10);
shop.visit("刘女士","刘女士");
shop.summary();
}
}