个人主页:日刷百题
系列专栏:〖C语言小游戏〗〖Linux〗〖数据结构〗 〖C语言〗
🌎欢迎各位→点赞👍+收藏⭐️+留言📝

写在前面:
递增单调栈:栈中元素从栈底到栈顶依次增大
递减单调栈:栈中元素从栈底到栈顶依次减小在学习完朴素的数据结构栈之后,单调栈作为栈的一种升级版应用,在某些情境下具有得天独厚的优越性:可将O(n²)的遍历复杂度降低至O(n)!
以下就是几种经典的单调栈运用问题。
一、字符串解码

思路:这题利用了栈,但不是单调栈,我们看到括号问题容易联想到有效括号问题也是利用栈
(1)遍历字符数组,当没有遇到‘]’时,将字符全部入栈
(2)若遇到‘]’,将字母一一出栈,入到临时栈,直到遇到‘[’停止
(3)此时将'['出栈,此时栈顶必然是数字字符,将数字字符全部转化为mulsize数字,出栈
(4)用2层嵌套循环,外层为mulsize,内层为临时栈的元素个数,将临时栈元素按mulszie次循环放进栈中,最后将临时栈初始化
(5)最后,字符遍历结束,栈中元素即为所求,此时将栈的末尾加上’\0’.
注:这里值得注意的地方有俩点
<1>在栈末尾插入‘\0’,得有扩容判断
<2>在将数字字符转化为mulsize时,字符数字是一个个出栈,为逆序,例如:100出栈为001,所以转化为数字的时候,要注意
typedef char DateType;
typedef struct Stack
{
DateType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
//初始化和销毁栈
void InitStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void DestoryStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = 0;
ps->capacity = 0;
}
//出栈和入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, DateType x)
{
assert(ps);
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps->capacity;
DateType* tmp = (DateType*)realloc(ps->a, sizeof(DateType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
return;
}
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
//栈的有效个数和栈顶元素
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
DateType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//判空
bool IsEmptyStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
char* decodeString(char* s) {
Stack ps;
Stack tmp;
InitStack(&ps);
InitStack(&tmp);
int len = strlen(s);
while ((*s) != '\0')
{
if ((*s) != ']')
{
StackPush(&ps, (*s));
}
else
{
while (StackTop(&ps) != '[')
{
char b = StackTop(&ps);
StackPop(&ps);
StackPush(&tmp, b);
}
StackPop(&ps);
int tmpsize = tmp.top;
int mulsize=0;
int i=0;
while (ps.top > 0 && ps.a[ps.top - 1] >= '0' && ps.a[ps.top - 1] <= '9')
{
mulsize =mulsize + pow(10,i)*(ps.a[ps.top - 1] - '0');
StackPop(&ps);
i++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < mulsize; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < tmpsize; j++)
{
char w = StackTop(&tmp);
StackPush(&ps, w);
StackPop(&tmp);
}
tmp.top = tmpsize;
}
}
if (tmp.a != NULL)
{
free(tmp.a);
tmp.a = NULL;
InitStack(&tmp);
}
s++;
}
DestoryStack(&tmp);
if (ps.top == ps.capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps.capacity == 0 ? 4 : 2 * ps.capacity;
DateType* tmp = (DateType*)realloc(ps.a, sizeof(DateType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
return 1;
}
ps.a = tmp;
ps.capacity = newcapacity;
}
ps.a[ps.top] = '\0';
return ps.a;
} 二、接雨水
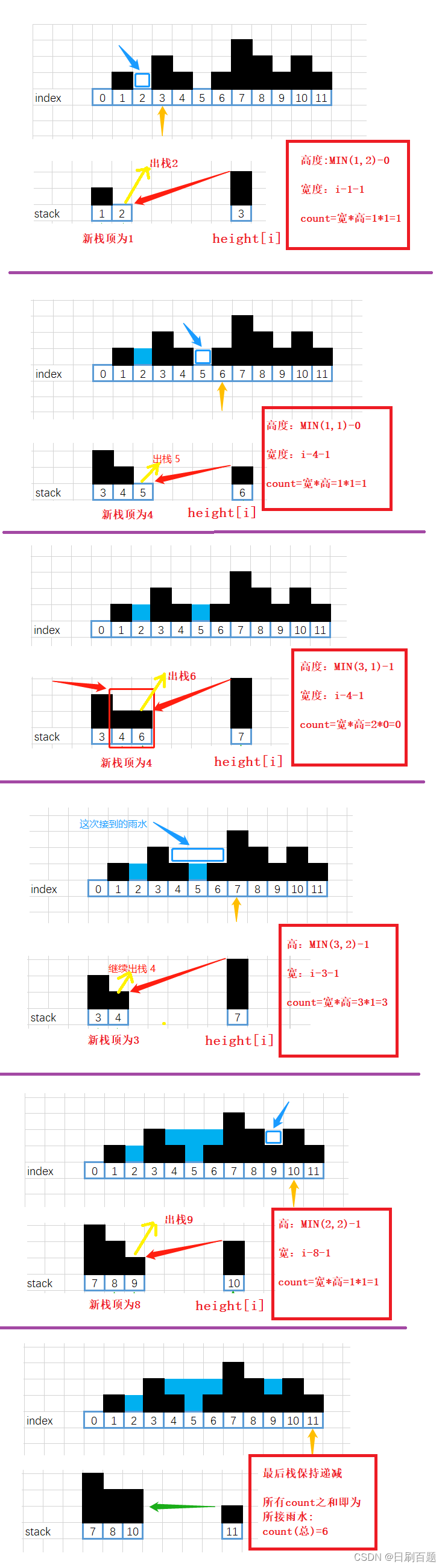
思路:这题思路比较巧妙,运用了单调递减栈
(1)创造栈用来存放数组元素下标
(2)遍历数组,若栈为空或者栈顶元素所对应的数组值大于等于数组元素,则直接入栈
(3)若栈顶元素所对应数组元素值小于数组元素,则做出判断,将栈顶元素保存,且出栈,再用此时的栈顶元素所对应的数组值与数组元素比较,俩个数的较小值减去原来保存的栈顶元素所对应数组值即为接雨水凹槽的高,此时数组下标与栈顶差值减1即为接雨水凹槽的宽,相乘即为所接雨水的面积,保持循环,直到栈为空或者栈为递减,退出循环,进行数组下一个元素比较。
上面思路听起来比较复杂,可以看图理解:
typedef int DateType;
typedef struct Stack
{
DateType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
//初始化和销毁
void InitStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void DestroyStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//出栈和入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, DateType x)
{
assert(ps);
if(ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 4;
DateType* tmp = (DateType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(DateType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
return;
}
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
ps->a = tmp;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
//栈顶元素和元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
DateType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//判空
bool IsEmptyStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
int MIN(int x, int y)
{
return x > y ? y : x;
}
int trap(int* height, int heightSize) {
Stack ps;
InitStack(&ps);
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < heightSize; i++)
{
while (ps.top > 0 && height[StackTop(&ps)] < height[i])
{
DateType tmp = StackTop(&ps);
StackPop(&ps);
if (ps.top == 0)
{
break;
}
int h = MIN(height[StackTop(&ps)], height[i]);
int width = i - StackTop(&ps) - 1;
count += (h - height[tmp]) * width;
}
StackPush(&ps, i);
}
DestroyStack(&ps);
return count;
}三、每日温度
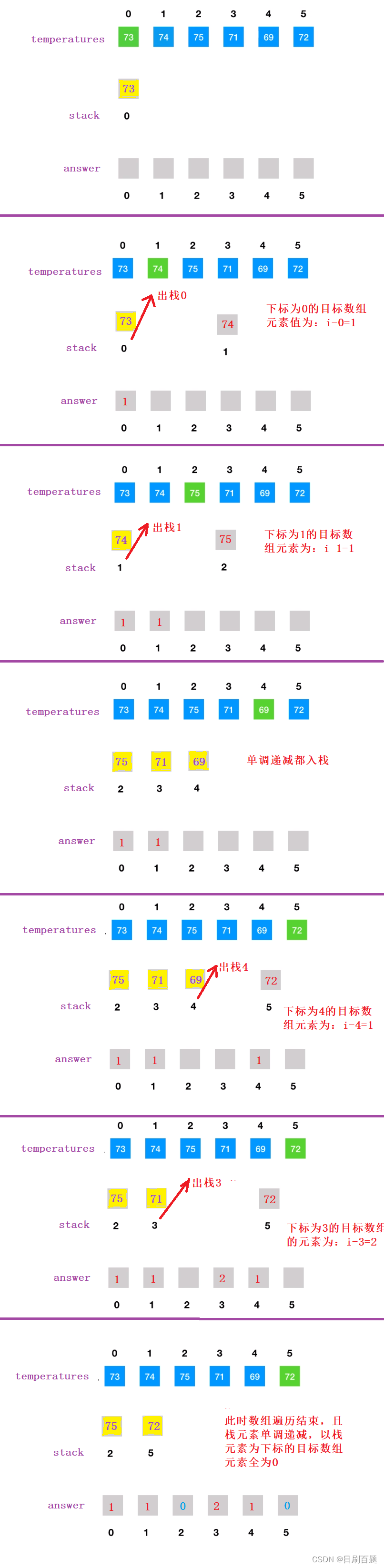
思路:这题思路比较巧妙,运用了单调递减栈和上面一题类似
(1)创造栈用来存放数组元素下标
(2)遍历数组,若栈为空或者栈顶元素所对应的数组值大于等于数组元素,则直接入栈
(3)若栈顶元素所对应数组元素值小于数组元素,则做出判断,将栈顶元素保存,且出栈,由于当前数组元素大于栈顶元素对应数组元素值,而且一定是第一个大于栈顶元素对应数组元素值,直接求出下标差(当前数组元素下标和栈顶元素差)就是二者的距离,放入所求目标数组内(数组下标为保存的栈顶元素)。继续看新的栈顶元素,循环往复,直到当前数组元素小于等于栈顶元素所对应数组值或者栈为空停止,然后将数组元素下标入栈,进行数组下一个元素比较
(3)数组遍历结束后,栈为单调递减栈,里面元素所对应数组值(气温)向后检索找不到比它高的温度,所以以这些栈元素为下标的目标数组元素全部置为0.
图解如下:
typedef int DateType;
typedef struct Stack
{
DateType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
//初始化和销毁
void InitStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void DestroyStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//出栈和入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, DateType x)
{
assert(ps);
if(ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 4;
DateType* tmp = (DateType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(DateType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
return;
}
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
ps->a = tmp;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
//栈顶元素和元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
DateType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//判空
bool IsEmptyStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
int* dailyTemperatures(int* temperatures, int temperaturesSize, int* returnSize) {
int *answer=(int *)malloc(sizeof(int)*temperaturesSize);
Stack st;
InitStack(&st);
for(int i=0;i<temperaturesSize;i++)
{
while(st.top>0&&temperatures[i]>temperatures[StackTop(&st)])
{
answer[StackTop(&st)]=i-StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
if(st.top==0)
{
break;
}
}
StackPush(&st,i);
}
while(st.top>0)
{
answer[StackTop(&st)]=0;
StackPop(&st);
}
* returnSize=temperaturesSize;
return answer;
}四、柱状图中最大的矩形
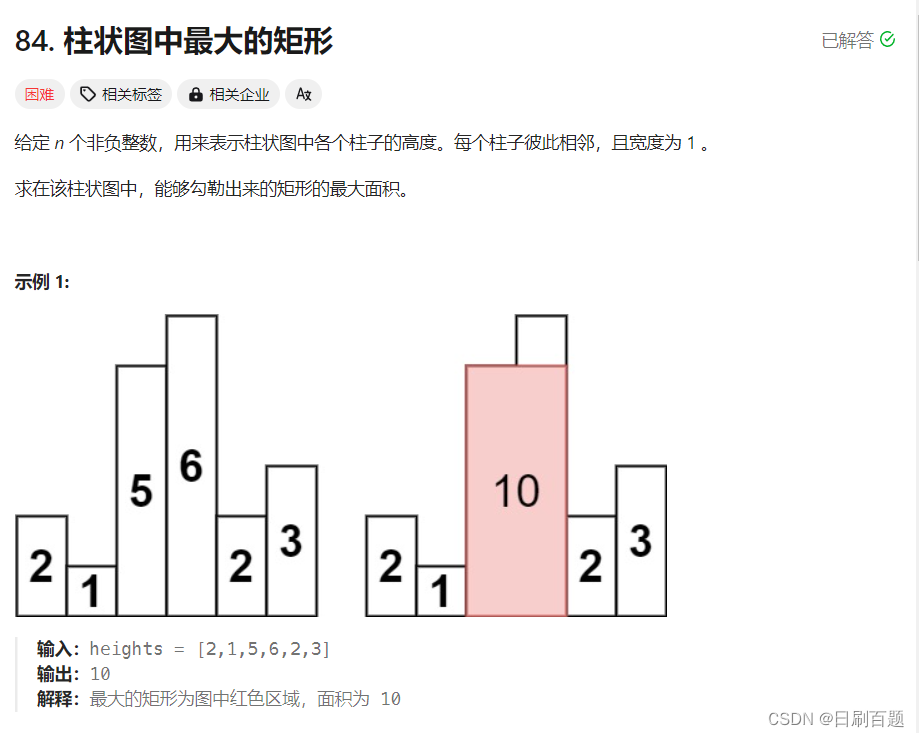
思路:这题思路与接雨水问题一样,不过此题用的是严格单调增栈
(1)创造栈用来存放数组元素下标
(2)遍历数组,若栈为空或者栈顶元素所对应的柱形高度小于当前柱形高度,则当前柱形高度的数组下标直接入栈
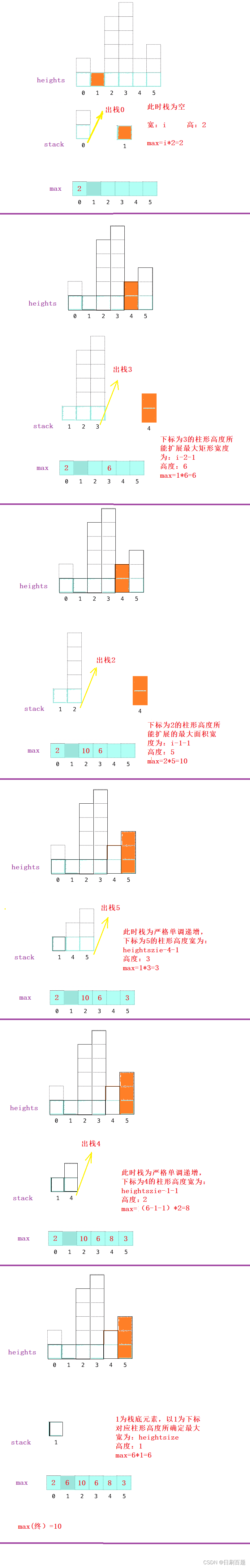
(3)若栈顶元素所对应数组元素值大于等于数组元素,则做出判断,将栈顶元素临时保存,且出栈,再用当前数组元素下标与栈顶元素做差-1即为临时保存的栈顶元素所对应柱形高度的宽,根据原来临时保存栈顶元素求出其对应的高,就可以求出该高度的最大矩形面积,,保持循环,直到栈为空或者栈为严格递增,退出循环,进行数组下一个元素比较。
(4)数组遍历结束,栈为严格单调递增栈,除了最后一个栈底元素外,其他栈元素对应柱形高度最大矩形宽度为数组长度减去当前栈元素左侧一个栈元素的值-1,栈底元素对应柱形高度最大矩形宽度为数组元素长度
注:这里面有几个注意的细节
<1>当栈元素为1个,且数组元素小于等于栈顶对应柱形高度,此时临时保存栈顶元素,出栈,此临时保存栈顶元素对应柱形高度所能扩展做大矩形宽度为:当前数组元素下标i减去临时保存的栈顶元素
<2>数组元素等于栈顶栈顶对应柱形高度时,虽然所求的最大矩形不是这个栈顶的最大矩形,但是要小于这个栈顶元素对应的最大矩形面积,不碍事,直到下一个数组元素严格小于栈顶元素对应柱形高度,此时所求的最大矩形面积即之前那个相等高度的最大矩形面积,所以不影响
图解如下:
typedef int DateType;
typedef struct Stack
{
DateType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}Stack;
//初始化和销毁
void InitStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
void DestroyStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
//出栈和入栈
void StackPush(Stack* ps, DateType x)
{
assert(ps);
if(ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
int newcapacity = ps->capacity == 0 ? 4 : ps->capacity * 4;
DateType* tmp = (DateType*)realloc(ps->a,sizeof(DateType) * newcapacity);
if (tmp == NULL)
{
perror("realloc fail:");
return;
}
ps->capacity = newcapacity;
ps->a = tmp;
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
void StackPop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
ps->top--;
}
//栈顶元素和元素个数
int StackSize(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
DateType StackTop(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
//判空
bool IsEmptyStack(Stack* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}
int MAX(int x, int y)
{
return x>y?x:y;
}
int largestRectangleArea(int* heights, int heightsSize) {
Stack st;
InitStack(&st);
int max = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < heightsSize; i++)
{
while (st.top>0 && heights[i] <= heights[StackTop(&st)])
{
int tmp = StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
if(st.top==0)
{
max=MAX(max, heights[tmp]*i);
break;
}
int width = i - StackTop(&st) - 1;
max = MAX(max, heights[tmp] * width);
}
StackPush(&st, i);//严格单调增
}
//遍历结束后,变为严格单调递增栈
while (st.top>0)
{
int tmp =StackTop(&st);
StackPop(&st);
if (st.top==0)
{
max = MAX(max, heights[tmp] * heightsSize);
break;
}
int width = heightsSize - StackTop(&st)-1 ;
max = MAX(max, heights[tmp] * width);
}
return max;
}总结:本篇文章讲解了单调栈的应用,为系列题目,有利于帮助理解单调栈的用法和这系列问题思路。
希望大家阅读完可以有所收获,同时也感谢各位铁汁们的支持。文章有任何问题可以在评论区留言,百题一定会认真阅读!