文章目录
- 题目
- 标题和出处
- 难度
- 题目描述
- 要求
- 示例
- 数据范围
- 前言
- 解法一
- 思路和算法
- 代码
- 复杂度分析
- 解法二
- 思路和算法
- 代码
- 复杂度分析
题目
标题和出处
标题:输出二叉树
出处:655. 输出二叉树
难度
6 级
题目描述
要求
给定二叉树的根结点 root \texttt{root} root,创建 m × n \texttt{m} \times \texttt{n} m×n 的字符串矩阵 res \texttt{res} res 表示二叉树的格式化输出。格式化输出矩阵应根据以下规则创建:
- 树的高度是 height \texttt{height} height,行数 m \texttt{m} m 应等于 height + 1 \texttt{height} + \texttt{1} height+1。
- 列数 n \texttt{n} n 应等于 2 height + 1 − 1 \texttt{2}^{\texttt{height} + \texttt{1}} - \texttt{1} 2height+1−1。
- 根结点放置在第一行的正中间(更正式而言,位于 res[0][(n - 1) / 2] \texttt{res[0][(n - 1) / 2]} res[0][(n - 1) / 2])。
- 对于每个放置在矩阵中 res[r][c] \texttt{res[r][c]} res[r][c] 位置的结点,将其左子结点放置在 res[r + 1][c − 2 height − r − 1 ] \texttt{res[r} + \texttt{1][c} - \texttt{2}^{\texttt{height} - \texttt{r} - \texttt{1}}\texttt{]} res[r+1][c−2height−r−1],右子结点放置在 res[r + 1][c + 2 height − r − 1 ] \texttt{res[r} + \texttt{1][c} + \texttt{2}^{\texttt{height} - \texttt{r} - \texttt{1}}\texttt{]} res[r+1][c+2height−r−1]。
- 重复该过程,直到所有结点都放置到矩阵中。
- 所有空单元格应包含空字符串 "" \texttt{""} ""。
返回创建的矩阵 res \texttt{res} res。
示例
示例 1:
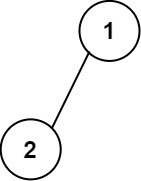
输入:
root
=
[1,2]
\texttt{root = [1,2]}
root = [1,2]
输出:
[["",
"1",
""],
\texttt{[["", "1", ""],}
[["", "1", ""],
["2",
"",
""]]
\texttt{ ["2", "", ""]]}
["2", "", ""]]
示例 2:
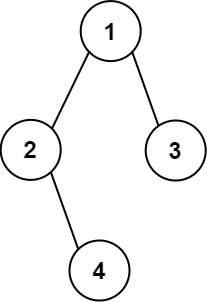
输入:
root
=
[1,2,3,null,4]
\texttt{root = [1,2,3,null,4]}
root = [1,2,3,null,4]
输出:
[["",
"",
"",
"1",
"",
"",
""],
\texttt{[["", "", "", "1", "", "", ""],}
[["", "", "", "1", "", "", ""],
["",
"2",
"",
"",
"",
"3",
""],
\texttt{ ["", "2", "", "", "", "3", ""],}
["", "2", "", "", "", "3", ""],
["",
"",
"4",
"",
"",
"",
""]]
\texttt{ ["", "", "4", "", "", "", ""]]}
["", "", "4", "", "", "", ""]]
数据范围
- 树中结点数目在范围 [1, 2 10 ] \texttt{[1, 2}^\texttt{10}\texttt{]} [1, 210] 内
- -99 ≤ Node.val ≤ 99 \texttt{-99} \le \texttt{Node.val} \le \texttt{99} -99≤Node.val≤99
- 树的高度在范围 [1, 10] \texttt{[1, 10]} [1, 10] 内
前言
这道题要求将给定的二叉树格式化输出,使用矩阵表示格式化输出的结果。由于矩阵的行数和列数由二叉树的高度决定,因此需要首先计算二叉树的高度,根据二叉树的高度计算矩阵的行数和列数,创建矩阵之后遍历二叉树并将每个结点值填入矩阵中的对应位置。
计算二叉树的高度可以使用「二叉树的最大深度」的做法,使用深度优先搜索或者广度优先搜索得到二叉树的高度。这道题中定义的二叉树的高度为从根结点到最远叶结点的路径上的边数,因此边界情况为只有一个结点的二叉树的高度是 0 0 0。
得到二叉树的高度 height \textit{height} height 之后,即可得到矩阵的行数 m = height + 1 m = \textit{height} + 1 m=height+1,列数 n = 2 m − 1 n = 2^m - 1 n=2m−1。创建矩阵之后,首先将根结点值填入矩阵的第 0 0 0 行第 n − 1 2 \dfrac{n - 1}{2} 2n−1 列,然后遍历二叉树的其余结点并填入矩阵中的对应位置。
当一个结点的位置确定之后,可以根据该结点在矩阵中的行列下标以及二叉树的高度决定其子结点的位置。如果一个结点位于第 row \textit{row} row 行第 column \textit{column} column 列,则其左子结点位于第 row + 1 \textit{row} + 1 row+1 行第 column − 2 height − row − 1 \textit{column} - 2^{\textit{height} - \textit{row} - 1} column−2height−row−1 列,其右子结点位于第 row + 1 \textit{row} + 1 row+1 行第 column + 2 height − row − 1 \textit{column} + 2^{\textit{height} - \textit{row} - 1} column+2height−row−1 列。
输出二叉树可以使用深度优先搜索或者广度优先搜索实现。
解法一
思路和算法
使用深度优先搜索输出二叉树时,首先将根结点值填入矩阵的第 0 0 0 行第 n − 1 2 \dfrac{n - 1}{2} 2n−1 列,然后计算出非空子结点在矩阵中的位置,继续遍历非空子树并将其余的结点值填入矩阵,直到所有结点遍历完毕,此时所有结点值都填入矩阵中的对应位置。
整个过程是一个递归的过程,递归的终止条件是当前结点为叶结点,此时将当前结点值填入矩阵中的对应位置,然后直接返回。对于其余情况,在将当前结点值填入矩阵中的对应位置之后,对非空子结点执行递归。
代码
class Solution {
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
int height;
public List<List<String>> printTree(TreeNode root) {
height = getHeight(root);
int m = height + 1;
int n = (1 << m) - 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
List<String> row = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
row.add("");
}
res.add(row);
}
dfs(root, 0, (n - 1) / 2);
return res;
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
TreeNode left = root.left, right = root.right;
if (left == null && right == null) {
return 0;
}
int leftHeight = left != null ? getHeight(left) : -1;
int rightHeight = right != null ? getHeight(right) : -1;
return Math.max(leftHeight, rightHeight) + 1;
}
public void dfs(TreeNode node, int row, int column) {
res.get(row).set(column, String.valueOf(node.val));
TreeNode left = node.left, right = node.right;
if (left != null) {
dfs(left, row + 1, column - (1 << (height - row - 1)));
}
if (right != null) {
dfs(right, row + 1, column + (1 << (height - row - 1)));
}
}
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度: O ( h × 2 h ) O(h \times 2^h) O(h×2h),其中 h h h 是二叉树的高度。矩阵的行数 m m m 和列数 n n n 满足 m = h + 1 m = h + 1 m=h+1, n = 2 h + 1 − 1 n = 2^{h + 1} - 1 n=2h+1−1,输出二叉树的时间复杂度是 O ( m n ) = O ( h × 2 h ) O(mn) = O(h \times 2^h) O(mn)=O(h×2h)。
-
空间复杂度: O ( h ) O(h) O(h),其中 h h h 是二叉树的高度。空间复杂度主要是递归调用的栈空间,取决于二叉树的高度。注意返回值不计入空间复杂度。
解法二
思路和算法
使用广度优先搜索输出二叉树时,使用两个队列分别存储待访问的结点和结点在矩阵中的位置,两个队列分别为结点队列和位置队列。初始时,将根结点入结点队列,将第 0 0 0 行第 n − 1 2 \dfrac{n - 1}{2} 2n−1 列入位置队列。
每次将一个结点从结点队列出队,并将一个位置从位置队列出队,出队的位置即为出队的结点在矩阵中的位置。将当前结点值填入矩阵中的对应位置,然后计算出非空子结点在矩阵中的位置,将非空子结点和对应位置分别入两个队列。重复该过程直到所有结点遍历完毕,此时所有结点值都填入矩阵中的对应位置。
代码
class Solution {
public List<List<String>> printTree(TreeNode root) {
int height = getHeight(root);
int m = height + 1;
int n = (1 << m) - 1;
List<List<String>> res = new ArrayList<List<String>>();
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
List<String> row = new ArrayList<String>();
for (int j = 0; j < n; j++) {
row.add("");
}
res.add(row);
}
Queue<TreeNode> nodeQueue = new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>();
Queue<int[]> locationQueue = new ArrayDeque<int[]>();
nodeQueue.offer(root);
locationQueue.offer(new int[]{0, (n - 1) / 2});
while (!nodeQueue.isEmpty()) {
TreeNode node = nodeQueue.poll();
int[] location = locationQueue.poll();
int row = location[0], column = location[1];
res.get(row).set(column, String.valueOf(node.val));
TreeNode left = node.left, right = node.right;
if (left != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(left);
locationQueue.offer(new int[]{row + 1, column - (1 << (height - row - 1))});
}
if (right != null) {
nodeQueue.offer(right);
locationQueue.offer(new int[]{row + 1, column + (1 << (height - row - 1))});
}
}
return res;
}
public int getHeight(TreeNode root) {
int depth = -1;
Queue<TreeNode> queue = new ArrayDeque<TreeNode>();
queue.offer(root);
while (!queue.isEmpty()) {
depth++;
int size = queue.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; i++) {
TreeNode node = queue.poll();
if (node.left != null) {
queue.offer(node.left);
}
if (node.right != null) {
queue.offer(node.right);
}
}
}
return depth;
}
}
复杂度分析
-
时间复杂度: O ( h × 2 h ) O(h \times 2^h) O(h×2h),其中 h h h 是二叉树的高度。矩阵的行数 m m m 和列数 n n n 满足 m = h + 1 m = h + 1 m=h+1, n = 2 h + 1 − 1 n = 2^{h + 1} - 1 n=2h+1−1,输出二叉树的时间复杂度是 O ( m n ) = O ( h × 2 h ) O(mn) = O(h \times 2^h) O(mn)=O(h×2h)。
-
空间复杂度: O ( 2 h ) O(2^h) O(2h),其中 h h h 是二叉树的高度。空间复杂度主要是队列空间,队列内元素个数不超过二叉树的结点数,高度为 h h h 的二叉树中最多有 2 h + 1 − 1 2^{h + 1} - 1 2h+1−1 个结点。注意返回值不计入空间复杂度。







![[网络安全]密码字典快速生成——在线网站](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/58c24b97e9684262883443886ee936e3.png)