一、路由的基本介绍
路由是计算机网络中的一个重要概念,它用于确定数据包从源地址到目的地址的路径。在网络中,路由器是负责转发数据包的设备。
下面是关于路由的基本知识和使用方法的介绍:
路由表:路由器通过路由表来确定数据包的下一跳。路由表中包含了目的网络的IP地址和对应的下一跳地址。当路由器接收到一个数据包时,它会查找路由表,找到与目的地址匹配的条目,并将数据包发送到相应的下一跳地址。
静态路由:静态路由是手动配置的路由,管理员需要手动添加路由表的条目。静态路由的优点是简单、可靠,适用于小型网络或者需要固定路由的场景。但是,静态路由不适用于大型网络或者网络拓扑经常变化的情况。
动态路由:动态路由是通过动态路由协议学习到的路由。动态路由协议有自己的路由算法,能够自动适应网络拓扑的变化。常见的动态路由协议有OSPF、IS-IS、BGP等。动态路由的优点是能够自动适应网络变化,减少管理员的配置工作量。但是,动态路由也需要一定的计算和通信开销。
路由选择:当到达同一目的地的多条路由具有相同的路由优先级时,路由开销最小的将成为当前的最优路由。路由开销可以根据不同的路由协议和网络条件进行计算,常见的开销指标包括带宽、延迟、可靠性等。
路由器配置:配置路由器的路由表可以使用命令行界面(CLI)或者图形用户界面(GUI)。管理员可以手动添加静态路由,也可以配置动态路由协议来学习路由。
二、路由指令-手动配置
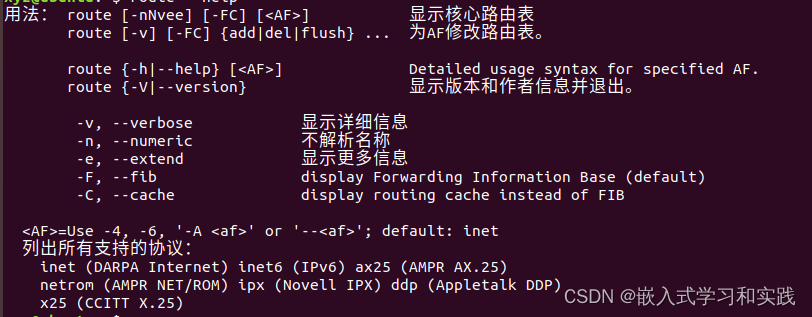
1. 路由帮助
route --help

2. 路由查找
route -n
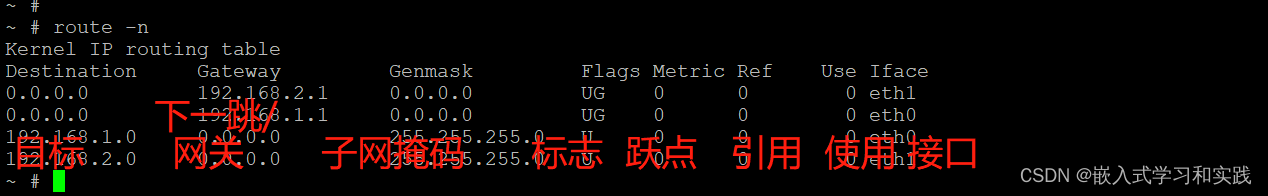
Destination Gateway Genmask Flags Metric Ref Use Iface
目标 下一跳/网关 子网掩码 标志 跃点 引用 使用 接口
OUTPUT
The output of the kernel routing table is organized in the following columns
Destination
The destination network or destination host.
Gateway
The gateway address or '*' if none set.
Genmask
The netmask for the destination net; '255.255.255.255' for a host destination and '0.0.0.0' for the default route.
Flags Possible flags include
U (route is up)
H (target is a host)
G (use gateway)
R (reinstate route for dynamic routing)
D (dynamically installed by daemon or redirect)
M (modified from routing daemon or redirect)
A (installed by addrconf)
C (cache entry)
! (reject route)
Metric The 'distance' to the target (usually counted in hops).
Ref Number of references to this route. (Not used in the Linux kernel.)
Use Count of lookups for the route. Depending on the use of -F and -C this will be either route cache misses (-F) or hits (-C).
Iface Interface to which packets for this route will be sent.
MSS Default maximum segment size for TCP connections over this route.
Window Default window size for TCP connections over this route.
irtt Initial RTT (Round Trip Time). The kernel uses this to guess about the best TCP protocol parameters without waiting on (possibly slow) answers.
HH (cached only)
The number of ARP entries and cached routes that refer to the hardware header cache for the cached route. This will be -1 if a hardware address is
not needed for the interface of the cached route (e.g. lo).
Arp (cached only)
Whether or not the hardware address for the cached route is up to date.
3. 路由添加
route add
示例
route add -net 192.168.2.15 netmask 255.255.255.255 metric 1024 gw 192.168.2.1 dev eth1
4. 路由删除
route del
或
route delete
示例
route del -net 192.168.2.15 netmask 255.255.255.255 metric 1024 gw 192.168.2.1 dev eth1
4. 其它
-net 就是说你这条路由目标是一个网络地址,或者说是一个网段;
-host 说你这个路由目标是一个主机地址,是一个到主机的路由;
官方参数有介绍
三、官方参数介绍
OPTIONS
-A family
use the specified address family (eg `inet'). Use route --help for a full list. You can use -6 as an alias for --inet6 and -4 as an alias for -A inet
-F operate on the kernel's FIB (Forwarding Information Base) routing table. This is the default.
-C operate on the kernel's routing cache.
-v select verbose operation.
-n show numerical addresses instead of trying to determine symbolic host names. This is useful if you are trying to determine why the route to your
nameserver has vanished.
-e use netstat(8)-format for displaying the routing table. -ee will generate a very long line with all parameters from the routing table.
del delete a route.
add add a new route.
target the destination network or host. You can provide an addresses or symbolic network or host name. Optionally you can use /prefixlen notation instead of
using the netmask option.
-net the target is a network.
-host the target is a host.
netmask NM
when adding a network route, the netmask to be used.
gw GW route packets via a gateway.
NOTE: The specified gateway must be reachable first. This usually means that you have to set up a static route to the gateway beforehand. If you
specify the address of one of your local interfaces, it will be used to decide about the interface to which the packets should be routed to. This is
a BSDism compatibility hack.
metric M
set the metric field in the routing table (used by routing daemons) to M. If this option is not specified the metric for inet6 (IPv6) address family
defaults to '1', for inet (IPv4) it defaults to '0'. You should always specify an explicit metric value to not rely on those defaults - they also
differ from iproute2.
mss M sets MTU (Maximum Transmission Unit) of the route to M bytes. Note that the current implementation of the route command does not allow the option to
set the Maximum Segment Size (MSS).
window W
set the TCP window size for connections over this route to W bytes. This is typically only used on AX.25 networks and with drivers unable to handle
back to back frames.
irtt I set the initial round trip time (irtt) for TCP connections over this route to I milliseconds (1-12000). This is typically only used on AX.25 net‐
works. If omitted the RFC 1122 default of 300ms is used.
reject install a blocking route, which will force a route lookup to fail. This is for example used to mask out networks before using the default route.
This is NOT for firewalling.
mod, dyn, reinstate
install a dynamic or modified route. These flags are for diagnostic purposes, and are generally only set by routing daemons.
dev If force the route to be associated with the specified device, as the kernel will otherwise try to determine the device on its own (by checking already
existing routes and device specifications, and where the route is added to). In most normal networks you won't need this.
If dev If is the last option on the command line, the word dev may be omitted, as it's the default. Otherwise the order of the route modifiers (met‐
ric netmask gw dev) doesn't matter.
四、官方示例
EXAMPLES
route add -net 127.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0 metric 1024 dev lo
adds the normal loopback entry, using netmask 255.0.0.0 and associated with the "lo" device (assuming this device was previously set up correctly
with ifconfig(8)).
route add -net 192.56.76.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 metric 1024 dev eth0
adds a route to the local network 192.56.76.x via "eth0". The word "dev" can be omitted here.
route del default
deletes the current default route, which is labeled "default" or 0.0.0.0 in the destination field of the current routing table.
route del -net 192.56.76.0 netmask 255.255.255.0
deletes the route. Since the Linux routing kernel uses classless addressing, you pretty much always have to specify the netmask that is same as as
seen in 'route -n' listing.
route add default gw mango
adds a default route (which will be used if no other route matches). All packets using this route will be gatewayed through the address of a node
named "mango". The device which will actually be used for that route depends on how we can reach "mango" - "mango" must be on directly reachable
route.
route add mango sl0
Adds the route to the host named "mango" via the SLIP interface (assuming that "mango" is the SLIP host).
route add -net 192.57.66.0 netmask 255.255.255.0 gw mango
This command adds the net "192.57.66.x" to be gatewayed through the former route to the SLIP interface.
route add -net 224.0.0.0 netmask 240.0.0.0 dev eth0
This is an obscure one documented so people know how to do it. This sets all of the class D (multicast) IP routes to go via "eth0". This is the cor‐
rect normal configuration line with a multicasting kernel.
route add -net 10.0.0.0 netmask 255.0.0.0 metric 1024 reject
This installs a rejecting route for the private network "10.x.x.x."
route -6 add 2001:0002::/48 metric 1 dev eth0
This adds a IPv6 route with the specified metric to be directly reachable via eth0.