一、实验目的
1.掌握ALU模块的组成和接口,理解ALU的功 能。
2.通过编程调用ALU模块计算斐波那契数。
3.掌握Verilog中多模块编程方法和实现。
二、实验内容
用 Verilog 设计一个算术运算单元 ALU,采 用纯组合逻辑设计,32bit 宽。
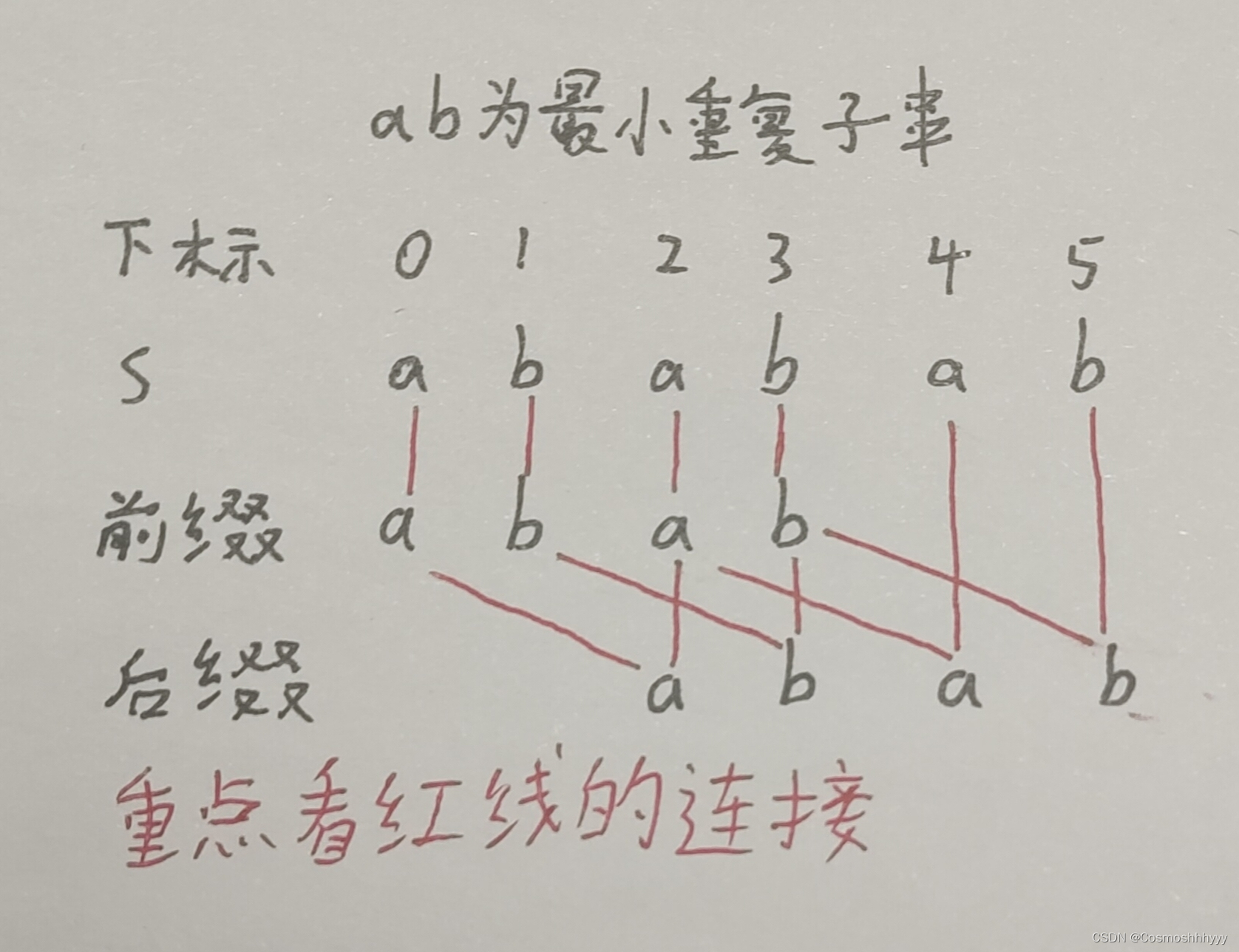
- 利用该 ALU 完成斐波那契数 f(n),其中 2<n<16。
- 可选
–改成3段式实现(已实现)
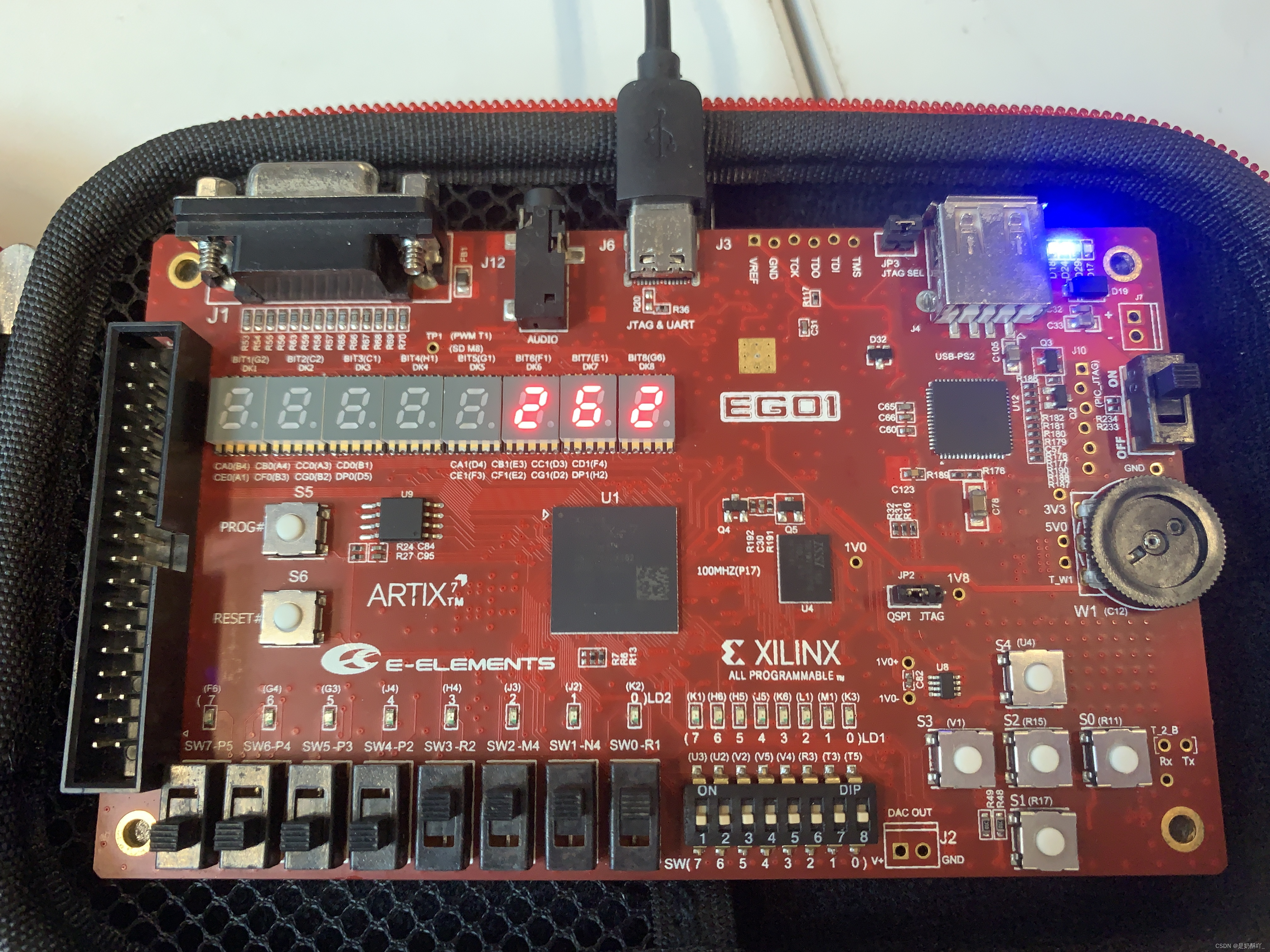
–用七段数码管输出(已实现)
三、实验程序
alu.v(加法器)
module alu(
input [31:0] a,
input [31:0] b,
input [3:0] op,
output reg[31:0] f,
output c
);
always @(*)
case(op)
4'b0000: f = 32'b0;
4'b0001: f = a + b;
4'b0010: f = a - b;
4'b0011: f = a & b;
4'b0100: f = a | b;
4'b0101: f = a ^ b;
default: f = 32'b0;
endcase
assign c = ~(|f);
endmodule
fib.v(三段式斐波那契数列)
module fib(
input clk,
input rst,
input [3:0] n,
output [31:0] result
);
reg[31:0] ra, rb;
wire[31:0] wf;
reg[3:0] count;
alu myalu(.a(ra),.b(rb),.op(4'b0001),.f(wf));
reg[1:0] cur_state, nex_state; // 现态和次态
// 状态转移
always @(posedge clk)
begin
if(rst==1)
cur_state<=2'b00;
else
cur_state<=nex_state;
end
// 状态转移条件
always @(*)
begin
case(cur_state)
2'b00:
nex_state<=2'b01;
2'b01:
nex_state<=2'b01;
endcase
end
// 状态输出
always @(posedge clk)
begin
case(cur_state)
2'b00:
begin
ra<=32'b1;
rb<=32'b1;
count<=4'b0011;
end
2'b01:
if(count<n)
begin
ra<=rb;
rb<=wf;
count<=count+1'b1;
end
endcase
end
assign result=wf;
endmodule
div.v(分频器)
module div(
input clk,
output clk_new
);
reg[17:0] q = 18'b0;
always @(posedge clk)
begin
q=q+1'b1;
end
assign clk_new=q[17];
endmodule
seven.v(七段数码管)
module seven(
input [3:0] data,
output reg[6:0] out
);
always @(*)
case (data)
4'b0000:out = 7'b1111110; // 7e
4'b0001:out = 7'b0110000; // 30
4'b0010:out = 7'b1101101; // 6d
4'b0011:out = 7'b1111001; // 79
4'b0100:out = 7'b0110011; // 33
4'b0101:out = 7'b1011011; // 5b
4'b0110:out = 7'b1011111; // 5f
4'b0111:out = 7'b1110000; // 70
4'b1000:out = 7'b1111111; // 7f
4'b1001:out = 7'b1111011; // 7b
4'b1010:out = 7'b1110111; // 77
4'b1011:out = 7'b0011111; // 1f
4'b1100:out = 7'b1001110; // 4e
4'b1101:out = 7'b0111101; // 3d
4'b1110:out = 7'b1001111; // 4f
4'b1111:out = 7'b1000111; // 47
default:out = 7'b1111110; //7e
endcase
endmodule
show.v(七段数码管显示)
module show(
input clk,
input rst,
input [11:0] result,
output reg[2:0] an,
output [6:0] out
);
wire clk_new;
div mydiv(.clk(clk),.clk_new(clk_new));
reg[3:0] data;
reg[1:0] cur_state,nex_state;
// 状态转移
// always @(posedge clk)
always @(posedge clk_new)
begin
if (rst)
cur_state<=2'b00;
else
cur_state<=nex_state;
end
// 状态转移条件
always @(*)
begin
case(cur_state)
2'b00:
nex_state<=2'b01;
2'b01:
nex_state<=2'b10;
2'b10:
nex_state<=2'b00;
endcase
end
// 状态输出
// always @(posedge clk)
always @(posedge clk_new)
begin
case(cur_state)
2'b00:
begin
an<=3'b01;
data<=result[3:0];
end
2'b01:
begin
an<=3'b010;
data<=result[7:4];
end
2'b10:
begin
an<=3'b100;
data<=result[11:8];
end
endcase
end
seven myseven(.data(data),.out(out));
endmodule
top.v(不用数码管显示)
module top(
input clk,
input rst,
input [3:0] n,
output [11:0] result
);
wire[31:0] temp;
fib myfib(.clk(clk),.rst(rst),.n(n),.result(temp));
assign result=temp[11:0];
endmodule
top.v(用数码管显示)
module top(
input clk,
input rst,
input [3:0] n,
output [2:0] an,
output [6:0] out
);
wire[31:0] temp;
fib myfib(.clk(clk),.rst(rst),.n(n),.result(temp));
show myshow(.clk(clk),.rst(rst),.result(temp[11:0]),.an(an),.out(out));
endmodule
四、仿真程序
mysim.v(不用数码管显示)
module mysim(
);
reg clk=1'b0;
reg rst=1'b1;
reg[3:0] n=4'b1110;
wire [11:0] result;
always
#10 clk=~clk;
initial
#11 rst=1'b0;
top mytop(.clk(clk),.rst(rst),.n(n),.result(result));
endmodule
mysim.v(用数码管显示)
module mysim(
);
reg clk=1'b0;
reg rst=1'b1;
reg[3:0] n=4'b1110;
wire[2:0] an;
wire[6:0] out;
always
#10 clk=~clk;
initial
#11 rst=1'b0;
top mytop(.clk(clk),.rst(rst),.n(n),.an(an),.out(out));
endmodule
五、仿真结果
不用数码管显示:
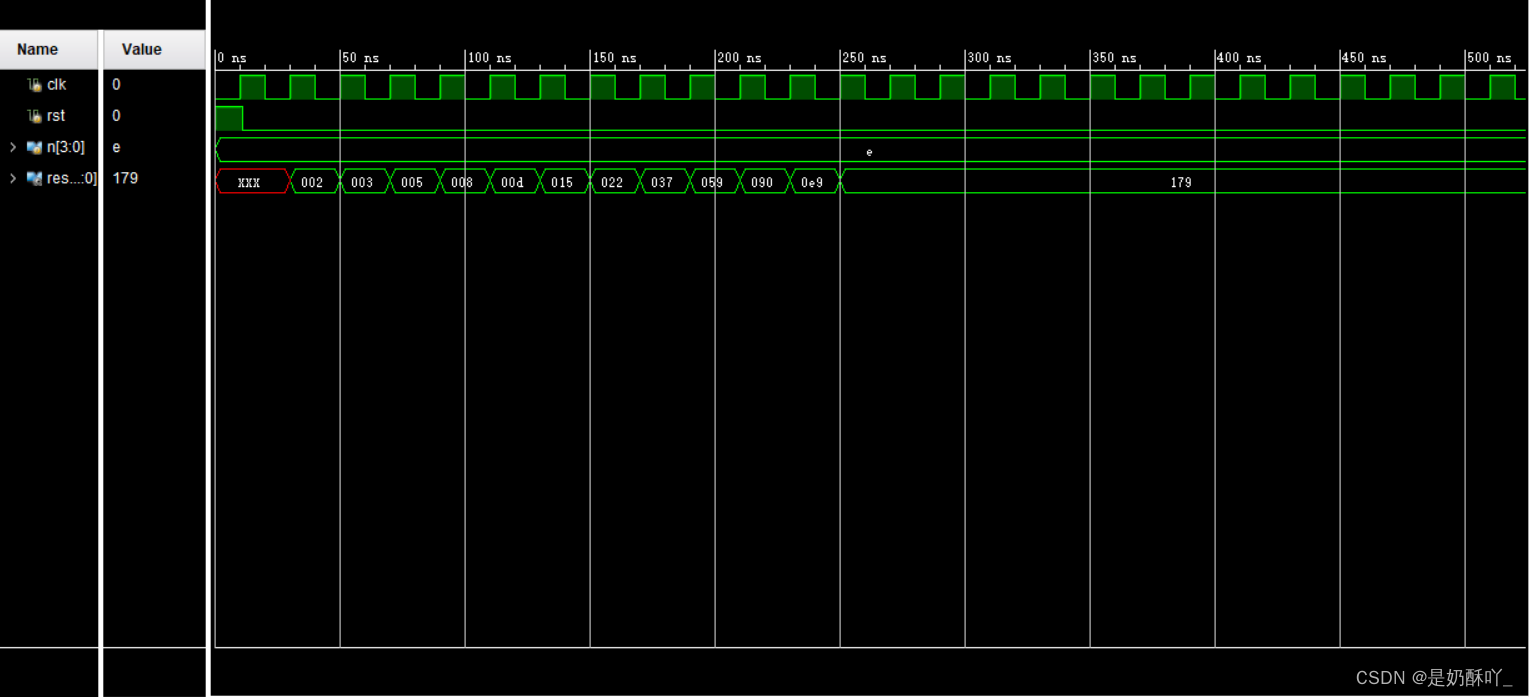
用数码管显示:
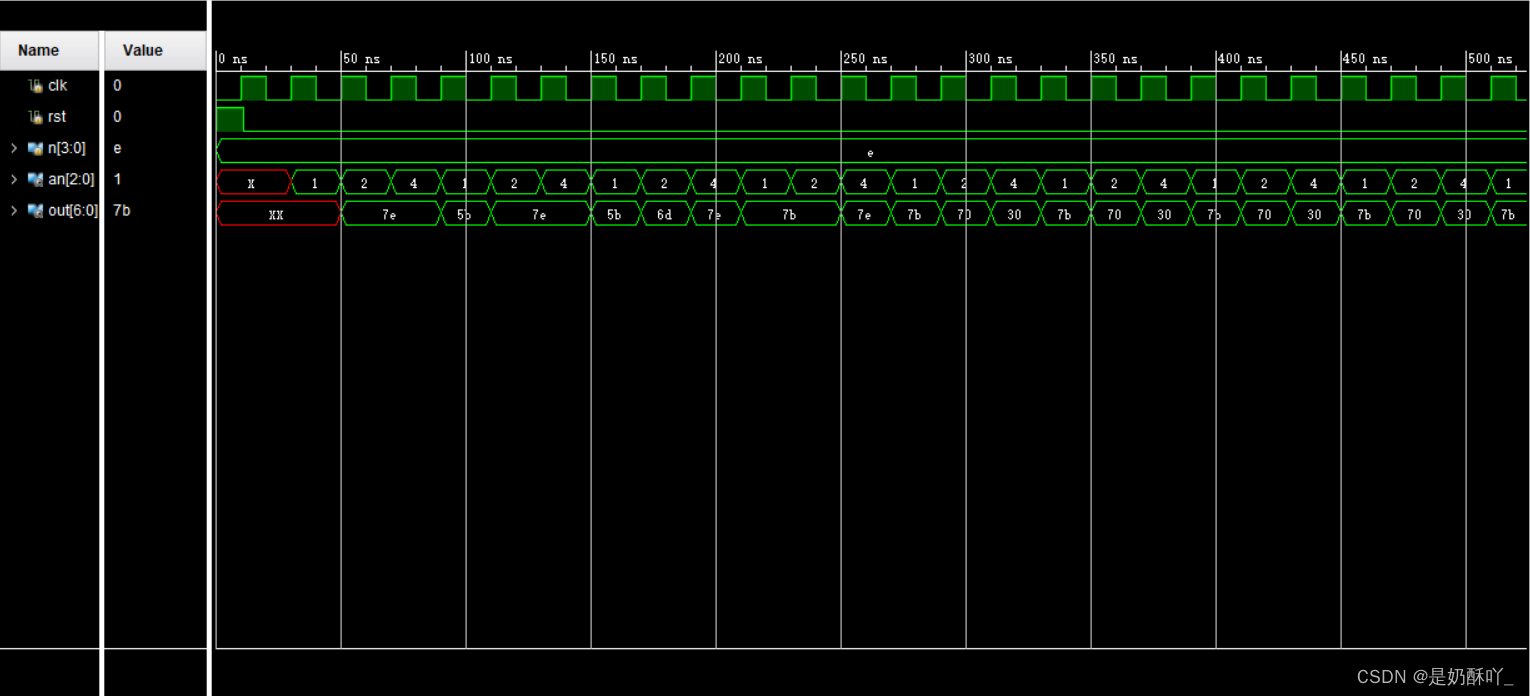
六、实验结果
用数码管显示