ShardingSphere
- 介绍
- ShardingSphere-JDBC
- Sharding-Sphere-Proxy
- ShardingSphere-Sidecar
- 混合架构
- 运行模式
- DistSQL
- 可拔插架构
- ShardingSphere的发展路线
- 主从复制
- ShardingSphere-JDBC功能
- SQL解析
- SQL支持程度
- SQL稳定支持
- SQL实验性支持
- MySQL不支持SQL清单
- 分页
- 数据分片
- 垂直分片
- 水平分片
- 问题
- 核心
- 表
- 数据节点
- 分片
- 行表达式
- 分布式主键
- 强制路由分片
- 分布式事务
- 本地事务
- XA事务
- 柔性事务
- 读写分离
- 读写分离带来的问题
- 使用规范
- 数据加密
- 影子库
- ShardingSphere-JDBC使用
- Java API
- 使用步骤
- 模式配置
- 数据源配置
- 规则配置
- 分片策略配置
- 标准分片策略配置
- 复合分片策略配置
- Hint分片策略配置
- 不分片策略配置
- 内置分片算法列表
- 分布式主键生成配置
- 内置分布式主键算法列表
- 读写分离配置
- 读写数据源配置
- 内置负载均衡算法列表
- 高可用
- 数据源配置
- 监听心跳配置
- 数据库发现类型配置
- 数据加密
- 加密表规则配置
- 加密列规则配置
- 加解密算法配置
- 内置加密算法列表
- 影子库
- 影子数据源配置
- 影子表配置
- 影子算法配置
- SQL解析
- 本地缓存配置
- 混合配置
- 单表拆分使用步骤
- Spring Boot 配置
- 模式配置
- 内存模式
- 单机模式
- 集群模式
- 数据源配置
- 本地数据源配置
- JNDI数据源配置
- 数据分片配置
- 读写分离配置
- 高可用配置
- 数据加密配置
- 影子库配置
- SQL解析配置
- 配置案例
- 属性配置
- 出现的问题
介绍
官网:https://shardingsphere.apache.org/index_zh.html
注册网站:http://shardingsphere.io
下载地址:https://shardingsphere.apache.org/document/current/cn/downloads/
pdf文档地址:https://shardingsphere.apache.org/pdf/shardingsphere_docs_cn.pdf
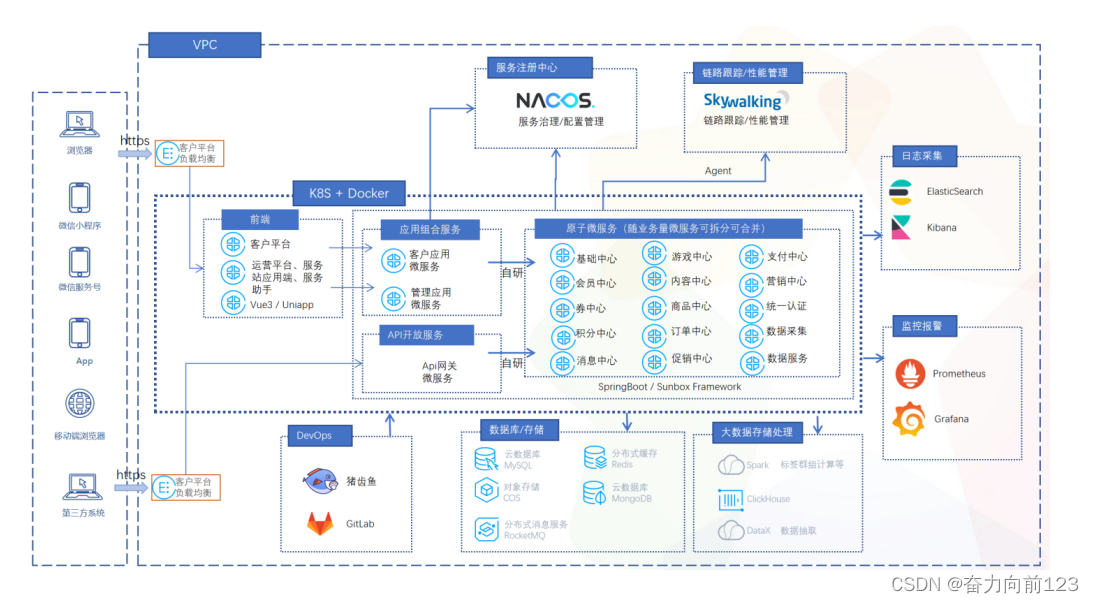
Apache ShardingSphere是一套开源的分布式数据库增强计算引擎,其通过可插拔架构构建基于数据库之上的生态系统,可以将任意数据库转换为分布式数据库,实现包括数据分片、弹性伸缩、加密脱敏等功能为代表的增强能力。
!! 表示实例化该类
! 表示自定义别名
- 表示可以包含一个或多个
[] 表示数组,可以与减号相互替换使用
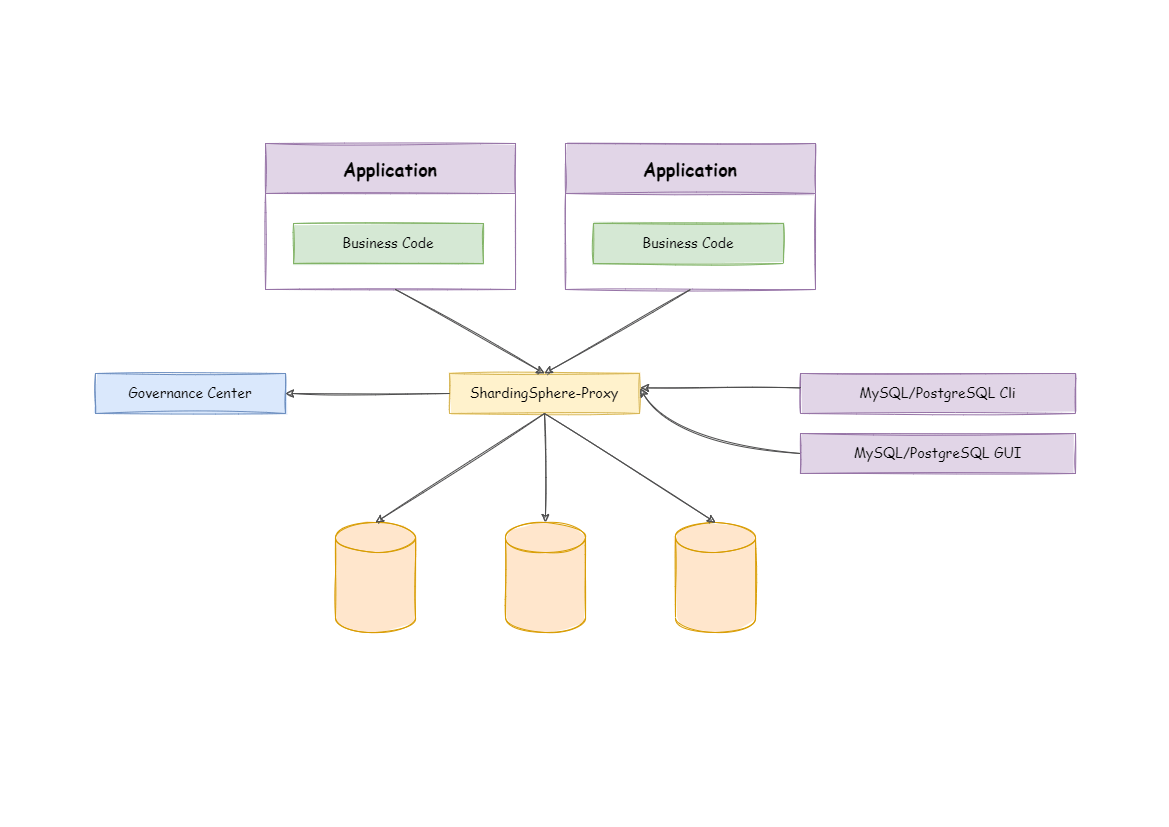
Apache ShardingSphere由JDBC、Proxy和Sidecar(规划中)这3款既能够独立部署,又支持混合部署配合使用的产品组成。 它们均提供标准化的基于数据库作为存储节点的增量功能,可适用于如Java同构、异构语言、云原生等各种多样化的应用场景。
关系型数据库当今依然占有巨大市场份额,是企业核心系统的基石,未来也难于撼动,我们更加注重在原有基础上提供增量,而非颠覆。
Apache ShardingSphere由ShardingSphere-JDBC和ShardingSphere-Proxy这2款既能够独立部署,又支持混合部署配合使用的产品组成。它们均提供标准化的基于数据库作为存储节点的增量功能,可适用于如Java同构、异构语言、云原生等各种多样化的应用场景。
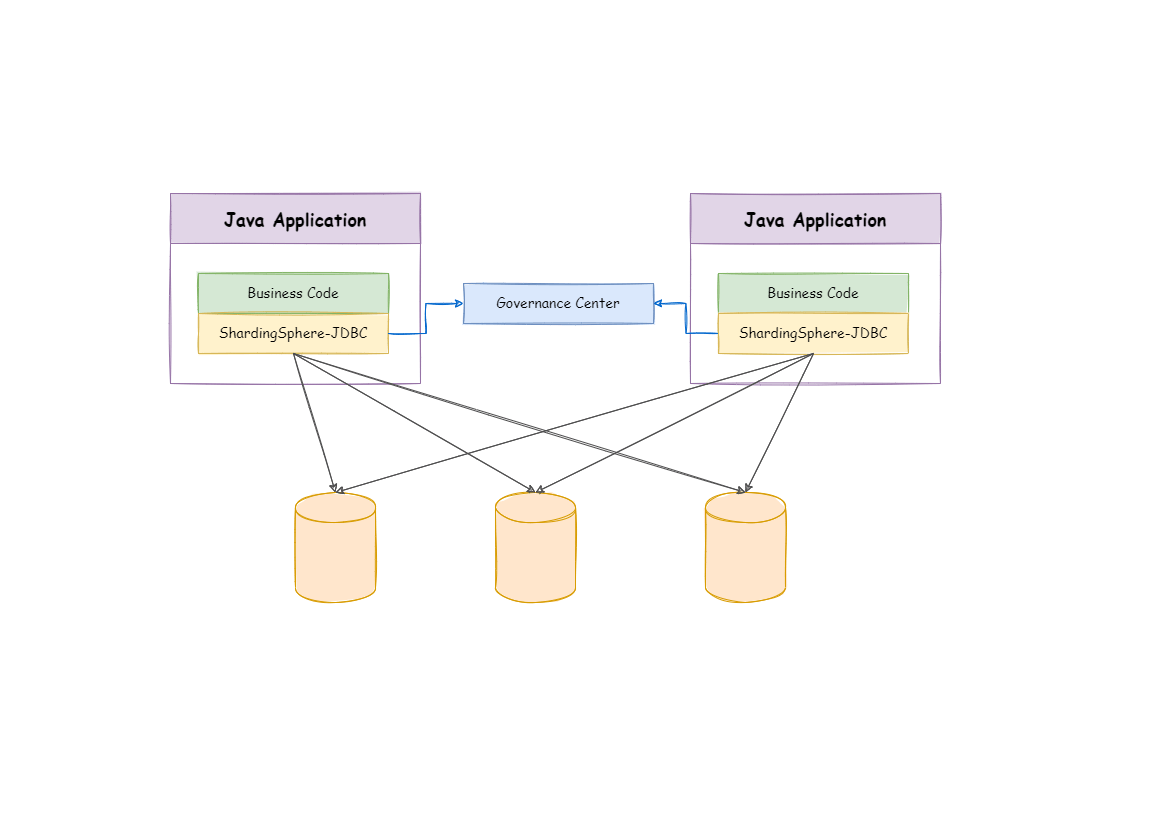
ShardingSphere-JDBC
ShardingSphere-JDBC
定位为轻量级Java框架,在Java的JDBC层提供的额外服务。它使用客户端直连数据库,以jar包形式提供服务,无需额外部署和依赖,可理解为增强版的JDBC驱动,完全兼容JDBC和各种ORM框架。
- 适用于任何基于JDBC的ORM框架,如:JPA, Hibernate, Mybatis, Spring JDBC Template或直接使用 JDBC。
- 支持任何第三方的数据库连接池,如:DBCP, C3P0, BoneCP, HikariCP 等。
- 支持任意实现JDBC规范的数据库,目前支持MySQL,PostgreSQL,Oracle,SQLServer以及任何可使用JDBC访问的数据库。
Sharding-Sphere-Proxy
ShardingSphere-Proxy
定位为透明化的数据库代理端,提供封装了数据库二进制协议的服务端版本,用于完成对异构语言的支持。目前提供MySQL和PostgreSQL(兼容openGauss等基于PostgreSQL的数据库)版本,它可以使用任何兼容MySQL/PostgreSQL协议的访问客户端(如:MySQL Command Client, MySQL Workbench,Navicat等)操作数据,对DBA更加友好。
- 向应用程序完全透明,可直接当做 MySQL/PostgreSQL 使用。
- 适用于任何兼容MySQL/PostgreSQL协议的的客户端。
ShardingSphere-Sidecar
ShardingSphere-Sidecar
定位为Kubernetes(K8S)的云原生数据库代理,以Sidecar的形式代理所有对数据库的访问。通过无中心、零侵入的方案提供与数据库交互的啮合层,即Database Mesh,又可称数据库网格。
Database Mesh的关注重点在于如何将分布式的数据访问应用与数据库有机串联起来,它更加关注的是交互,是将杂乱无章的应用与数据库之间的交互进行有效地梳理。使用Database Mesh,访问数据库的应用和数据库终将形成一个巨大的网格体系,应用和数据库只需在网格体系中对号入座即可,它们都是被啮合层所治理的对象。

三者对比
| ShardingSphere-JDBC | ShardingSphere-Proxy | ShardingSphere-Sidecar | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 数据库 | 任意 | MySQL/PostgreSQL | MySQL/PostgreSQL |
| 连接消耗数 | 高 | 低 | 高 |
| 异构语言 | 仅Java | 任意 | 任意 |
| 性能 | 损耗低 | 损耗略高 | 损耗低 |
| 无中心化 | 是 | 否 | 是 |
| 静态入口 | 无 | 有 | 无 |
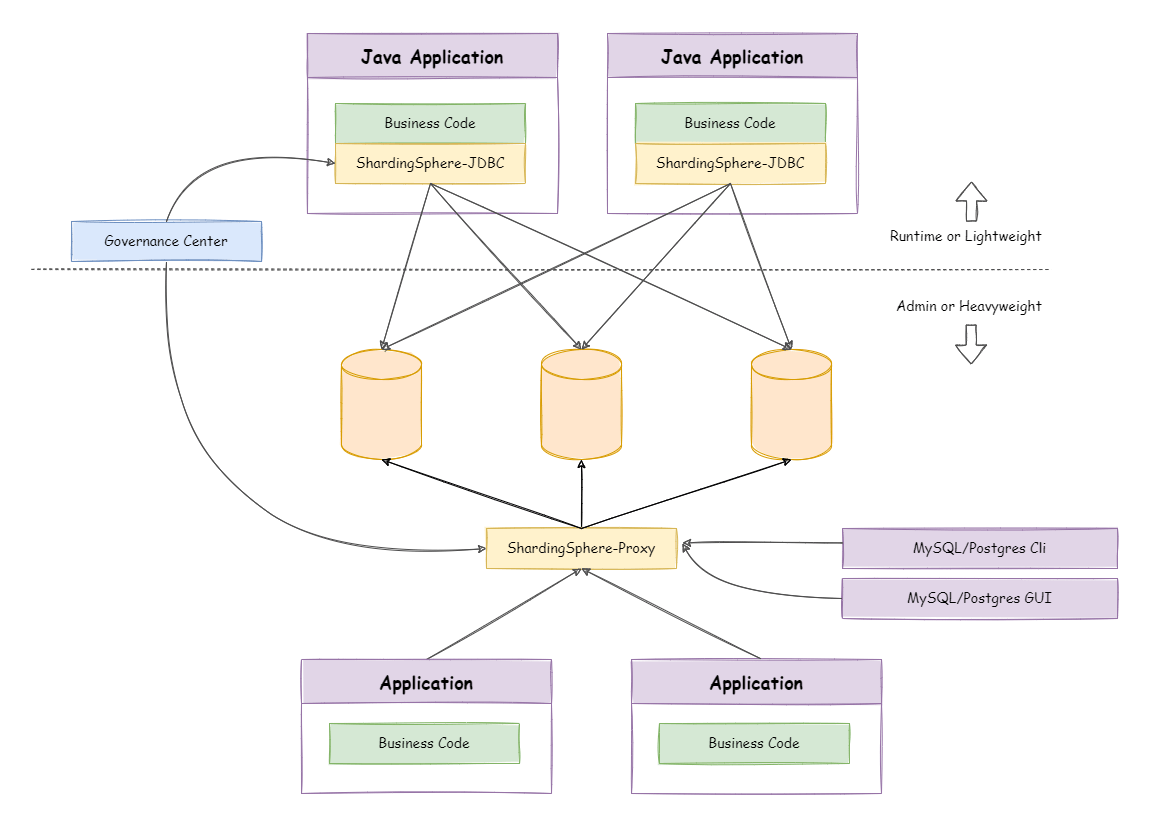
混合架构
ShardingSphere-JDBC采用无中心化架构,与应用程序共享资源,适用于Java开发的高性能的轻量级OLTP应用。
ShardingSphere-Proxy提供静态入口以及异构语言的支持,独立于应用程序部署,适用于OLAP应用以及对分片数据库进行管理和运维的场景。
OLTP:联机事务处理过程,也称为面向交易的处理过程,其基本特征是前台接收的用户数据可以立即传送到计算中心进行处理,并在很短的时间内给出处理结果,是对用户操作快速响应的方式之一。
OLAP:联机分析处理是一种软件技术,它使分析人员能够迅速、一致、交互地从各个方面观察信息,以达到深入理解数据的目的。它具有FASMI(Fast Analysis of Shared Multidimensional Information),即共享多维信息的快速分析的特征。其中F是快速性(Fast),指系统能在数秒内对用户的多数分析要求做出反应;A是可分析性(Analysis),指用户无需编程就可以定义新的专门计算,将其作为分析的一部分,并以用户所希望的方式给出报告;M是多维性(Multi dimensional),指提供对数据分析的多维视图和分析;I是信息性(Information),指能及时获得信息,并且管理大容量信息。
Apache ShardingSphere是多接入端共同组成的生态圈。通过混合使用ShardingSphere-JDBC和ShardingSphere-Proxy,并采用同一注册中心统一配置分片策略,能够灵活的搭建适用于各种场景的应用系统,使得架构师更加自由地调整适合于当前业务的最佳系统架构。
| 解决方案/功能 | 分布式数据库 | 数据安全 | 数据库网关 | 全链路压测 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 数据分片 | 数据加密 | 异构数据库支持 | 影子库 | |
| 读写分离 | 行级权限(TODO) | SQL方言转换(TODO) | 可观测性 | |
| 分布式事务 | SQL审计(TODO) | |||
| 弹性压缩 | SQL防火墙(TODO) | |||
| 高可用 |
运行模式
内存模式
初始化配置或执行SQL等造成的元数据结果变更的操作,仅在当前进程中生效。适用于集成测试的环境启动,方便开发人员在整合功能测试中集成 Apache ShardingSphere而无需清理运行痕迹。
单机模式
能够将数据源和规则等元数据信息持久化,但无法将元数据同步至多个Apache ShardingSphere实例,无法在集群环境中相互感知。通过某一实例更新元数据之后,会导致其他实例由于获取不到最新的元数据而产生不一致的错误。 适用于工程师在本地搭建Apache ShardingSphere环境。
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| path | String | 元数据存储路径 | .shardingsphere |
集群模式
提供了多个 Apache ShardingSphere 实例之间的元数据共享和分布式场景下状态协调的能力。 在真实部署上线的生产环境,必须使用集群模式。它能够提供计算能力水平扩展和高可用等分布式系统必备的能力。 集群环境需要通过独立部署的注册中心来存储元数据和协调节点状态。
Zookeeper持久化
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| retryIntervalMilliseconds | int | 重试间隔毫秒数 | 500 |
| maxRetries | int | 客户端连接最大重试次数 | 3 |
| timeToLiveSeconds | int | 临时数据失效的秒数 | 60 |
| operationTimeoutMilliseconds | int | 客户端操作超时的毫秒数 | 500 |
| digest | String | 登陆认证密码 |
Etcd持久化
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| timeToLiveSeconds | long | 临时数据失效的秒数 | 30 |
| connectionTimeout | long | 连接超时秒数 | 30 |
DistSQL
DistSQL(Distributed SQL分布式SQL)是Apache ShardingSphere特有的操作语言。它与标准SQL的使用方式完全一致,用于提供增量功能的SQL级别操作能力。
DistSQL让用户可以像操作数据库一样操作Apache ShardingSphere,使其从面向开发人员的框架和中间件转变为面向运维人员的数据库产品。
打破中间件和数据库之间的界限,让开发者像使用数据库一样使用Apache ShardingSphere,是DistSQL的设计目标。
-
DistSQL 细分为 RDL、RQL 和 RAL 三种类型。
- RDL(Resource & Rule Definition Language)负责资源和规则的创建、修改和删除
- RQL(Resource & Rule Query Language)负责资源和规则的查询和展现
- RAL(Resource & Rule Administration Language)负责 Hint、事务类型切换、分片执行计划查询等管理功能
-
注意:DistSQL只能用于ShardingSphere-Proxy,ShardingSphere-JDBC暂不提供。
可拔插架构
3层结构:L1内核层、L2功能层、L3生态层
L1内核层
是数据库基本能力的抽象,其所有组件均必须存在,但具体实现方式可通过可插拔的方式更换。主要包括查询优化器、分布式事务引擎、分布式执行引擎、权限引擎和调度引擎等。
L2功能层
用于提供增量能力,其所有组件均是可选的,可以包含零至多个组件。组件之间完全隔离,互无感知,多组件可通过叠加的方式相互配合使用。主要包括数据分片、读写分离、数据库高可用、数据加密、影子库等。用户自定义功能可完全面向Apache ShardingSphere定义的顶层接口进行定制化扩展,而无需改动内核代码。
L3生态层
用于对接和融入现有数据库生态,包括数据库协议、SQL解析器和存储适配器,分别对应于Apache ShardingSphere以数据库协议提供服务的方式、SQL方言操作数据的方式以及对接存储节点的数据库类型。
ShardingSphere的发展路线
5.x版本,面向插件的微内核,所有的在这三层都是可拔插的,更多的功能被添加
主从复制
ShardingSphere-JDBC功能
maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-jdbc-core-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${latest.release.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.shardingsphere/shardingsphere-jdbc-core-spring-boot-starter -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-jdbc-core-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>5.1.2</version>
</dependency>
application.ymal
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: ds_0, ds_1
ds_0:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo_ds_0?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password:
ds_1:
type: com.zaxxer.hikari.HikariDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
jdbcUrl: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/demo_ds_1?serverTimezone=UTC&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password:
rules:
sharding:
tables:
...
SQL解析
SQL是使用者与数据库交流的标准语言。SQL解析引擎负责将SQL字符串解析为抽象语法树,供Apache ShardingSphere理解并实现其增量功能。
目前支持MySQL, PostgreSQL, SQLServer, Oracle, openGauss以及符合SQL92规范的SQL方言。由于SQL语法的复杂性,目前仍然存在少量不支持的 SQL。
SQL支持程度
兼容全部常用的路由至单数据节点的SQL;路由至多数据节点的SQL由于场景复杂,分为稳定支持、实验性支持和不支持这三种情况。
SQL稳定支持
全面支持DML、DDL、DCL、TCL和常用DAL。支持分页、去重、排序、分组、聚合、表关联等复杂查询。支持PostgreSQL和openGauss数据库 SCHEMA DDL和DML语句。
运算表达式保护分片键
SELECT * FROM t_order WHERE to_date(create_time, 'yyyy-mm-dd') = '2019-01-01';
假设create_time为分片键,无法通过SQL字面提取用于分片的值,将导致全路由。
会导致慢SQL
| SQL示例 | 必要条件 |
|---|---|
| SELECT * FROM (SELECT * FROM tbl_name WHERE col1 = ?) o WHERE o.col1 = ? | 子查询和外层查询在同一分片后的数据节点 |
| INSERT INTO tbl_name (col1, col2, …) SELECT col1, col2, … FROM tbl_name WHERE col3 = ? | INSERT 表和 SELECT 表相同表或绑定表 |
| REPLACE INTO tbl_name (col1, col2, …) SELECT col1, col2, … FROM tbl_name WHERE col3 = ? | REPLACE 表和 SELECT 表相同表或绑定表 |
SQL实验性支持
实验性支持特指使用Federation执行引擎提供支持。该引擎处于快速开发中,用户虽基本可用,但仍需大量优化,是实验性产品。
| SQL示例 | 必要条件 |
|---|---|
| SELECT * FROM (SELECT * FROM tbl_name WHERE col1 = ?) o WHERE o.col1 = ? | 子查询和外层查询不在同一分片后的数据节点 |
| 慢 SQL | 原因 |
|---|---|
| SELECT * FROM tbl_name WHERE to_date(create_time, ‘yyyy-mm-dd’) = ? | 分片键在运算表达式中,导致全路由 |
| 不支持的 SQL | 原因 | 解决方案 |
|---|---|---|
| INSERT INTO tbl_name (col1, col2, …) SELECT * FROM tbl_name WHERE col3 = ? | SELECT 子句不支持 * 和内置分布式主键生成器 | 无 |
| REPLACE INTO tbl_name (col1, col2, …) SELECT * FROM tbl_name WHERE col3 = ? | SELECT 子句不支持 * 和内置分布式主键生成器 | 无 |
| SELECT MAX(tbl_name.col1) FROM tbl_name | 查询列是函数表达式时,查询列前不能使用表名 | 使用表别名 |
MySQL不支持SQL清单
MySQL不支持清单
| SQL |
|---|
| CLONE LOCAL DATA DIRECTORY = ‘clone_dir’ |
| INSTALL COMPONENT ‘file://component1’, ‘file://component2’ |
| UNINSTALL COMPONENT ‘file://component1’, ‘file://component2’ |
| REPAIR TABLE t_order |
| OPTIMIZE TABLE t_order |
| CHECKSUM TABLE t_order |
| CHECK TABLE t_order |
| SET RESOURCE GROUP group_name |
| DROP RESOURCE GROUP group_name |
| CREATE RESOURCE GROUP group_name TYPE = SYSTEM |
| ALTER RESOURCE GROUP rg1 VCPU = 0-63 |
用户和角色
| SQL |
|---|
| CREATE USER ‘finley’@‘localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘password’ |
| ALTER USER ‘finley’@‘localhost’ IDENTIFIED BY ‘new_password’ |
| DROP USER ‘finley’@‘localhost’; |
| CREATE ROLE ‘app_read’ |
| DROP ROLE ‘app_read’ |
| SHOW CREATE USER finley |
| SET PASSWORD = ‘auth_string’ |
| SET ROLE DEFAULT; |
授权
| SQL |
|---|
| GRANT ALL ON db1.* TO ‘jeffrey’@‘localhost’ |
| GRANT SELECT ON world.* TO ‘role3’; |
| GRANT ‘role1’, ‘role2’ TO ‘user1’@‘localhost’ |
| REVOKE INSERT ON . FROM ‘jeffrey’@‘localhost’ |
| REVOKE ‘role1’, ‘role2’ FROM ‘user1’@‘localhost’ |
| REVOKE ALL PRIVILEGES, GRANT OPTION FROM user_or_role |
| SHOW GRANTS FOR ‘jeffrey’@‘localhost’ |
| SHOW GRANTS FOR CURRENT_USER |
| FLUSH PRIVILEGES |
分页
查询偏移量过大的分页会导致数据库获取数据性能低下,以MySQL为例:
SELECT * FROM t_order ORDER BY id LIMIT 1_000_000, 10
这句SQL会使得MySQL在无法利用索引的情况下跳过1000000条记录后,再获取10条记录,其性能可想而知。而在分库分表的情况下(假设分为2个库),为了保证数据的正确性,SQL会改写为:
SELECT * FROM t_order ORDER BY id LIMIT 0, 1000010
即将偏移量前的记录全部取出,并仅获取排序后的最后10条记录。这会在数据库本身就执行很慢的情况下,进一步加剧性能瓶颈。因为原SQL仅需要传输10条记录至客户端,而改写之后的SQL则会传输1000010*2的记录至客户端。(这里为什么是*2的记录)。
ShardingSphere的优化
ShardingSphere进行了2个方面的优化。
首先,采用流式处理+归并排序的方式来避免内存的过量占用。由于SQL改写不可避免的占用了额外的带宽,但并不会导致内存暴涨。与直觉不同,大多数人认为ShardingSphere会将1000010*2记录全部加载至内存,进而占用大量内存而导致内存溢出。但由于每个结果集的记录是有序的,因此 ShardingSphere每次比较仅获取各个分片的当前结果集记录,驻留在内存中的记录仅为当前路由到的分片的结果集的当前游标指向而已。按归并思想合并m个长度为n的已排序数组,时间复杂度为 O(mn(log m)),一般分片数量m都较小,可以认为时间复杂度为 O(n),性能损耗很小。
其次,ShardingSphere对仅落至单分片的查询进行进一步优化。落至单分片查询的请求并不需要改写SQL也可以保证记录的正确性,因此在此种情况下,ShardingSphere并未进行SQL改写,从而达到节省带宽的目的。
数据分片
出现的原因
传统的将数据集中存储至单一节点的解决方案,在性能、可用性和运维成本这三方面已经难于满足海量数据的场景。
从性能方面来说,由于关系型数据库大多采用B+树类型的索引,在数据量超过阈值的情况下,索引深度的增加也将使得磁盘访问的IO次数增加,进而导致查询性能的下降; 同时,高并发访问请求也使得集中式数据库成为系统的最大瓶颈。
从可用性的方面来讲,服务化的无状态性,能够达到较小成本的随意扩容,这必然导致系统的最终压力都落在数据库之上。 而单一的数据节点,或者简单的主从架构,已经越来越难以承担。数据库的可用性,已成为整个系统的关键。
从运维成本方面考虑,当一个数据库实例中的数据达到阈值以上,对于DBA的运维压力就会增大。数据备份和恢复的时间成本都将随着数据量的大小而愈发不可控。一般来讲,单一数据库实例的数据的阈值在1TB之内,是比较合理的范围。
在传统的关系型数据库无法满足互联网场景需要的情况下,将数据存储至原生支持分布式的NoSQL的尝试越来越多。但NoSQL对SQL的不兼容性以及生态圈的不完善,使得它们在与关系型数据库的博弈中始终无法完成致命一击,而关系型数据库的地位却依然不可撼动。
数据分片指按照某个维度将存放在单一数据库中的数据分散地存放至多个数据库或表中以达到提升性能瓶颈以及可用性的效果。数据分片的有效手段是对关系型数据库进行分库和分表。分库和分表均可以有效的避免由数据量超过可承受阈值而产生的查询瓶颈。除此之外,分库还能够用于有效的分散对数据库单点的访问量;分表虽然无法缓解数据库压力,但却能够提供尽量将分布式事务转化为本地事务的可能,一旦涉及到跨库的更新操作,分布式事务往往会使问题变得复杂。使用多主多从的分片方式,可以有效的避免数据单点,从而提升数据架构的可用性。
通过分库和分表进行数据的拆分来使得各个表的数据量保持在阈值以下,以及对流量进行疏导应对高访问量,是应对高并发和海量数据系统的有效手段。数据分片的拆分方式又分为垂直分片和水平分片。
分库还能够用于有效的分散对数据库单点的访问量,分表够提供尽量将分布式事务转化为本地事务的可能
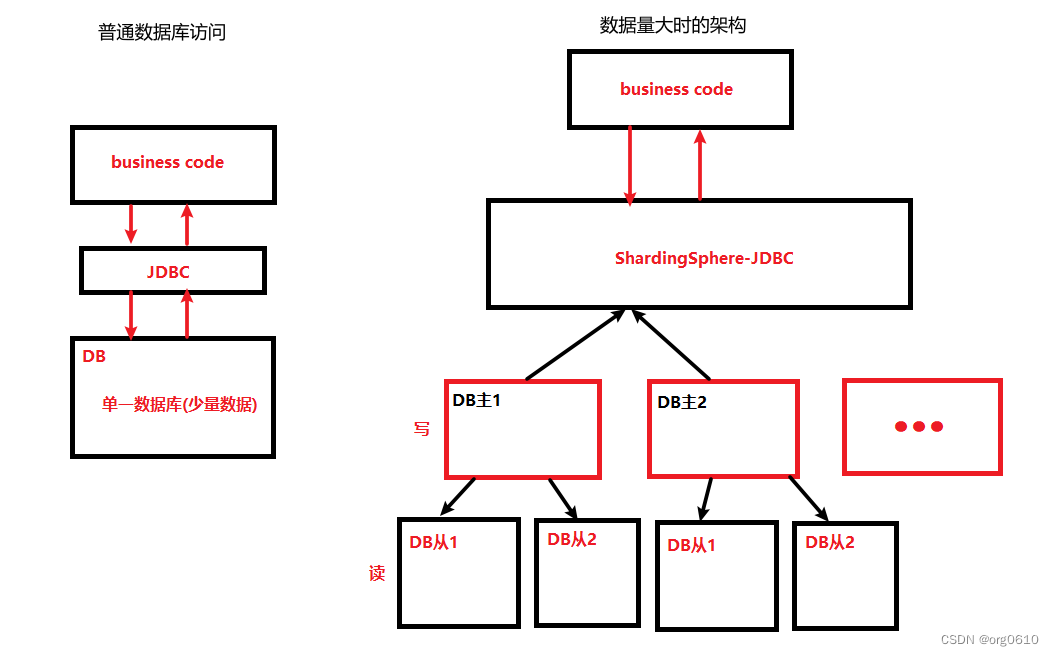
使用ShardingSphere-JDBC,可以将单一数据库中的数据按业务分至多个数据(垂直拆分),在根据表中数据量的大小考虑是否需要将表进行水平拆分。
两个点需要会搭建。
1.搭建数据库集群
2.实现读写分离
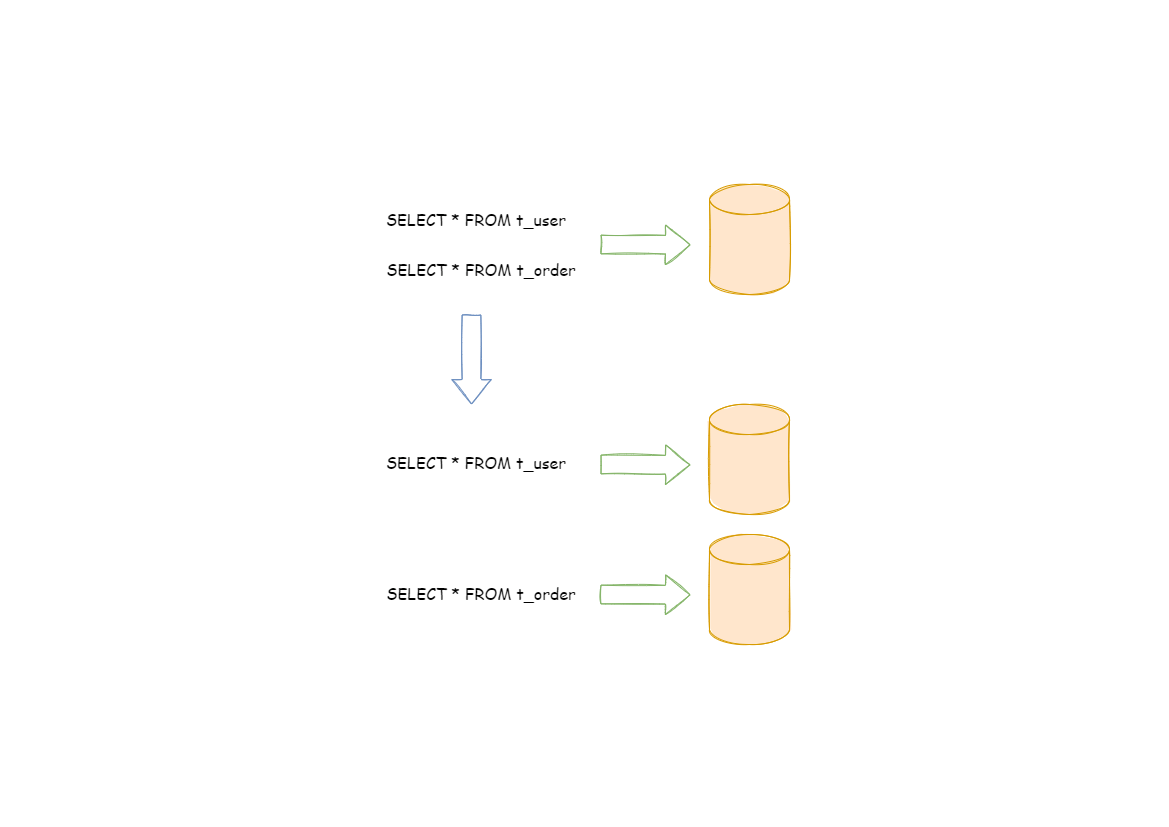
垂直分片
按照业务拆分的方式称为垂直分片,又称为纵向拆分,它的核心理念是专库专用。在拆分之前,一个数据库由多个数据表构成,每个表对应着不同的业务。而拆分之后,则是按照业务将表进行归类,分布到不同的数据库中,从而将压力分散至不同的数据库。下图展示了根据业务需要,将用户表和订单表垂直分片到不同的数据库的方案。(官网图)
水平分片
水平分片又称为横向拆分。相对于垂直分片,它不再将数据根据业务逻辑分类,而是通过某个字段(或某几个字段),根据某种规则将数据分散至多个库或表中,每个分片仅包含数据的一部分。 例如:根据主键分片,偶数主键的记录放入0库(或表),奇数主键的记录放入1库(或表)。
水平分片从理论上突破了单机数据量处理的瓶颈,并且扩展相对自由,是数据分片的标准解决方案。
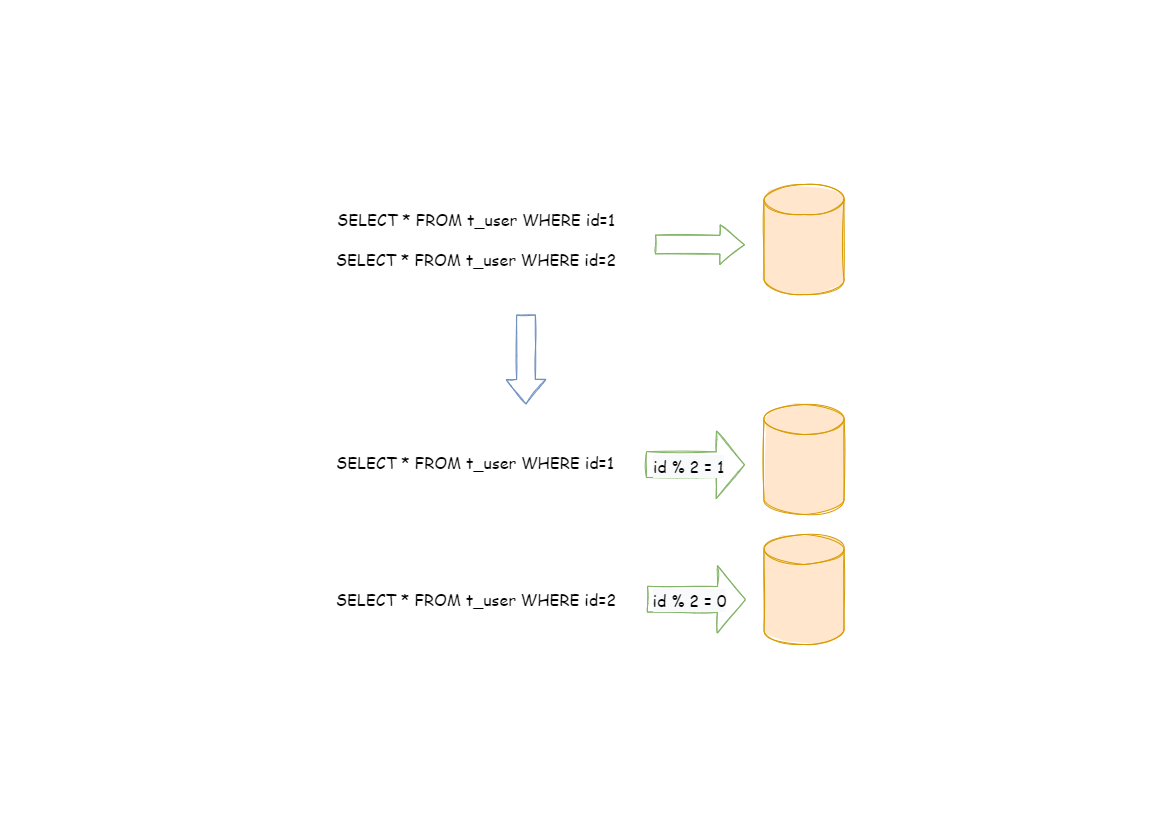
问题
虽然数据分片解决了性能、可用性以及单点备份恢复等问题,但分布式的架构在获得了收益的同时,也引入了新的问题。
1.对数据库的管理变得繁琐。
2.能够正确的运行在单节点数据库中的SQL,在分片之后的数据库中并不一定能够正确运行。
3.分布式事务,尽量使用同库不同表(本地事务)。基于XA的分布式事务由于在并发度高的场景中性能无法满足需要,并未被互联网巨头大规模使用,他们大多采用最终一致性的柔性事务代替强一致事务。
尽量透明化分库分表所带来的影响,让使用方尽量像使用一个数据库一样使用水平分片之后的数据库集群,是Apache ShardingSphere数据分片模块的主要设计目标。
核心
表
表
表是透明化数据分片的关键概念。Apache ShardingSphere通过提供多样化的表类型,适配不同场景下的数据分片需求。
逻辑表
相同结构的水平拆分数据库(表)的逻辑名称,是SQL中表的逻辑标识。例:订单数据根据主键尾数拆分为10张表,分别是t_order_0到t_order_9,他们的逻辑表名为t_order。
真实表
数据库中真实存在的表。在水平拆分的数据库中真实存在的物理表。即上个示例中的t_order_0到t_order_9。
绑定表
指分片规则一致的一组分片表。使用绑定表进行多表关联查询时,必须使用分片键进行关联,否则会出现笛卡尔积关联或跨库关联,从而影响查询效率。例如:t_order表和t_order_item表,均按照order_id分片,并且使用order_id进行关联,则此两张表互为绑定表关系。绑定表之间的多表关联查询不会出现笛卡尔积关联,关联查询效率将大大提升。举例说明,如果SQL为:
select i.* from t_order o join t_order_item i on i.order_id = o.order_id where ...
在不配置绑定表关系时,假设分片键order_id将数值10路由至第0片,将数值11路由至第1片,那么路由后的SQL应该为4条,它们呈现为笛卡尔积
select i.* from t_order_0 o join t_order_item_0 i on i.order_id = o.order_id where ...
select i.* from t_order_0 o join t_order_item_1 i on i.order_id = o.order_id where ...
select i.* from t_order_1 o join t_order_item_0 i on i.order_id = o.order_id where ...
select i.* from t_order_1 o join t_order_item_1 i on i.order_id = o.order_id where ...
在配置绑定表关系,并且使用order_id进行关联后,路由的SQL应该为2条:
select i.* from t_order_0 o join t_order_item_0 i on i.order_id = o.order_id where ...
select i.* from t_order_1 o join t_order_item_1 i on i.order_id = o.order_id where ...
其中t_order表由于指定了分片条件,ShardingSphere将会以它作为整个绑定表的主表。所有路由计算将会只使用主表的策略,那么 t_order_item表的分片计算将会使用t_order的条件。
广播表
指所有的分片数据源中都存在的表,表结构及其数据在每个数据库中均完全一致。适用于数据量不大且需要与海量数据的表进行关联查询的场景,例如:字典表。
单表
指所有的分片数据源中仅唯一存在的表。适用于数据量不大且无需分片的表。
数据节点
数据节点
数据节点是数据分片的最小单元,由数据源名称和真实表组成。例:ds_0.t_order_0。
逻辑表与真实表的映射关系,可分为均匀分布和自定义分布两种形式。
均匀分布
指数据表在每个数据源内呈现均匀分布的态势, 例如:
db0
├── t_order0
└── t_order1
db1
├── t_order0
└── t_order1
数据节点的配置如下:
db0.t_order0, db0.t_order1, db1.t_order0, db1.t_order1
行表达式写法:
db$->{0..1}.t_order$->{0..1}
自定义分布
指数据表呈现有特定规则的分布,例如:
db0
├── t_order0
└── t_order1
db1
├── t_order2
├── t_order3
└── t_order4
数据节点的配置如下:
db0.t_order0, db0.t_order1, db1.t_order2, db1.t_order3, db1.t_order4
行表达式写法:
db0.t_order${0..1}, db1.t_order${2..4}
分片
分片键
用于将数据库(表)水平拆分的数据库字段。例:将订单表中的订单主键的尾数取模分片,则订单主键为分片字段。SQL中如果无分片字段,将执行全路由,性能较差。除了对单分片字段的支持,Apache ShardingSphere也支持根据多个字段进行分片。
分片算法
用于将数据分片的算法,支持=、>=、<=、>、<、BETWEEN和IN进行分片。分片算法可由开发者自行实现,也可使用Apache ShardingSphere 内置的分片算法语法糖,灵活度非常高。
对于只有一个分片键的使用=和IN进行分片的 SQL,可以使用行表达式代替编码方式配置。
行表达式内部的表达式本质上是一段Groovy代码,可以根据分片键进行计算的方式,返回相应的真实数据源或真实表名称。
ds${id % 10} 表示id为0的路由到后缀为0的数据源,id为1的路由到后缀为1的数据源
自动化分片算法
分片算法语法糖,用于便捷的托管所有数据节点,使用者无需关注真实表的物理分布。包括取模、哈希、范围、时间等常用分片算法的实现。
自定义分片算法
提供接口让应用开发者自行实现与业务实现紧密相关的分片算法,并允许使用者自行管理真实表的物理分布。自定义分片算法又分为:
1.标准分片算法
2.复合分片算法
3.Hint分片算法
- 标准分片算法
用于处理使用单一键作为分片键的=、IN、BETWEEN AND、>、<、>=、<=进行分片的场景。
- 复合分片算法
用于处理使用多键作为分片键进行分片的场景,包含多个分片键的逻辑较复杂,需要应用开发者自行处理其中的复杂度。
- Hint分片算法
用于处理使用Hint行分片的场景。
分片策略
包含分片键和分片算法,由于分片算法的独立性,将其独立抽离。真正可用于分片操作的是分片键+分片算法,也就是分片策略。
强制分片路由
对于分片字段并非由SQL而是其他外置条件决定的场景,可使用SQL Hint注入分片值。例:按照员工登录主键分库,而数据库中并无此字段。SQL Hint支持通过Java API和SQL注释(待实现)两种方式使用。详情请参见强制分片路由。
行表达式
语法介绍
行表达式的使用非常直观,只需要在配置中使用${ expression }或$->{ expression }标识行表达式即可。目前支持数据节点和分片算法这两个部分的配置。行表达式的内容使用的是Groovy的语法,Groovy能够支持的所有操作,行表达式均能够支持。例如:
${begin..end} 表示范围区间begin到end 如${1..4}
${[unit1, unit2, unit_x]} 表示枚举值
行表达式中如果出现连续多个${ expression } 或$->{ expression }表达式,整个表达式最终的结果将会根据每个子表达式的结果进行笛卡尔积组合。
${['online', 'offline']}_table${1..3} 解析为:
online_table1 online_table2 online_table3 offline_table1 offline_table2 offline_table3
db$->{0..1}.t_order_0$->{0..9}, db$->{0..1}.t_order_$->{10..20} 表示db0.t_order_00- t_order_20
分布式主键
解决不同实际表之间主键自增一致的问题。
Apache ShardingSphere不仅提供了内置的分布式主键生成器,例如UUID、SNOWFLAKE、还抽离出分布式主键生成器的接口,方便用户自行实现自定义的自增主键生成器。
UUID
采用UUID.randomUUID() 的方式产生分布式主键。是36位的字符串
NanoID
生成长度为21的字符串分布式主键。
SNOWFLAKE
在分片规则配置模块可配置每个表的主键生成策略,默认使用雪花算法(snowflake)生成64bit的长整型数据。8ge'zi
雪花算法是由 Twitter 公布的分布式主键生成算法,它能够保证不同进程主键的不重复性,以及相同进程主键的有序性。
雪花算法原理
在同一个进程中,它首先是通过时间位保证不重复,如果时间相同则是通过序列位保证。同时由于时间位是单调递增的,且各个服务器如果大体做了时间同步,那么生成的主键在分布式环境可以认为是总体有序的,这就保证了对索引字段的插入的高效性。例如MySQL的Innodb存储引擎的主键。
使用雪花算法生成的主键,二进制表示形式包含4部分,从高位到低位分表为:1bit符号位、41bit时间戳位、10bit工作进程位以及12bit序列号位。
1.符号位:恒为0
2.时间戳位:41位的时间戳可以容纳的毫秒数是2的41次幂,一年所使用的毫秒数是:365*24*60*60*1000。通过计算可知:69.73年
Apache ShardingSphere的雪花算法的时间纪元从2016年11月1日零点开始,可以使用到2086年,相信能满足绝大部分系统的要求。
3.工作进程位:该标志在Java进程内是唯一的,如果是分布式应用部署应保证每个工作进程的id是不同的。该值默认为0,可通过属性设置。
4.序列化位:该序列是用来在同一个毫秒内生成不同的ID。如果在这个毫秒内生成的数量超过4096(2的12次幂),那么生成器会等待到下个毫秒继续生成。
时钟回拨
服务器时钟回拨会导致产生重复序列,因此默认分布式主键生成器提供了一个最大容忍的时钟回拨毫秒数。如果时钟回拨的时间超过最大容忍的毫秒数阈值,则程序报错;如果在可容忍的范围内,默认分布式主键生成器会等待时钟同步到最后一次主键生成的时间后再继续工作。最大容忍的时钟回拨毫秒数的默认值为0,可通过属性设置。
强制路由分片
在一些应用场景中,分片条件并不存在于SQL,而存在于外部业务逻辑。 因此需要提供一种通过外部指定分片结果的方式,在 Apache ShardingSphere中叫做Hint。
实现机制
Apache ShardingSphere使用ThreadLocal管理分片键值。可以通过编程的方式向HintManager中添加分片条件,该分片条件仅在当前线程内生效。
除了通过编程的方式使用强制分片路由,Apache ShardingSphere还可以通过SQL中的特殊注释的方式引用Hint,使开发者可以采用更加透明的方式使用该功能。
指定了强制分片路由的SQL将会无视原有的分片逻辑,直接路由至指定的真实数据节点。
分布式事务
虽然Apache ShardingSphere希望能够完全兼容所有的分布式事务场景,并在性能上达到最优,但在CAP定理所指导下,分布式事务必然有所取舍。Apache ShardingSphere希望能够将分布式事务的选择权交给使用者,在不同的场景用使用最适合的分布式事务解决方案。
本地事务
怎么样才能支持,如果数据另一边没有数据修改,达到出现异常效果,事务回滚。
支持项
- 完全支持非跨库事务,例如:仅分表,或分库但是路由的结果在单库中
- 完全支持因逻辑异常导致的跨库事务。例如:同一事务中,跨两个库更新。更新完毕后,抛出空指针,则两个库的内容都能够回滚。
不支持项
- 不支持因网络、硬件异常导致的跨库事务。例如:同一事务中,跨两个库更新,更新完毕后、未提交之前,第一个库宕机,则只有第二个库数据提交,且无法回滚。
@Transactional(rollbackFor = Exception.class)
public boolean creatOrder(Order order){
int result1 = orderMapper.add(order);
Product product = new Product();
product.setName(order.getName());
product.setSale(order.getCount());
int result2 = productMapper.update(product);
String s = null;
s.toString();
return (result1 == 1) && (result2 == 1);
}
//实现了支持项的效果,在Service出现逻辑异常时,实现了事务的回滚,测试的Service没有实现接口,使用的CGLIB的动态代理处理事务的回滚。

XA事务
两阶段事务提交采用的是X/OPEN组织所定义的DTP模型所抽象的AP(应用程序), TM(事务管理器)和RM(资源管理器)概念来保证分布式事务的强一致性。其中TM与RM间采用XA的协议进行双向通信。与传统的本地事务相比,XA事务增加了准备阶段,数据库除了被动接受提交指令外,还可以反向通知调用方事务是否可以被提交。TM可以收集所有分支事务的准备结果,并于最后进行原子提交,以保证事务的强一致性。
Java通过定义JTA接口实现了XA模型,JTA接口中的ResourceManager需要数据库厂商提供XA驱动实现,TransactionManager则需要事务管理器的厂商实现,传统的事务管理器需要同应用服务器绑定,因此使用的成本很高。而嵌入式的事务管器可以通过jar形式提供服务,同Apache ShardingSphere集成后,可保证分片后跨库事务强一致性。
通常,只有使用了事务管理器厂商所提供的XA事务连接池,才能支持XA的事务。Apache ShardingSphere在整合XA事务时,采用分离XA事务管理和连接池管理的方式,做到对应用程序的零侵入。
maven依赖
<!-- 使用 XA 事务时,需要引入此模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-transaction-xa-core</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- https://mvnrepository.com/artifact/org.apache.shardingsphere/shardingsphere-transaction-xa-core -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-transaction-xa-core</artifactId>
<version>5.1.2</version>
</dependency>
<!-- 使用 BASE 事务时,需要引入此模块 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-transaction-base-seata-at</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
springboot使用
配置事务管理器
@Configuration
@EnableTransactionManagement
public class TransactionConfiguration {
@Bean
public PlatformTransactionManager txManager(final DataSource dataSource) {
return new DataSourceTransactionManager(dataSource);
}
@Bean
public JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate(final DataSource dataSource) {
return new JdbcTemplate(dataSource);
}
}
使用分布式事务
@Transactional
@ShardingSphereTransactionType(TransactionType.XA) // 支持TransactionType.LOCAL, TransactionType.XA, TransactionType.BASE
public void insert() {
jdbcTemplate.execute("INSERT INTO t_order (user_id, status) VALUES (?, ?)", (PreparedStatementCallback<Object>) ps -> {
ps.setObject(1, i);
ps.setObject(2, "init");
ps.executeUpdate();
});
}
支持项
- 支持数据分片后的跨库事务
- 两阶段提交保证操作的原子性和数据的强一致性
- 服务宕机重启后,提交/回滚中的事务可自动恢复
- 支持同时使用 XA 和非 XA 的连接池
不支持项
- 服务宕机后,在其它机器上恢复提交/回滚中的数据
- Savepoint
- 事务块内,SQL 执行出现异常,执行 Commit,数据保持一致
柔性事务
柔性事务在2008年发表的一篇论文中被最早提到,它提倡采用最终一致性放宽对强一致性的要求,以达到事务处理并发度的提升。
TCC和Saga是两种常见实现方案。他们主张开发者自行实现对数据库的反向操作,来达到数据在回滚时仍能够保证最终一致性。SEATA实现了SQL 反向操作的自动生成,可以使柔性事务不再必须由开发者介入才能使用。
Apache ShardingSphere集成了SEATA作为柔性事务的使用方案。
支持项
- 支持数据分片后的跨库事务
- 支持RC隔离级别
- 通过undo快照进行事务回滚
- 支持服务宕机后的,自动恢复提交中的事务
不支持项
- 不支持除RC之外的隔离级别
读写分离
####读写分离出现的原因
数据库的访问日益增加。对于同一时刻有着大并发读操作和较少的写操作的应用系统来说,将数据库拆分为主库和从库,主库负责处理事务性的增删改操作,从库负责查理查询操作,能够有效的避免由数据更新导致的行锁,使得整个系统的查询性能得到极大的改善。
通过一主多从的配置方式,可以将查询请求均匀的分散到多个数据副本,能够进一步的提升系统的处理能力。使用多主多从的方式,不但能够提升系统的吞吐量,还能够提升系统的可用性,可以达到在任何一个数据库宕机,甚至磁盘物理损坏的情况下仍然不影响系统的正常运行。
与将数据根据分片键打散至各个数据节点的水平分片不同,读写分离则是根据SQL语义的分析,将读操作和写操作分别路由至主库与从库。
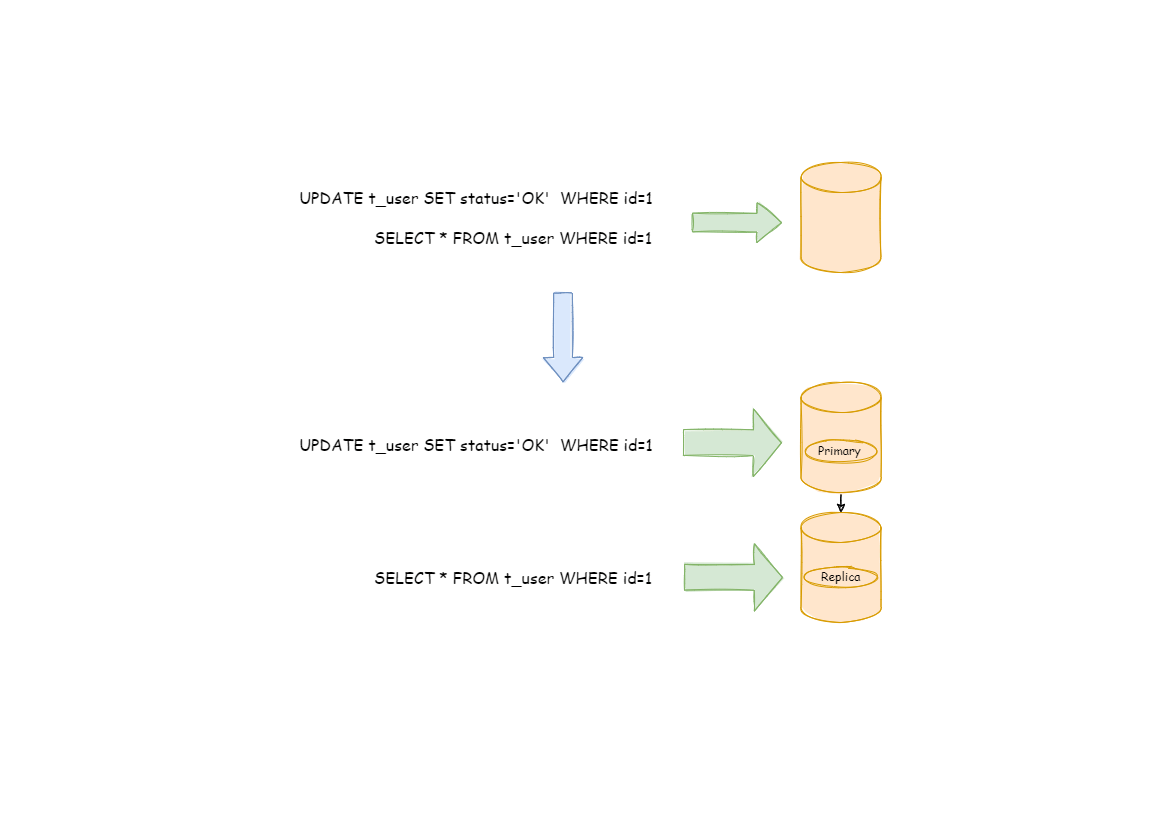
读写分离的数据节点中的数据内容是一致的,而水平分片的每个数据节点的数据内容却并不相同。将水平分片和读写分离联合使用,能够更加有效的提升系统性能。
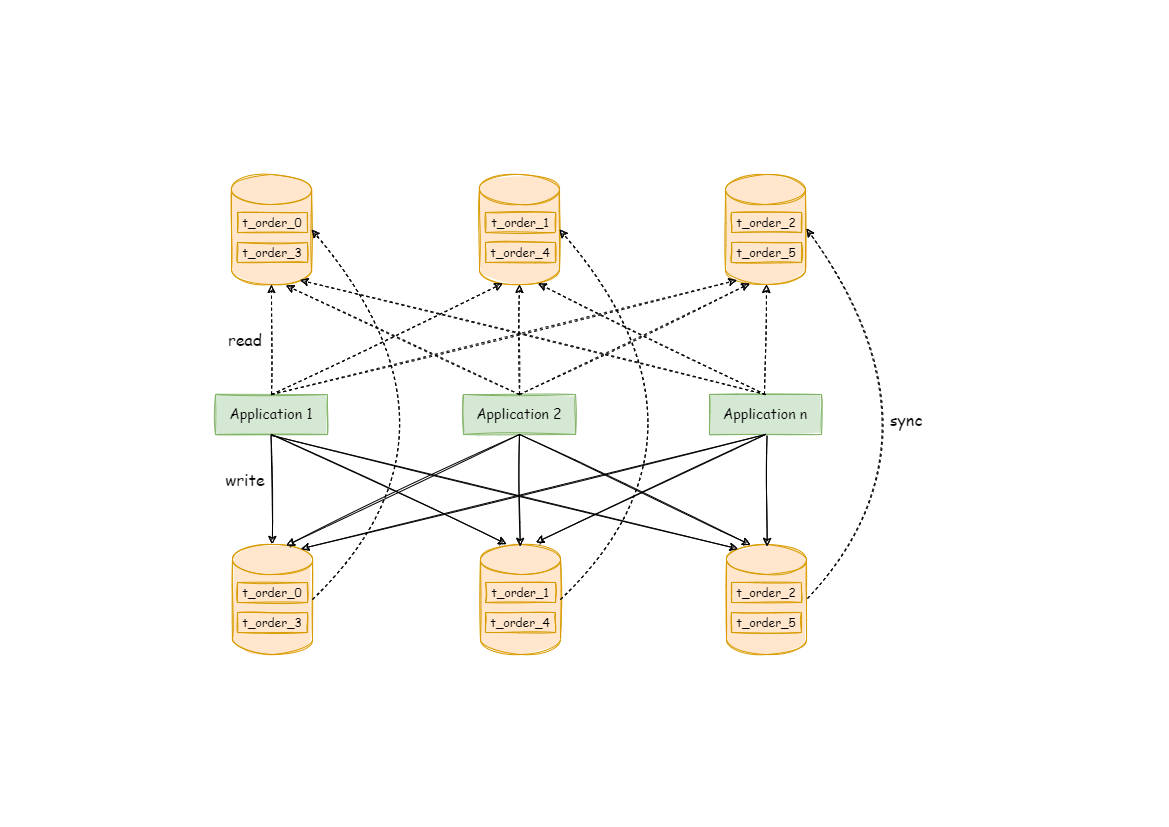
读写分离带来的问题
读写分离虽然可以提升系统的吞吐量和可用性,但同时也带来了数据不一致的问题。这包括多个主库之间的数据一致性,以及主库与从库之间的数据一致性的问题。并且,读写分离也带来了与数据分片同样的问题,它同样会使得应用开发和运维人员对数据库的操作和运维变得更加复杂。数据分片与读写分离一同使用时,应用程序与数据库集群之间的复杂拓扑关系。
- 添加、更新以及删除数据操作所使用的数据库,目前仅支持单主库。
- 查询数据操作所使用的数据库,可支持多从库。
- 将主库的数据异步的同步到从库的操作。由于主从同步的异步性,从库与主库的数据会短时间内不一致。
- 通过负载均衡策略将查询请求疏导至不同从库。
使用规范
支持项
- 提供一主多从的读写分离配置,可独立使用,也可配合数据分片使用;
- 事务中的数据读写均用主库;
- 基于Hint的强制主库路由。
不支持项
- 主库和从库的数据同步;
- 主库和从库的数据同步延迟导致的数据不一致;
- 主库多写;
- 主从库间的事务一致性。主从模型中,事务中的数据读写均用主库。
数据加密
影子库
ShardingSphere-JDBC使用
ShardingSphere-JDBC提供了4种配置方式,用于不同的使用场景。通过配置,应用开发者可以灵活的使用数据分片、读写分离、数据加密、影子库等功能,并且能够叠加使用。
需要注意的是,规则项之间的叠加使用是通过数据源名称和表名称关联的。如果前一个规则是面向数据源聚合的,下一个规则在配置数据源时,则需要使用前一个规则配置的聚合后的逻辑数据源名称;同理,如果前一个规则是面向表聚合的,下一个规则在配置表时,则需要使用前一个规则配置的聚合后的逻辑表名称。
Java API
Java API是ShardingSphere-JDBC中所有配置方式的基础,其他配置最终都将转化成为Java API的配置方式。
Java API是最繁琐也是最灵活的配置方式,适合需要通过编程进行动态配置的场景下使用。
使用步骤
maven依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-jdbc-core</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
构建数据源
ShardingSphere-JDBC 的Java API通过Schema名称、运行模式、数据源集合、规则集合以及属性配置组成。
通过ShardingSphereDataSourceFactory工厂创建的ShardingSphereDataSource实现自JDBC的标准接口DataSource。
String schemaName = "foo_schema"; //指定逻辑Schema名称
ModeConfiguration modeConfig = ... //构建运行模式
Map<String, DataSource> dataSourceMap = ... //构建真实数据源
Collection<RuleConfiguration> ruleConfigs = ... //构建具体规则
Properties props = ... // 构建属性配置
DataSource dataSource = ShardingSphereDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(schemaName, modeConfig, dataSourceMap, ruleConfigs, props);
使用数据源
可通过DataSource选择使用原生JDBC,或 JPA、Hibernate、MyBatis 等 ORM 框架。
//原生JDBC
//创建ShardingSphereDataSource
DataSource dataSource = ShardingSphereDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(schemaName, modeConfig, dataSourceMap, ruleConfigs, props);
String sql = "SELECT i.* FROM t_order o JOIN t_order_item i ON o.order_id=i.order_id WHERE o.user_id=? AND o.order_id=?";
try (
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement ps = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
ps.setInt(1, 10);
ps.setInt(2, 1000);
try (ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
while(rs.next()) {
// ...
}
}
}
模式配置
构建数据源ShardingSphereDataSource实例需要ModeConfiguration实例参数
ModeConfiguration modeConfig = ... //构建运行模式
//模式配置类全称
org.apache.shardingsphere.infra.config.mode.ModeConfiguration;
可配置属性
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| type | String | 运行模式类型 可选配置:Memory、Standalone、Cluster | Memory |
| repository | PersistRepositoryConfiguration | 持久化仓库配置Memory类型无需持久化,可以为 null,Standalone类型使用StandalonePersistRepositoryConfiguration,Cluster类型使用ClusterPersistRepositoryConfiguration | |
| overwrite | boolean | 是否使用本地配置覆盖持久化配置 | false |
Standalone配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.mode.repository.standalone.StandalonePersistRepositoryConfiguration;//类全称
可配置属性:
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| type | String | 持久化仓库类型 |
| props | Properties | 持久化仓库所需属性 |
Cluster配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.mode.repository.cluster.ClusterPersistRepositoryConfiguration
可配置属性:
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| type | String | 持久化仓库类型 |
| namespace | String | 注册中心命名空间 |
| serverLists | String | 注册中心连接地址 |
| props | Properties | 持久化仓库所需属性 |
数据源配置
Map<String, DataSource> dataSourceMap = ... //构建真实数据源
//数据库驱动为MySQL,连接池为HikariCP,可以更换为其他数据库驱动和连接池。
Map<String, DataSource> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<>();
// 配置第 1 个数据源
HikariDataSource dataSource1 = new HikariDataSource();
dataSource1.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource1.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1");
dataSource1.setUsername("root");
dataSource1.setPassword("");
dataSourceMap.put("ds_1", dataSource1);
// 配置第 2 个数据源
HikariDataSource dataSource2 = new HikariDataSource();
dataSource2.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource2.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_2");
dataSource2.setUsername("root");
dataSource2.setPassword("");
dataSourceMap.put("ds_2", dataSource2);
//...
规则配置
Collection<RuleConfiguration> ruleConfigs = ... //构建具体规则
#####数据分片
org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.config.ShardingRuleConfiguration;//可配置属性
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| tables (+) | Collection<ShardingTableRuleConfiguration> | 分片表规则列表 | - |
| autoTables (+) | Collection<ShardingAutoTableRuleConfiguration> | 自动化分片表规则列表 | - |
| bindingTableGroups (*) | Collection<String> | 绑定表规则列表 | 无 |
| broadcastTables (*) | Collection<String> | 广播表规则列表 | 无 |
| defaultDatabaseShardingStrategy (?) | ShardingStrategyConfiguration | 默认分库策略 | 不分片 |
| defaultTableShardingStrategy (?) | ShardingStrategyConfiguration | 默认分表策略 | 不分片 |
| defaultKeyGenerateStrategy (?) | KeyGeneratorConfiguration | 默认自增列生成器配置 | 雪花算法 |
| defaultShardingColumn (?) | String | 默认分片列名称 | 无 |
| shardingAlgorithms (+) | Map<String, ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration> | 分片算法名称和配置 | 无 |
| keyGenerators (?) | Map<String, ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration> | 自增列生成算法名称和配置 | 无 |
######分片表配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.config.ShardingTableRuleConfiguration;//分片表可配置属性
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| logicTable | String | 分片逻辑表名称 | - |
| actualDataNodes (?) | String | 由数据源名 + 表名组成,以小数点分隔。 多个表以逗号分隔,支持行表达式 | 使用已知数据源与逻辑表名称生成数据节点,用于广播表或只分库不分表且所有库的表结构完全一致的情况 |
| databaseShardingStrategy (?) | ShardingStrategyConfiguration | 分库策略 | 使用默认分库策略 |
| tableShardingStrategy (?) | ShardingStrategyConfiguration | 分表策略 | 使用默认分表策略 |
| keyGenerateStrategy (?) | KeyGeneratorConfiguration | 自增列生成器 | 使用默认自增主键生成器 |
######自动分片表配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.config.ShardingAutoTableRuleConfiguration;//自动分片表可配置属性
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| logicTable | String | 分片逻辑表名称 | - |
| actualDataSources (?) | String | 数据源名称,多个数据源以逗号分隔 | 使用全部配置的数据源 |
| shardingStrategy (?) | ShardingStrategyConfiguration | 分片策略 | 使用默认分片策略 |
| keyGenerateStrategy (?) | KeyGeneratorConfiguration | 自增列生成器 | 使用默认自增主键生成器 |
分片策略配置
ShardingStrategyConfiguration
标准分片策略配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.config.strategy.sharding.StandardShardingStrategyConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| shardingColumn | String | 分片列名称 |
| shardingAlgorithmName | String | 分片算法名称 |
复合分片策略配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.config.strategy.sharding.ComplexShardingStrategyConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| shardingColumns | String | 分片列名称,多个列以逗号分隔 |
| shardingAlgorithmName | String | 分片算法名称 |
Hint分片策略配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.config.strategy.sharding.HintShardingStrategyConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| shardingAlgorithmName | String | 分片算法名称 |
不分片策略配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.config.strategy.sharding.NoneShardingStrategyConfiguration;
//可配置属性:无
自动分片算法
内置分片算法列表
MOD 取模分片算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| sharding-count | int | 分片数量 |
HASH_MOD 哈希取模算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| sharding-count | int | 分片数量 |
VOLUME_RANGE基于分片容量的范围分片算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| range-lower | long | 范围下界,超过边界的数据会报错 |
| range-upper | long | 范围上界,超过边界的数据会报错 |
| sharding-volume | long | 分片容量 |
BOUNDARY_RANGE基于分片边界的范围分片算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| sharding-ranges | String | 分片的范围边界,多个范围边界以逗号分隔 |
AUTO_INTERVAL自动时间段分片算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| datetime-lower | String | 分片的起始时间范围,时间戳格式:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss |
| datetime-upper | String | 分片的结束时间范围,时间戳格式:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss |
| sharding-seconds | long | 单一分片所能承载的最大时间,单位:秒,允许分片键的时间戳格式的秒带有时间精度,但秒后的时间精度会被自动抹去 |
标准分片算法
INLINE 行表达式分片算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| algorithm-expression | String | 分片算法的行表达式 | |
| allow-range-query-with-inline-sharding (?) | boolean | 是否允许范围查询。注意:范围查询会无视分片策略,进行全路由 | false |
INTERVAL 时间范围分片算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| datetime-pattern | String | 分片键的时间戳格式,必须遵循 Java DateTimeFormatter 的格式。例如:yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss | |
| datetime-lower | String | 时间分片下界值,格式与 datetime-pattern 定义的时间戳格式一致 | |
| datetime-upper (?) | String | 时间分片上界值,格式与 datetime-pattern 定义的时间戳格式一致 | 当前时间 |
| sharding-suffix-pattern | String | 分片数据源或真实表的后缀格式,必须遵循 Java DateTimeFormatter 的格式,必须和 datetime-interval-unit 保持一致。例如:yyyyMM | |
| datetime-interval-amount (?) | int | 分片键时间间隔,超过该时间间隔将进入下一分片 | 1 |
| datetime-interval-unit (?) | String | 分片键时间间隔单位,必须遵循 Java ChronoUnit 的枚举值。例如:MONTHS | DAYS |
复合分片算法
COMPLEX_INLINE 复合行表达式分片算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| sharding-columns (?) | String | 分片列名称,多个列用逗号分隔。如不配置无法则不能校验 | |
| algorithm-expression | String | 分片算法的行表达式 | |
| allow-range-query-with-inline-sharding (?) | boolean | 是否允许范围查询。注意:范围查询会无视分片策略,进行全路由 | false |
Hint分片算法
HINT_INLINE Hint行表达式分片算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| algorithm-expression (?) | String | 分片算法的行表达式 | ${value} |
Hint分片使用的场景
- 分片字段不存在 SQL 和数据库表结构中,而存在于外部业务逻辑。
- 强制在主库进行某些数据操作。
- 强制在指定数据库进行某些数据操作。
实现org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.sharding.hint.HintShardingAlgorithm接口。Apache ShardingSphere在进行路由时,将会从HintManager中获取分片值进行路由操作。
rules:
- !SHARDING
tables:
t_order:
actualDataNodes: demo_ds_${0..1}.t_order_${0..1}
databaseStrategy:
hint:
algorithmClassName: xxx.xxx.xxx.HintXXXAlgorithm
tableStrategy:
hint:
algorithmClassName: xxx.xxx.xxx.HintXXXAlgorithm
defaultTableStrategy:
none:
defaultKeyGenerateStrategy:
type: SNOWFLAKE
column: order_id
props:
sql-show: true
HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
添加分片键值
-
使用
hintManager.addDatabaseShardingValue来添加数据源分片键值。 -
使用
hintManager.addTableShardingValue来添加表分片键值。 -
分库不分表情况下,强制路由至某一个分库时,可使用
hintManager.setDatabaseShardingValue方式添加分片。
清除分片键值
分片键值保存在ThreadLocal 中,所以需要在操作结束时调用 hintManager.close() 来清除 ThreadLocal 中的内容。
hintManager 实现了 AutoCloseable 接口,可推荐使用 try with resource 自动关闭。
// Sharding database and table with using HintManager
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_order";
try (HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
hintManager.addDatabaseShardingValue("t_order", 1);
hintManager.addTableShardingValue("t_order", 2);
try (ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
while (rs.next()) {
// ...
}
}
}
// Sharding database without sharding table and routing to only one database with using HintManager
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_order";
try (HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
hintManager.setDatabaseShardingValue(3);
try (ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
while (rs.next()) {
// ...
}
}
}
使用Hint路由指定数据库
String sql = "SELECT * FROM t_order";
try (HintManager hintManager = HintManager.getInstance();
Connection conn = dataSource.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = conn.prepareStatement(sql)) {
hintManager.setDataSourceName("ds_0");
try (ResultSet rs = preparedStatement.executeQuery()) {
while (rs.next()) {
// ...
}
}
}
自定义类分片算法
CLASS_BASED
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| strategy | String | 分片策略类型,支持 STANDARD、COMPLEX 或 HINT(不区分大小写) |
| algorithmClassName | String | 分片算法全限定名 |
分布式主键生成配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.sharding.api.config.strategy.keygen.KeyGenerateStrategyConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| column | String | 分布式序列列名称 |
| keyGeneratorName | String | 分布式序列算法名称 |
内置分布式主键算法列表
SNOWFLAKE 雪花算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| max-vibration-offset (?) | int | 最大抖动上限值,范围[0, 4096)。注:若使用此算法生成值作分片值,建议配置此属性。此算法在不同毫秒内所生成的 key 取模 2^n (2^n一般为分库或分表数) 之后结果总为 0 或 1。为防止上述分片问题,建议将此属性值配置为 (2^n)-1 | 1 |
| max-tolerate-time-difference-milliseconds (?) | long | 最大容忍时钟回退时间,单位:毫秒 | 10 毫秒 |
UUID
无配置属性
读写分离配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.readwritesplitting.api.ReadwriteSplittingRuleConfiguration;//配置类
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| dataSources (+) | Collection<ReadwriteSplittingDataSourceRuleConfiguration> | 读写数据源配置 |
| loadBalancers (*) | Map<String, ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration> | 从库负载均衡算法配置 |
读写数据源配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.readwritesplitting.api.rule.ReadwriteSplittingDataSourceRuleConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| name | String | 读写分离数据源名称 | - |
| type | String | 读写分离类型,分为静态和动态。如 Static、Dynamic | - |
| props | Properties | 读写分离所需属性,如静态:write-data-source-name、read-data-source-names,动态:auto-aware-data-source-name | - |
| loadBalancerName (?) | String | 读库负载均衡算法名称 | 轮询负载均衡算法 |
server:
port: 80
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: ds_0,ds_0-read0,ds_0-read1,ds_1
ds_0:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://106.15.234.93:3307/d1?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: 1024
ds_0-read0:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://106.15.234.93:3308/d1?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: 1024
ds_0-read1:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://106.15.234.93:3309/d1?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: 1024
ds_1:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://106.15.234.93:3306/ds_1?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: 1024
rules:
sharding:
tables:
order:
actual-data-nodes: logic_1.order_$->{0..1}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: order-table
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: order-snowflake
product:
actual-data-nodes: ds_1.product_$->{0..1}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: product-table
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: product-snowflake
sharding-algorithms:
order-table:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: order_$->{id % 2}
product-table:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: product_$->{id % 2}
key-generators:
order-snowflake:
type: SNOWFLAKE
product-snowflake:
type: SNOWFLAKE
readwrite-splitting:
data-sources:
logic_1:
type: Static
props:
write-data-source-name: ds_0
read-data-source-names: ds_0-read0,ds_0-read1
load-balancer-name: read-random
load-balancers:
read-random:
type: ROUND_ROBIN
props:
sql-show: true
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.study.pojo
配置负载均衡算法没有用。但是如果类型写错误,服务器不能启动

内置负载均衡算法列表
ROUND_ROBIN 轮询算法
RANDOM 随机访问算法
WEIGHT 权重访问算法
| 属性名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| - <read-data_source-name> (+) | double | 属性名字使用读库名字,参数填写读库对应的权重值。权重参数范围最小值 > 0,合计 <= Double.MAX_VALUE。 |
高可用
org.apache.shardingsphere.dbdiscovery.api.config.DatabaseDiscoveryRuleConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| dataSources (+) | Collection<DatabaseDiscoveryDataSourceRuleConfiguration> | 数据源配置 |
| discoveryHeartbeats (+) | Map<String, DatabaseDiscoveryHeartBeatConfiguration> | 监听心跳配置 |
| discoveryTypes (+) | Map<String, ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration> | 数据库发现类型配置 |
数据源配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.dbdiscovery.api.config.rule.DatabaseDiscoveryDataSourceRuleConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| groupName (+) | String | 数据库发现组名称 | - |
| dataSourceNames (+) | Collection<String> | 数据源名称,多个数据源用逗号分隔 如:ds_0, ds_1 | - |
| discoveryHeartbeatName (+) | String | 监听心跳名称 | - |
| discoveryTypeName (+) | String | 数据库发现类型名称 | - |
监听心跳配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.dbdiscovery.api.config.rule.DatabaseDiscoveryHeartBeatConfiguration
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| props (+) | Properties | 监听心跳属性配置,keep-alive-cron 属性配置cron表达式,如:‘0/5 * * * * ?’ | - |
数据库发现类型配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.infra.config.algorithm.ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| type (+) | String | 数据库发现类型,如:MGR、openGauss | - |
| props (?) | Properties | 数据库发现类型配置,如 MGR 的 group-name 属性配置 | - |
数据加密
org.apache.shardingsphere.encrypt.api.config.EncryptRuleConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| tables (+) | Collection<EncryptTableRuleConfiguration> | 加密表规则配置 | |
| encryptors (+) | Map<String, ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration> | 加解密算法名称和配置 | |
| queryWithCipherColumn (?) | boolean | 是否使用加密列进行查询。在有原文列的情况下,可以使用原文列进行查询 | true |
加密表规则配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.encrypt.api.config.rule.EncryptTableRuleConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| name | String | 表名称 |
| columns (+) | Collection<EncryptColumnRuleConfiguration> | 加密列规则配置列表 |
| queryWithCipherColumn (?) | boolean | 该表是否使用加密列进行查询 |
加密列规则配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.encrypt.api.config.rule.EncryptColumnRuleConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| logicColumn | String | 逻辑列名称 |
| cipherColumn | String | 密文列名称 |
| assistedQueryColumn (?) | String | 查询辅助列名称 |
| plainColumn (?) | String | 原文列名称 |
| encryptorName | String | 加密算法名称 |
加解密算法配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.infra.config.algorithm.ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| name | String | 加解密算法名称 |
| type | String | 加解密算法类型 |
| properties | Properties | 加解密算法属性配置 |
内置加密算法列表
MD5 加密算法
AES 加密算法
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| aes-key-value | String | AES 使用的 KEY |
RC4 加密算法
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| rc4-key-value | String | RC4 使用的 KEY |
SM3 加密算法
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| sm3-salt | String | SM3 使用的 SALT(空或 8 Bytes) |
SM4加密算法
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| sm4-key | String | SM4 使用的 KEY (16 Bytes) |
| sm4-mode | String | SM4 使用的 MODE (CBC 或 ECB) |
| sm4-iv | String | SM4 使用的 IV (MODE 为 CBC 时需指定,16 Bytes) |
| sm4-padding | String | SM4 使用的 PADDING (PKCS5Padding 或 PKCS7Padding,暂不支持 NoPadding) |
影子库
org.apache.shardingsphere.shadow.api.config.ShadowRuleConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| dataSources | Map<String, ShadowDataSourceConfiguration> | 影子数据源映射名称和配置 | |
| tables | Map<String, ShadowTableConfiguration> | 影子表名称和配置 | |
| defaultShadowAlgorithmName | String | 默认影子算法名称 | |
| shadowAlgorithms | Map<String, ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration> | 影子算法名称和配置 | 无 |
影子数据源配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.shadow.api.config.datasource.ShadowDataSourceConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| sourceDataSourceName | String | 生产数据源名称 |
| shadowDataSourceName | String | 影子数据源名称 |
影子表配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.shadow.api.config.table.ShadowTableConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| dataSourceNames | Collection<String> | 影子表关联影子数据源映射名称列表 |
| shadowAlgorithmNames | Collection<String> | 影子表关联影子算法名称列表 |
影子算法配置
SQL解析
org.apache.shardingsphere.parser.config.SQLParserRuleConfiguration;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| sqlCommentParseEnabled (?) | boolean | 是否解析 SQL 注释 |
| parseTreeCache (?) | CacheOption | 解析语法树本地缓存配置 |
| sqlStatementCache (?) | CacheOption | SQL 语句本地缓存配置 |
本地缓存配置
org.apache.shardingsphere.sql.parser.api.CacheOption;
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| initialCapacity | int | 本地缓存初始容量 | 语法树本地缓存默认值 128,SQL 语句缓存默认值 2000 |
| maximumSize | long | 本地缓存最大容量 | 语法树本地缓存默认值 1024,SQL 语句缓存默认值 65535 |
| concurrencyLevel | int | 本地缓存并发级别,最多允许线程并发更新的个数 | 4 |
混合配置
混合配置的规则项之间的叠加使用是通过数据源名称和表名称关联的。
如果前一个规则是面向数据源聚合的,下一个规则在配置数据源时,则需要使用前一个规则配置的聚合后的逻辑数据源名称;同理,如果前一个规则是面向表聚合的,下一个规则在配置表时,则需要使用前一个规则配置的聚合后的逻辑表名称。
/* 数据源配置 */
HikariDataSource writeDataSource0 = new HikariDataSource();
writeDataSource0.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
writeDataSource0.setJdbcUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/db0?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8");
writeDataSource0.setUsername("root");
writeDataSource0.setPassword("");
HikariDataSource writeDataSource1 = new HikariDataSource();
// ...忽略其他数据库配置项
HikariDataSource read0OfwriteDataSource0 = new HikariDataSource();
// ...忽略其他数据库配置项
HikariDataSource read1OfwriteDataSource0 = new HikariDataSource();
// ...忽略其他数据库配置项
HikariDataSource read0OfwriteDataSource1 = new HikariDataSource();
// ...忽略其他数据库配置项
HikariDataSource read1OfwriteDataSource1 = new HikariDataSource();
// ...忽略其他数据库配置项
Map<String, DataSource> datasourceMaps = new HashMap<>(6);
datasourceMaps.put("write_ds0", writeDataSource0);
datasourceMaps.put("write_ds0_read0", read0OfwriteDataSource0);
datasourceMaps.put("write_ds0_read1", read1OfwriteDataSource0);
datasourceMaps.put("write_ds1", writeDataSource1);
datasourceMaps.put("write_ds1_read0", read0OfwriteDataSource1);
datasourceMaps.put("write_ds1_read1", read1OfwriteDataSource1);
/* 分片规则配置 */
// 表达式 ds_${0..1} 枚举值表示的是主从配置的逻辑数据源名称列表
ShardingTableRuleConfiguration tOrderRuleConfiguration = new ShardingTableRuleConfiguration("t_order", "ds_${0..1}.t_order_${[0, 1]}");
tOrderRuleConfiguration.setKeyGenerateStrategy(new KeyGenerateStrategyConfiguration("order_id", "snowflake"));
tOrderRuleConfiguration.setTableShardingStrategy(new StandardShardingStrategyConfiguration("order_id", "tOrderInlineShardingAlgorithm"));
Properties tOrderShardingInlineProps = new Properties();
tOrderShardingInlineProps.setProperty("algorithm-expression", "t_order_${order_id % 2}");
tOrderRuleConfiguration.getShardingAlgorithms().putIfAbsent("tOrderInlineShardingAlgorithm", new ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration("INLINE",tOrderShardingInlineProps));
ShardingTableRuleConfiguration tOrderItemRuleConfiguration = new ShardingTableRuleConfiguration("t_order_item", "ds_${0..1}.t_order_item_${[0, 1]}");
tOrderItemRuleConfiguration.setKeyGenerateStrategy(new KeyGenerateStrategyConfiguration("order_item_id", "snowflake"));
tOrderRuleConfiguration.setTableShardingStrategy(new StandardShardingStrategyConfiguration("order_item_id", "tOrderItemInlineShardingAlgorithm"));
Properties tOrderItemShardingInlineProps = new Properties();
tOrderItemShardingInlineProps.setProperty("algorithm-expression", "t_order_item_${order_item_id % 2}");
tOrderRuleConfiguration.getShardingAlgorithms().putIfAbsent("tOrderItemInlineShardingAlgorithm", new ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration("INLINE",tOrderItemShardingInlineProps));
ShardingRuleConfiguration shardingRuleConfiguration = new ShardingRuleConfiguration();
shardingRuleConfiguration.getTables().add(tOrderRuleConfiguration);
shardingRuleConfiguration.getTables().add(tOrderItemRuleConfiguration);
shardingRuleConfiguration.getBindingTableGroups().add("t_order, t_order_item");
shardingRuleConfiguration.getBroadcastTables().add("t_bank");
// 默认分库策略
shardingRuleConfiguration.setDefaultDatabaseShardingStrategy(new StandardShardingStrategyConfiguration("user_id", "default_db_strategy_inline"));
Properties defaultDatabaseStrategyInlineProps = new Properties();
defaultDatabaseStrategyInlineProps.setProperty("algorithm-expression", "ds_${user_id % 2}");
shardingRuleConfiguration.getShardingAlgorithms().put("default_db_strategy_inline", new ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration("INLINE", defaultDatabaseStrategyInlineProps));
// 分布式序列算法配置
Properties snowflakeProperties = new Properties();
shardingRuleConfiguration.getKeyGenerators().put("snowflake", new ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration("SNOWFLAKE", snowflakeProperties));
/* 数据加密规则配置 */
Properties encryptProperties = new Properties();
encryptProperties.setProperty("aes-key-value", "123456");
EncryptColumnRuleConfiguration columnConfigAes = new EncryptColumnRuleConfiguration("username", "username", "", "username_plain", "name_encryptor");
EncryptColumnRuleConfiguration columnConfigTest = new EncryptColumnRuleConfiguration("pwd", "pwd", "assisted_query_pwd", "", "pwd_encryptor");
EncryptTableRuleConfiguration encryptTableRuleConfig = new EncryptTableRuleConfiguration("t_user", Arrays.asList(columnConfigAes, columnConfigTest));
Map<String, ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration> encryptAlgorithmConfigs = new LinkedHashMap<>(2, 1);
encryptAlgorithmConfigs.put("name_encryptor", new ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration("AES", encryptProperties));
encryptAlgorithmConfigs.put("pwd_encryptor", new ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration("assistedTest", encryptProperties));
EncryptRuleConfiguration encryptRuleConfiguration = new EncryptRuleConfiguration(Collections.singleton(encryptTableRuleConfig), encryptAlgorithmConfigs);
/* 读写分离规则配置 */
Properties readwriteProps1 = new Properties();
readwriteProps1.setProperty("write-data-source-name", "write_ds0");
readwriteProps1.setProperty("read-data-source-names", "write_ds0_read0, write_ds0_read1");
ReadwriteSplittingDataSourceRuleConfiguration dataSourceConfiguration1 = new ReadwriteSplittingDataSourceRuleConfiguration("ds_0", "Static", readwriteProps1, "roundRobin");
Properties readwriteProps2 = new Properties();
readwriteProps2.setProperty("write-data-source-name", "write_ds0");
readwriteProps2.setProperty("read-data-source-names", "write_ds1_read0, write_ds1_read1");
ReadwriteSplittingDataSourceRuleConfiguration dataSourceConfiguration2 = new ReadwriteSplittingDataSourceRuleConfiguration("ds_1", "Static", readwriteProps2, "roundRobin");
// 负载均衡算法
Map<String, ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration> loadBalanceMaps = new HashMap<>(1);
loadBalanceMaps.put("roundRobin", new ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration("ROUND_ROBIN", new Properties()));
ReadwriteSplittingRuleConfiguration readWriteSplittingyRuleConfiguration = new ReadwriteSplittingRuleConfiguration(Arrays.asList(dataSourceConfiguration1, dataSourceConfiguration2), loadBalanceMaps);
/* 其他配置 */
Properties otherProperties = new Properties();
otherProperties.setProperty("sql-show", "true");
/* shardingDataSource 就是最终被 ORM 框架或其他 jdbc 框架引用的数据源名称 */
DataSource shardingDataSource = ShardingSphereDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(datasourceMaps, Arrays.asList(shardingRuleConfiguration, readWriteSplittingyRuleConfiguration, encryptRuleConfiguration), otherProperties);
单表拆分使用步骤
//1.构建直连数据库的数据源,放入map集合
DruidDataSource dataSource1 = new DruidDataSource();
dataSource1.setDriverClassName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver");
dataSource1.setUrl("jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1?useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8");
ataSource1.setUsername("root");
dataSource1.setPassword("1024");
Map<String, DataSource> dataSourceMap = new HashMap<String, DataSource>();
dataSourceMap.put("ds_1",dataSource1);
//2.分表规则配置
Collection<RuleConfiguration> ruleConfigs = new ArrayList<RuleConfiguration>();
ShardingRuleConfiguration shardingRuleConfiguration = new ShardingRuleConfiguration();//数据分片规则
ShardingTableRuleConfiguration shardingTableRuleConfiguration = new ShardingTableRuleConfiguration("user","ds_1.user_${0..1}");//表分片规则
StandardShardingStrategyConfiguration standardShardingStrategyConfiguration = new StandardShardingStrategyConfiguration("id","tUserInlineShardingAlgorithm");
Properties tUserShardingInlineProps = new Properties();
tUserShardingInlineProps.setProperty("algorithm-expression", "user_${id % 2}");
shardingTableRuleConfiguration.setTableShardingStrategy(standardShardingStrategyConfiguration);//表分片策略设
shardingRuleConfiguration.getShardingAlgorithms().putIfAbsent("tUserInlineShardingAlgorithm",new ShardingSphereAlgorithmConfiguration("INLINE",tUserShardingInlineProps));//分片算法设置
shardingRuleConfiguration.getTables().add(shardingTableRuleConfiguration);//分片表配置加入规则
//3.获取数据源
DataSource dataSource = ShardingSphereDataSourceFactory.createDataSource(dataSourceMap,ruleConfigs,props);
//4.查询
final Connection connection = dataSource.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from user order by id";
final PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
final ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()){
System.out.println(resultSet.getLong("id"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getInt("age"));
System.out.println(resultSet.getString("name"));
System.out.println("============");
}
//这里取值不能使用下标,获取不到值。
Spring Boot 配置
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-jdbc-core-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>${shardingsphere.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.shardingsphere</groupId>
<artifactId>shardingsphere-jdbc-core-spring-boot-starter</artifactId>
<version>5.1</version>
</dependency>
模式配置
缺省默认为内存模式
spring.shardingsphere.mode.type= #运行模式类型。可选配置:Memory、Standalone、Cluster
spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository= #持久化仓库配置。Memory 类型无需持久化
spring.shardingsphere.mode.overwrite= #是否使用本地配置覆盖持久化配置
内存模式
spring.shardingsphere.mode.tyep=Memory
单机模式
spring.shardingsphere.mode.type=Standalone
spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.type= # 持久化仓库类型
spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.props.<key>= # 持久化仓库所需属性
spring.shardingsphere.mode.overwrite= # 是否使用本地配置覆盖持久化配置
集群模式
spring.shardingsphere.mode.type=Cluster
spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.type= # 持久化仓库类型
spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.props.namespace= # 注册中心命名空间
spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.props.server-lists= # 注册中心连接地址
spring.shardingsphere.mode.repository.props.<key>= # 持久化仓库所需属性
spring.shardingsphere.mode.overwrite= # 是否使用本地配置覆盖持久化配置
数据源配置
本地数据源配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names= #真实数据源名称,多个数据源用逗号区分
# <actual-data-source-name> 表示真实数据源名称
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.<actual-data-source-name>.type= # 数据库连接池全类名
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.<actual-data-source-name>.driver-class-name= # 数据库驱动类名,以数据库连接池自身配置为准
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.<actual-data-source-name>.jdbc-url= # 数据库 URL 连接,以数据库连接池自身配置为准
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.<actual-data-source-name>.username= # 数据库用户名,以数据库连接池自身配置为准
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.<actual-data-source-name>.password= # 数据库密码,以数据库连接池自身配置为准
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.<actual-data-source-name>.<xxx>= # ... 数据库连接池的其它属性
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: ds_0,ds_1
ds_0:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
username: root
password: 1024
ds_1:
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://106.15.234.93:3306/ds_1?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
username: root
password: 1024
JNDI数据源配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names= # 真实数据源名称,多个数据源用逗号区分
# <actual-data-source-name> 表示真实数据源名称
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.<actual-data-source-name>.jndi-name= # 数据源 JNDI
# 配置真实数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names=ds1,ds2
# 配置第 1 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds1.jndi-name=java:comp/env/jdbc/ds1
# 配置第 2 个数据源
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.ds2.jndi-name=java:comp/env/jdbc/ds2
数据分片配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names= # 省略数据源配置,请参考使用手册
# 标准分片表配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.<table-name>.actual-data-nodes= # 由数据源名.表名组成,多个表以逗号分隔,支持行表达式。缺省表示使用已知数据源与逻辑表名称生成数据节点,用于广播表(即每个库中都需要一个同样的表用于关联查询,多为字典表)或只分库不分表且所有库的表结构完全一致的情况
# 分库策略,缺省表示使用默认分库策略,以下的分片策略只能选其一
# 用于单分片键的标准分片场景
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.<table-name>.database-strategy.standard.sharding-column= # 分片列名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.<table-name>.database-strategy.standard.sharding-algorithm-name= # 分片算法名称
# 用于多分片键的复合分片场景
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.<table-name>.database-strategy.complex.sharding-columns= # 分片列名称,多个列以逗号分隔
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.<table-name>.database-strategy.complex.sharding-algorithm-name= # 分片算法名称
# 用于 Hint 的分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.<table-name>.database-strategy.hint.sharding-algorithm-name= # 分片算法名称
# 分表策略,同分库策略
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.<table-name>.table-strategy.xxx= # 省略
# 自动分片表配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.auto-tables.<auto-table-name>.actual-data-sources= # 数据源名
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.auto-tables.<auto-table-name>.sharding-strategy.standard.sharding-column= # 分片列名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.auto-tables.<auto-table-name>.sharding-strategy.standard.sharding-algorithm-name= # 自动分片算法名称
# 分布式序列策略配置
# 主键自动生成设置,使用这个要在sql语句中不写插入主键的
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.<table-name>.key-generate-strategy.column= # 分布式序列列名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.<table-name>.key-generate-strategy.key-generator-name= # 分布式序列算法名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.binding-tables[0]= # 绑定表规则列表
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.binding-tables[1]= # 绑定表规则列表
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.binding-tables[x]= # 绑定表规则列表
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.broadcast-tables[0]= # 广播表规则列表
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.broadcast-tables[1]= # 广播表规则列表
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.broadcast-tables[x]= # 广播表规则列表
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-database-strategy.xxx= # 默认数据库分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-table-strategy.xxx= # 默认表分片策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-key-generate-strategy.xxx= # 默认分布式序列策略
spring.shardingsphere.sharding.default-sharding-column= # 默认分片列名称
# 分片算法配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.sharding-algorithms.<sharding-algorithm-name>.type= # 分片算法类型
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.sharding-algorithms.<sharding-algorithm-name>.props.xxx= # 分片算法属性配置
# 分布式序列算法配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.key-generators.<key-generate-algorithm-name>.type= # 分布式序列算法类型
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.key-generators.<key-generate-algorithm-name>.props.xxx= # 分布式序列算法属性配置
读写分离配置
注意:读写分离,写只能是一个数据源,读可以是多个数据源。
两个从节点,分两表,默认负载均衡算法是0库查0biao,1库查1表
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names= # 省略数据源配置,请参考使用手册
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.<readwrite-splitting-data-source-name>.type= # 读写分离类型,如: Static,Dynamic
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.<readwrite-splitting-data-source-name>.props.auto-aware-data-source-name= # 自动发现数据源名称(与数据库发现配合使用)
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.<readwrite-splitting-data-source-name>.props.write-data-source-name= # 写数据源名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.<readwrite-splitting-data-source-name>.props.read-data-source-names= # 读数据源名称,多个从数据源用逗号分隔
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.<readwrite-splitting-data-source-name>.load-balancer-name= # 负载均衡算法名称
# 负载均衡算法配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.load-balancers.<load-balance-algorithm-name>.type= # 负载均衡算法类型
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.load-balancers.<load-balance-algorithm-name>.props.xxx= # 负载均衡算法属性配置
高可用配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names= # 省略数据源配置,请参考使用手册
spring.shardingsphere.rules.database-discovery.data-sources.<database-discovery-data-source-name>.data-source-names= # 数据源名称,多个数据源用逗号分隔 如:ds_0, ds_1
spring.shardingsphere.rules.database-discovery.data-sources.<database-discovery-data-source-name>.discovery-heartbeat-name= # 检测心跳名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.database-discovery.data-sources.<database-discovery-data-source-name>.discovery-type-name= # 数据库发现类型名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.database-discovery.discovery-heartbeats.<discovery-heartbeat-name>.props.keep-alive-cron= # cron 表达式,如:'0/5 * * * * ?'
spring.shardingsphere.rules.database-discovery.discovery-types.<discovery-type-name>.type= # 数据库发现类型,如:MGR、openGauss
spring.shardingsphere.rules.database-discovery.discovery-types.<discovery-type-name>.props.group-name= # 数据库发现类型必要参数,如 MGR 的 group-name
数据加密配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names= # 省略数据源配置,请参考使用手册
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.tables.<table-name>.query-with-cipher-column= # 该表是否使用加密列进行查询
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.tables.<table-name>.columns.<column-name>.cipher-column= # 加密列名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.tables.<table-name>.columns.<column-name>.assisted-query-column= # 查询列名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.tables.<table-name>.columns.<column-name>.plain-column= # 原文列名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.tables.<table-name>.columns.<column-name>.encryptor-name= # 加密算法名称
# 加密算法配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.encryptors.<encrypt-algorithm-name>.type= # 加密算法类型
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.encryptors.<encrypt-algorithm-name>.props.xxx= # 加密算法属性配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.queryWithCipherColumn= # 是否使用加密列进行查询。在有原文列的情况下,可以使用原文列进行查询
影子库配置
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names= # 省略数据源配置,请参考使用手册
spring.shardingsphere.rules.shadow.data-sources.shadow-data-source.source-data-source-name= # 生产数据源名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.shadow.data-sources.shadow-data-source.shadow-data-source-name= # 影子数据源名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.shadow.tables.<table-name>.data-source-names= # 影子表关联影子数据源名称列表(多个值用","隔开)
spring.shardingsphere.rules.shadow.tables.<table-name>.shadow-algorithm-names= # 影子表关联影子算法名称列表(多个值用","隔开)
spring.shardingsphere.rules.shadow.defaultShadowAlgorithmName= # 默认影子算法名称,选配项。
spring.shardingsphere.rules.shadow.shadow-algorithms.<shadow-algorithm-name>.type= # 影子算法类型
spring.shardingsphere.rules.shadow.shadow-algorithms.<shadow-algorithm-name>.props.xxx= # 影子算法属性配置
SQL解析配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sql-parser.sql-comment-parse-enabled= # 是否解析SQL注释
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sql-parser.sql-statement-cache.initial-capacity= # SQL语句本地缓存初始容量
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sql-parser.sql-statement-cache.maximum-size= # SQL语句本地缓存最大容量
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sql-parser.sql-statement-cache.concurrency-level= # SQL语句本地缓存并发级别,最多允许线程并发更新的个数
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sql-parser.parse-tree-cache.initial-capacity= # 解析树本地缓存初始容量
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sql-parser.parse-tree-cache.maximum-size= # 解析树本地缓存最大容量
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sql-parser.parse-tree-cache.concurrency-level= # 解析树本地缓存并发级别,最多允许线程并发更新的个数
配置案例
# 数据源配置
# 数据源名称,多数据源以逗号分隔
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.names= write-ds0,write-ds1,write-ds0-read0,write-ds1-read0
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.write-ds0.jdbc-url=jdbc:mysql://ip:port/database?
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.write-ds0.type= #数据库连接池类名称
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.write-ds0.driver-class-name= #数据库驱动类名
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.write-ds0.username= #数据库用户名
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.write-ds0.password= #数据库密码
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.write-ds0.xxx= #数据库连接池的其它属性
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.write-ds1.jdbc-url= # 数据库URL连接
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.write-ds0-read0.jdbc-url= # 数据库URL连接
spring.shardingsphere.datasource.write-ds1-read0.jdbc-url= # 数据库 URL 连接
# 分片规则配置
# 分库策略
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.default-database-strategy.standard.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.default-database-strategy.standard.sharding-algorithm-name=default-database-strategy-inline
# 绑定表规则,多组绑定规则使用数组形式配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.binding-tables[0]=t_user,t_user_detail # 绑定表名称,多个表之间以逗号分隔
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.binding-tables[1]= # 绑定表名称,多个表之间以逗号分隔
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.binding-tables[x]= # 绑定表名称,多个表之间以逗号分隔
# 广播表规则配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.broadcast-tables= # 广播表名称,多个表之间以逗号分隔
# 分表策略
# 表达式ds_$->{0..1}枚举的数据源为读写分离配置的逻辑数据源名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.t_user.actual-data-nodes=ds_$->{0..1}.t_user_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.standard.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.t_user.table-strategy.standard.sharding-algorithm-name=user-table-strategy-inline
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.t_user_detail.actual-data-nodes=ds_$->{0..1}.t_user_detail_$->{0..1}
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.t_user_detail.table-strategy.standard.sharding-column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.t_user_detail.table-strategy.standard.sharding-algorithm-name=user-detail-table-strategy-inline
# 数据加密配置
# t_user使用分片规则配置的逻辑表名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.tables.t_user.columns.username.cipher-column=username
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.tables.t_user.columns.username.encryptor-name=name-encryptor
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.tables.t_user.columns.pwd.cipher-column=pwd
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.tables.t_user.columns.pwd.encryptor-name=pwd-encryptor
# 数据加密算法配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.encryptors.name-encryptor.type=AES
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.encryptors.name-encryptor.props.aes-key-value=123456abc
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.encryptors.pwd-encryptor.type=AES
spring.shardingsphere.rules.encrypt.encryptors.pwd-encryptor.props.aes-key-value=123456abc
# 分布式主键生成配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generate-strategy.column=user_id
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.tables.t_user.key-generate-strategy.key-generator-name=snowflake
# 分片算法配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.sharding-algorithms.default-database-strategy-inline.type=INLINE
# 表达式ds_$->{user_id % 2}枚举的数据源为读写分离配置的逻辑数据源名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.sharding-algorithms.default-database-strategy-inline.algorithm-expression=ds_$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.sharding-algorithms.user-table-strategy-inline.type=INLINE
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.sharding-algorithms.user-table-strategy-inline.algorithm-expression=t_user_$->{user_id % 2}
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.sharding-algorithms.user-detail-table-strategy-inline.type=INLINE
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.sharding-algorithms.user-detail-table-strategy-inline.algorithm-expression=t_user_detail_$->{user_id % 2}
# 分布式序列算法配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.sharding.key-generators.snowflake.type=SNOWFLAKE
# 读写分离策略配置
# ds_0,ds_1 为读写分离配置的逻辑数据源名称
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.ds_0.type=Static
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.ds_0.props.write-data-source-name=write-ds0
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.ds_0.props.read-data-source-names=write-ds0-read0,write-ds0-read1
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.ds_0.load-balancer-name=read-random
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.ds_1.type=Static
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.ds_1.props.write-data-source-name=write-ds1
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.ds_1.props.read-data-source-names=write-ds1-read0,write-ds1-read1
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.data-sources.ds_1.load-balancer-name=read-random
# 负载均衡算法配置
spring.shardingsphere.rules.readwrite-splitting.load-balancers.read-random.type=RANDOM
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: ds_1
ds_1:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1
username: root
password: 1024
rules:
sharding:
tables:
user:
actual-data-nodes: ds_1.user_$->{0..1}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: user-table-strategy-inline
default-table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-algorithm-name:
user-table-strategy-inline:
type: INLINE
algorithm-expression: user_$->{id % 2}
props:
sql-show: true
属性配置
| 名称 | 数据类型 | 说明 | 默认值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| sql-show (?) | boolean | 是否在日志中打印 SQL 打印 SQL 可以帮助开发者快速定位系统问题。日志内容包含:逻辑 SQL,真实 SQL 和 SQL 解析结果。 如果开启配置,日志将使用 Topic ShardingSphere-SQL,日志级别是 INFO | false |
| sql-simple (?) | boolean | 是否在日志中打印简单风格的 SQL | false |
| kernel-executor-size (?) | int | 用于设置任务处理线程池的大小每个ShardingSphereDataSource 使用一个独立的线程池,同一个 JVM 的不同数据源不共享线程池 | infinite |
| max-connections-size-per-query (?) | int | 一次查询请求在每个数据库实例中所能使用的最大连接数 | 1 |
| check-table-metadata-enabled (?) | boolean | 在程序启动和更新时,是否检查分片元数据的结构一致性 | false |
| check-duplicate-table-enabled (?) | boolean | 在程序启动和更新时,是否检查重复表 | false |
| sql-federation-enabled (?) | boolean | 是否开启联邦查询 | false |
##ShardingSphere-Proxy
不能插入数据的原因就是配置错误
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: ds_0,ds_1
ds_0:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1
username: root
password: 1024
ds_1:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://106.15.234.93:3306/ds_1? serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8 #数据库配置一样了
username: root
password: 1024
rules:
sharding:
tables:
user:
actual-data-nodes: ds_$->{0..1}.user_$->{0..1}
database-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: database-strategy
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: user-table
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: snowflake
sharding-algorithms:
database-strategy:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: ds_$->{id % 2}
user-table:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: user_$->{id % 2}
props:
sql-show: true
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: ds_0,ds_1
ds_0:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1
username: root
password: 1024
ds_1:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://106.15.234.93:3306/ds_1?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: 1024
rules:
sharding:
default-database-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: default-database-strategy-inline
tables:
user:
actual-data-nodes: logic_1.user_$->{0..1}
database-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: database-strategy
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: user-table
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: snowflake
sharding-algorithms: #缩进
database-strategy:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: logic_1
user-table:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: user_$->{id % 2}
default-database-strategy-inline:
type: INLINE
algorithm-expression: ds_$->{id % 2}
key-generators:
snowflake:
type: SNOWFLAKE
readwrite-splitting:
data-sources:
logic_1:
type: Static
props:
write-data-source-name: ds_0
read-data-source-names: ds_1
props:
sql-show: true
能插入数据
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: m1,m2
m1:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1?useSSL=false&autoReconnect=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: 1024
m2:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.cj.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_2?useSSL=false&autoReconnect=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: 1024
rules:
sharding:
tables:
user:
actual-data-nodes: m1.user_$->{0..1}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: user_inline
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: snowflake
key-generators:
snowflake:
type: SNOWFLAKE
sharding-algorithms:
user_inline:
type: inline
props:
algorithm-expression: user_$->{id % 2}
props:
sql-show: true
mybatis:
type-aliases-package: com.study.pojo
mapper-locations: classpath:com/study/mapper/*.xml
修改成功,同样的配置无法成功的原因是分片算法配置和逻辑表在同一级别。
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: ds_1,ds_2
ds_1:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1
username: root
password: 1024
ds_2:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driver-class-name: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_2?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: 1024
rules:
sharding:
tables:
user:
actual-data-nodes: ds_1.user_$->{0..1}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: user_sharding_algorithm
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: user_id_snowflake
sharding-algorithms:
user_sharding_algorithm:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: user_$->{id % 2}
key-generators:
user_id_snowflake:
type: SNOWFLAKE
props:
sql-show: true
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:com/study/mapper/*.mapper
type-aliases-package: com.study.pojo
spring:
shardingsphere:
datasource:
names: ds_0,ds_1
ds_0:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/ds_1
username: root
password: 1024
ds_1:
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
driverClassName: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
url: jdbc:mysql://106.15.234.93:3306/ds_1?serverTimezone=GMT%2b8&useSSL=false&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=UTF-8
username: root
password: 1024
rules:
sharding:
tables:
user:
actual-data-nodes: ds_0.user_$->{0..1}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: id
sharding-algorithm-name: user_sharding_algorithm
key-generate-strategy:
column: id
key-generator-name: user_id_snowflake
order:
actual-data-nodes: ds_1.order_$->{0..1}
table-strategy:
standard:
sharding-column: order_id
sharding-algorithm-name: order_sharding_algorithm
key-generate-strategy:
column: order_id
key-generator-name: order_id_snowflake
sharding-algorithms:
user_sharding_algorithm:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: user_$->{id % 2}
order_sharding_algorithm:
type: INLINE
props:
algorithm-expression: order_$->{order_id % 2}
key-generators:
user_id_snowflake:
type: SNOWFLAKE
order_id_snowflake:
type: SNOWFLAKE
readwrite-splitting:
data-sources:
logic_1:
type: Static
props:
write-data-source-name: ds_0,ds_1
read-data-source-names: ds_0,ds_1
props:
sql-show: true
mybatis:
mapper-locations: classpath:com/study/mapper/*.mapper
type-aliases-package: com.study.pojo
出现的问题
- actual-data-nodes: ds_KaTeX parse error: Expected group after '_' at position 14: ->{0..1}.user_̲->{0…1}.写成了,Invalid format for actual data nodes: ‘ds_0’;
- 配置无法成功的原因是分片算法配置和逻辑表在同一级别,yaml配置错误
- 不能修改分片库和分片表的列的属性。Can not update sharding key since the updated value will change user’s data nodes.
- 无法加载配置文件,Type is required见 https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_47748878/article/details/126821338