目录
一、Starter机制
1.1 什么是 SpringBoot Starter
1.2 SpringBoot Starter 的作用
1.3 Starter的应用场景
二、案例
2.1 模拟短信发送模版
2.2 AOP实现日志切面模版
一、Starter机制
1.1 什么是 SpringBoot Starter
Spring Boot Starter是Spring Boot框架提供的一种便利机制,用于简化项目的依赖管理和配置。它是一组预定义的依赖项和配置的集合,可以通过添加相应的Starter来快速引入和配置特定的功能或技术栈。
Spring Boot Starter的命名通常遵循一种约定,即以
spring-boot-starter-为前缀,后跟具体的功能或技术名称。例如:
spring-boot-starter-web: 用于构建Web应用程序的Starter。spring-boot-starter-data-jpa: 集成Spring Data JPA,简化对数据库的访问。spring-boot-starter-security: 集成Spring Security,提供安全认证和授权功能。spring-boot-starter-test: 用于编写测试的Starter。
1.2 SpringBoot Starter 的作用
在我们的日常开发工作中,可能会需要开发一个通用模块,以供其它工程复用。SpringBoot就为我们提供这样的功能机制,我们可以把我们的通用模块封装成一个个starter,这样其它工程复用的时候只需要在pom中引用依赖即可,由SpringBoot为我们完成自动装配, 简直不要太爽。
SpringBoot会自动通过classpath路径下的类发现需要的Bean,并注册进IOC容器。SpringBoot提供了针对日常企业应用研发各种场景的spring-boot-starter依赖模块。
所有这些依赖模块都遵循着约定的默认配置,并允许我们调整这些配置,即遵循“约定大于配置”的理念。
1.3 Starter的应用场景
1)通用模块-短信发送模块
2)基于AOP技术实现日志切面
3)分布式雪花ID,Long转String,解决精度问题
4)微服务项目的数据库连接池配置
5)微服务项目的每个模块都要访问redis数据库,每个模块都要配置redisTemplate
1、spring-boot-starter-web:
- 应用场景: 用于构建Web应用程序,包括RESTful API的开发。
- 依赖: 包括Spring MVC、嵌入式Servlet容器(如Tomcat)、JSON处理器等。
2、spring-boot-starter-data-jpa:
- 应用场景: 用于使用Spring Data JPA进行持久化操作,简化数据库访问。
- 依赖: 包括Hibernate、Spring Data JPA、数据源等。
3、spring-boot-starter-security:
- 应用场景: 提供身份验证和授权功能,用于保护应用程序的安全性。
- 依赖: 包括Spring Security、密码加密工具、身份验证和授权相关的依赖项。
4、spring-boot-starter-thymeleaf:
- 应用场景: 用于构建使用Thymeleaf模板引擎的Web应用程序。
- 依赖: 包括Thymeleaf、Spring Web等。
5、spring-boot-starter-data-rest:
- 应用场景: 用于构建RESTful API,自动将JPA实体暴露为REST资源。
- 依赖: 包括Spring Data REST、Spring MVC等。
6、spring-boot-starter-test:
- 应用场景: 用于编写单元测试和集成测试。
- 依赖: 包括JUnit、Spring Test等。
7、spring-boot-starter-amqp:
- 应用场景: 用于与消息队列(如RabbitMQ)进行集成。
- 依赖: 包括Spring AMQP、RabbitMQ客户端等。
8、spring-boot-starter-batch:
- 应用场景: 用于构建批处理作业。
- 依赖: 包括Spring Batch、数据库驱动等。
9、spring-boot-starter-data-redis:
- 应用场景: 用于与Redis进行集成。
- 依赖: 包括Spring Data Redis、Jedis等。
10、spring-boot-starter-log4j2:
- 应用场景: 使用Log4j2进行日志记录。
- 依赖: 包括Log4j2、Logback等。
二、案例
2.1 模拟短信发送模版
1、引入pom依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>2、创建配置类Properties
package com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/**
* 短信服务配置类
*
* @author 云村小威
* @create 2023-12-14 19:09
*/
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "sms")
public class SmsProperties {
private String accessKeyId;//访问ID、即帐号
private String accessKeySecret;//访问凭证,即密码
private String enable; //启动开关
}
@ConfigurationProperties 注解是Spring Boot中用于绑定配置属性的注解。它的主要作用是将配置文件中的属性值绑定到Java对象的属性上,使得可以通过这些Java对象方便地访问配置属性。
在上述示例中,
SmsProperties类使用了@ConfigurationProperties注解,并指定了prefix属性为"sms"。这意味着配置文件中以sms为前缀的属性值会被绑定到SmsProperties类的对应属性上。例如,如果配置文件中有sms.accessKeyId=My Application和sms.accessKeySecret=123,那么这两个值就会被绑定到accessKeyId和accessKeySecret属性上。.yml:
3、编写短信业务功能
ISmsService:
package com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.service;
public interface ISmsService {
/**
* 发送短信
* @param phone 要发送的手机号
* @param data 要发送的内容
*/
void send(String phone, String data);
}
SmsServiceImpl:
package com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.service;
import com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.SmsProperties;
public class SmsServiceImpl implements ISmsService {
private SmsProperties smsProperties;
public SmsServiceImpl(SmsProperties smsProperties) {
this.smsProperties = smsProperties;
}
@Override
public void send(String phone, String data) {
String key = smsProperties.getAccessKeyId();
String secret = smsProperties.getAccessKeySecret();
System.out.println("接入短信系统,Key=" + key + ",Secret=" + secret);
System.out.println("短信发送,phone=" + phone + "data=" + data);
}
}
这里不用@Service注解交给spring管理的原因是我们需要自定义(如:smss.enable)动态调用该类。
4、创建自动配置类
package com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart;
import com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.service.ISmsService;
import com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.service.SmsServiceImpl;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
/**
* @author 云村小威
* @create 2023-12-14 19:21
*/
@Configuration
//开启配置加载
@EnableConfigurationProperties({SmsProperties.class})
//添加一个条件 sms.enable
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "sms",name = "enable",havingValue = "true")
public class SmsConfig {
//控制当前的service是否加载到spring里面去
@Autowired
private SmsProperties smsProperties;
@Bean
public ISmsService smsService(){
return new SmsServiceImpl(smsProperties);
}
}
这是一个 Spring Boot 的配置类,它负责配置与短信服务相关的 bean,并且通过条件判断 (@ConditionalOnProperty) 控制是否加载这些配置。
解析:
-
@Configuration: 这个注解表示这是一个配置类,用于定义和配置 Spring Bean。 -
@EnableConfigurationProperties({SmsProperties.class}): 这个注解用于开启对SmsProperties类的配置属性的支持。SmsProperties类是一个用于封装短信服务的配置属性的类,通过这个注解,Spring Boot 会自动注入这些属性。-
@ConditionalOnProperty: 这个注解用于在满足指定条件的情况下才加载这个配置类。在这里,它的条件是sms.enable属性的值必须为 "true",即只有当配置文件中的sms.enable=true时,这个配置类才会生效。
-
-
@Autowired注解:表示要自动注入SmsProperties类型的 bean。这个 bean 是通过@EnableConfigurationProperties开启的配置属性注入。 -
@Bean public ISmsService smsService() {...}: 这个方法定义了一个名为smsService的 Bean,并且返回了一个ISmsService的实例,通常是SmsServiceImpl。这个方法使用了@Bean注解,表示这是一个 Spring Bean 的定义。
5、编写spring.factories文件加载自动配置类
在resources下新建META-INF文件夹,然后创建spring.factories文件;

在该文件中加入如下配置,该配置指定上步骤中定义的配置类为自动装配的配置:
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.SmsConfig6、打包安装
打开Maven插件执行 install 命令;
可在配置的maven仓库中查看该项目同包名的目录下找到该依赖
7、在其它项目引用并测试
一、引入依赖
<!--模拟短信验证启动器-->
<dependency>
<!--属下包名-->
<groupId>com.ycxw</groupId>
<!--项目名-->
<artifactId>smsspringbootstart</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
</dependency>该属性值参考编写的机制模块pom:
二、配置application.yml
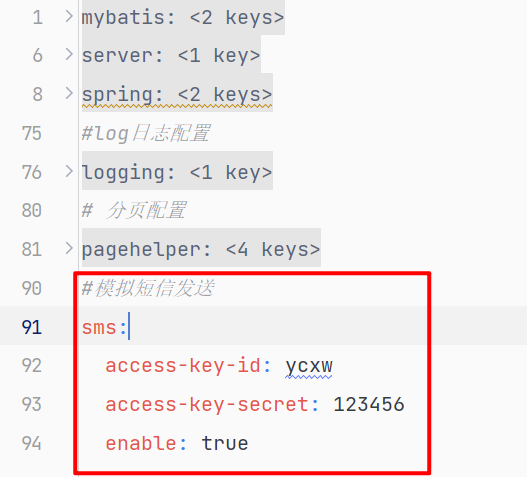
enable: true 表示请用该模块,false则不启:
三、测试类测试
package com.ycxw.boot;
import com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.service.ISmsService;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
@SpringBootTest
class BootApplicationTests {
@Autowired
private ISmsService smsService;
@Test
void contextLoads() {
smsService.send("17883838312","hello");
}
}
运行结果:

2.2 AOP实现日志切面模版
1、编写日志启动类
package com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.properties;
import lombok.Data;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.ConfigurationProperties;
/**
* 日志启动配置类
*
* @author 云村小威
* @create 2023-12-14 19:09
*/
@Data
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "weblog")
public class WebLogProperties {
private boolean enabled;
public WebLogProperties() {
}
}
2、编写日志切面
package com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.config;
import lombok.extern.slf4j.Slf4j;
import org.aspectj.lang.JoinPoint;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.AfterReturning;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Aspect;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Before;
import org.aspectj.lang.annotation.Pointcut;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.RequestContextHolder;
import org.springframework.web.context.request.ServletRequestAttributes;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import java.util.Arrays;
@Aspect
@Component
@Slf4j
public class WebLogAspect {
//定义切入点匹配所有以 "Controller" 结尾的类中的所有方法
@Pointcut("execution(* *..*Controller.*(..))")
public void webLog() {
}
@Before("webLog()")
public void doBefore(JoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
// 接收到请求,记录请求内容
ServletRequestAttributes attributes = (ServletRequestAttributes) RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes();
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest();
// 记录当前请求内容
log.info("开始服务:{}", request.getRequestURL().toString());
log.info("客户端IP :{}", request.getRemoteAddr());
log.info("参数值 :{}", Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
/*在切入点返回结果后执行的通知。记录返回值。*/
@AfterReturning(returning = "ret", pointcut = "webLog()")
public void doAfterReturning(Object ret) throws Throwable {
// 处理完请求,返回内容
log.info("返回值 : {}", ret);
}
}
@Aspect:该注解表明这是一个切面类,用于定义横切关注点(cross-cutting concerns),即在应用程序中横跨多个模块的共享行为。
@Component:将这个切面类标记为Spring的组件,以便Spring容器能够自动扫描并注册它。
@Slf4j:Lombok 提供的注解,用于自动生成日志变量log。
@Pointcut("execution(* *..*Controller.*(..))"):定义切入点,匹配所有以 "Controller" 结尾的类中的所有方法。这个切入点用于捕获Web层的所有请求。
@Before("webLog()"):在切入点之前执行的通知(Advice)。在方法执行前,记录请求相关的信息。
@AfterReturning(returning = "ret", pointcut = "webLog()"):在切入点返回结果后执行的通知。记录返回值。
ServletRequestAttributes:Spring提供的用于封装HTTP请求的对象,可以通过它获取请求相关的信息。
RequestContextHolder.getRequestAttributes():获取当前线程的RequestAttributes,这里是获取ServletRequestAttributes。
HttpServletRequest request = attributes.getRequest():获取当前请求的HttpServletRequest对象。
log.info("开始服务:{}", request.getRequestURL().toString()):记录请求的URL。
log.info("客户端IP :{}", request.getRemoteAddr()):记录客户端的IP地址。
log.info("参数值 :{}", Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs())):记录请求的方法参数值。
log.info("返回值 : {}", ret):记录请求处理完后的返回值。
这个切面类主要用于记录Web请求的一些关键信息,包括请求的URL、客户端IP、请求参数以及方法的返回值。这对于在开发和调试阶段更好地了解系统运行状态是很有帮助的。
3、创建自动配置类
package com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.config;
import com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.properties.WebLogProperties;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnMissingBean;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.condition.ConditionalOnProperty;
import org.springframework.boot.context.properties.EnableConfigurationProperties;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties({WebLogProperties.class})
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix = "weblog", value = "enabled")
public class WebLogConfig {
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean
public WebLogAspect webLogAspect() {
return new WebLogAspect();
}
}
该注解表示只有在容器中不存在名为
@ConditionalOnMissingBean:webLogAspect的Bean时,才会创建这个Bean。这样,如果用户已经定义了自己的WebLogAspectBean,这个自定义的 Bean 将不会被替换。这个方法返回一个
public WebLogAspect webLogAspect() {...}:WebLogAspect的实例,作为一个Bean注册到Spring容器中。如果满足了@ConditionalOnProperty和@ConditionalOnMissingBean的条件,这个Bean将被创建。
这个配置类的作用是在特定的配置条件下,创建一个 WebLogAspect 的Bean,并将其纳入Spring容器的管理。通过条件注解,可以在特定的配置条件下控制Bean的创建和生效。
4、添加spring.factories文件加载自动配置类
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.SmsConfig,\com.ycxw.smsspringbootstart.config.WebLogConfig5、在其他项目中导入该模块依赖
方法同上案例👆
6、编写 .yml 启动配置

7、运行项目调用Controller层方法接口测试

将weblog配置下的enabled属性设为 false 则不在记录请求日志信息



![[Linux] LVS负载均衡群集+NAT部署](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/a460580f32f542acac50a370124c46e4.png)