又开始搞点云了,现在用的是Intel的realsense。
看网上步骤都挺繁琐的,本文搭建只需要5分钟。直接用官方提供的属性表,不用自行添加任何包含目录、库目录。
第一分钟:用Visual Studio新建一个工程(此时你是没有intel.realsense.props的,往后看)
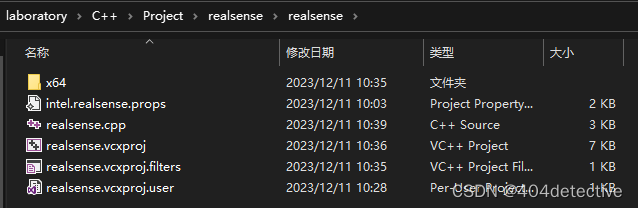
第二分钟:把默认安装目录添加系统变量
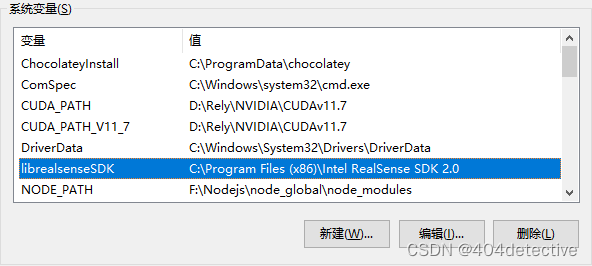
第三分钟:进入目录找到该目录下的intel.realsense.props文件,进行如下修改,放到你刚才建的工程里。
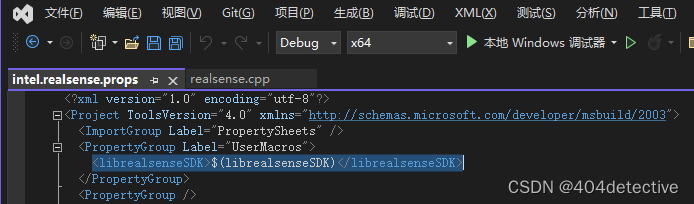
第四分钟:
打开工程,添加现有属性表,也就是添加刚才你弄得intel.realsense.props这个文件。
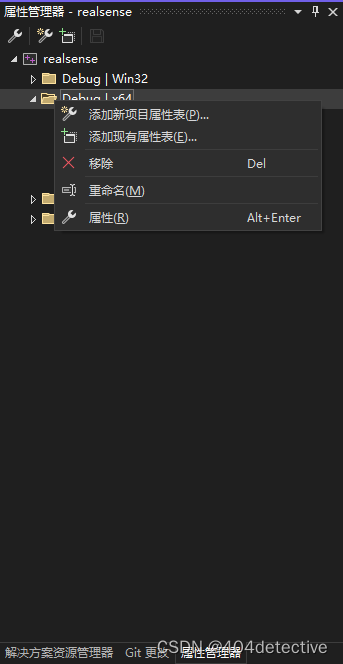
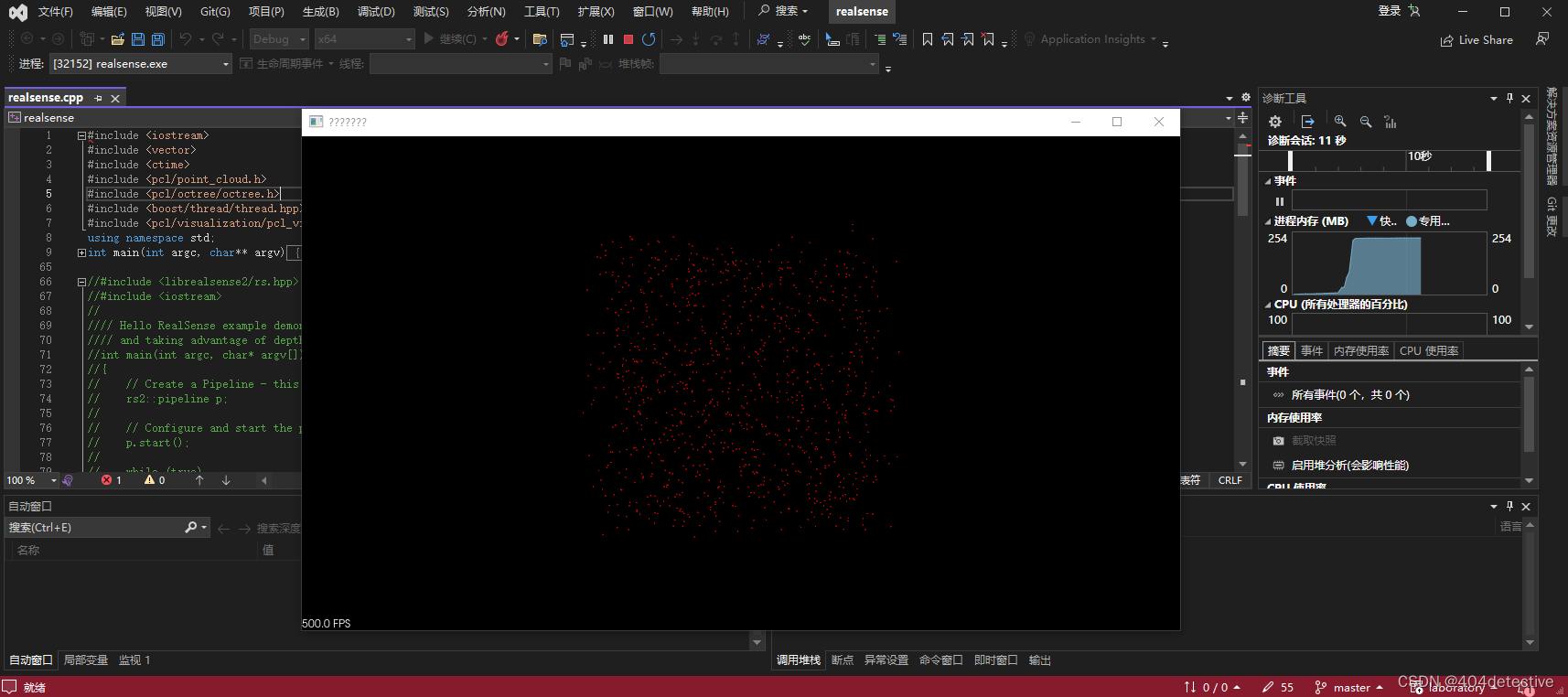
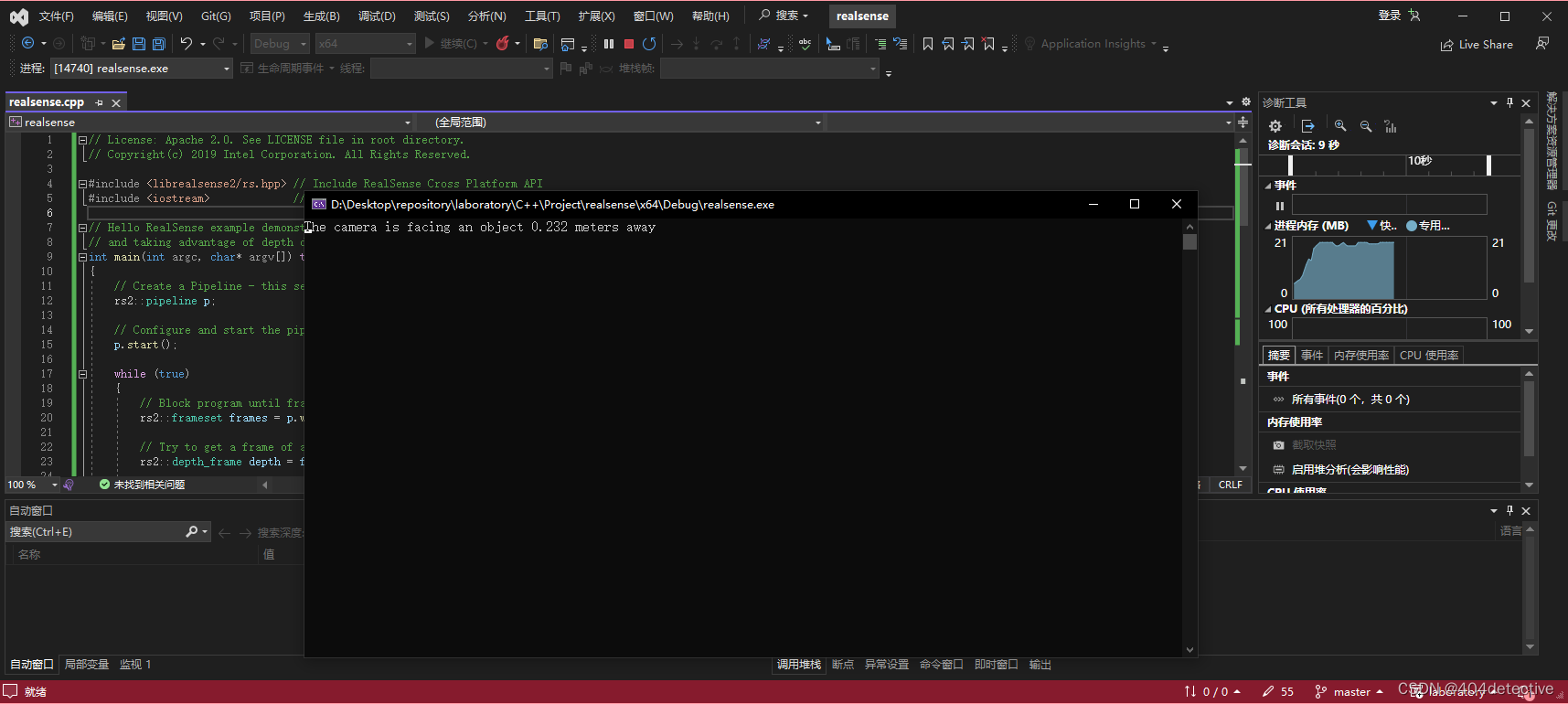
第五分钟:已经结束了。跑个官方例程看看。
#include <librealsense2/rs.hpp> // Include RealSense Cross Platform API
#include <iostream> // for cout
// Hello RealSense example demonstrates the basics of connecting to a RealSense device
// and taking advantage of depth data
int main(int argc, char* argv[]) try
{
// Create a Pipeline - this serves as a top-level API for streaming and processing frames
rs2::pipeline p;
// Configure and start the pipeline
p.start();
while (true)
{
// Block program until frames arrive
rs2::frameset frames = p.wait_for_frames();
// Try to get a frame of a depth image
rs2::depth_frame depth = frames.get_depth_frame();
// Get the depth frame's dimensions
auto width = depth.get_width();
auto height = depth.get_height();
// Query the distance from the camera to the object in the center of the image
float dist_to_center = depth.get_distance(width / 2, height / 2);
// Print the distance
std::cout << "The camera is facing an object " << dist_to_center << " meters away \r";
}
return EXIT_SUCCESS;
}
catch (const rs2::error& e)
{
std::cerr << "RealSense error calling " << e.get_failed_function() << "(" << e.get_failed_args() << "):\n " << e.what() << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
catch (const std::exception& e)
{
std::cerr << e.what() << std::endl;
return EXIT_FAILURE;
}
显示中心点到相机的深度距离
1.13.1版本点云库配合VS2022的配置请看另一篇