一、前言 / INTRODUCTION
本篇文章我们再来看下如何在Selenium中使用缓存
页面对象模型是UI自动化测试中的一种很好的设计模式,我们使用@FindBy和@FindAll注释来标记Page Object中的WebElement。
本次要讲的@CacheLookup是一个非常重要但被忽视的注释,它可以帮助我们使测试运行得更快。
在Selenium中,CacheLookup是一个注解,用于标记页面对象模型(Page Object Model)中的元素。当使用CacheLookup注解时,Selenium会在第一次查找元素时将其缓存起来,以便后续的查找操作可以直接使用缓存的元素,而不需要再次查找页面上的元素。
二、举个常规的例子 / EXAMPLE

首先让我们了解一下Selenium在PageObject模型中什么时候调用FindElement。每当使用页面对象中的WebElement执行某些操作时,都会触发FindElement从网页中查找WebElement的最新版本。这个查找基本上是一个FindElement REST请求到浏览器的Web驱动程序。这个查找是代码中最耗时的部分之一。
我们用Page Object模式来创建一个demo
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.How;
/**
* 类说明:PO
*/
public class TesterRoadPO {
@FindBy(how = How.NAME, using = "firstname")
public WebElement firsName;
@FindBy(how = How.NAME, using = "lastname")
public WebElement lastName;
}
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.PageFactory;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
/**
* 类说明:demo
*/
public class TesterRoadDemo {
@Test
public void testerRoadDemo() {
ChromeOptions chromeOptions = new ChromeOptions();
chromeOptions.addArguments("--remote-allow-origins=*");
// 为了理解使用PageObjects对web元素的操作是如何工作的,
// 我们将保存chrome驱动的所有日志。下面的语句对我们有所帮助
// 将所有日志保存在名为TesterRoadLog.txt的文件中
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.logfile", "src/main/resources/TesterRoadLog.txt");
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(chromeOptions);
driver.get("http://127.0.0.1:8080/");
// 初始化Page object
TesterRoadPO pageObject = PageFactory.initElements(driver, TesterRoadPO.class);
pageObject.firsName.sendKeys("Road");
pageObject.lastName.sendKeys("Tester");
pageObject.firsName.getText();
pageObject.lastName.getText();
driver.close();
driver.quit();
}
}
在上述代码中,调用了四次FindBy,查找元素和获取文本,我们来看下日志文件
[12.654][INFO]: COMMAND FindElement {
"using": "name",
"value": "firstname"
}
[12.654][INFO]: Waiting for pending navigations...
[12.717][INFO]: Done waiting for pending navigations. Status: ok
[12.851][INFO]: Waiting for pending navigations...
[12.854][INFO]: Done waiting for pending navigations. Status: ok
[12.854][INFO]: RESPONSE FindElement {
"ELEMENT": "0.8984444413515806-1"
}
[12.860][INFO]: COMMAND TypeElement {
"id": "0.8984444413515806-1",
"value": [ "Road" ]
}
[12.860][INFO]: Waiting for pending navigations...
[12.861][INFO]: Done waiting for pending navigations. Status: ok
[13.045][INFO]: Waiting for pending navigations...
[13.050][INFO]: Done waiting for pending navigations. Status: ok
[13.050][INFO]: RESPONSE TypeElement
[13.053][INFO]: COMMAND FindElement {
"using": "name",
"value": "lastname"
}
[13.053][INFO]: Waiting for pending navigations...
[13.054][INFO]: Done waiting for pending navigations. Status: ok
[13.074][INFO]: Waiting for pending navigations...
[13.082][INFO]: Done waiting for pending navigations. Status: ok
[13.082][INFO]: RESPONSE FindElement {
"ELEMENT": "0.8984444413515806-2"
}
[13.086][INFO]: COMMAND TypeElement {
"id": "0.8984444413515806-2",
"value": [ "Tester" ]
}
在日志中,我们可以看到对于每个语句都有对FindElement和TypeElement调用。对日志文件的进一步调查将显示,对于每个getText调用,都将有一个FindElement和GetElementText调用。
我们在WebElement上执行的每一个操作都会进行调用,那么无疑将会花费更多的时间。那么我们如何才能使的测试更快,花费更少的时间?
现在我也找了很多测试的朋友,做了一个分享技术的交流群,共享了很多我们收集的技术文档和视频教程。
如果你不想再体验自学时找不到资源,没人解答问题,坚持几天便放弃的感受
可以加入我们一起交流。而且还有很多在自动化,性能,安全,测试开发等等方面有一定建树的技术大牛
分享他们的经验,还会分享很多直播讲座和技术沙龙
可以免费学习!划重点!开源的!!!
qq群号:310357728【暗号:csdn999】
三、CacheLookup 注解/ @CacheLookup

@CacheLookup可以帮助我们控制何时缓存WebElement,何时不缓存。当这个注释应用于WebElement时,它会让Selenium保留WebElement的缓存,而不是每次都从网页中搜索WebElement。可以节省大量的时间。
import org.openqa.selenium.WebElement;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.CacheLookup;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.FindBy;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.How;
/**
* 类说明:PO中使用CacheLookup缓存元素
*/
public class TesterRoadPO {
@FindBy(how = How.NAME, using = "firstname")
public WebElement firsName;
@FindBy(how = How.NAME, using = "firstname")
@CacheLookup
public WebElement firsNameCached;
}
import io.github.bonigarcia.wdm.WebDriverManager;
import org.openqa.selenium.WebDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeDriver;
import org.openqa.selenium.chrome.ChromeOptions;
import org.openqa.selenium.support.PageFactory;
import org.testng.annotations.Test;
/**
* 类说明:未使用CacheLookup和使用CacheLookup对比
*/
public class TesterRoadDemo {
@Test
public void testerRoadDemo() {
ChromeOptions chromeOptions = new ChromeOptions();
chromeOptions.addArguments("--remote-allow-origins=*");
// 为了理解使用PageObjects对web元素的操作是如何工作的,
// 我们将保存chrome驱动的所有日志。下面的语句对我们有所帮助
// 将所有日志保存在名为TesterRoadLog.txt的文件中
System.setProperty("webdriver.chrome.logfile", "src/main/resources/TesterRoadLog.txt");
WebDriverManager.chromedriver().setup();
WebDriver driver = new ChromeDriver(chromeOptions);
driver.get("http://127.0.0.1:8080/");
// 初始化Page object
TesterRoadPO pageObject = PageFactory.initElements(driver, TesterRoadPO.class);
pageObject.firsName.sendKeys("TesterRoad");
// 首先尝试从未缓存的WebElement获取文本。
// 查看执行1000个getText操作的时间
long withoutCacheStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
pageObject.firsName.getText();
}
long withoutCacheEndTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("未使用缓存花费的时间: " + ((withoutCacheEndTime - withoutCacheStartTime) / 1000));
// 现在我们在缓存的元素上重复同样的操作
// 查看执行相同操作1000次所需的时间
long withCacheStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
pageObject.firsNameCached.getText();
}
long withCacheEndTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("使用缓存花费的时间: " + ((withCacheEndTime - withCacheStartTime) / 1000));
driver.close();
driver.quit();
}
}
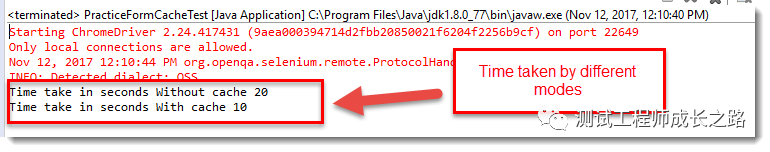
在输出中,我们可以清楚地看到,与非缓存版本相比,缓存版本的WebElement执行相同操作的时间减少了50%。
四、写在后面 / WRITE LATER

既然使用CacheLookup可以提高50%的效率,那么我们在项目中全部使用CacheLookup岂不美哉,NO,NO,NO,那到不尽然,比如像动态元素(像id之类,很多都是动态的)就不要使用CacheLookup了,我们要在合适的场景下去合理使用CacheLookup
END今天的分享就到此结束了,点赞关注不迷路!