目录
4.1 If函数语法格式
4.2 CASE WHEN 条件表达式格式
4.3 update与 case when
4.4 练习题1
4.5 练习题2
4.6 练习题3-行转列
4.7 牛客练习题
4.8 LeetCode练习题
4.1 If函数语法格式
IF(expr1,expr2,expr3)解释:
如果表达式expr1=true(expr1 <> 0 and expr1 <> NULL),返回expr2,否则返回expr3,IF() 的返回值为数字值或字符串值,具体情况视其所在语境而定。
常用示例:
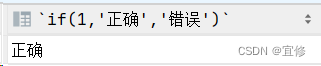
expr1参数为1,结果为真,返回正确
select if(1,'正确','错误');结果:
4.2 CASE WHEN 条件表达式格式
1. 格式1:简单case函数
**简单CASE函数**
CASE 条件参数名称
WHEN 参数值1 THEN '显示值1'
WHEN 参数值2 THEN '显示值2'
...
ELSE '显示其他值' END2. 格式2:case搜索函数
CASE WHEN condition THEN result
[WHEN...THEN...]
ELSE result
ENDcondition是一个返回布尔类型的表达式,
如果表达式返回true,则整个函数返回相应result的值,
如果表达式皆为false,则返回ElSE后result的值,
如果省略了ELSE子句,则返回NULL。
4.3 update与 case when
当我们有时候要更新 数据库中 同一个字段 根据不同情况更新不同的值,可以用
update Table set field = (case XX when XXXX then XXX
when xxxx then xxxxxx
else xxxx
end)4.4 练习题1
数据库
drop table if exists `students`;
create table students
(
stu_code varchar(10) null,
stu_name varchar(10) null,
stu_sex int null,
stu_score int null
);
# 其中stu_sex字段,0表示男生,1表示女生。
INSERT INTO students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) VALUES ('xm', '小明', 0, 88);
INSERT INTO students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) VALUES ('xl', '夏磊', 0, 55);
INSERT INTO students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) VALUES ('xf', '晓峰', 0, 45);
INSERT INTO students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) VALUES ('xh', '小红', 1, 89);
INSERT INTO students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) VALUES ('xn', '小妮', 1, 77);
INSERT INTO students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) VALUES ('xy', '小一', 1, 99);
INSERT INTO students (stu_code, stu_name, stu_sex, stu_score) VALUES ('xs', '小时', 1, 45);
场景1-不同状态下展示为不同的值
题目:
现在学校想要根据学生分数(stu_score)划分等级,score<60返回不及格,score>=60返回及格,score>=80返回优秀。请返回学生的分数(stu_score)和等级(score_cut)
根据示例,你的查询应返回以下结果:
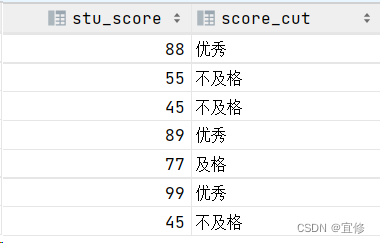
SQL代码:
select stu_score,
case when stu_score<60 then '不及格'
when stu_score>=60 and stu_score<80 then '及格'
when stu_score>=80 then '优秀'
end as 'score_cut'
from students;场景2- 统计不同状态下的值
现老师要统计班中,有多少男同学,多少女同学,并统计男同学中有几人及格,女同学中有几人及格,要求用一个SQL输出结果。其中stu_sex字段,0表示男生,1表示女生。
根据示例,你的查询应返回以下结果:
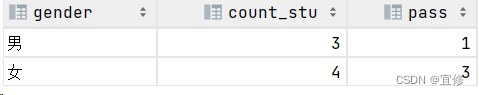
select case when stu_sex=0 then '男'
when stu_sex=1 then '女'
end 'gender',
count(*) as 'count_stu',
sum(if(stu_score>=60,1,0)) as 'pass'
from students
group by gender;场景3- update与case when相结合
请你编写一个解决方案来交换所有的 '男' 和 '女' (即,将所有 '女' 变为 '男' ,反之亦然),仅使用 单个 update 语句 ,且不产生中间临时表。其中stu_sex字段,0表示男生,1表示女生。
注意,你必须仅使用一条 update 语句,且 不能 使用 select 语句。
根据示例,你的查询应返回以下结果:

update students set stu_sex=(case stu_sex when 0 then 1
when 1 then 0
end);4.5 练习题2
数据库
drop table if exists `energy_test`;
drop table if exists `p_price`;
-- auto-generated definition
create table energy_test
(
e_code varchar(2) null,
e_value decimal(5, 2) null,
e_type int null
);
# 其中,E_TYPE表示能耗类型,0表示水耗,1表示电耗,2表示热耗
INSERT INTO energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) VALUES ('北京', 28.50, 0);
INSERT INTO energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) VALUES ('北京', 23.50, 1);
INSERT INTO energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) VALUES ('北京', 28.12, 2);
INSERT INTO energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) VALUES ('北京', 12.30, 0);
INSERT INTO energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) VALUES ('北京', 15.46, 1);
INSERT INTO energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) VALUES ('上海', 18.88, 0);
INSERT INTO energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) VALUES ('上海', 16.66, 1);
INSERT INTO energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) VALUES ('上海', 19.99, 0);
INSERT INTO energy_test (e_code, e_value, e_type) VALUES ('上海', 10.05, 0);
-- auto-generated definition
create table p_price
(
p_price decimal(5, 2) null comment '价格',
p_level int null comment '等级',
p_limit int null comment '阈值'
)
comment '电能耗单价表';
INSERT INTO p_price (p_price, p_level, p_limit) VALUES (1.20, 0, 10);
INSERT INTO p_price (p_price, p_level, p_limit) VALUES (1.70, 1, 30);
INSERT INTO p_price (p_price, p_level, p_limit) VALUES (2.50, 2, 50);
energy_test
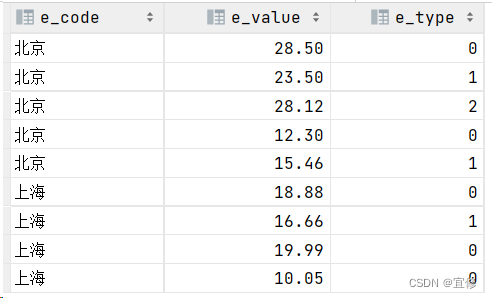
p_price

场景1 - 配合聚合函数做统计
现要求统计各个城市,总共使用了多少水耗、电耗、热耗,使用一条SQL语句输出结果 有能耗表如下:其中,E_TYPE表示能耗类型,0表示水耗,1表示电耗,2表示热耗
根据示例,你的查询应返回以下结果:
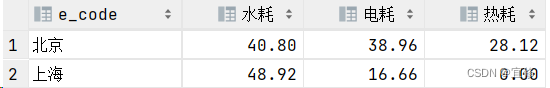
select e_code,
sum(if(e_type=0,e_value,0)) as '水耗',
sum(if(e_type=1,e_value,0)) as '电耗',
sum(if(e_type=2,e_value,0)) as '热耗'
from energy_test
group by e_code;场景2-使用子查询
根据城市用电量多少,计算用电成本。假设电能耗单价分为三档,根据不同的能耗值,使用相应价格计算成本。 P_limit为每个档次的上限。当能耗值(e_value)小于10时,使用P_LEVEL=0时的P_PRICE的值,能耗值大于10小于30使用P_LEVEL=1时的P_PRICE的值…
根据示例,你的查询应返回以下结果:

select e_code,
e_value,
case when e_value<(select p_limit from p_price where p_level=0) then (select p_price from p_price where p_level=0)
when e_value>=(select p_limit from p_price where p_level=0) and e_value<(select p_limit from p_price where p_level=1) then (select p_price from p_price where p_level=1)
when e_value>=(select p_limit from p_price where p_level=1) then (select p_price from p_price where p_level=2)
end as 'price'
from energy_test
where e_type=1;4.6 练习题3-行转列
数据库
drop table if exists `user_col_comments`;
-- auto-generated definition
create table user_col_comments
(
column_name varchar(50) null comment '列名',
comment varchar(100) null comment '列的备注'
);
INSERT INTO user_col_comments (column_name, comment) VALUES ('SHI_SHI_CODE', '设施编号');
INSERT INTO user_col_comments (column_name, comment) VALUES ('SHUI_HAO', '水耗');
INSERT INTO user_col_comments (column_name, comment) VALUES ('RE_HAO', '热耗');
INSERT INTO user_col_comments (column_name, comment) VALUES ('YAN_HAO', '盐耗');
INSERT INTO user_col_comments (column_name, comment) VALUES ('OTHER', '其他');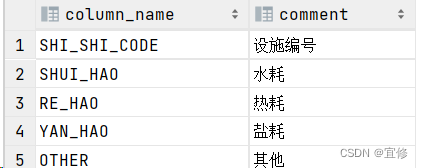
问题:将上表的行列进行转换显示
根据示例,你的查询应返回以下结果:

select max(if(column_name='SHI_SHI_CODE',comment,'')) as 'SHI_SHI_CODE',
max(if(column_name='YAN_HAO',comment,'')) as 'YAN_HAO',
max(if(column_name='RE_HAO',comment,'')) as 'RE_HAO',
max(if(column_name='SHUI_HAO',comment,'')) as 'SHUI_HAO',
max(if(column_name='OTHER',comment,'')) as 'OTHER'
from user_col_comments;4.7 牛客练习题
SQL26 - 计算25岁以上和以下的用户数量
4.8 LeetCode练习题
-
LeetCode_1873. 计算特殊奖金
-
LeetCode_627. 变更性别
-
LeetCode_608. 树节点
-
LeetCode_1393. 股票的资本损益