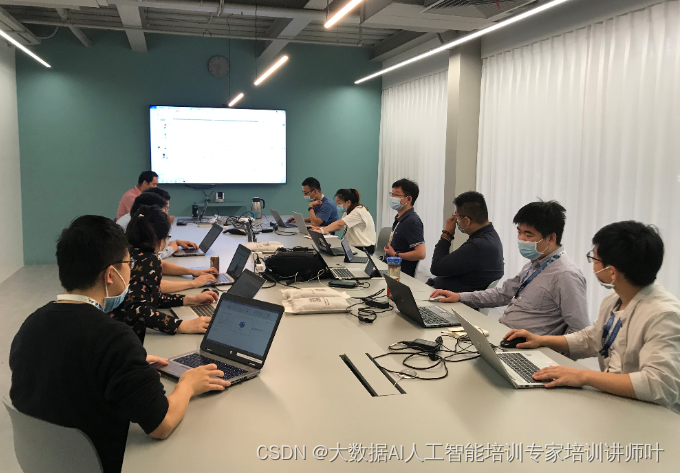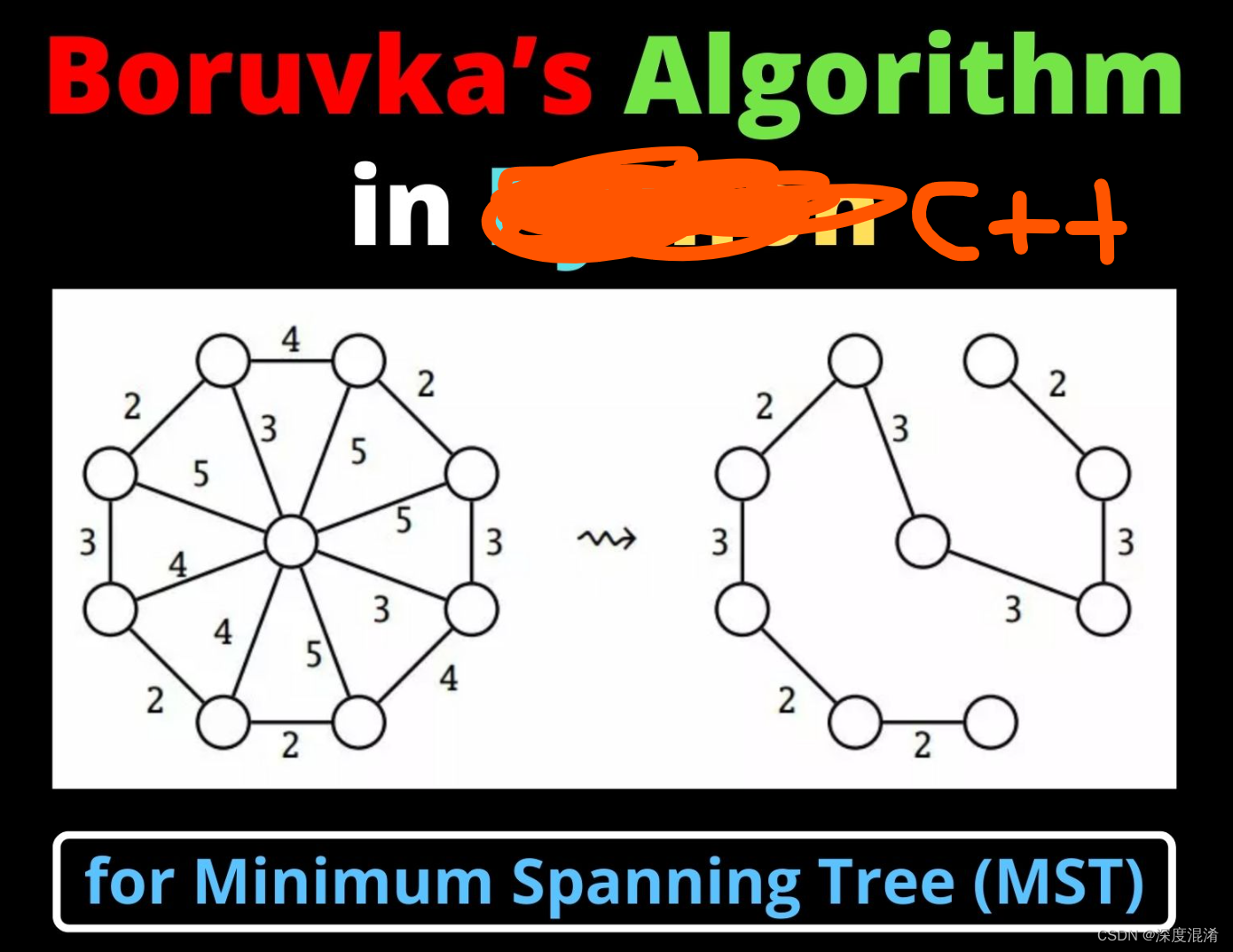
1 文本格式
// Boruvka's algorithm to find Minimum Spanning
// Tree of a given connected, undirected and
// weighted graph
#include <stdio.h>
// a structure to represent a weighted edge in graph
struct Edge
{
int src, dest, weight;
};
// a structure to represent a connected, undirected
// and weighted graph as a collection of edges.
struct Graph
{
// V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges
int V, E;
// graph is represented as an array of edges.
// Since the graph is undirected, the edge
// from src to dest is also edge from dest
// to src. Both are counted as 1 edge here.
Edge* edge;
};
// A structure to represent a subset for union-find
struct subset
{
int parent;
int rank;
};
// Function prototypes for union-find (These functions are defined
// after boruvkaMST() )
int find(struct subset subsets[], int i);
void Union(struct subset subsets[], int x, int y);
// The main function for MST using Boruvka's algorithm
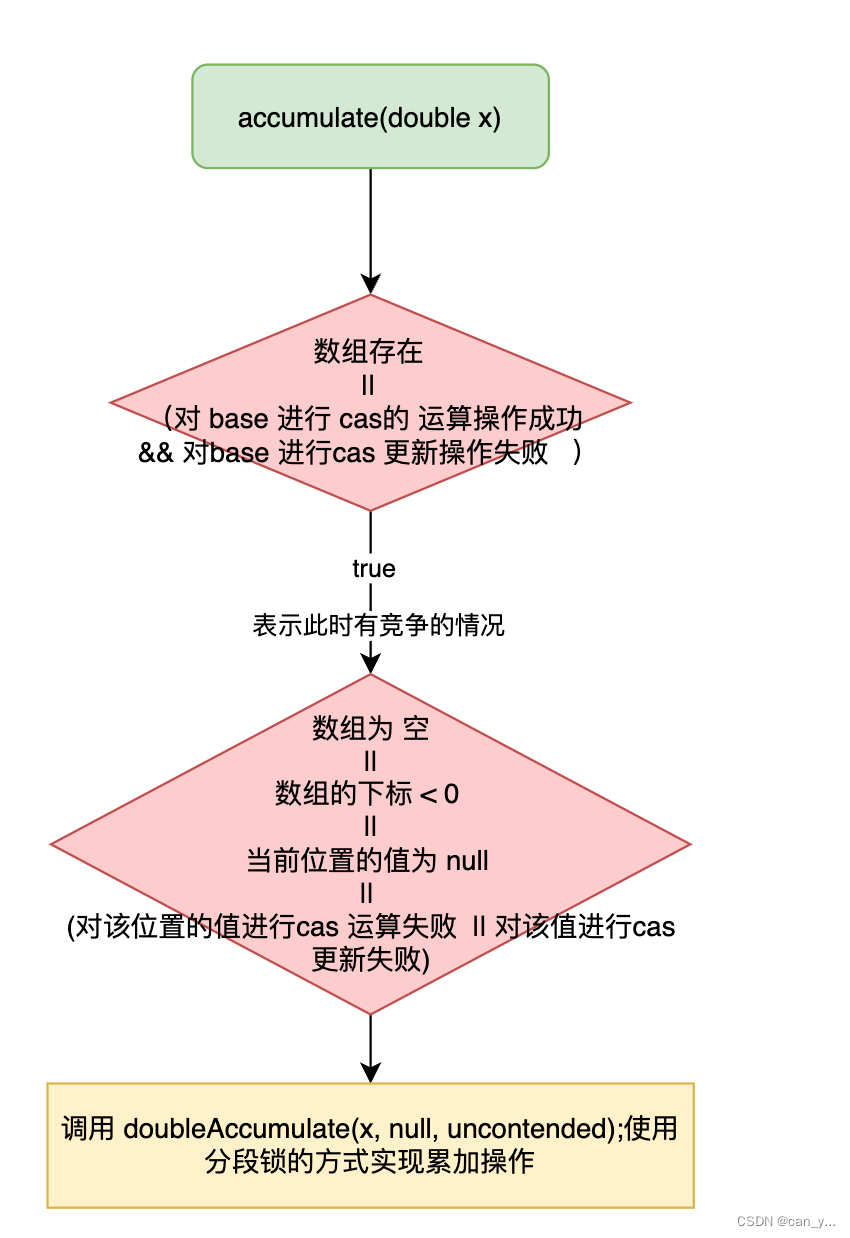
void boruvkaMST(struct Graph* graph)
{
// Get data of given graph
int V = graph->V, E = graph->E;
Edge *edge = graph->edge;
// Allocate memory for creating V subsets.
struct subset *subsets = new subset[V];
// An array to store index of the cheapest edge of
// subset. The stored index for indexing array 'edge[]'
int *cheapest = new int[V];
// Create V subsets with single elements
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
cheapest[v] = -1;
}
// Initially there are V different trees.
// Finally there will be one tree that will be MST
int numTrees = V;
int MSTweight = 0;
// Keep combining components (or sets) until all
// compnentes are not combined into single MST.
while (numTrees > 1)
{
// Everytime initialize cheapest array
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
cheapest[v] = -1;
}
// Traverse through all edges and update
// cheapest of every component
for (int i=0; i<E; i++)
{
// Find components (or sets) of two corners
// of current edge
int set1 = find(subsets, edge[i].src);
int set2 = find(subsets, edge[i].dest);
// If two corners of current edge belong to
// same set, ignore current edge
if (set1 == set2)
continue;
// Else check if current edge is closer to previous
// cheapest edges of set1 and set2
else
{
if (cheapest[set1] == -1 ||
edge[cheapest[set1]].weight > edge[i].weight)
cheapest[set1] = i;
if (cheapest[set2] == -1 ||
edge[cheapest[set2]].weight > edge[i].weight)
cheapest[set2] = i;
}
}
// Consider the above picked cheapest edges and add them
// to MST
for (int i=0; i<V; i++)
{
// Check if cheapest for current set exists
if (cheapest[i] != -1)
{
int set1 = find(subsets, edge[cheapest[i]].src);
int set2 = find(subsets, edge[cheapest[i]].dest);
if (set1 == set2)
continue;
MSTweight += edge[cheapest[i]].weight;
printf("Edge %d-%d included in MST\n",
edge[cheapest[i]].src, edge[cheapest[i]].dest);
// Do a union of set1 and set2 and decrease number
// of trees
Union(subsets, set1, set2);
numTrees--;
}
}
}
printf("Weight of MST is %d\n", MSTweight);
return;
}
// Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E)
{
Graph* graph = new Graph;
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = new Edge[E];
return graph;
}
// A utility function to find set of an element i
// (uses path compression technique)
int find(struct subset subsets[], int i)
{
// find root and make root as parent of i
// (path compression)
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent =
find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
// A function that does union of two sets of x and y
// (uses union by rank)
void Union(struct subset subsets[], int x, int y)
{
int xroot = find(subsets, x);
int yroot = find(subsets, y);
// Attach smaller rank tree under root of high
// rank tree (Union by Rank)
if (subsets[xroot].rank < subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
else if (subsets[xroot].rank > subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
// If ranks are same, then make one as root and
// increment its rank by one
else
{
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
subsets[xroot].rank++;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
/* Let us create following weighted graph
10
0--------1
| \ |
6| 5\ |15
| \ |
2--------3
4 */
int V = 4; // Number of vertices in graph
int E = 5; // Number of edges in graph
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
// add edge 0-1
graph->edge[0].src = 0;
graph->edge[0].dest = 1;
graph->edge[0].weight = 10;
// add edge 0-2
graph->edge[1].src = 0;
graph->edge[1].dest = 2;
graph->edge[1].weight = 6;
// add edge 0-3
graph->edge[2].src = 0;
graph->edge[2].dest = 3;
graph->edge[2].weight = 5;
// add edge 1-3
graph->edge[3].src = 1;
graph->edge[3].dest = 3;
graph->edge[3].weight = 15;
// add edge 2-3
graph->edge[4].src = 2;
graph->edge[4].dest = 3;
graph->edge[4].weight = 4;
boruvkaMST(graph);
return 0;
}
2 代码格式
// Boruvka's algorithm to find Minimum Spanning
// Tree of a given connected, undirected and
// weighted graph
#include <stdio.h>
// a structure to represent a weighted edge in graph
struct Edge
{
int src, dest, weight;
};
// a structure to represent a connected, undirected
// and weighted graph as a collection of edges.
struct Graph
{
// V-> Number of vertices, E-> Number of edges
int V, E;
// graph is represented as an array of edges.
// Since the graph is undirected, the edge
// from src to dest is also edge from dest
// to src. Both are counted as 1 edge here.
Edge* edge;
};
// A structure to represent a subset for union-find
struct subset
{
int parent;
int rank;
};
// Function prototypes for union-find (These functions are defined
// after boruvkaMST() )
int find(struct subset subsets[], int i);
void Union(struct subset subsets[], int x, int y);
// The main function for MST using Boruvka's algorithm
void boruvkaMST(struct Graph* graph)
{
// Get data of given graph
int V = graph->V, E = graph->E;
Edge *edge = graph->edge;
// Allocate memory for creating V subsets.
struct subset *subsets = new subset[V];
// An array to store index of the cheapest edge of
// subset. The stored index for indexing array 'edge[]'
int *cheapest = new int[V];
// Create V subsets with single elements
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
subsets[v].parent = v;
subsets[v].rank = 0;
cheapest[v] = -1;
}
// Initially there are V different trees.
// Finally there will be one tree that will be MST
int numTrees = V;
int MSTweight = 0;
// Keep combining components (or sets) until all
// compnentes are not combined into single MST.
while (numTrees > 1)
{
// Everytime initialize cheapest array
for (int v = 0; v < V; ++v)
{
cheapest[v] = -1;
}
// Traverse through all edges and update
// cheapest of every component
for (int i=0; i<E; i++)
{
// Find components (or sets) of two corners
// of current edge
int set1 = find(subsets, edge[i].src);
int set2 = find(subsets, edge[i].dest);
// If two corners of current edge belong to
// same set, ignore current edge
if (set1 == set2)
continue;
// Else check if current edge is closer to previous
// cheapest edges of set1 and set2
else
{
if (cheapest[set1] == -1 ||
edge[cheapest[set1]].weight > edge[i].weight)
cheapest[set1] = i;
if (cheapest[set2] == -1 ||
edge[cheapest[set2]].weight > edge[i].weight)
cheapest[set2] = i;
}
}
// Consider the above picked cheapest edges and add them
// to MST
for (int i=0; i<V; i++)
{
// Check if cheapest for current set exists
if (cheapest[i] != -1)
{
int set1 = find(subsets, edge[cheapest[i]].src);
int set2 = find(subsets, edge[cheapest[i]].dest);
if (set1 == set2)
continue;
MSTweight += edge[cheapest[i]].weight;
printf("Edge %d-%d included in MST\n",
edge[cheapest[i]].src, edge[cheapest[i]].dest);
// Do a union of set1 and set2 and decrease number
// of trees
Union(subsets, set1, set2);
numTrees--;
}
}
}
printf("Weight of MST is %d\n", MSTweight);
return;
}
// Creates a graph with V vertices and E edges
struct Graph* createGraph(int V, int E)
{
Graph* graph = new Graph;
graph->V = V;
graph->E = E;
graph->edge = new Edge[E];
return graph;
}
// A utility function to find set of an element i
// (uses path compression technique)
int find(struct subset subsets[], int i)
{
// find root and make root as parent of i
// (path compression)
if (subsets[i].parent != i)
subsets[i].parent =
find(subsets, subsets[i].parent);
return subsets[i].parent;
}
// A function that does union of two sets of x and y
// (uses union by rank)
void Union(struct subset subsets[], int x, int y)
{
int xroot = find(subsets, x);
int yroot = find(subsets, y);
// Attach smaller rank tree under root of high
// rank tree (Union by Rank)
if (subsets[xroot].rank < subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[xroot].parent = yroot;
else if (subsets[xroot].rank > subsets[yroot].rank)
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
// If ranks are same, then make one as root and
// increment its rank by one
else
{
subsets[yroot].parent = xroot;
subsets[xroot].rank++;
}
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
/* Let us create following weighted graph
10
0--------1
| \ |
6| 5\ |15
| \ |
2--------3
4 */
int V = 4; // Number of vertices in graph
int E = 5; // Number of edges in graph
struct Graph* graph = createGraph(V, E);
// add edge 0-1
graph->edge[0].src = 0;
graph->edge[0].dest = 1;
graph->edge[0].weight = 10;
// add edge 0-2
graph->edge[1].src = 0;
graph->edge[1].dest = 2;
graph->edge[1].weight = 6;
// add edge 0-3
graph->edge[2].src = 0;
graph->edge[2].dest = 3;
graph->edge[2].weight = 5;
// add edge 1-3
graph->edge[3].src = 1;
graph->edge[3].dest = 3;
graph->edge[3].weight = 15;
// add edge 2-3
graph->edge[4].src = 2;
graph->edge[4].dest = 3;
graph->edge[4].weight = 4;
boruvkaMST(graph);
return 0;
}
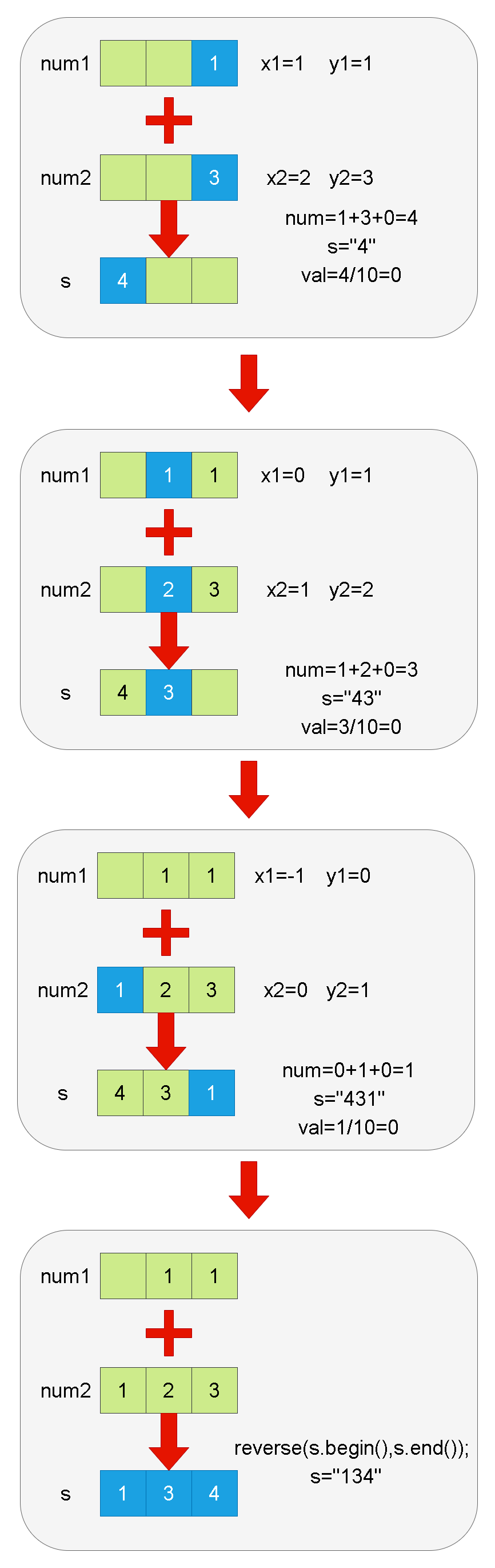

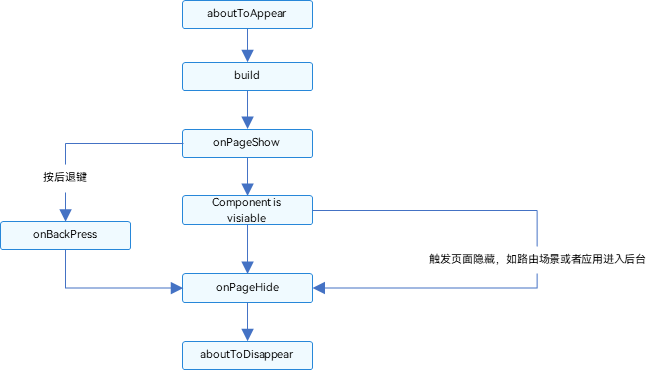
![[ROS2] --- 通信接口](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/78d6260117384619a54a1c86ffd546f0.png)