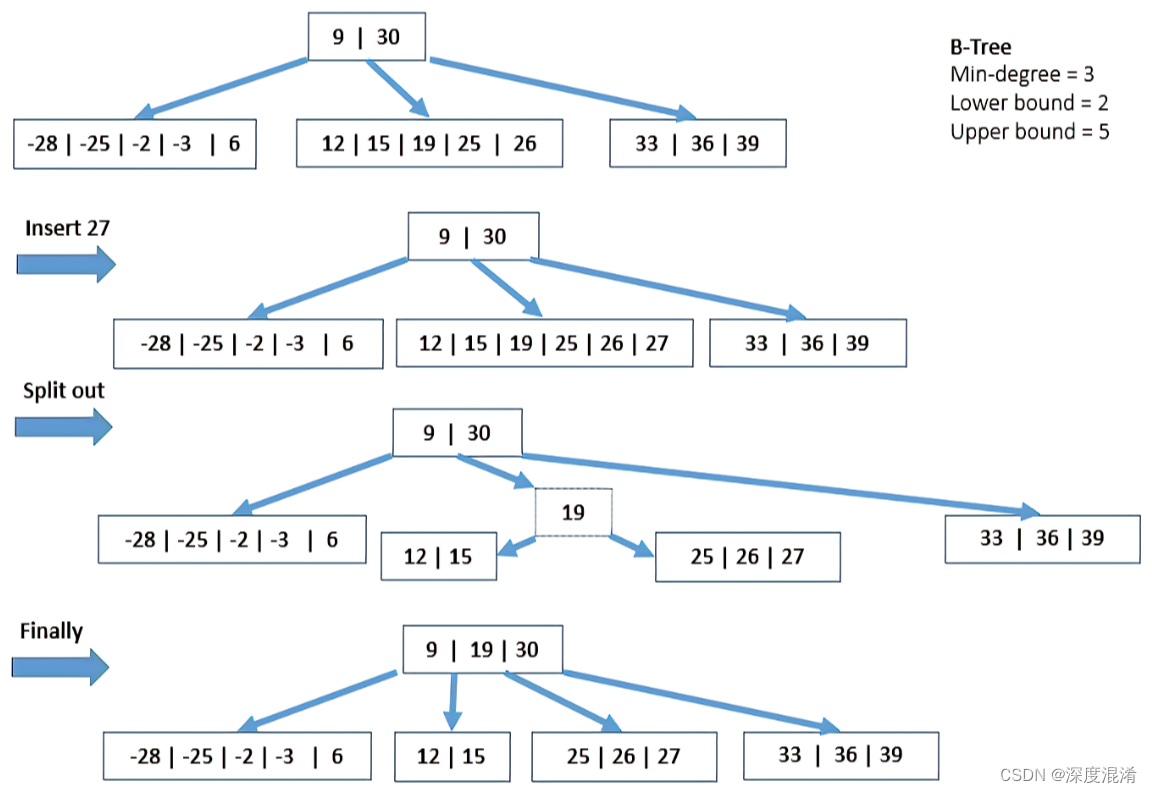
1 文本格式
#include<iostream>;
using namespace std;
// A BTree node
class BTreeNode
{
int* keys; // An array of keys
int t; // Minimum degree (defines the range for number of keys)
BTreeNode** C; // An array of child pointers
int n; // Current number of keys
bool leaf; // Is true when node is leaf. Otherwise false
public:
BTreeNode(int _t, bool _leaf); // Constructor
// A function to traverse all nodes in a subtree rooted with this node
void traverse();
// A function to search a key in subtree rooted with this node.
BTreeNode* search(int k); // returns NULL if k is not present.
// A function that returns the index of the first key that is greater
// or equal to k
int findKey(int k);
// A utility function to insert a new key in the subtree rooted with
// this node. The assumption is, the node must be non-full when this
// function is called
void insertNonFull(int k);
// A utility function to split the child y of this node. i is index
// of y in child array C[]. The Child y must be full when this
// function is called
void splitChild(int i, BTreeNode* y);
// A wrapper function to remove the key k in subtree rooted with
// this node.
void remove(int k);
// A function to remove the key present in idx-th position in
// this node which is a leaf
void removeFromLeaf(int idx);
// A function to remove the key present in idx-th position in
// this node which is a non-leaf node
void removeFromNonLeaf(int idx);
// A function to get the predecessor of the key- where the key
// is present in the idx-th position in the node
int getPred(int idx);
// A function to get the successor of the key- where the key
// is present in the idx-th position in the node
int getSucc(int idx);
// A function to fill up the child node present in the idx-th
// position in the C[] array if that child has less than t-1 keys
void fill(int idx);
// A function to borrow a key from the C[idx-1]-th node and place
// it in C[idx]th node
void borrowFromPrev(int idx);
// A function to borrow a key from the C[idx+1]-th node and place it
// in C[idx]th node
void borrowFromNext(int idx);
// A function to merge idx-th child of the node with (idx+1)th child of
// the node
void merge(int idx);
// Make BTree friend of this so that we can access private members of
// this class in BTree functions
friend class BTree;
};
class BTree
{
BTreeNode* root; // Pointer to root node
int t; // Minimum degree
public:
// Constructor (Initializes tree as empty)
BTree(int _t)
{
root = NULL;
t = _t;
}
void traverse()
{
if (root != NULL) root->traverse();
}
// function to search a key in this tree
BTreeNode* search(int k)
{
return (root == NULL) ? NULL : root->search(k);
}
// The main function that inserts a new key in this B-Tree
void insert(int k);
// The main function that removes a new key in thie B-Tree
void remove(int k);
};
BTreeNode::BTreeNode(int t1, bool leaf1)
{
// Copy the given minimum degree and leaf property
t = t1;
leaf = leaf1;
// Allocate memory for maximum number of possible keys
// and child pointers
keys = new int[2 * t - 1];
C = new BTreeNode * [2 * t];
// Initialize the number of keys as 0
n = 0;
}
// A utility function that returns the index of the first key that is
// greater than or equal to k
int BTreeNode::findKey(int k)
{
int idx = 0;
while (idx < n && keys[idx] < k)
++idx;
return idx;
}
// A function to remove the key k from the sub-tree rooted with this node
void BTreeNode::remove(int k)
{
int idx = findKey(k);
// The key to be removed is present in this node
if (idx < n && keys[idx] == k)
{
// If the node is a leaf node - removeFromLeaf is called
// Otherwise, removeFromNonLeaf function is called
if (leaf)
removeFromLeaf(idx);
else
removeFromNonLeaf(idx);
}
else
{
// If this node is a leaf node, then the key is not present in tree
if (leaf)
{
cout << " The key" << k << " is does not exist in the tree\n";
return;
}
// The key to be removed is present in the sub-tree rooted with this node
// The flag indicates whether the key is present in the sub-tree rooted
// with the last child of this node
bool flag = ((idx == n) ? true : false);
// If the child where the key is supposed to exist has less that t keys,
// we fill that child
if (C[idx]->n < t)
fill(idx);
// If the last child has been merged, it must have merged with the previous
// child and so we recurse on the (idx-1)th child. Else, we recurse on the
// (idx)th child which now has atleast t keys
if (flag && idx > n)
C[idx - 1]->remove(k);
else
C[idx]->remove(k);
}
return;
}
// A function to remove the idx-th key from this node - which is a leaf node
void BTreeNode::removeFromLeaf(int idx)
{
// Move all the keys after the idx-th pos one place backward
for (int i = idx + 1; i < n; ++i)
keys[i - 1] = keys[i];
// Reduce the count of keys
n--;
return;
}
// A function to remove the idx-th key from this node - which is a non-leaf node
void BTreeNode::removeFromNonLeaf(int idx)
{
int k = keys[idx];
// If the child that precedes k (C[idx]) has atleast t keys,
// find the predecessor 'pred' of k in the subtree rooted at
// C[idx]. Replace k by pred. Recursively delete pred
// in C[idx]
if (C[idx]->n > = t)
{
int pred = getPred(idx);
keys[idx] = pred;
C[idx]->remove(pred);
}
// If the child C[idx] has less that t keys, examine C[idx+1].
// If C[idx+1] has atleast t keys, find the successor 'succ' of k in
// the subtree rooted at C[idx+1]
// Replace k by succ
// Recursively delete succ in C[idx+1]
else if (C[idx + 1]->n > = t)
{
int succ = getSucc(idx);
keys[idx] = succ;
C[idx + 1]->remove(succ);
}
// If both C[idx] and C[idx+1] has less that t keys,merge k and all of C[idx+1]
// into C[idx]
// Now C[idx] contains 2t-1 keys
// Free C[idx+1] and recursively delete k from C[idx]
else
{
merge(idx);
C[idx]->remove(k);
}
return;
}
// A function to get predecessor of keys[idx]
int BTreeNode::getPred(int idx)
{
// Keep moving to the right most node until we reach a leaf
BTreeNode* cur = C[idx];
while (!cur->leaf)
cur = cur->C[cur->n];
// Return the last key of the leaf
return cur->keys[cur->n - 1];
}
int BTreeNode::getSucc(int idx)
{
// Keep moving the left most node starting from C[idx+1] until we reach a leaf
BTreeNode* cur = C[idx + 1];
while (!cur->leaf)
cur = cur->C[0];
// Return the first key of the leaf
return cur->keys[0];
}
// A function to fill child C[idx] which has less than t-1 keys
void BTreeNode::fill(int idx)
{
// If the previous child(C[idx-1]) has more than t-1 keys, borrow a key
// from that child
if (idx != 0 && C[idx - 1]->n > = t)
borrowFromPrev(idx);
// If the next child(C[idx+1]) has more than t-1 keys, borrow a key
// from that child
else if (idx != n && C[idx + 1]->n > = t)
borrowFromNext(idx);
// Merge C[idx] with its sibling
// If C[idx] is the last child, merge it with its previous sibling
// Otherwise merge it with its next sibling
else
{
if (idx != n)
merge(idx);
else
merge(idx - 1);
}
return;
}
// A function to borrow a key from C[idx-1] and insert it
// into C[idx]
void BTreeNode::borrowFromPrev(int idx)
{
BTreeNode* child = C[idx];
BTreeNode* sibling = C[idx - 1];
// The last key from C[idx-1] goes up to the parent and key[idx-1]
// from parent is inserted as the first key in C[idx]. Thus, the loses
// sibling one key and child gains one key
// Moving all key in C[idx] one step ahead
for (int i = child->n - 1; i > = 0; --i)
child->keys[i + 1] = child->keys[i];
// If C[idx] is not a leaf, move all its child pointers one step ahead
if (!child->leaf)
{
for (int i = child->n; i > = 0; --i)
child->C[i + 1] = child->C[i];
}
// Setting child's first key equal to keys[idx-1] from the current node
child->keys[0] = keys[idx - 1];
// Moving sibling's last child as C[idx]'s first child
if (!child->leaf)
child->C[0] = sibling->C[sibling->n];
// Moving the key from the sibling to the parent
// This reduces the number of keys in the sibling
keys[idx - 1] = sibling->keys[sibling->n - 1];
child->n += 1;
sibling->n -= 1;
return;
}
// A function to borrow a key from the C[idx+1] and place
// it in C[idx]
void BTreeNode::borrowFromNext(int idx)
{
BTreeNode* child = C[idx];
BTreeNode* sibling = C[idx + 1];
// keys[idx] is inserted as the last key in C[idx]
child->keys[(child->n)] = keys[idx];
// Sibling's first child is inserted as the last child
// into C[idx]
if (!(child->leaf))
child->C[(child->n) + 1] = sibling->C[0];
//The first key from sibling is inserted into keys[idx]
keys[idx] = sibling->keys[0];
// Moving all keys in sibling one step behind
for (int i = 1; i < sibling->n; ++i)
sibling->keys[i - 1] = sibling->keys[i];
// Moving the child pointers one step behind
if (!sibling->leaf)
{
for (int i = 1; i < = sibling->n; ++i)
sibling->C[i - 1] = sibling->C[i];
}
// Increasing and decreasing the key count of C[idx] and C[idx+1]
// respectively
child->n += 1;
sibling->n -= 1;
return;
}
// A function to merge C[idx] with C[idx+1]
// C[idx+1] is freed after merging
void BTreeNode::merge(int idx)
{
BTreeNode* child = C[idx];
BTreeNode* sibling = C[idx + 1];
// Pulling a key from the current node and inserting it into (t-1)th
// position of C[idx]
child->keys[t - 1] = keys[idx];
// Copying the keys from C[idx+1] to C[idx] at the end
for (int i = 0; i < sibling->n; ++i)
child->keys[i + t] = sibling->keys[i];
// Copying the child pointers from C[idx+1] to C[idx]
if (!child->leaf)
{
for (int i = 0; i < = sibling->n; ++i)
child->C[i + t] = sibling->C[i];
}
// Moving all keys after idx in the current node one step before -
// to fill the gap created by moving keys[idx] to C[idx]
for (int i = idx + 1; i < n; ++i)
keys[i - 1] = keys[i];
// Moving the child pointers after (idx+1) in the current node one
// step before
for (int i = idx + 2; i < = n; ++i)
C[i - 1] = C[i];
// Updating the key count of child and the current node
child->n += sibling->n + 1;
n--;
// Freeing the memory occupied by sibling
delete(sibling);
return;
}
// The main function that inserts a new key in this B-Tree
void BTree::insert(int k)
{
// If tree is empty
if (root == NULL)
{
// Allocate memory for root
root = new BTreeNode(t, true);
root->keys[0] = k; // Insert key
root->n = 1; // Update number of keys in root
}
else // If tree is not empty
{
// If root is full, then tree grows in height
if (root->n == 2 * t - 1)
{
// Allocate memory for new root
BTreeNode* s = new BTreeNode(t, false);
// Make old root as child of new root
s->C[0] = root;
// Split the old root and move 1 key to the new root
s->splitChild(0, root);
// New root has two children now. Decide which of the
// two children is going to have new key
int i = 0;
if (s->keys[0] < k)
i++;
s->C[i]->insertNonFull(k);
// Change root
root = s;
}
else // If root is not full, call insertNonFull for root
root->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
// A utility function to insert a new key in this node
// The assumption is, the node must be non-full when this
// function is called
void BTreeNode::insertNonFull(int k)
{
// Initialize index as index of rightmost element
int i = n - 1;
// If this is a leaf node
if (leaf == true)
{
// The following loop does two things
// a) Finds the location of new key to be inserted
// b) Moves all greater keys to one place ahead
while (i > = 0 && keys[i] > k)
{
keys[i + 1] = keys[i];
i--;
}
// Insert the new key at found location
keys[i + 1] = k;
n = n + 1;
}
else // If this node is not leaf
{
// Find the child which is going to have the new key
while (i > = 0 && keys[i] > k)
i--;
// See if the found child is full
if (C[i + 1]->n == 2 * t - 1)
{
// If the child is full, then split it
splitChild(i + 1, C[i + 1]);
// After split, the middle key of C[i] goes up and
// C[i] is splitted into two. See which of the two
// is going to have the new key
if (keys[i + 1] < k)
i++;
}
C[i + 1]->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
// A utility function to split the child y of this node
// Note that y must be full when this function is called
void BTreeNode::splitChild(int i, BTreeNode* y)
{
// Create a new node which is going to store (t-1) keys
// of y
BTreeNode* z = new BTreeNode(y->t, y->leaf);
z->n = t - 1;
// Copy the last (t-1) keys of y to z
for (int j = 0; j < t - 1; j++)
z->keys[j] = y->keys[j + t];
// Copy the last t children of y to z
if (y->leaf == false)
{
for (int j = 0; j < t; j++)
z->C[j] = y->C[j + t];
}
// Reduce the number of keys in y
y->n = t - 1;
// Since this node is going to have a new child,
// create space of new child
for (int j = n; j > = i + 1; j--)
C[j + 1] = C[j];
// Link the new child to this node
C[i + 1] = z;
// A key of y will move to this node. Find location of
// new key and move all greater keys one space ahead
for (int j = n - 1; j > = i; j--)
keys[j + 1] = keys[j];
// Copy the middle key of y to this node
keys[i] = y->keys[t - 1];
// Increment count of keys in this node
n = n + 1;
}
// Function to traverse all nodes in a subtree rooted with this node
void BTreeNode::traverse()
{
// There are n keys and n+1 children, traverse through n keys
// and first n children
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// If this is not leaf, then before printing key[i],
// traverse the subtree rooted with child C[i].
if (leaf == false)
C[i]->traverse();
cout << " " << keys[i];
}
// Print the subtree rooted with last child
if (leaf == false)
C[i]->traverse();
}
// Function to search key k in subtree rooted with this node
BTreeNode* BTreeNode::search(int k)
{
// Find the first key greater than or equal to k
int i = 0;
while (i< n && k > keys[i])
i++;
// If the found key is equal to k, return this node
if (keys[i] == k)
return this;
// If key is not found here and this is a leaf node
if (leaf == true)
return NULL;
// Go to the appropriate child
return C[i]->search(k);
}
void BTree::remove(int k)
{
if (!root)
{
cout << " The tree is empty\n";
return;
}
// Call the remove function for root
root->remove(k);
// If the root node has 0 keys, make its first child as the new root
// if it has a child, otherwise set root as NULL
if (root->n == 0)
{
BTreeNode* tmp = root;
if (root->leaf)
root = NULL;
else
root = root->C[0];
// Free the old root
delete tmp;
}
return;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
BTree t(3); // A B-Tree with minimum degree 3
t.insert(1);
t.insert(3);
t.insert(7);
t.insert(10);
t.insert(11);
t.insert(13);
t.insert(14);
t.insert(15);
t.insert(18);
t.insert(16);
t.insert(19);
t.insert(24);
t.insert(25);
t.insert(26);
t.insert(21);
t.insert(4);
t.insert(5);
t.insert(20);
t.insert(22);
t.insert(2);
t.insert(17);
t.insert(12);
t.insert(6);
cout << " Traversal of tree constructed is\n";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(6);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 6\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(13);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 13\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(7);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 7\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(4);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 4\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(2);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 2\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(16);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 16\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}
2 代码格式
#include<iostream>;
using namespace std;
// A BTree node
class BTreeNode
{
int* keys; // An array of keys
int t; // Minimum degree (defines the range for number of keys)
BTreeNode** C; // An array of child pointers
int n; // Current number of keys
bool leaf; // Is true when node is leaf. Otherwise false
public:
BTreeNode(int _t, bool _leaf); // Constructor
// A function to traverse all nodes in a subtree rooted with this node
void traverse();
// A function to search a key in subtree rooted with this node.
BTreeNode* search(int k); // returns NULL if k is not present.
// A function that returns the index of the first key that is greater
// or equal to k
int findKey(int k);
// A utility function to insert a new key in the subtree rooted with
// this node. The assumption is, the node must be non-full when this
// function is called
void insertNonFull(int k);
// A utility function to split the child y of this node. i is index
// of y in child array C[]. The Child y must be full when this
// function is called
void splitChild(int i, BTreeNode* y);
// A wrapper function to remove the key k in subtree rooted with
// this node.
void remove(int k);
// A function to remove the key present in idx-th position in
// this node which is a leaf
void removeFromLeaf(int idx);
// A function to remove the key present in idx-th position in
// this node which is a non-leaf node
void removeFromNonLeaf(int idx);
// A function to get the predecessor of the key- where the key
// is present in the idx-th position in the node
int getPred(int idx);
// A function to get the successor of the key- where the key
// is present in the idx-th position in the node
int getSucc(int idx);
// A function to fill up the child node present in the idx-th
// position in the C[] array if that child has less than t-1 keys
void fill(int idx);
// A function to borrow a key from the C[idx-1]-th node and place
// it in C[idx]th node
void borrowFromPrev(int idx);
// A function to borrow a key from the C[idx+1]-th node and place it
// in C[idx]th node
void borrowFromNext(int idx);
// A function to merge idx-th child of the node with (idx+1)th child of
// the node
void merge(int idx);
// Make BTree friend of this so that we can access private members of
// this class in BTree functions
friend class BTree;
};
class BTree
{
BTreeNode* root; // Pointer to root node
int t; // Minimum degree
public:
// Constructor (Initializes tree as empty)
BTree(int _t)
{
root = NULL;
t = _t;
}
void traverse()
{
if (root != NULL) root->traverse();
}
// function to search a key in this tree
BTreeNode* search(int k)
{
return (root == NULL) ? NULL : root->search(k);
}
// The main function that inserts a new key in this B-Tree
void insert(int k);
// The main function that removes a new key in thie B-Tree
void remove(int k);
};
BTreeNode::BTreeNode(int t1, bool leaf1)
{
// Copy the given minimum degree and leaf property
t = t1;
leaf = leaf1;
// Allocate memory for maximum number of possible keys
// and child pointers
keys = new int[2 * t - 1];
C = new BTreeNode * [2 * t];
// Initialize the number of keys as 0
n = 0;
}
// A utility function that returns the index of the first key that is
// greater than or equal to k
int BTreeNode::findKey(int k)
{
int idx = 0;
while (idx < n && keys[idx] < k)
++idx;
return idx;
}
// A function to remove the key k from the sub-tree rooted with this node
void BTreeNode::remove(int k)
{
int idx = findKey(k);
// The key to be removed is present in this node
if (idx < n && keys[idx] == k)
{
// If the node is a leaf node - removeFromLeaf is called
// Otherwise, removeFromNonLeaf function is called
if (leaf)
removeFromLeaf(idx);
else
removeFromNonLeaf(idx);
}
else
{
// If this node is a leaf node, then the key is not present in tree
if (leaf)
{
cout << " The key" << k << " is does not exist in the tree\n";
return;
}
// The key to be removed is present in the sub-tree rooted with this node
// The flag indicates whether the key is present in the sub-tree rooted
// with the last child of this node
bool flag = ((idx == n) ? true : false);
// If the child where the key is supposed to exist has less that t keys,
// we fill that child
if (C[idx]->n < t)
fill(idx);
// If the last child has been merged, it must have merged with the previous
// child and so we recurse on the (idx-1)th child. Else, we recurse on the
// (idx)th child which now has atleast t keys
if (flag && idx > n)
C[idx - 1]->remove(k);
else
C[idx]->remove(k);
}
return;
}
// A function to remove the idx-th key from this node - which is a leaf node
void BTreeNode::removeFromLeaf(int idx)
{
// Move all the keys after the idx-th pos one place backward
for (int i = idx + 1; i < n; ++i)
keys[i - 1] = keys[i];
// Reduce the count of keys
n--;
return;
}
// A function to remove the idx-th key from this node - which is a non-leaf node
void BTreeNode::removeFromNonLeaf(int idx)
{
int k = keys[idx];
// If the child that precedes k (C[idx]) has atleast t keys,
// find the predecessor 'pred' of k in the subtree rooted at
// C[idx]. Replace k by pred. Recursively delete pred
// in C[idx]
if (C[idx]->n > = t)
{
int pred = getPred(idx);
keys[idx] = pred;
C[idx]->remove(pred);
}
// If the child C[idx] has less that t keys, examine C[idx+1].
// If C[idx+1] has atleast t keys, find the successor 'succ' of k in
// the subtree rooted at C[idx+1]
// Replace k by succ
// Recursively delete succ in C[idx+1]
else if (C[idx + 1]->n > = t)
{
int succ = getSucc(idx);
keys[idx] = succ;
C[idx + 1]->remove(succ);
}
// If both C[idx] and C[idx+1] has less that t keys,merge k and all of C[idx+1]
// into C[idx]
// Now C[idx] contains 2t-1 keys
// Free C[idx+1] and recursively delete k from C[idx]
else
{
merge(idx);
C[idx]->remove(k);
}
return;
}
// A function to get predecessor of keys[idx]
int BTreeNode::getPred(int idx)
{
// Keep moving to the right most node until we reach a leaf
BTreeNode* cur = C[idx];
while (!cur->leaf)
cur = cur->C[cur->n];
// Return the last key of the leaf
return cur->keys[cur->n - 1];
}
int BTreeNode::getSucc(int idx)
{
// Keep moving the left most node starting from C[idx+1] until we reach a leaf
BTreeNode* cur = C[idx + 1];
while (!cur->leaf)
cur = cur->C[0];
// Return the first key of the leaf
return cur->keys[0];
}
// A function to fill child C[idx] which has less than t-1 keys
void BTreeNode::fill(int idx)
{
// If the previous child(C[idx-1]) has more than t-1 keys, borrow a key
// from that child
if (idx != 0 && C[idx - 1]->n > = t)
borrowFromPrev(idx);
// If the next child(C[idx+1]) has more than t-1 keys, borrow a key
// from that child
else if (idx != n && C[idx + 1]->n > = t)
borrowFromNext(idx);
// Merge C[idx] with its sibling
// If C[idx] is the last child, merge it with its previous sibling
// Otherwise merge it with its next sibling
else
{
if (idx != n)
merge(idx);
else
merge(idx - 1);
}
return;
}
// A function to borrow a key from C[idx-1] and insert it
// into C[idx]
void BTreeNode::borrowFromPrev(int idx)
{
BTreeNode* child = C[idx];
BTreeNode* sibling = C[idx - 1];
// The last key from C[idx-1] goes up to the parent and key[idx-1]
// from parent is inserted as the first key in C[idx]. Thus, the loses
// sibling one key and child gains one key
// Moving all key in C[idx] one step ahead
for (int i = child->n - 1; i > = 0; --i)
child->keys[i + 1] = child->keys[i];
// If C[idx] is not a leaf, move all its child pointers one step ahead
if (!child->leaf)
{
for (int i = child->n; i > = 0; --i)
child->C[i + 1] = child->C[i];
}
// Setting child's first key equal to keys[idx-1] from the current node
child->keys[0] = keys[idx - 1];
// Moving sibling's last child as C[idx]'s first child
if (!child->leaf)
child->C[0] = sibling->C[sibling->n];
// Moving the key from the sibling to the parent
// This reduces the number of keys in the sibling
keys[idx - 1] = sibling->keys[sibling->n - 1];
child->n += 1;
sibling->n -= 1;
return;
}
// A function to borrow a key from the C[idx+1] and place
// it in C[idx]
void BTreeNode::borrowFromNext(int idx)
{
BTreeNode* child = C[idx];
BTreeNode* sibling = C[idx + 1];
// keys[idx] is inserted as the last key in C[idx]
child->keys[(child->n)] = keys[idx];
// Sibling's first child is inserted as the last child
// into C[idx]
if (!(child->leaf))
child->C[(child->n) + 1] = sibling->C[0];
//The first key from sibling is inserted into keys[idx]
keys[idx] = sibling->keys[0];
// Moving all keys in sibling one step behind
for (int i = 1; i < sibling->n; ++i)
sibling->keys[i - 1] = sibling->keys[i];
// Moving the child pointers one step behind
if (!sibling->leaf)
{
for (int i = 1; i < = sibling->n; ++i)
sibling->C[i - 1] = sibling->C[i];
}
// Increasing and decreasing the key count of C[idx] and C[idx+1]
// respectively
child->n += 1;
sibling->n -= 1;
return;
}
// A function to merge C[idx] with C[idx+1]
// C[idx+1] is freed after merging
void BTreeNode::merge(int idx)
{
BTreeNode* child = C[idx];
BTreeNode* sibling = C[idx + 1];
// Pulling a key from the current node and inserting it into (t-1)th
// position of C[idx]
child->keys[t - 1] = keys[idx];
// Copying the keys from C[idx+1] to C[idx] at the end
for (int i = 0; i < sibling->n; ++i)
child->keys[i + t] = sibling->keys[i];
// Copying the child pointers from C[idx+1] to C[idx]
if (!child->leaf)
{
for (int i = 0; i < = sibling->n; ++i)
child->C[i + t] = sibling->C[i];
}
// Moving all keys after idx in the current node one step before -
// to fill the gap created by moving keys[idx] to C[idx]
for (int i = idx + 1; i < n; ++i)
keys[i - 1] = keys[i];
// Moving the child pointers after (idx+1) in the current node one
// step before
for (int i = idx + 2; i < = n; ++i)
C[i - 1] = C[i];
// Updating the key count of child and the current node
child->n += sibling->n + 1;
n--;
// Freeing the memory occupied by sibling
delete(sibling);
return;
}
// The main function that inserts a new key in this B-Tree
void BTree::insert(int k)
{
// If tree is empty
if (root == NULL)
{
// Allocate memory for root
root = new BTreeNode(t, true);
root->keys[0] = k; // Insert key
root->n = 1; // Update number of keys in root
}
else // If tree is not empty
{
// If root is full, then tree grows in height
if (root->n == 2 * t - 1)
{
// Allocate memory for new root
BTreeNode* s = new BTreeNode(t, false);
// Make old root as child of new root
s->C[0] = root;
// Split the old root and move 1 key to the new root
s->splitChild(0, root);
// New root has two children now. Decide which of the
// two children is going to have new key
int i = 0;
if (s->keys[0] < k)
i++;
s->C[i]->insertNonFull(k);
// Change root
root = s;
}
else // If root is not full, call insertNonFull for root
root->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
// A utility function to insert a new key in this node
// The assumption is, the node must be non-full when this
// function is called
void BTreeNode::insertNonFull(int k)
{
// Initialize index as index of rightmost element
int i = n - 1;
// If this is a leaf node
if (leaf == true)
{
// The following loop does two things
// a) Finds the location of new key to be inserted
// b) Moves all greater keys to one place ahead
while (i > = 0 && keys[i] > k)
{
keys[i + 1] = keys[i];
i--;
}
// Insert the new key at found location
keys[i + 1] = k;
n = n + 1;
}
else // If this node is not leaf
{
// Find the child which is going to have the new key
while (i > = 0 && keys[i] > k)
i--;
// See if the found child is full
if (C[i + 1]->n == 2 * t - 1)
{
// If the child is full, then split it
splitChild(i + 1, C[i + 1]);
// After split, the middle key of C[i] goes up and
// C[i] is splitted into two. See which of the two
// is going to have the new key
if (keys[i + 1] < k)
i++;
}
C[i + 1]->insertNonFull(k);
}
}
// A utility function to split the child y of this node
// Note that y must be full when this function is called
void BTreeNode::splitChild(int i, BTreeNode* y)
{
// Create a new node which is going to store (t-1) keys
// of y
BTreeNode* z = new BTreeNode(y->t, y->leaf);
z->n = t - 1;
// Copy the last (t-1) keys of y to z
for (int j = 0; j < t - 1; j++)
z->keys[j] = y->keys[j + t];
// Copy the last t children of y to z
if (y->leaf == false)
{
for (int j = 0; j < t; j++)
z->C[j] = y->C[j + t];
}
// Reduce the number of keys in y
y->n = t - 1;
// Since this node is going to have a new child,
// create space of new child
for (int j = n; j > = i + 1; j--)
C[j + 1] = C[j];
// Link the new child to this node
C[i + 1] = z;
// A key of y will move to this node. Find location of
// new key and move all greater keys one space ahead
for (int j = n - 1; j > = i; j--)
keys[j + 1] = keys[j];
// Copy the middle key of y to this node
keys[i] = y->keys[t - 1];
// Increment count of keys in this node
n = n + 1;
}
// Function to traverse all nodes in a subtree rooted with this node
void BTreeNode::traverse()
{
// There are n keys and n+1 children, traverse through n keys
// and first n children
int i;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
// If this is not leaf, then before printing key[i],
// traverse the subtree rooted with child C[i].
if (leaf == false)
C[i]->traverse();
cout << " " << keys[i];
}
// Print the subtree rooted with last child
if (leaf == false)
C[i]->traverse();
}
// Function to search key k in subtree rooted with this node
BTreeNode* BTreeNode::search(int k)
{
// Find the first key greater than or equal to k
int i = 0;
while (i< n && k > keys[i])
i++;
// If the found key is equal to k, return this node
if (keys[i] == k)
return this;
// If key is not found here and this is a leaf node
if (leaf == true)
return NULL;
// Go to the appropriate child
return C[i]->search(k);
}
void BTree::remove(int k)
{
if (!root)
{
cout << " The tree is empty\n";
return;
}
// Call the remove function for root
root->remove(k);
// If the root node has 0 keys, make its first child as the new root
// if it has a child, otherwise set root as NULL
if (root->n == 0)
{
BTreeNode* tmp = root;
if (root->leaf)
root = NULL;
else
root = root->C[0];
// Free the old root
delete tmp;
}
return;
}
// Driver program to test above functions
int main()
{
BTree t(3); // A B-Tree with minimum degree 3
t.insert(1);
t.insert(3);
t.insert(7);
t.insert(10);
t.insert(11);
t.insert(13);
t.insert(14);
t.insert(15);
t.insert(18);
t.insert(16);
t.insert(19);
t.insert(24);
t.insert(25);
t.insert(26);
t.insert(21);
t.insert(4);
t.insert(5);
t.insert(20);
t.insert(22);
t.insert(2);
t.insert(17);
t.insert(12);
t.insert(6);
cout << " Traversal of tree constructed is\n";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(6);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 6\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(13);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 13\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(7);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 7\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(4);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 4\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(2);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 2\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
t.remove(16);
cout << " Traversal of tree after removing 16\n ";
t.traverse();
cout << endl;
return 0;
}





![BUUCTF [CISCN2019 华北赛区 Day2 Web1]Hack World 1(SQL注入之布尔盲注)](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/img_convert/c53885cce0b7313f2d9ce9cb13ff56ae.png)