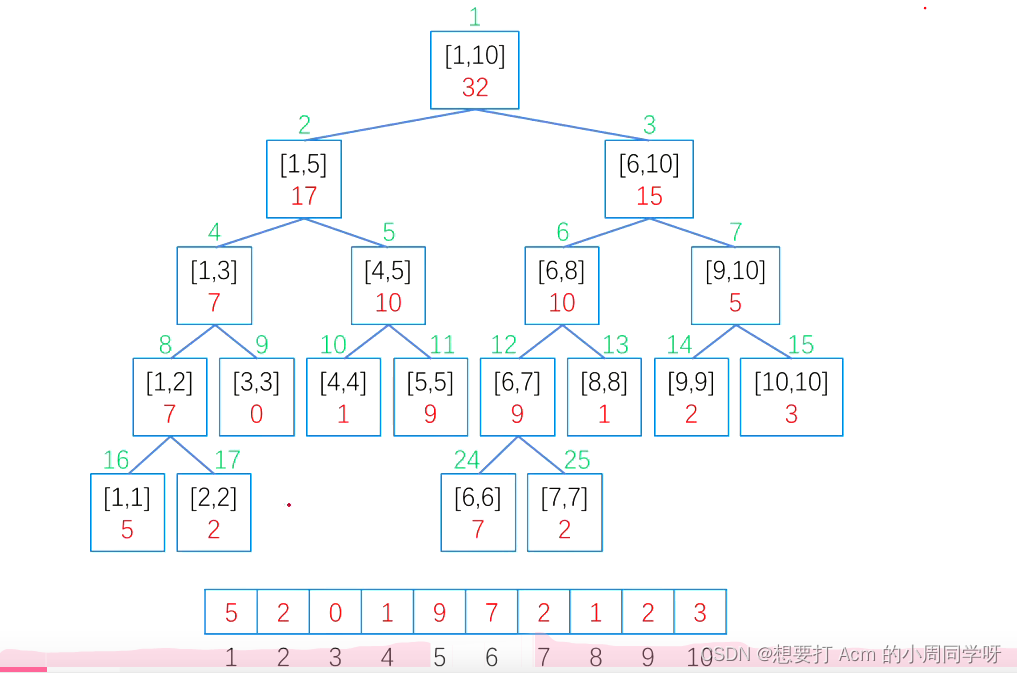

线段树的基础模板代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 100005
#define int long long
#define lc p << 1 // 2*i
#define rc p << 1 | 1 // 2*i+1
int n, m;
int w[N];
struct node
{
int l, r, sum, add;
} tr[N * 4];
// 构建线段树
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;
}
void pushdown(int p)
{
if (tr[p].add)
{
tr[lc].sum += tr[p].add * (tr[lc].r - tr[lc].l + 1),
tr[rc].sum += tr[p].add * (tr[rc].r - tr[rc].l + 1),
tr[lc].add += tr[p].add,
tr[rc].add += tr[p].add,
tr[p].add = 0;
}
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = {l, r, w[l], 0};
if (l == r)
return;
int mid = l + r >> 1;
build(lc, l, mid);
build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
int query(int p, int x, int y)
{ // 区查
if (x <= tr[p].l && tr[p].r <= y)
return tr[p].sum;
int m = tr[p].l + tr[p].r >> 1;
pushdown(p);
int sum = 0;
if (x <= m)
sum += query(lc, x, y);
//
if (y > m)
sum += query(rc, x, y);
return sum;
}
void update(int p, int x, int y, int k)
{
// 修改区间的值'
if (x <= tr[p].l && tr[p].r <= y)
{
tr[p].sum += (tr[p].r - tr[p].l + 1) * k;
tr[p].add += k;
return;
}
int mid = tr[p].l + tr[p].r >> 1;
pushdown(p); // 先下沉
if (x <= mid)
{
update(lc, x, y, k);
}
if (y > mid)
{
update(rc, x, y, k);
}
pushup(p); // 再上乘
}
// 区间修改 对于区间[4,9] 内的每个数字
signed main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++)
{
int x;
cin >> x;
w[i] = x;
}
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a, x, y, k;
cin >> a >> x >> y;
if (a == 1)
{
cin >> k;
update(1, x, y, k);
}
else if (a == 2)
{
cout << query(1, x, y) << endl;
}
}
}

对点进行修改,从跟节点进入,找到根节点,将根节点的值修改下

查询区间

区间修改如果直接修改容易看出来时间复杂度是on的
懒惰修改
修改上面区间的sum值,
https://ac.nowcoder.com/acm/contest/63746/A
题目,采用线段树的代码来解决问题
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#define int long long
#define N 200005
#define lc p << 1
#define rc p << 1 | 1
int n, m;
struct node
{
int l, r, sum, add;
} tr[N * 4];
int w[N];
void pushup(int p)
{
tr[p].sum = tr[lc].sum + tr[rc].sum;
}
void pushdown(int p)
{
if (tr[p].add)
//^异或运算
{
tr[lc].add ^= tr[p].add; //
tr[rc].add ^= tr[p].add;
tr[lc].sum = tr[lc].r - tr[lc].l + 1 - tr[lc].sum;
tr[rc].sum = tr[rc].r - tr[rc].l + 1 - tr[rc].sum;
tr[p].add = 0;
}
}
void build(int p, int l, int r)
{
tr[p] = {l, r};
if (l == r)
{
tr[p].sum = w[l];
return;
}
int mid = l + r >> 1;
build(lc, l, mid);
build(rc, mid + 1, r);
pushup(p);
}
int query(int p, int x, int y)
{ // 区查
// 如果以及完全覆盖掉
if (x <= tr[p].l && tr[p].r <= y)
return tr[p].sum;
int m = tr[p].l + tr[p].r >> 1; // 没有完全覆盖就裂开
pushdown(p);
int sum = 0; // 定义局部变量 递归进入
if (x <= m)
sum += query(lc, x, y);
//
if (y > m)
sum += query(rc, x, y);
return sum;
}
// 查询时不变的 修改会发生变化
void update(int p, int x, int y)
{
// 修改区间的值'
if (x <= tr[p].l && tr[p].r <= y)
{
// 如果符合了
// 区间修改
tr[p].add ^= 1;//和1进行异或取反
tr[p].sum = tr[p].r - tr[p].l + 1 - tr[p].sum;
return;
}
int mid = tr[p].l + tr[p].r >> 1;
pushdown(p); // 先下沉
if (x <= mid)
{
update(lc, x, y);
}
if (y > mid)
{
update(rc, x, y);
}
pushup(p); // 再上乘
}
signed main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
string s;
cin >> s;
for (int i = 0; i < s.length(); i++)
{
w[i + 1] = s[i] - '0';
}
build(1, 1, n);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++)
{
int a, x, y;
cin >> a >> x >> y;
if (a == 0)
{
update(1, x, y);
}
else if (a == 1)
{
cout << query(1, x, y) << endl;
}
}
}