JAVA Future源码解析
文章目录
- JAVA Future源码解析
- 前言
- 一、传统异步实现的弊端
- 二、what is Future ?
- 2.1 Future的基本概念
- 2.2Future 接口方法解析
- 2.2.1 取消任务执行cancel
- 2.2.2 检索任务是否被取消 isCancelled
- 2.2.3 检索任务是否完成 isDone
- 2.2.3 检索任务计算结果 get
- 三、RunnableFuture使Future可运行
- 四、FutureTask获取计算结果
- 4.1 FutureTask基本介绍
- 4.2 FutureTask方法解析
- 4.2.1 FutureTask构造方法
- 4.2.2 异步运算方法run
- 4.2.3 保存运算结果set
- 4.2.4 保存异常结果setException
- 4.2.5 唤醒等待线程finishCompletion
- 4.2.6 获取异步计算结果get
- 4.2.7 取消运算任务cancel
- 总结
前言
在使用JAVA语言开发系统中,使用异步任务是很常见的,比如:文件导入、导出;定时任务;大批量数据运算;日志记录等。这些操作可能会经过复杂的业务处理以至于花费较长的时间。通常来说,这些需要通过长时间的处理流程,我们都会采用异步进行处理,而不是让客户在前端一直等待直至处理完成。所谓异步,简单而言就是开启一个新线程,将这些复杂运算放入新线程中进行处理。Thread是JAVA中的线程对象,它实现了Runnable接口,如果要开启一个新的线程,那么就必须创建一个Thread对象,调用start方法。
一、传统异步实现的弊端
在JDK1.5之前(未引入Future这种模式,Future是在JDK1.5引入),对于异步处理时,我们无法直接获取异步线程处理完成的结果,也就是说无法在调用Thread.start之后,通过Thread获取异步处理计算的结果返还给我们。接口Runnable中的run方法设计返回形式时Void,因此我们无法通过该形式获取异步计算的最终结果。
这种任务只强调执行过程而不需要追溯最终结果,比如文件的导入、导出、定时任务等,它们的最终结果并不影响后续操作。
然而在现实生活中,有很多事情既关注执行过程也在乎最终结果,如果最终结果并不是你想要的,那么将无法进行后续。
这里举一个例子:
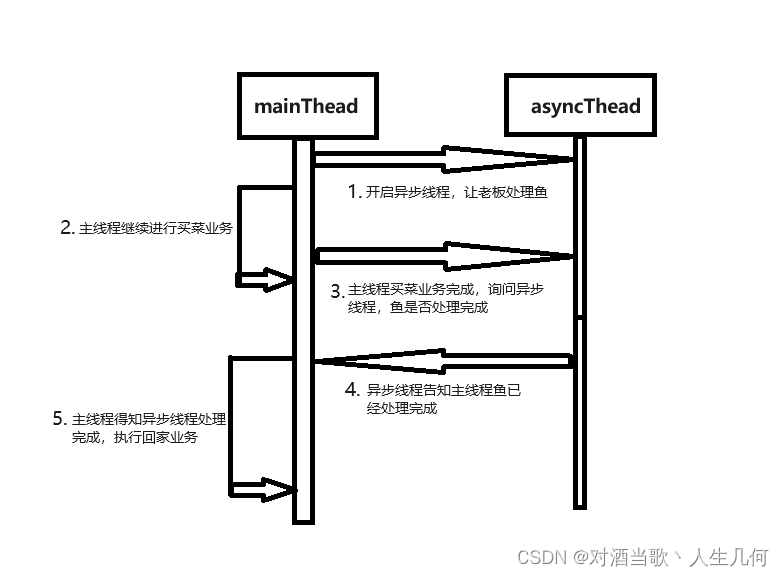
你去菜市场买菜,你买了一条鱼,你可以让老板先将鱼处理好后你再来拿,在处理鱼这段时间里,你可以继续去买点别的东西。等将你需要的东西买完,你再去问老板鱼处理好了没有,如果处理好了,你就将鱼带回家,否则等着老板处理完再回家。这个例子中,买菜相当于主线程(mainThread),而让卖鱼老板处理鱼相当于异步线程(asyncThread),回家相当于后续的业务。
当你买完菜(mainThread处理完必要的业务逻辑),需要询问卖鱼老板是否将鱼处理完成(询问asyncThread线程的处理结果),如果卖鱼老板处理完成(asyncThread处理完成并返回想要的结果),则将鱼带回家,否则等待卖鱼老板处理(mainThread等待asyncThread处理完成并返回想要的结果),直至处理完成才能回家。这个例子中,如果鱼没处理完成(asyncThread并未计算完成),则mainThread需要等待,此时回家这个业务将受到影响,也就是异步计算的结果影响了后续业务流程。
为了能更好的解决以上问题,JDK1.5版本引入了Future,Future提供了可获取异步计算结果的特性,它可以检索整个异步计算时的状态(新建,执行中,计算完成,取消),提供get方法阻塞获取异步计算结果。
二、what is Future ?
2.1 Future的基本概念
JDK1.5引入Future接口,用于定义提供获取异步计算结果,在源码注释中有这样一段话对Future进行描述:
/**
* A {@code Future} represents the result of an asynchronous
* computation 返回一个异步计算结果. Methods are provided to check if the computation is
* complete, to wait for its completion 方法提交检测任务计算结果是否完成,或者等待其完成,
* and to retrieve the result of
* the computation 检索结算的结果. The result can only be retrieved using method
* {@code get} when the computation has completed, blocking if
* necessary until it is ready 当调用get尝试获取计算结果时,如果计算未完成,则会一直阻塞等待,直至计算完成.
* Cancellation is performed by the
* {@code cancel} method取消操作. Additional methods are provided to
* determine(确定) if the task completed normally or was cancelled. Once a
* computation has completed, the computation cannot be cancelled.扩展方法提供确定一个任务是否正常完成还是被取消,
* 一旦计算完成,那么就不能被取消。
* If you would like to use a {@code Future} for the sake
* of cancellability but not provide a usable result, you can
* declare types of the form {@code Future<?>} and
* return {@code null} as a result of the underlying(基础) task.
* 如果你想让任务具有可取消性但是不提供可靠的结果,你可以定义一个Future类型的并且返回null作为基础结果
大概意思: Future可返回异步计算的结果,提供了检测任务计算状态以及获取计算结果的方法。获取任务计算结果只能通过Future接口中的get方法获取,并且如果在异步计算未完成之前调用了get方法,那么线程将阻塞直至异步计算完成并返回结果。还可以通过cancel方法尝试取消任务,一旦任务计算完成,那么任务不能被取消。
以上注释描述大体讲诉了Future的作用,一句话概括就是:
Future 提供检查异步计算是否完成,可以尝试取消任务,可以获取异步计算的最终结果
2.2Future 接口方法解析
在Future接口中定义了五个最基本的方法,别分是cacnel、isCancelled、isDone、get(分阻塞和阻塞超时),本小节将分别阐述这五个方法使用的场景:
2.2.1 取消任务执行cancel
cancel的字面意思就是取消,该方法的作用是尝试取消任务。如果任务已经计算完成或者已经被取消再或者因为某些原因不能被取消,那么该操作将失败(返回false)。如果在任务还未开始进行计算之前调用cancel方法,则取消成功后该任务将不会被执行,并且返回true表示任务取消成功,如果任务已经在允许中,则通过参数mayInterruptIfRunning来判断是否需要取消已经在运行中的任务,如果参数mayInterruptIfRunning为true,则表示正在执行中的任务允许被取消,否则,应该等待任务完成。如果调用cancel返回成功,则后续调用isDone或者是isCancelled应该总是返回true。
/**
* Attempts to cancel execution of this task. 尝试取消任务执行
* This attempt will fail if the task has already completed, has already been cancelled,
* or could not be cancelled for some other reason. 如果任务已经计算完成或者已经被取消再或者因为某些原因不能被取消,那么该操作将失败。
* If successful,and this task has not started when {@code cancel} is called,
* this task should never run.如果任务在没有运行时调用cancel取消成功,则这个任务将不会再被执行
* If the task has already started, 如果任务已经在运行中
* then the {@code mayInterruptIfRunning} parameter determines
* whether the thread executing this task should be interrupted in
* an attempt to stop the task. 参数 mayInterruptIfRunning将决定执行中的任务是否应该尝试停止任务
*
* <p>After this method returns, subsequent calls to {@link #isDone} will
* always return {@code true}. Subsequent calls to {@link #isCancelled}
* will always return {@code true} if this method returned {@code true}.如果调用cancel返回成功,则后续调用isDone或者是isCancelled应该总是返回true
*
* @param mayInterruptIfRunning {@code true} if the thread executing this
* task should be interrupted; otherwise, in-progress tasks are allowed
* to complete 如果参数mayInterruptIfRunning为true,则表示正在执行中的任务允许被取消,否则,应该等待任务完成
* @return {@code false} if the task could not be cancelled,
* typically because it has already completed normally; 返回false表示任务不能为取消,最典型的案例就是任务已经正常完成计算。
* {@code true} otherwise
*/
boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning);
2.2.2 检索任务是否被取消 isCancelled
isCancelled方法用于检索任务是否被取消,在调用cancel方法成功后,调用isCancelled方法则返回true表示当前任务已经被成功取消。
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this task was cancelled before it completed
* normally.如果任务再正常完成之前被取消则返回true
*
* @return {@code true} if this task was cancelled before it completed
*/
boolean isCancelled();
2.2.3 检索任务是否完成 isDone
isDone方法用于检索任务计算是否完成,如果任务完成则返回true,要注意的是任务完成可能是因为正常的计算完成或者是出现异常以及是被取消,出现以上情况导致任务完成,调用isDone依然会返回true.
/**
* Returns {@code true} if this task completed. 如果任务完成则返回true
*
* Completion may be due to normal termination, an exception, or
* cancellation -- in all of these cases, this method will return
* {@code true}. 完成意味着正常终止或者出现异常以及被取消,以上这些原因都会返回true
*
* @return {@code true} if this task completed
*/
boolean isDone();
2.2.3 检索任务计算结果 get
get方法用于获取当前异步计算的结果,如果在异步计算未完成之前调用get,那么线程将阻塞等待计算完成。如果在阻塞等待过程中调用了cancel方法取消任务,则抛出CancellationException ,如果是在计算中出现异常,则抛出ExecutionException 异常。
/**
* Waits if necessary for the computation to complete, and then
* retrieves its result. 等待任务计算完成并返回结果
*
* @return the computed result
* @throws CancellationException if the computation was cancelled 计算被取消,抛出异常
* @throws ExecutionException if the computation threw an
* exception 计算时抛出异常
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted
* while waiting 在等待时线程中断,抛出异常
*/
V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException;
/**
* Waits if necessary for at most the given time for the computation
* to complete, and then retrieves its result, if available. 在指定时间内返回计算结果
*
* @param timeout the maximum time to wait 最大等待时间
* @param unit the time unit of the timeout argument 时间单位,通常用(秒,分,时)
* @return the computed result 计算的结果
* @throws CancellationException if the computation was cancelled
* @throws ExecutionException if the computation threw an
* exception
* @throws InterruptedException if the current thread was interrupted
* while waiting
* @throws TimeoutException if the wait timed out
*/
V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException;
三、RunnableFuture使Future可运行
在第二小节中已经介绍了Future的基本概念和使用场景。但是如何能让Future在一个异步线程中运行起来?我们知道在JAVA中要开启新的线程有两种方式,一个是继承Thread类并重写run方法,另一个就是实现Runnable接口,将具体逻辑写道Runable的run方法里,然后新建一个Thread对象,将实现Ruannble的类通过构造函数放入Thread,调用start运行。
/**
* @Author: DI.YIN
* @Date: 2023/12/1 14:57
* @Version:
* @Description:
**/
public class RunnableImp implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("实现Runnable,实现run方法具体逻辑");
}
}
/**
* @Author: DI.YIN
* @Date: 2023/12/1 14:58
* @Version:
* @Description:
**/
public class NewMain {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Runnable runnable = new RunnableImp();
new Thread(runnable).start();
}
}
RunnableFuture采用第二种方式,RunnableFuture接口继承Runnable和Future,这样一来,RunnableFuture相当于是一个Runnable的扩展接口,包含了Runnable和Future的特性。从而实现RunnableFuture的实现类也可以在Thread中运行。
/**
* A {@link Future} that is {@link Runnable}. Successful execution of
* the {@code run} method causes completion of the {@code Future}
* and allows access to its results. Future就是一个Runnable,在成功执行run方法后可以获取计算结果,并且允许获取这个结果
* @see FutureTask
* @see Executor
* @since 1.6
* @author Doug Lea
* @param <V> The result type returned by this Future's {@code get} method
*/
public interface RunnableFuture<V> extends Runnable, Future<V> {
/**
* Sets this Future to the result of its computation
* unless it has been cancelled.
*/
void run();
}
四、FutureTask获取计算结果
4.1 FutureTask基本介绍
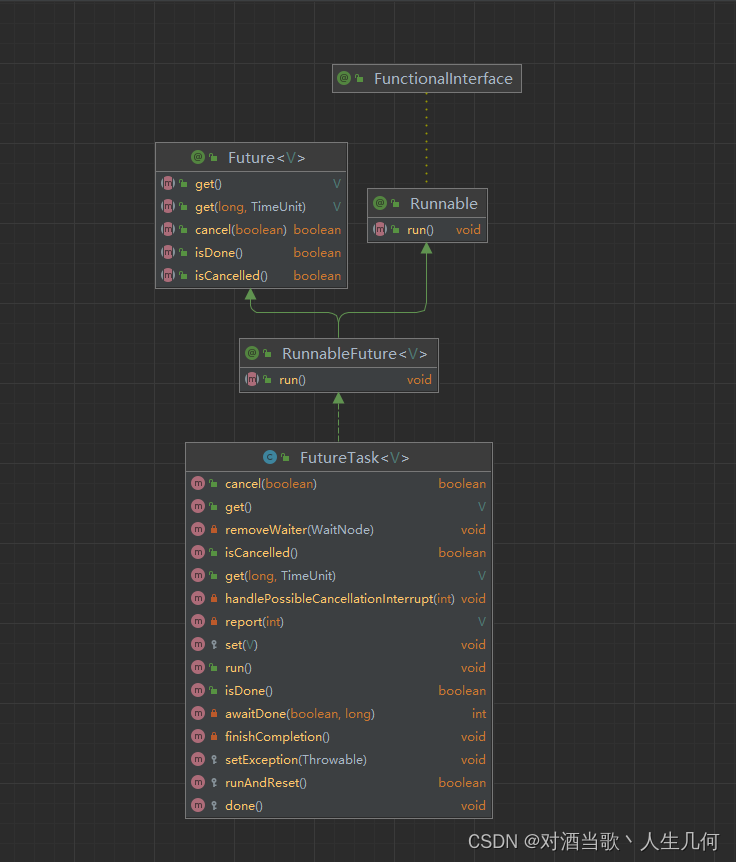
FutureTask是RunnableFuture的实现类,它实现了Future、Runnable、RunnableFuture中定义的方法,结构图如下:
在JDK源码注释中有写道该类的职责如下:
/**
* A cancellable asynchronous computation 可取消的异步计算.
* This class provides a base implementation of {@link Future},
* with methods to start and cancel a computation,
* query to see if the computation is complete, and
* retrieve the result of the computation. 该类提供了Future最基本的实现,包括开始和取消计算,查询任务是否计算完成,检索计算结果
* The result can only be retrieved when the computation has completed; 计算结果只有在计算完成后才能检索
* the {@code get} methods will block if the computation has not yet completed. get方法将阻塞直到任务计算完成
* Once the computation has completed, the computation cannot be restarted
* or cancelled (unless the computation is invoked using
* {@link #runAndReset}).一旦计算完成则不能进行重复计算或者取消,除非使用runAndReset方法
*
* <p>A {@code FutureTask} can be used to wrap a {@link Callable} or
* {@link Runnable} object. FutureTask用于包装Callable或者Runnable
* Because {@code FutureTask} implements{@code Runnable}, 因为FutureTask实现Runnable接口
* a {@code FutureTask} can be submitted to an {@link Executor} for execution.FutureTask可以提交到Executor中执行
*
* <p>In addition to serving as a standalone class, this class provides
* {@code protected} functionality that may be useful when creating
* customized task classes.
*
* @param <V> The result type returned by this FutureTask's {@code get} methods
* @author Doug Lea
* @since 1.5
*/
大概意思就是: FutureTask类为Future接口提供了最基本的实现,该类实现了Future中取消任务、检索任务计算状态以及获取计算结果等功能。通过get方法获取任务结果的最终结果,如果在调用get方法时任务还未计算完成,则将阻塞直至计算完成并返回最终结果。FutureTask可用于包装Runnable或者是Callable,因为FutureTask实现了Runnable接口,所以FutureTask可以当作Runnable的实现类放入线程中执行。
FutureTask使用七个不同的状态来管理整个任务的生命周期,依次为:
NEW(新建状态):创建一个FutureTask对象时,默认的状态为新建
COMPLETING(计算中):当任务计算完成调用set或者setException方法赋值结果值时,会将状态从NEW转为COMPLETING
NORMAL(正常):当计算完成将结果值设置完成后,会将状态从COMPLETING变为NORMAL
EXCEPTIONAL:当计算出现异常,将异常赋值给最终值之后,会将状态从COMPLETING转为EXCEPTIONAL
CANCELLED(已取消):调用cancel时,对于还未运行的任务,尝试将状态从NEW转为CANCELLED
INTERRUPTING(中断中):取消任务时,对于已经运行的任务,尝试将状态转为INTERRUPTING
INTERRUPTED(已中断): 取消任务时,对于正在取消的任务,尝试将状态从INTERRUPTING转INTERRUPTED
具体状态之间可能有的转化如下:
NEW -> COMPLETING -> NORMAL
NEW -> COMPLETING -> EXCEPTIONAL
NEW -> CANCELLED
NEW -> INTERRUPTING -> INTERRUPTED
FutureTask中定义了四个重要的属性,分别是callable,outcome,runner,waiters:
/**
* The underlying callable; nulled out after running
*/
private Callable<V> callable;
/**
* The result to return or exception to throw from get() 调用get方法时返回的结果或者异常
*/
private Object outcome; // 结果 non-volatile, protected by state reads/writes
/**
* The thread running the callable;可用的线程 CASed during run()
*/
private volatile Thread runner;
/**
* Treiber stack of waiting threads
*/
private volatile WaitNode waiters;
Callable与Runnable的不同之处在于,Callalbe的call方法带有返回值,而Runnable没有,并且Callable不能直接在Thread中直接运行,而Runnable可以。因此对于如果想要获取一个异步运算的结果,就可以在一个Runnable的实现类中重新run方法,然后在run方法中调用Callable的call方法获取运算结果,将运算结果保存起来返回给调用者。这种思路正是FutureTask所做的。FutureTask使用属性outcome来保存最终的结算结果,再通过外部调用其get方法将outcome返回给调用者。runner用于维护当前运算线程,waiters类似于一个链表,用于存储调用者线程。同时FutureTask中还使用CAS来控制其状态的改变,如果您不熟悉CAS,你可以参数一下文章Java CAS 原理详解
4.2 FutureTask方法解析
在4.1小节我们已经对FutureTask进行了基本介绍,通过对FutureTask的继承实现关系我们得知,FutureTask类似于一个曾强的Runnable实现类,内部维护一个Callable的是实现类,在开启新线程调用FutureTask的run方法时,在run方法里调用Callable的call方法获取计算最终值,并赋值给属性outcome,调用者可以通过FutureTask.get方法获取outcome的值。以下我们将通过源码介绍FutureTask基本方法的实现:
4.2.1 FutureTask构造方法
FutureTask提供了两个带参的构造函数:
/**
* Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the
* given {@code Callable}.
*
* @param callable the callable task
* @throws NullPointerException if the callable is null
*/
public FutureTask(Callable<V> callable) {
if (callable == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
this.callable = callable;
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
/**
* Creates a {@code FutureTask} that will, upon running, execute the
* given {@code Runnable}, and arrange that {@code get} will return the
* given result on successful completion.
*
* @param runnable the runnable task
* @param result the result to return on successful completion. If
* you don't need a particular result, consider using
* constructions of the form:
* {@code Future<?> f = new FutureTask<Void>(runnable, null)}
* @throws NullPointerException if the runnable is null
*/
public FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) {
this.callable = Executors.callable(runnable, result);
this.state = NEW; // ensure visibility of callable
}
FutureTask(Callable callable) 构造函数要求传入一个Callable 接口的实现类,并将该类赋值给属性callable,将状态属性state初始化为NEW 。
FutureTask(Runnable runnable, V result) 则是将传入的Runnable 和结果Result通过Executors构建成一个RunnableAdapter对象:
/**
* Returns a {@link Callable} object that, when
* called, runs the given task and returns the given result. This
* can be useful when applying methods requiring a
* {@code Callable} to an otherwise resultless action.
* @param task the task to run
* @param result the result to return
* @param <T> the type of the result
* @return a callable object
* @throws NullPointerException if task null
*/
public static <T> Callable<T> callable(Runnable task, T result) {
if (task == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
return new RunnableAdapter<T>(task, result);
}
RunnableAdapter对象也是Callable的是实现类,通过调用RunnableAdapter.call从而来触发Runnable.run,执行完成后将给定的result结果返回。两个构造函数的区别在于,一个是由我们自己创建好Callable的是实现类,另一个则是由FutureTask自己内部去创建,并且在运算完成后,返回我们自定义的结果。
/**
* A callable that runs given task and returns given result
*/
static final class RunnableAdapter<T> implements Callable<T> {
final Runnable task;
final T result;
RunnableAdapter(Runnable task, T result) {
this.task = task;
this.result = result;
}
public T call() {
task.run();
return result;
}
}
4.2.2 异步运算方法run
FutureTask相当于一个Runnable的增强是实现类,因此当它放入线程中运行时,线程会调用FutureTask.run的方法,其源码如下所示:
/**
* 任务计算,线程运算真正的run方法(runnable中的run)
*/
public void run() {
//如果状态不是NEW装状态或者runner不是null,则直接返回
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
//如果callable不为null并且状态为NEW
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;//计算结果
boolean ran;
try {
//调用callable计算获取结果
result = c.call();//调用callable计算结果
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
//抛出异常则计算结果置为空,ran为false,表示运算失败
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);//设置有异常结果
}
if (ran)
set(result);//设置正确结果
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
}
当调用run方法时,首先判断当前state是否为新建,并且尝试通过CAS将属性runner(runnerOffset是runner属性在类中物理偏移地址)从null设置为当前线程(Thread.currentThread()),如果不满足以上两个条件,则直接结束运算。
//如果状态不是NEW装状态或者runner不是null,则直接返回
if (state != NEW ||
!UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, runnerOffset,
null, Thread.currentThread()))
return;
如果满足以上条件,则判断属性callable是否不为空,并且state是否满足NEW状态,如果判断通过,则调用Callalbe.call方法进行真实逻辑运行并返回运算结果,由此可见Callable.call才是真正的运算逻辑,也就是我们的业务代码。如果运算成功没有抛出异常,则将ran标识为true,表示本次运算正常,通过set方法将运算的结果赋值给属性outcome,最后将runner置null便于GC。
try {
Callable<V> c = callable;
//如果callable不为null并且状态为NEW
if (c != null && state == NEW) {
V result;//计算结果
boolean ran;
try {
//调用callable计算获取结果
result = c.call();//调用callable计算结果
ran = true;
} catch (Throwable ex) {
//抛出异常则计算结果置为空,ran为false,表示运算失败
result = null;
ran = false;
setException(ex);//设置有异常结果
}
if (ran)
set(result);//设置正确结果
}
} finally {
// runner must be non-null until state is settled to
// prevent concurrent calls to run()
runner = null;
// state must be re-read after nulling runner to prevent
// leaked interrupts
int s = state;
if (s >= INTERRUPTING)
handlePossibleCancellationInterrupt(s);
}
4.2.3 保存运算结果set
在4.2.2中,我们看到如果运算正常,则将调用set方法保存计算结果。而set方法也比较简单,先通过CAS将状态从NEW转为COMPLETING,再将传入的result赋值给属性outcome以便于保存结果。赋值完成后通过CAS将状态设置为NORMAL表示任务运算完成。调用finishCompletion方法唤醒那些调用get方法阻塞的线程,最后将属性callalbe置null便于GC。
/**
* Sets the result of this future to the given value unless
* this future has already been set or has been cancelled.
* 设置指定返回的值,除非在此之前已经设定或者已经被取消
* <p>This method is invoked internally by the {@link #run} method
* upon successful completion of the computation. 在计算完成之后,该方法由run方法内部调用
*
* @param v the value
*/
protected void set(V v) {
//通过CAS将状态从NEW转为COMPLETING
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = v;
//如果设置结果成功,将状态从COMPLETING设置为NORMAL,标志任务完成
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, NORMAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
4.2.4 保存异常结果setException
在4.2.2中,我们看到如果运算抛出异常,则将调用setException方法保存异常结果。通过CAS将状态从NEW转换为COMPLETING,将异常结果赋值给outcome ,最后将状态设置为EXCEPTIONAL。
/**
* Causes this future to report an {@link ExecutionException}
* with the given throwable as its cause, unless this future has
* already been set or has been cancelled. 设置异常,除非在此之前已经设定或者已经被取消
*
* <p>This method is invoked internally by the {@link #run} method
* upon failure of the computation. 该方法将在run方法中计算失败时被调用
*
* @param t the cause of failure
*/
protected void setException(Throwable t) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW, COMPLETING)) {
outcome = t;
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, EXCEPTIONAL); // final state
finishCompletion();
}
}
4.2.5 唤醒等待线程finishCompletion
finishCompletion方法一般在调用set或者setException方法时,由其内部调用。正如你在4.2.3和4.2.4所看到的,该方法的作用是遍历链表waiters(里面存储着调用get方法阻塞休眠的线程),唤醒等待线程(LockSupport.unpark)并将其移出链表,最后将属性callable置null便于GC。
/**
* Removes and signals all waiting threads, invokes done(), and
* nulls out callable.
*/
private void finishCompletion() {
// assert state > COMPLETING;
for (WaitNode q; (q = waiters) != null; ) {
if (UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset, q, null)) {
for (; ; ) {
Thread t = q.thread;
if (t != null) {
q.thread = null;
//唤醒阻塞休眠线程
LockSupport.unpark(t);
}
WaitNode next = q.next;
if (next == null)
break;
q.next = null; // unlink to help gc
q = next;
}
break;
}
}
done();
callable = null; // to reduce footprint
}
4.2.6 获取异步计算结果get
get方法一般用于获取异步计算结果,在FutureTask中提供了两种获取计算结果的方法,分永久阻塞和超时阻塞。永久阻塞表示当运算未完成时,则一直阻塞等待,另一种则是指定等待时间,如果超过指定时间,则抛出TimeoutException异常。
/**
* @throws CancellationException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public V get() throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException { //获取计算结果
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING) //如果当前线程状态小于等于1,则阻塞等待计算完成
s = awaitDone(false, 0L);
return report(s);
}
/**
* @throws CancellationException {@inheritDoc}
*/
public V get(long timeout, TimeUnit unit)
throws InterruptedException, ExecutionException, TimeoutException { //定时等待,如果超时抛出TimeoutException异常
if (unit == null)
throw new NullPointerException();
int s = state;
if (s <= COMPLETING &&
(s = awaitDone(true, unit.toNanos(timeout))) <= COMPLETING)
throw new TimeoutException();
return report(s);
}
我们以永久阻塞为例,在调用get方法时,首先获取当前任务状态state,如果state小于等于COMPLETING,表示当前任务还未运行或者是正在计算中,则调用awaitDone方法等待运算完成。awaitDone主要用于判断当前线程是否应该放入waiters链表中阻塞等待。
private int awaitDone(boolean timed, long nanos)
throws InterruptedException {
//如果是定时等待,则计算等待到时期限
final long deadline = timed ? System.nanoTime() + nanos : 0L;
WaitNode q = null;
boolean queued = false;
for (; ; ) {
if (Thread.interrupted()) { //如果当前线程中断,则抛出InterruptedException异常
removeWaiter(q);
throw new InterruptedException();
}
int s = state;
if (s > COMPLETING) { //如果状态大于COMPLETING,则清除节点线程并返回状态state
if (q != null)
q.thread = null;
return s;
} else if (s == COMPLETING) // cannot time out yet 此时可能正在赋值,将当前正在执行的线程让出 CPU 时间片,
// 线程状态 Running(运行中) 执行后会变为 Ready(就绪) 状态
Thread.yield();
else if (q == null)
q = new WaitNode();//创建节点对象
else if (!queued)
queued = UNSAFE.compareAndSwapObject(this, waitersOffset,
q.next = waiters, q);//放入链表
else if (timed) {
nanos = deadline - System.nanoTime();
if (nanos <= 0L) { //超时等待,移除节点
removeWaiter(q);
return state;
}
LockSupport.parkNanos(this, nanos); //阻塞指定时间
} else
LockSupport.park(this); //永久阻塞
}
}
当计算完成时,调用report方法获取计算结果,如果当前任务状态为NORMAL则返回outcome存储的计算结果,如果当前状态大于等于取消,则抛出CancellationException异常,再不满足条件,则直接抛出执行异常ExecutionException。
/**
* 由get方法调用
* Returns result or throws exception for completed task. 返回计算结果或者异常
*
* @param s completed state value 完成的状态值
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
private V report(int s) throws ExecutionException {
Object x = outcome;
if (s == NORMAL) //状态为正常完成,则返回计算结果
return (V) x;
if (s >= CANCELLED) //状态大于取消状态,则取消异常
throw new CancellationException();
throw new ExecutionException((Throwable) x);
}
4.2.7 取消运算任务cancel
FutureTask中提供了取消任务运算的方法cancel,通过参数mayInterruptIfRunning来控制是否允许取消已经再允许中的任务,如果mayInterruptIfRunning为false,表示不允许取消已经在运行中的任务,如果此时任务为NEW状态,则通过CAS将状态该为CANCELLED。否则直接返回false。如果mayInterruptIfRunning为true,则通过Thread.interrupt中断线程,将状态改为INTERRUPTED。最后调用finishCompletion唤醒阻塞线程。
public boolean cancel(boolean mayInterruptIfRunning) {
if (!(state == NEW &&
UNSAFE.compareAndSwapInt(this, stateOffset, NEW,
mayInterruptIfRunning ? INTERRUPTING : CANCELLED))) {
return false;
}
try { // in case call to interrupt throws exception
if (mayInterruptIfRunning) { //如果允许终端正在允许的线程,则调用interrupt进行中断
try {
Thread t = runner;
if (t != null)
t.interrupt();
} finally { // final state
UNSAFE.putOrderedInt(this, stateOffset, INTERRUPTED);
}
}
} finally {
finishCompletion();
}
return true;
}
总结
总体来说FutureTask在Runnable的基础上增加了任务取消、获取计算结果等特性,弥补了Runnable的缺陷。FutureTask的源码相对于简单且易读。比较适合初学者学习。在本章中并未讲诉完整个FutureTask的源码,如isCancelled、isDone等方法的实现,这些将留给阁下来探索。