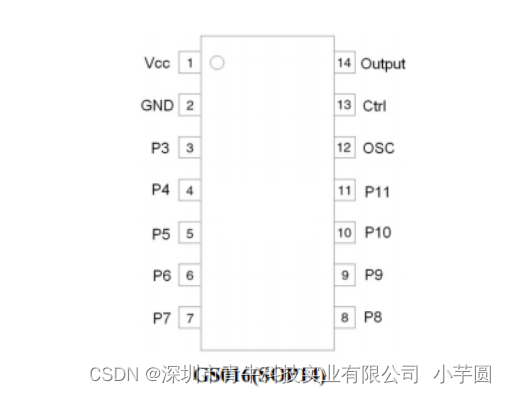
1 文本格式
// CPP code to find the nth term of the Baum Sweet Sequence
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int nthBaumSweetSeq(int n)
{
// bitset stores bitwise representation
bitset<32> bs(n);
// len stores the number of bits in the
// binary of n. builtin_clz() function gives
// number of zeroes present before the
// leading 1 in binary of n
int len = 32 - __builtin_clz(n);
int baum = 1; // nth term of baum sequence
for (int i = 0; i < len;) {
int j = i + 1;
// enter into a zero block
if (bs[i] == 0) {
int cnt = 1;
// loop to run through each zero block
// in binary representation of n
for (j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
// counts consecutive zeroes
if (bs[j] == 0)
cnt++;
else
break;
}
// check if the number of consecutive
// zeroes is odd
if (cnt % 2 == 1)
baum = 0;
}
i = j;
}
return baum;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 8;
cout << nthBaumSweetSeq(n);
return 0;
}
2 代码格式
// CPP code to find the nth term of the Baum Sweet Sequence
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int nthBaumSweetSeq(int n)
{
// bitset stores bitwise representation
bitset<32> bs(n);
// len stores the number of bits in the
// binary of n. builtin_clz() function gives
// number of zeroes present before the
// leading 1 in binary of n
int len = 32 - __builtin_clz(n);
int baum = 1; // nth term of baum sequence
for (int i = 0; i < len;) {
int j = i + 1;
// enter into a zero block
if (bs[i] == 0) {
int cnt = 1;
// loop to run through each zero block
// in binary representation of n
for (j = i + 1; j < len; j++) {
// counts consecutive zeroes
if (bs[j] == 0)
cnt++;
else
break;
}
// check if the number of consecutive
// zeroes is odd
if (cnt % 2 == 1)
baum = 0;
}
i = j;
}
return baum;
}
// Driver Code
int main()
{
int n = 8;
cout << nthBaumSweetSeq(n);
return 0;
}