目录
- 1.概述
- 2.结构
- 3.案例实现
- 3.1.“白箱”备忘录模式
- 3.2.”黑箱”备忘录模式
- 4.优缺点
- 5.使用场景
1.概述
(1)备忘录模式 (Memento Pattern) 又称为快照模式,是一种行为型设计模式,它提供了一种保存和恢复对象状态的机制。备忘录模式允许在不破坏封装性的前提下,捕获一个对象的内部状态,并将其保存在一个备忘录 (Memento) 对象中。随后,可以使用备忘录对象将对象状态恢复到之前保存的状态。
(2)很多软件都提供了撤销 (Undo) 操作,如 Word、记事本、Photoshop、IDEA 等软件在编辑时按 Ctrl+Z 组合键时能撤销当前操作,使文档恢复到之前的状态;还有在浏览器中的后退键、数据库事务管理中的回滚操作、玩游戏时的中间结果存档功能、数据库与操作系统的备份操作、棋类游戏中的悔棋功能等都属于这类。
2.结构
(1)备忘录模式的主要角色如下:
- 发起人 (Originator) 角色:记录当前时刻的内部状态信息,提供创建备忘录和恢复备忘录数据的功能,实现其他业务功能,它可以访问备忘录里的所有信息。
- 备忘录 (Memento) 角色:负责存储发起人的内部状态,在需要的时候提供这些内部状态给发起人。
- 管理者 (Caretaker) 角色:对备忘录进行管理,提供保存与获取备忘录的功能,但其不能对备忘录的内容进行访问与修改。
(2)除此之外,备忘录有两个等效的接口:
- 窄接口:管理者对象(和其他发起人对象之外的任何对象)看到的是备忘录的窄接口 (narror Interface),这个窄接口只允许他把备忘录对象传给其他的对象。
- 宽接口:与管理者看到的窄接口相反,发起人对象可以看到一个宽接口 (wide Interface),这个宽接口允许它读取所有的数据,以便根据这些数据恢复这个发起人对象的内部状态。
3.案例实现
【例】游戏挑战 Boss:游戏中的某个场景,一游戏角色有生命力、攻击力、防御力等数据,在打 Boss 前和后一定会不一样的,我们允许玩家如果感觉与 Boss 决斗的效果不理想可以让游戏恢复到决斗之前的状态。
3.1.“白箱”备忘录模式
备忘录角色对任何对象都提供一个接口,即宽接口,备忘录角色的内部所存储的状态就对所有对象公开。类图如下:
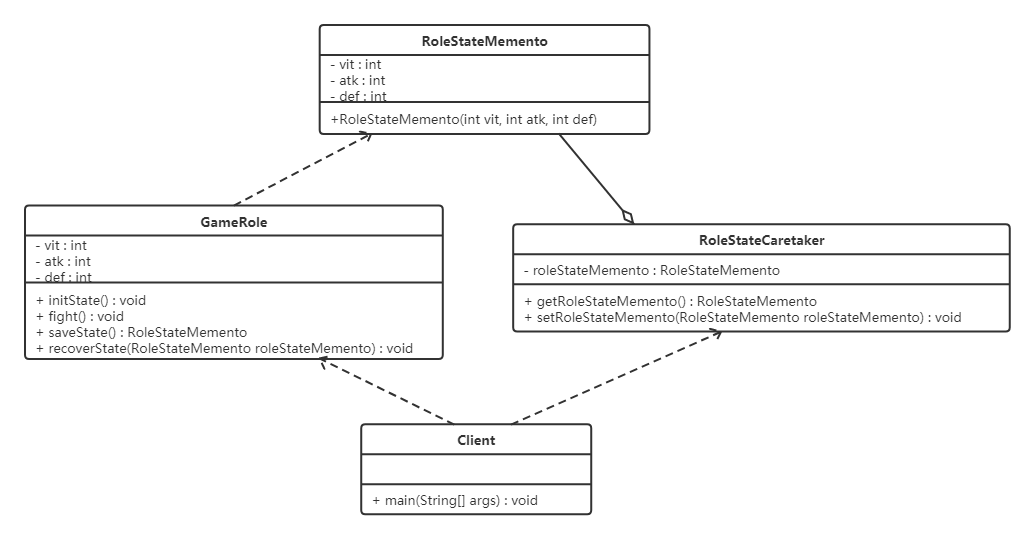
具体实现代码如下:
RoleStateMemento.java(备忘录角色)
//备忘录角色类(存储历史状态)
public class RoleStateMemento {
//生命力
private int vit;
//攻击力
private int atk;
//防御力
private int def;
public RoleStateMemento() {
}
public RoleStateMemento(int vit, int atk, int def) {
this.vit = vit;
this.atk = atk;
this.def = def;
}
public int getVit() {
return vit;
}
public void setVit(int vit) {
this.vit = vit;
}
public int getAtk() {
return atk;
}
public void setAtk(int atk) {
this.atk = atk;
}
public int getDef() {
return def;
}
public void setDef(int def) {
this.def = def;
}
}
GameRole.java(发起人角色)
//游戏角色类(发起人角色)
public class GameRole {
//生命力
private int vit;
//攻击力
private int atk;
//防御力
private int def;
//初始化内部状态
public void initState(){
this.vit = 100;
this.atk = 100;
this.def = 100;
}
//战斗
public void fight(){
this.vit = 0;
this.atk = 0;
this.def = 0;
}
//保存角色状态功能
public RoleStateMemento saveState(){
return new RoleStateMemento(vit,atk,def);
}
//恢复角色状态
public void recoverState(RoleStateMemento roleStateMemento){
//将备忘录对象中存储的状态赋值给当前对象成员
this.vit = roleStateMemento.getVit();
this.atk = roleStateMemento.getAtk();
this.def = roleStateMemento.getDef();
}
//展示状态功能
public void stateDisplay(){
System.out.println("角色生命力:" + vit);
System.out.println("角色攻击力:" + atk);
System.out.println("角色防御力:" + def);
}
public int getVit() {
return vit;
}
public void setVit(int vit) {
this.vit = vit;
}
public int getAtk() {
return atk;
}
public void setAtk(int atk) {
this.atk = atk;
}
public int getDef() {
return def;
}
public void setDef(int def) {
this.def = def;
}
}
RoleStateCaretaker.java(管理者角色)
//备忘录对象管理对象
public class RoleStateCaretaker {
//声明RoleStateMemento类型的变量
private RoleStateMemento roleStateMemento;
public RoleStateMemento getRoleStateMemento() {
return roleStateMemento;
}
public void setRoleStateMemento(RoleStateMemento roleStateMemento) {
this.roleStateMemento = roleStateMemento;
//白箱
//roleStateMemento.setAtk(100);
}
}
Client.java
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("---------------大战 Boss 前-----------------");
//创建游戏角色对象
GameRole gameRole = new GameRole();
//初始化状态操作
gameRole.initState();
gameRole.stateDisplay();
//将该游戏角色内部状态进行备份
//创建管理者对象
RoleStateCaretaker roleStateCaretaker = new RoleStateCaretaker();
roleStateCaretaker.setRoleStateMemento(gameRole.saveState());
System.out.println("---------------大战 Boss 后-----------------");
//损耗严重
gameRole.fight();
gameRole.stateDisplay();
System.out.println("---------------恢复之前的状态-----------------");
gameRole.recoverState(roleStateCaretaker.getRoleStateMemento());
gameRole.stateDisplay();
}
}
结果如下:
---------------大战 Boss 前-----------------
角色生命力:100
角色攻击力:100
角色防御力:100
---------------大战 Boss 后-----------------
角色生命力:0
角色攻击力:0
角色防御力:0
---------------恢复之前的状态-----------------
角色生命力:100
角色攻击力:100
角色防御力:100
分析:白箱备忘录模式是破坏封装性的。但是通过程序员自律,同样可以在一定程度上实现模式的大部分用意。
3.2.”黑箱”备忘录模式
备忘录角色对发起人对象提供一个宽接口,而为其他对象提供一个窄接口。在Java语言中,实现双重接口的办法就是将备忘录类设计成发起人类的内部成员类。 将 RoleStateMemento 设为 GameRole 的内部类,从而将 RoleStateMemento 对象封装在GameRole 里面;在外面提供一个标识接口 Memento 给 RoleStateCaretaker 及其他对象使用。这样 GameRole 类看到的是 RoleStateMemento 所有的接口,而 RoleStateCaretaker 及其他对象看到的仅仅是标识接口 Memento 所暴露出来的接口,从而维护了封装型。其类图如下:
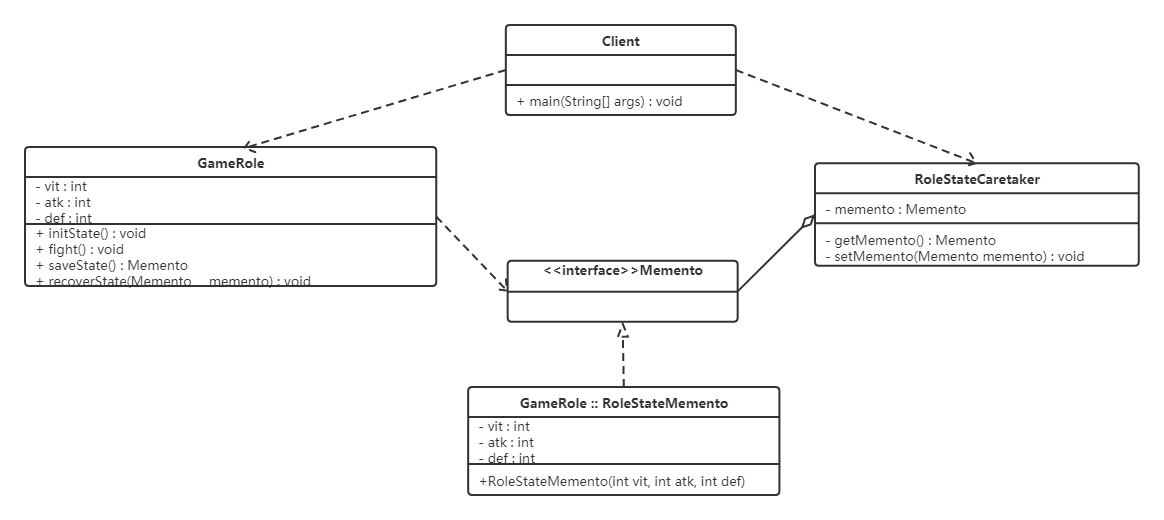
具体实现代码如下:
Memento.java(备忘录接口)
//备忘录接口,对外提供窄接口
public interface Memento {
}
GameRole.java(发起人角色)
//游戏角色类(属于发起人角色)
public class GameRole {
private int vit; //生命力
private int atk; //攻击力
private int def; //防御力
//初始化内部状态
public void initState() {
this.vit = 100;
this.atk = 100;
this.def = 100;
}
//战斗
public void fight() {
this.vit = 0;
this.atk = 0;
this.def = 0;
}
//保存角色状态功能
public Memento saveState() {
return new RoleStateMemento(vit,atk,def);
}
//恢复角色状态
public void recoverState(Memento memento) {
RoleStateMemento roleStateMemento = (RoleStateMemento) memento;
//将备忘录对象中存储的状态赋值给当前对象的成员
this.vit = roleStateMemento.getVit();
this.atk = roleStateMemento.getAtk();
this.def = roleStateMemento.getDef();
}
//展示状态功能
public void stateDisplay() {
System.out.println("角色生命力:" + vit);
System.out.println("角色攻击力:" + atk);
System.out.println("角色防御力:" + def);
}
public int getVit() {
return vit;
}
public void setVit(int vit) {
this.vit = vit;
}
public int getAtk() {
return atk;
}
public void setAtk(int atk) {
this.atk = atk;
}
public int getDef() {
return def;
}
public void setDef(int def) {
this.def = def;
}
//在内部定义备忘录内部类 RoleStateMemento (该内部类设置为私有的)
private class RoleStateMemento implements Memento {
private int vit; //生命力
private int atk; //攻击力
private int def; //防御力
public RoleStateMemento(int vit, int atk, int def) {
this.vit = vit;
this.atk = atk;
this.def = def;
}
public RoleStateMemento() {
}
public int getVit() {
return vit;
}
public void setVit(int vit) {
this.vit = vit;
}
public int getAtk() {
return atk;
}
public void setAtk(int atk) {
this.atk = atk;
}
public int getDef() {
return def;
}
public void setDef(int def) {
this.def = def;
}
}
}
RoleStateCaretaker.java(管理者角色)
//备忘录对象管理对象
public class RoleStateCaretaker {
/*
负责人角色类 RoleStateCaretaker 能够得到的备忘录对象是以 Memento 为接口的,由于
这个接口仅仅是一个标识接口,因此负责人角色不可能改变这个备忘录对象的内容。
*/
//声明RoleStateMemento类型的变量
private Memento memento;
public Memento getMemento() {
return memento;
}
public void setMemento(Memento memento) {
this.memento = memento;
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("---------------大战 Boss 前-----------------");
//创建游戏角色对象
GameRole gameRole = new GameRole();
gameRole.initState();//初始化状态操作
gameRole.stateDisplay();
//将该游戏角色内部状态进行备份
//创建管理者对象
RoleStateCaretaker roleStateCaretaker = new RoleStateCaretaker();
roleStateCaretaker.setMemento(gameRole.saveState());
System.out.println("---------------大战 Boss 后-----------------");
//损耗严重
gameRole.fight();
gameRole.stateDisplay();
System.out.println("---------------恢复之前的状态-----------------");
gameRole.recoverState(roleStateCaretaker.getMemento());
gameRole.stateDisplay();
}
}
结果与“黑箱”备忘录模式的一样。
4.优缺点
(1)备忘录模式是一种行为型设计模式,用于捕获和恢复对象的内部状态。备忘录模式具有以下优点和缺点:
- 优点:
- 备忘录模式可以在不破坏对象封装性的情况下保存和恢复对象的状态。它将状态的获取和修改分离开来,有助于实现对象的单一职责原则。
- 备忘录模式提供了一种灵活和可扩展的方式来保存和恢复对象状态。可以动态地创建备忘录对象,并将其存储在任何地方,以满足不同的需求。
- 备忘录模式可以简化备份和还原操作。通过将对象状态保存到备忘录对象中,可以轻松地实现撤销、重做和历史记录等功能。
- 备忘录模式对客户端透明,客户端无需关心对象状态的保存和恢复过程。这减少了客户端和对象之间的耦合性,提高了代码的可维护性和灵活性。
- 缺点:
- 备忘录模式可能会增加内存消耗。当对象的状态较大或状态变化频繁时,需要存储大量的备忘录对象,从而增加了内存开销。
- 备忘录模式的实现可能涉及到对象的深拷贝操作,这可能会导致性能下降。
- 备忘录模式无法防止其他对象直接访问备忘录对象,从而破坏对象的封装性。需要在设计和实现过程中注意安全性和可靠性。
(2)综上所述,备忘录模式是一种有用的设计模式,可以有效地管理对象的状态。然而,在应用时需要权衡其优点和缺点,并根据具体情况确定是否使用备忘录模式。
5.使用场景
(1)备忘录模式适用于以下场景:
- 保存和还原对象状态。如文本编辑器中的撤销和重做操作、游戏中的存档和读档等。
- 需要创建快照的应用程序。比如数据备份、快照生成器等应用场景。
- 实现草稿箱功能。将用户输入的内容保存到备忘录对象中,用户可以随时从备忘录对象中恢复已保存的内容。
- 实现事务的回滚功能。比如数据库事务中的回滚操作、操作系统中的系统还原等。
- 需要保存历史记录的应用程序。比如浏览器中的访问历史记录、绘图工具中的历史记录等。
(2)总的来说,备忘录模式适用于所有需要保存和恢复对象状态的应用场景。备忘录模式可以帮助实现对象的可撤销性、可恢复性和灵活性,并简化备份和还原操作。