1 卷积介绍
1.1 什么是卷积
卷积(convolution),是一种运算,你可以类比于加,减,乘,除,矩阵的点乘与叉乘等等,它有自己的运算规则,卷积的符号是星号*。表达式为:
连续卷积表达式:

离散卷积表达式为:
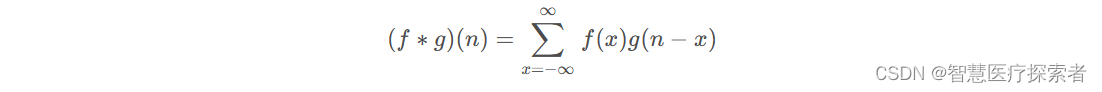
从参数上来看,x + (n-x) = n,可以类比为x + y = n,也就是说f, g的参数满足规律y = -x + n,即g的参数是f的参数先翻转再平移n。把g从右边褶到左边去,也就是卷积的卷的由来。然后在这个位置对两个函数的对应点相乘,然后相加,这个过程是卷积的积的过程。
因此卷积的过程可以理解为:翻转,滑动,叠加。其中翻转指的是g,滑动指的是n值在不断改变。最终将他们相乘相加。
1.2 卷积的意义
在泛函分析中,卷积、旋积或褶积是通过两个函数f和g生成第三个函数的一种数学运算,其本质是一种特殊的积分变换,表征函数f与g经过翻转和平移的重叠部分函数值乘积对重叠长度的积分。
如果将参加卷积的一个函数看作区间的指示函数,卷积还可以被看作是“滑动平均”的推广。卷积的意义如下:
-
模拟生物视觉:卷积操作模拟了人眼对图像进行观察、辨认的过程,因此卷积在图像处理领域应用广泛。它可以帮助我们理解人类视觉系统如何工作,并且为我们提供了一种有效的处理图像和语音的方法。
-
提升算法性能:卷积神经网络(CNN)是目前深度学习中最重要的模型之一,其基本结构就是卷积层,卷积操作在图像识别、语音识别和自然语言处理等领域提升了算法的性能。这使得卷积成为了现代机器学习和人工智能的重要组成部分。
-
数据压缩:卷积可以通过降维和滤波等操作减小数据的尺寸,从而实现数据的压缩。这对于处理大规模数据、实现数据存储和传输非常有用。
1.3 图像的卷积处理
对图像的blur操作,即降噪平滑操作,就是使用的卷积运算,最终的效果取决于卷积核的设置。以单通道卷积为例。
均值卷积核,就是认为目标像素点的值是周围值的平均数,即周围各点对它的影响是一样的,此处卷积核以3X3为例。

高斯滤波认为各个像素点距离核中心的距离不一样,导致颜色的贡献程度不一样,因此给不同的点不同的权重。取图像中的部分像素点

我们把这个矩阵看成f(x,y)函数,下标为参数,像素点的值为函数结果,那么要求f(1,1)处的卷积运算结果,因为现在是二维函数了,因此对应的卷积表达式为:
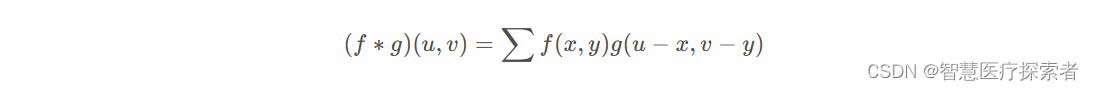
对应到本例u=1, v=1

我们来构建g(1-x, 1-y)函数,暂定为3X3的矩阵,我们知道目标点f(1,1)要对应g(0,0),如果将g(0,0)设置在核的中心,那么根据下标展开之后我们就可以构建出g

有了g函数之后,就可以执行运算了,注意运算的时候 f 和 g 的参数要符合卷积公式,即
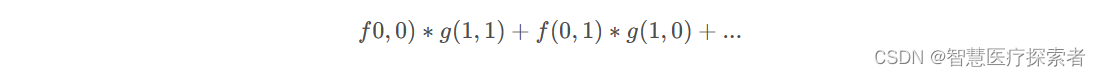
其实这样就够了,但是便于理解和说明,我们将矩阵先沿着X轴翻转,再沿Y轴翻转,中心点在 g(0,0) 处,得到
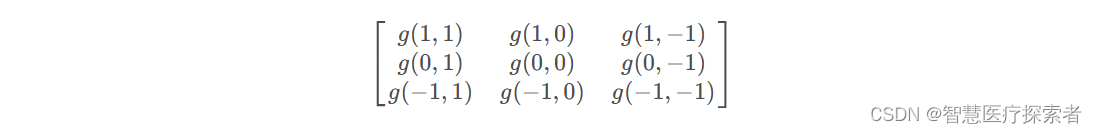
虽然翻转了,但是运算公式没有变化,只是从观察上更好一一对应,也更方便计算。
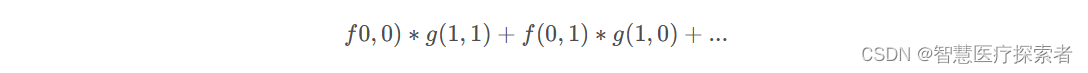
注意,将卷积核盖在目标像素点上面,将对应的像素点相乘相加,这种运算应该叫互相关运算(cross-correlation),通过将g进行翻转,使得卷积运算变成了互相关运算,将翻转之后的矩阵称为卷积核,并且在设计卷积核的时候就是参照互相关运算来的,而不会去关心真正的卷积运算。因此在实际应用中通常是直接去构建这个最终的矩阵。
在后续的计算中,将结果赋值给f(1,1),然后向右平移一格,达到边界后向下平移一格继续从左边开始卷积。整个过程中最外一层无法被算到,解决的方法是将原图像向外扩大一圈像素点并设置为0。通过设置不同的卷积核来达到不同的结果,这是机器视觉的基础操作。
2 pytorch中的卷积
CNN是深度学习的重中之重,而conv1D,conv2D,和conv3D又是CNN的核心,所以理解conv的工作原理就变得尤为重要,卷积中几个核心概念如下:
-
卷积运算:卷积核在输入信号(图像)上滑动,相应位置上进行乘加。
-
卷积核:又称为滤波器,过滤器,可认为是某种特征。
-
卷积过程类似于用一个模版去图像上寻找与它相似的区域,与卷积核模式越相似,激活值越高,从而实现特征提取。
-
卷积维度:一般情况下 ,卷积核在几个维度上滑动就是几维卷积。
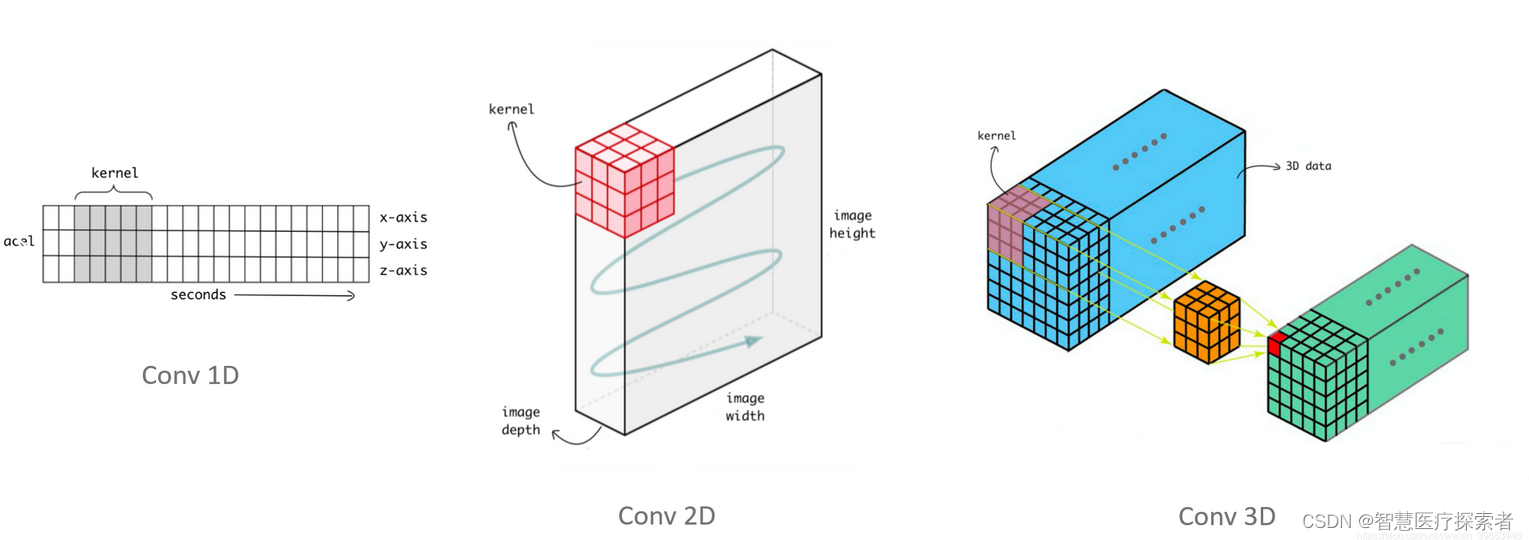
2.1 一维卷积nn.Conv1d
一维卷积nn.Conv1d主要用于文本数据,只对宽度进行卷积,对高度不卷积。通常,输入大小为word_embedding_dim * max_length,其中,word_embedding_dim为词向量的维度,max_length为句子的最大长度。卷积核窗口在句子长度的方向上滑动,进行卷积操作。
2.1.1 函数原型
torch.nn.Conv1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None)参数说明:
-
in_channels (int) – 输入通道数;在文本应用中,即为词向量的维度;
-
out_channels (int) – :输出通道数,等价于卷积核个数;
-
kernel_size (int or tuple) – 卷积核大小;卷积核的第二个维度由
in_channels决定,所以实际上卷积核的大小为kernel_size * in_channels -
stride (int or tuple, optional) – 卷积步长,默认为 1;
-
padding (int or tuple, optional) – Zero-padding,默认为 0;对输入的每一条边,补充0的层数;
-
padding_mode (string, optional) – ‘zeros’, ‘reflect’, ‘replicate’ or ‘circular’. Default: ‘zeros’;
-
dilation (int or tuple, optional) – 空洞卷积尺寸,默认为 1;
-
groups (int, optional) – 分组卷积设置,Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1;
-
bias (bool, optional) – If True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: True。
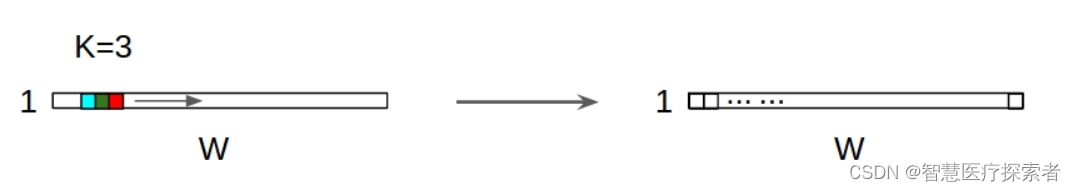
2.1.2 原理示意图

1D输入上的1D卷积示意图:
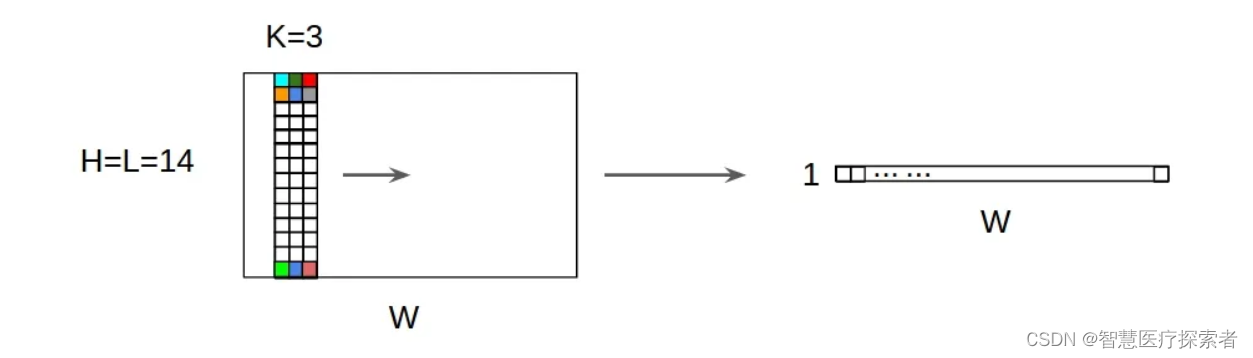
2D输入上的1D卷积示意图
说明:
-
对于一个卷积核(kernel),不管是1D输入还是2D输入,其输出都是1D矩阵;
-
卷积核的高度必须与输入特征图的高度相匹配;即 input = [W,L], filter = [k,L] output = [W];
-
对于多个卷积核的情况,其经过Conv1D之后,输出堆叠为2D矩阵,如果卷积核的个数为N,则输出的尺寸为 1D x N
-
1D卷积常用在时间序列数据的建模上。
尺寸计算:

注意:
-
其中, N表示卷积核个数;
表示输入通道数;
表示输入的长度;
-
必须与 Conv1D 中设置的 in_channels (int) 相等。
-
= Conv1D 中设置的 out_channels。
2.1.3 示例代码
输入:批大小为32,句子的最大长度为35,词向量维度为256
目标:句子分类,共2类
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
conv1 = nn.Conv1d(in_channels=256, out_channels=100, kernel_size=2)
input = torch.randn(32, 35, 256)
input = input.permute(0, 2, 1)
output = conv1(input)
print(output.shape)假设window_size = [3, 4, 5, 6],即共有四个卷积核,基于上述代码,具体计算过程如下:
- 原始输入大小为
(32, 35, 256),经过permute(0, 2, 1)操作后,输入的大小变为(32, 256, 35); - 使用1个卷积核进行卷积,可得到1个大小为
32 x 100 x 1的输出,共4个卷积核,故共有4个大小为32 x 100 x 1的输出; - 将上一步得到的4个结果在
dim = 1上进行拼接,输出大小为32 x 400 x 1; view操作后,输出大小变为32 x 400;- 全连接,最终输出大小为
32 x 2,即分别预测为2类的概率大小。
2.2 二维卷积Conv2D
二维卷积nn.Conv2d通常用于图像数据,对宽度和高度都进行卷积。
2.2.1 函数原型
class torch.nn.Conv2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None)参数说明:
-
in_channels (int) – 输入通道数;
-
out_channels (int) – :输出通道数,等价于卷积核个数;
-
kernel_size (int or tuple) – 卷积核大小;
-
stride (int or tuple, optional) – 卷积步长,默认为 1;
-
padding (int or tuple, optional) – Zero-padding,默认为 0;
-
padding_mode (string, optional) – ‘zeros’, ‘reflect’, ‘replicate’ or ‘circular’. Default: ‘zeros’;
-
dilation (int or tuple, optional) – 空洞卷积尺寸,默认为 1;
-
groups (int, optional) – 分组卷积设置,Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1;
-
bias (bool, optional) – If True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: True。
2.2.2 原理示意图
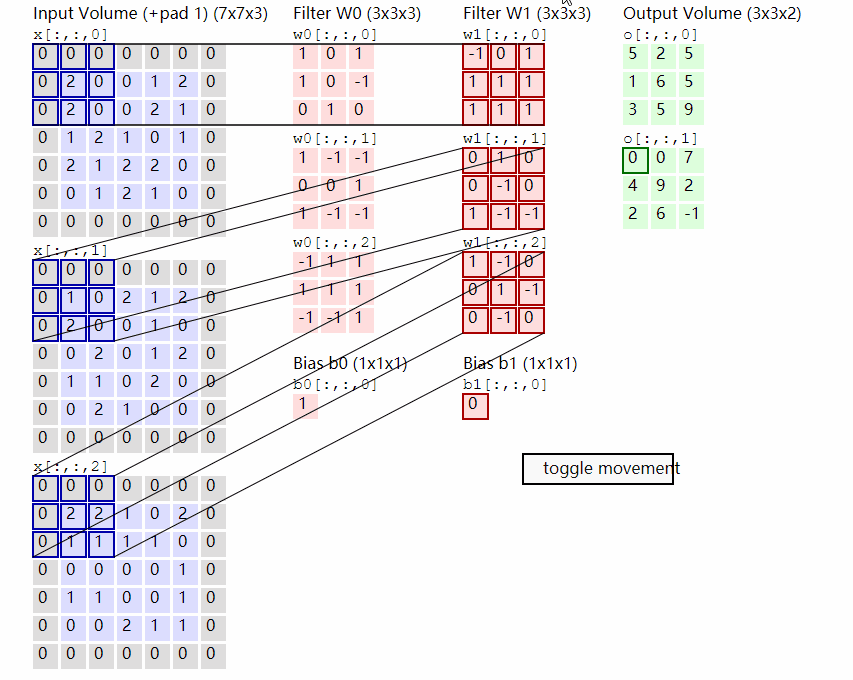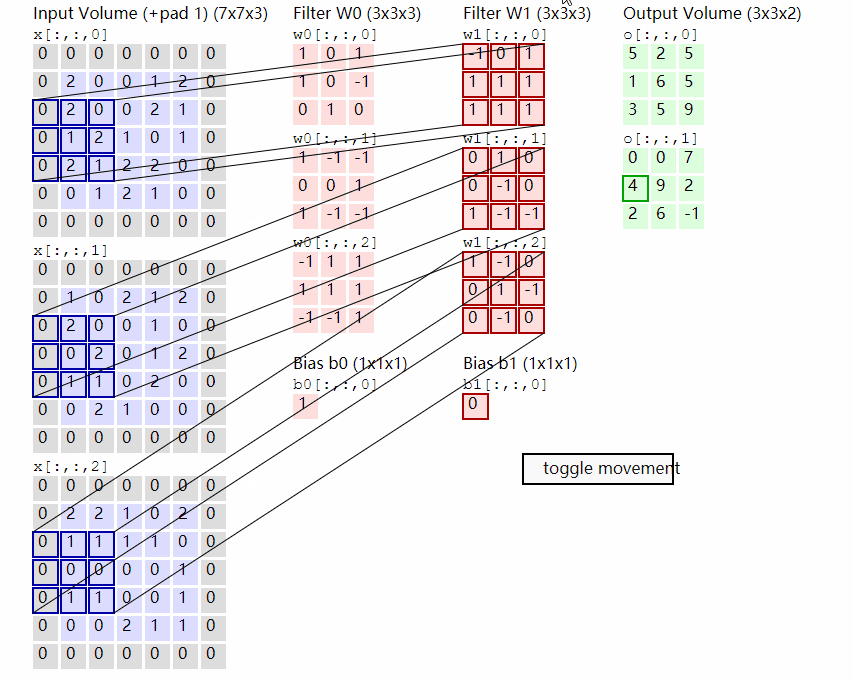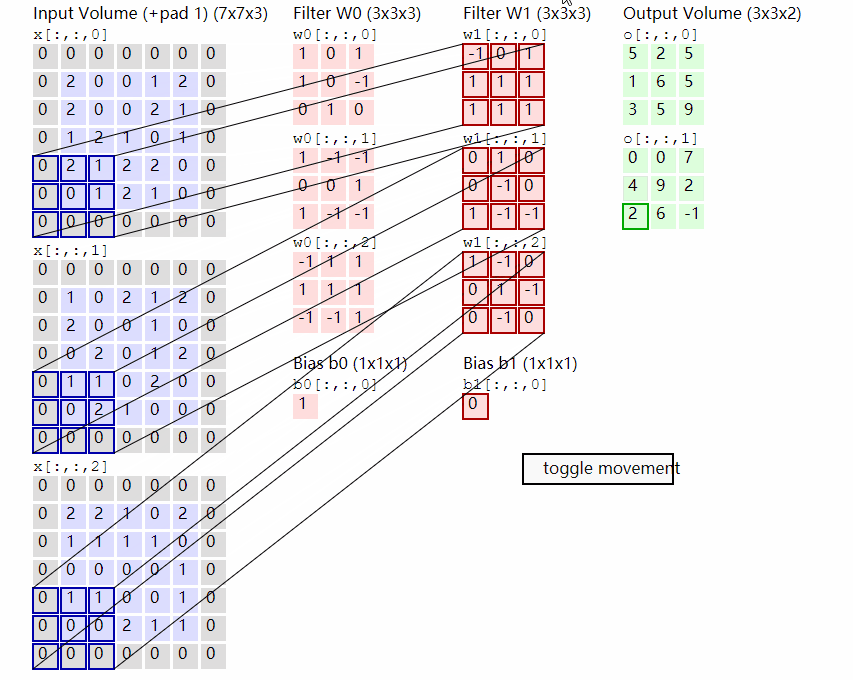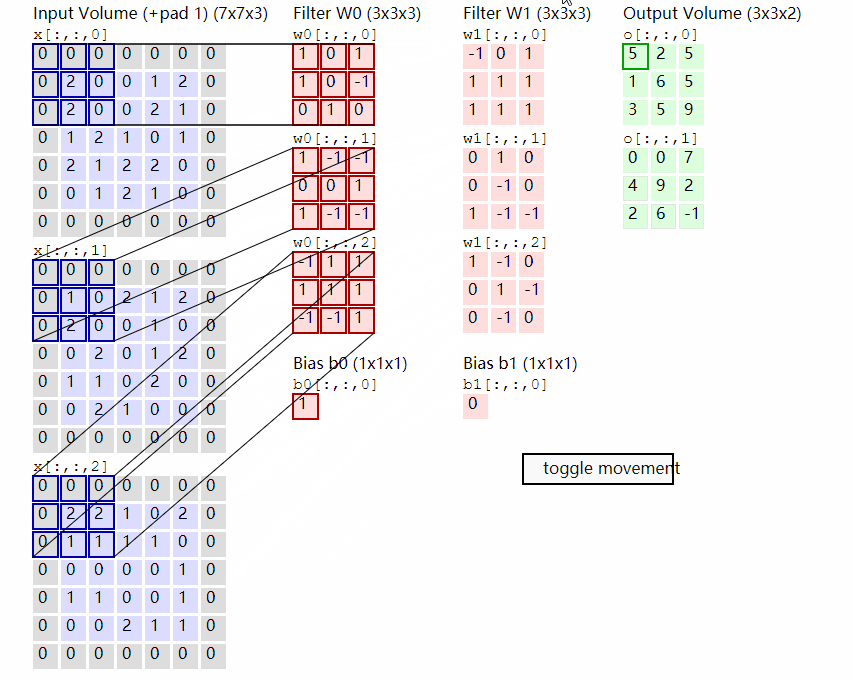
输出计算:

2.2.3 示例代码
假设现有大小为32 x 32的图片样本,输入样本的channels为1,该图片可能属于10个类中的某一类。CNN框架定义如下:
class CNN(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
nn.Model.__init__(self)
self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(1, 6, 5) # 输入通道数为1,输出通道数为6
self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(6, 16, 5) # 输入通道数为6,输出通道数为16
self.fc1 = nn.Linear(5 * 5 * 16, 120)
self.fc2 = nn.Linear(120, 84)
self.fc3 = nn.Linear(84, 10)
def forward(self, x):
# 输入x -> conv1 -> relu -> 2x2窗口的最大池化
x = self.conv1(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
# 输入x -> conv2 -> relu -> 2x2窗口的最大池化
x = self.conv2(x)
x = F.relu(x)
x = F.max_pool2d(x, 2)
# view函数将张量x变形成一维向量形式,总特征数不变,为全连接层做准备
x = x.view(x.size()[0], -1)
x = F.relu(self.fc1(x))
x = F.relu(self.fc2(x))
x = self.fc3(x)
return x网络整体结构:[conv + relu + pooling] * 2 + FC * 3
原始输入样本的大小:32 x 32 x 1
-
第一次卷积:使用6个大小为
5 x 5的卷积核,故卷积核的规模为(5 x 5) x 6;卷积操作的stride参数默认值为1 x 1,32 - 5 + 1 = 28,并且使用ReLU对第一次卷积后的结果进行非线性处理,输出大小为28 x 28 x 6; -
第一次卷积后池化:
kernel_size为2 x 2,输出大小变为14 x 14 x 6; -
第二次卷积:使用16个卷积核,故卷积核的规模为
(5 x 5 x 6) x 16;使用ReLU对第二次卷积后的结果进行非线性处理,14 - 5 + 1 = 10,故输出大小为10 x 10 x 16; -
第二次卷积后池化:
kernel_size同样为2 x 2,输出大小变为5 x 5 x 16; -
第一次全连接:将上一步得到的结果铺平成一维向量形式,5 x 5 x 16 = 400,即输入大小为
400 x 1,W大小为120 x 400,输出大小为120 x 1; -
第二次全连接,W大小为
84 x 120,输入大小为120 x 1,输出大小为84 x 1; -
第三次全连接:W大小为
10 x 84,输入大小为84 x 1,输出大小为10 x 1,即分别预测为10类的概率值。
2.3 三维卷积Conv3D
3D卷积常用于医学影像图像分割以及视频中的动作检测
2.3.1 函数原型
class torch.nn.Conv3d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, dilation=1, groups=1, bias=True, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None)参数说明:
-
in_channels (int) – 输入通道数;
-
out_channels (int) – :输出通道数,等价于卷积核个数;
-
kernel_size (int or tuple) – 卷积核大小;
-
stride (int or tuple, optional) – 卷积步长,默认为 1;
-
padding (int or tuple, optional) – Zero-padding,默认为 0;
-
padding_mode (string, optional) – ‘zeros’, ‘reflect’, ‘replicate’ or ‘circular’. Default: ‘zeros’;
-
dilation (int or tuple, optional) – 空洞卷积尺寸,默认为 1;
-
groups (int, optional) – 分组卷积设置,Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1;
-
bias (bool, optional) – If True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: True。
2.3.2 原理示意图
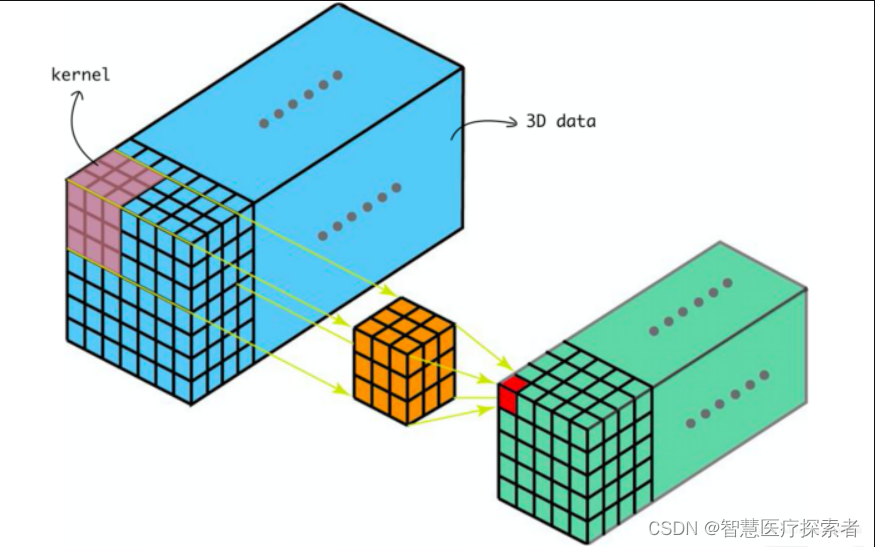
动态执行示意图:
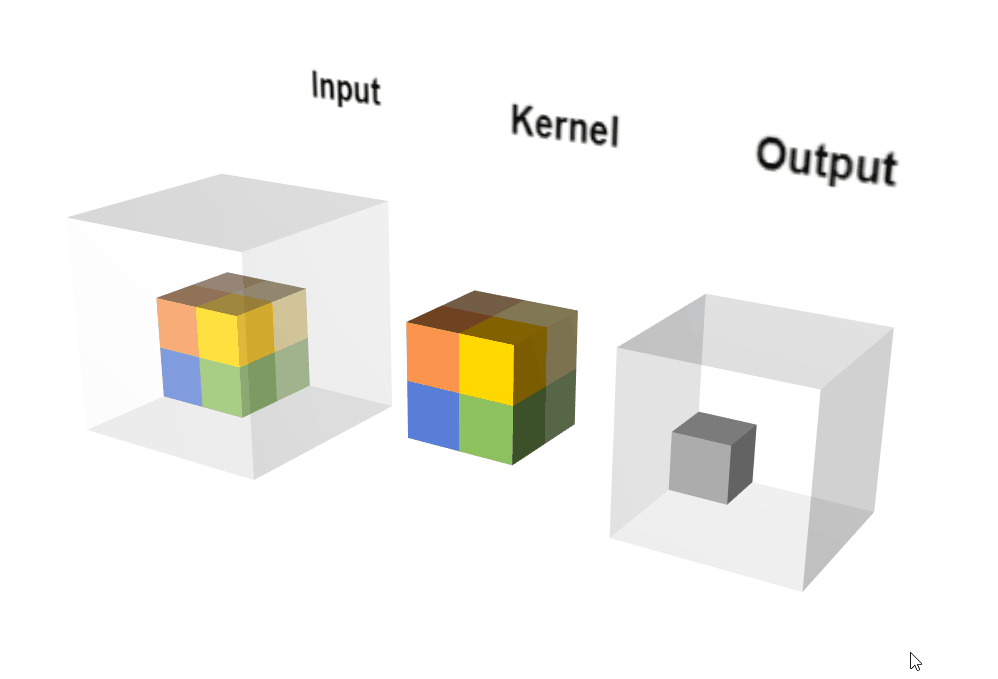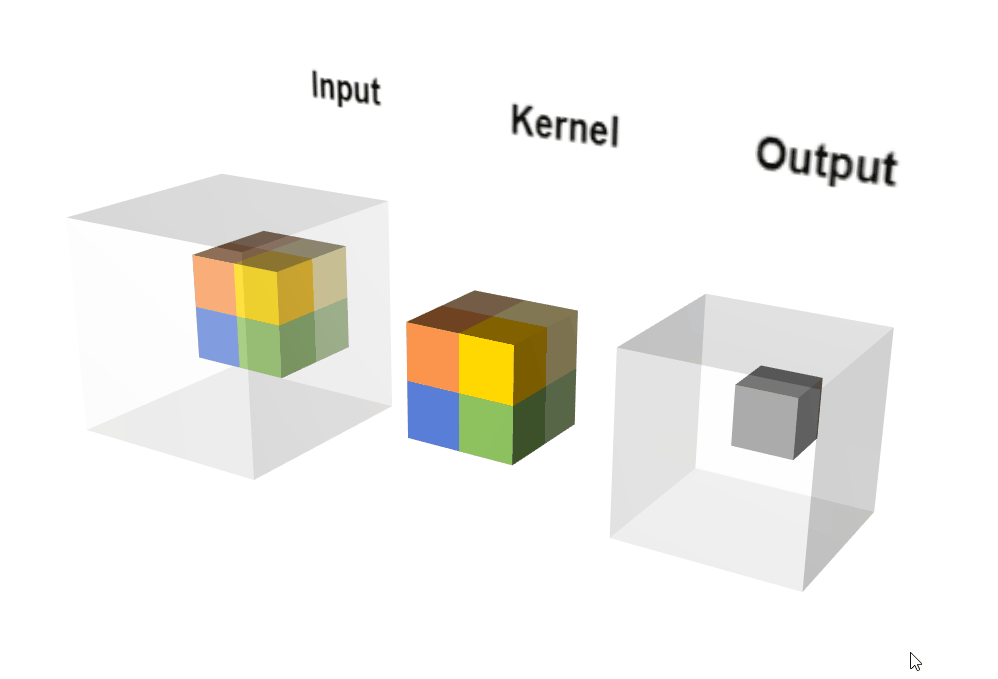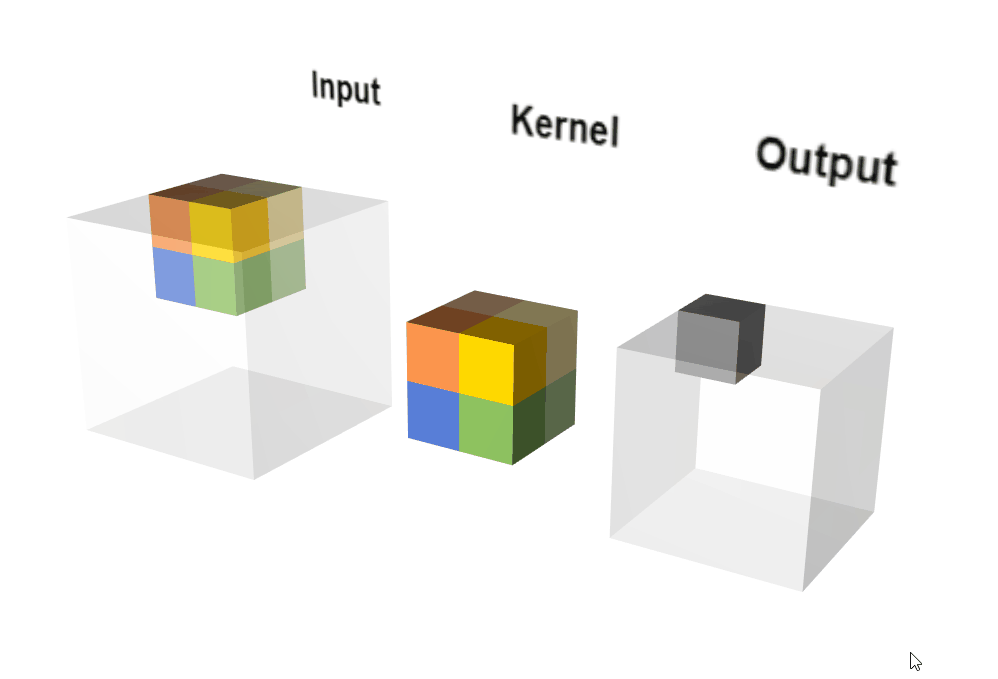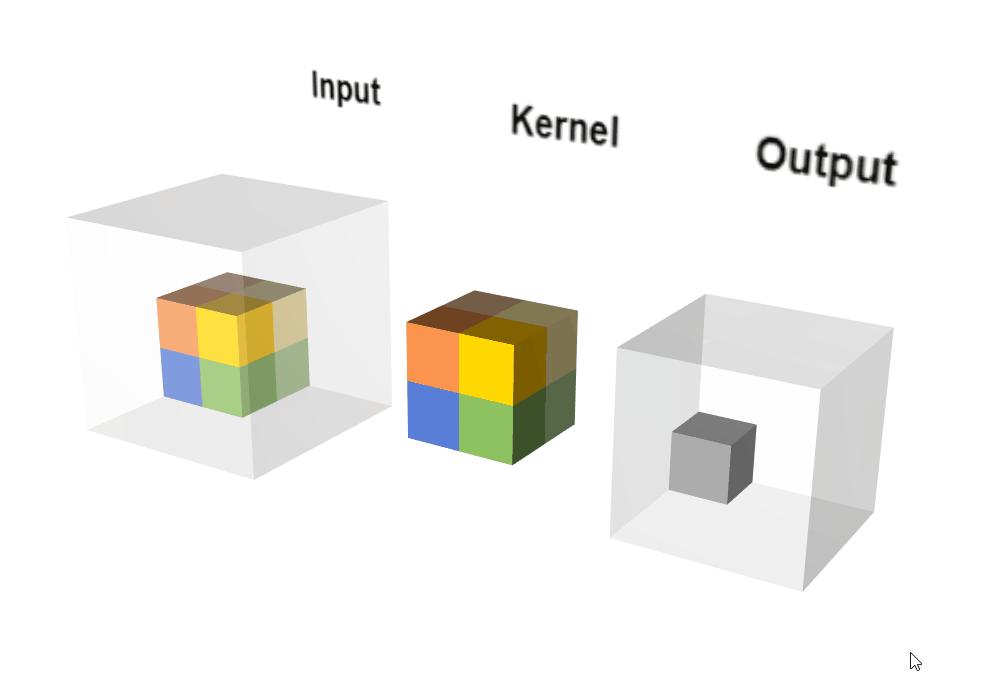
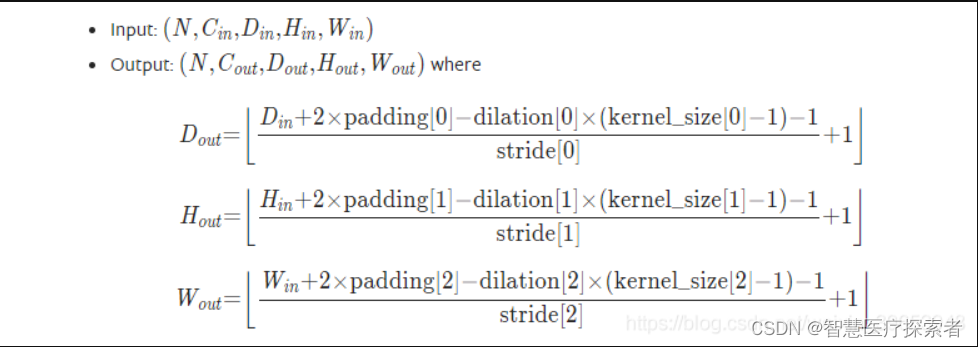
输出计算:
2.4 空洞卷积
空洞卷积诞生于图像分割领域,比如FCN网络,首先像传统的CNN一样,先卷积后池化,经过池化层之后,图像尺寸降低,感受野增大,但是因为图像分割需要实现像素级的输出,所以要将经过池化之后的较小的特征图通过转置卷积(反卷积)降采样到与原始图像相同的尺寸。之前的池化操作使得原特征图中的每个像素都具有较大的感受野,因此FCN中的两个关键:一是通过池化层增大感受野,二是通过转置卷积增大图像尺寸。在先减小后增大的过程中,肯定会丢失信息,那么能否不同池化层也可以使得网络具有较大的感受野呢?空洞卷积应运而生。
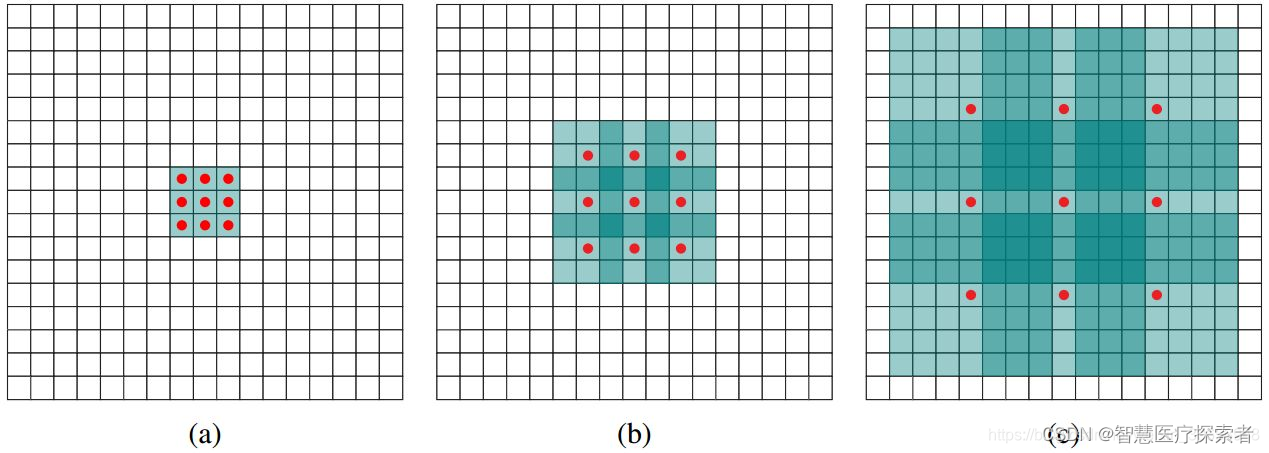
原理示意图如下: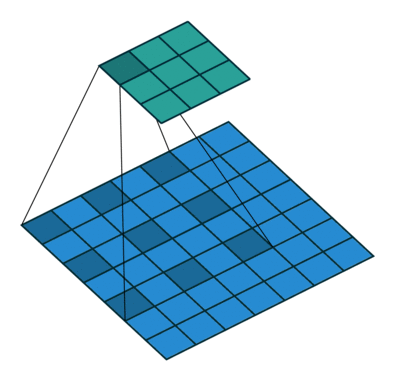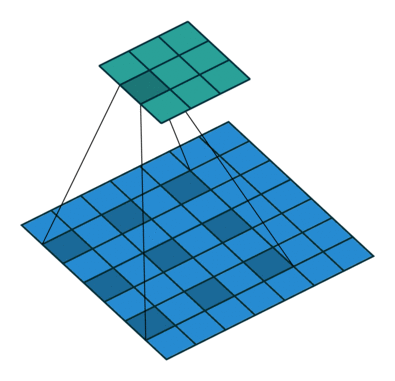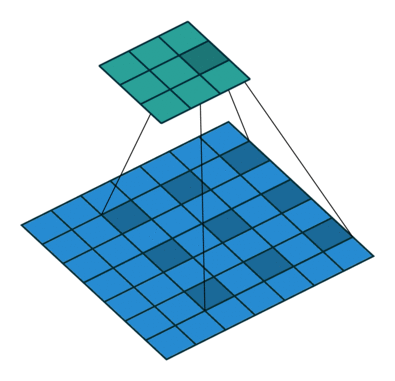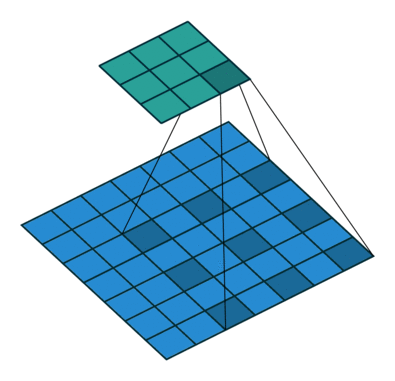
-
(a)图 对应3x3的1-dilated conv,和普通的卷积操作一样;
-
(b)图 对应3x3的2-dilated conv,实际的卷积 kernel size 还是 3x3,但是空洞为1,也就是对于一个7x7的图像patch,只有9个红色的点和3x3的kernel发生卷积操作,其余的点略过。也可以理解为kernel的size为7x7,但是只有图中的9个点的权重不为0,其余都为0。 可以看到虽然kernel size只有3x3,但是这个卷积的感受野已经增大到了7x7(如果考虑到这个2-dilated conv的前一层是一个1-dilated conv的话,那么每个红点就是1-dilated的卷积输出,所以感受野为3x3,所以1-dilated和2-dilated合起来就能达到7x7的conv);
-
(c)图 是4-dilated conv操作,同理跟在两个1-dilated和2-dilated conv的后面,能达到15x15的感受野。对比传统的conv操作,3层3x3的卷积加起来,stride为1的话,只能达到(kernel-1)*layer+1=7的感受野,也就是和层数layer成线性关系,而dilated conv的感受野是指数级的增长。
-
dilated的好处是不做pooling损失信息的情况下,加大了感受野,让每个卷积输出都包含较大范围的信息。在图像需要全局信息或者语音文本需要较长的sequence信息依赖的问题中,都能很好的应用dilated conv,比如图像分割[3]、语音合成WaveNet[2]、机器翻译ByteNet[1]中。
2.5 转置卷积
卷积是使输出大小变小的过程。 因此,而反卷积(deconvolution)可以进行向上采样以增大输出大小。但是,反卷积并代表卷积的逆过程。因此它也被称为向上卷积或转置卷积(transposed convolution)。 当使用分数步幅时,也称为分数步幅卷积(fractional stride convolution)。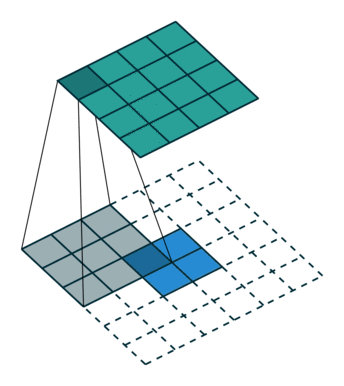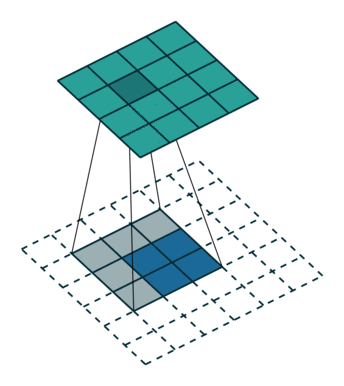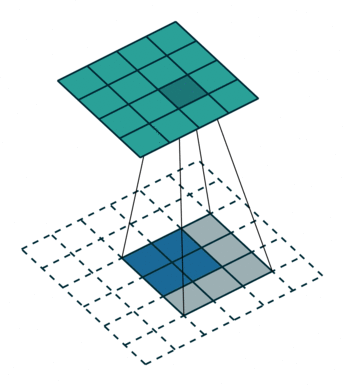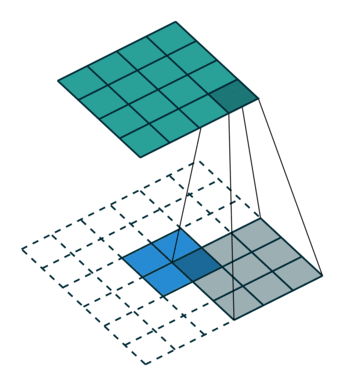
正常卷积:
假设图像尺寸为 4×4,卷积核为 3×3,padding=0,stride=1;
图像:;卷积核:
;输出:
转置卷积:
假设图像尺寸为 2×2 ,卷积核为 3×3,padding=0,stride=1;
图像:;卷积核:
;输出:
ConvTranspose1d
class torch.nn.ConvTranspose1d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None)-
in_channels (int) – Number of channels in the input image
-
out_channels (int) – Number of channels produced by the convolution
-
kernel_size (int or tuple) – Size of the convolving kernel
-
stride (int or tuple, optional) – Stride of the convolution. Default: 1
-
padding (int or tuple, optional) – dilation * (kernel_size - 1) - padding zero-padding will be added to both sides of the input. Default: 0
-
output_padding (int or tuple, optional) – Additional size added to one side of the output shape. Default: 0
-
groups (int, optional) – Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
-
bias (bool, optional) – If True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default: True
-
dilation (int or tuple, optional) – Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
输出计算:

ConvTranspose2d
class torch.nn.ConvTranspose2d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None)-
in_channels (int
) – Number of channels in the input image -
out_channels (int
) – Number of channels produced by the convolution -
kernel_size (int or tuple) – Size of the convolving kernel
-
stride (int or tuple, optional) – Stride of the convolution. Default: 1
-
padding (int or tuple, optional) –
dilation * (kernel_size - 1) - paddingzero-padding will be added to both sides of each dimension in the input. Default: 0 -
output_padding (int or tuple, optional) – Additional size added to one side of each dimension in the output shape. Default: 0
-
groups (int, optional) – Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
-
bias (bool, optional) – If
True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default:True -
dilation (int or tuple, optional) – Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
输出计算:

ConvTranspose3d
class torch.nn.ConvTranspose3d(in_channels, out_channels, kernel_size, stride=1, padding=0, output_padding=0, groups=1, bias=True, dilation=1, padding_mode='zeros', device=None, dtype=None)-
in_channels (int) – Number of channels in the input image
-
out_channels (int) – Number of channels produced by the convolution
-
kernel_size (int or tuple) – Size of the convolving kernel
-
stride (int or tuple, optional) – Stride of the convolution. Default: 1
-
padding (int or tuple, optional) –
dilation * (kernel_size - 1) - paddingzero-padding will be added to both sides of each dimension in the input. Default: 0 -
output_padding (int or tuple, optional) – Additional size added to one side of each dimension in the output shape. Default: 0
-
groups (int, optional) – Number of blocked connections from input channels to output channels. Default: 1
-
bias (bool, optional) – If
True, adds a learnable bias to the output. Default:True -
dilation (int or tuple, optional) – Spacing between kernel elements. Default: 1
输出计算:

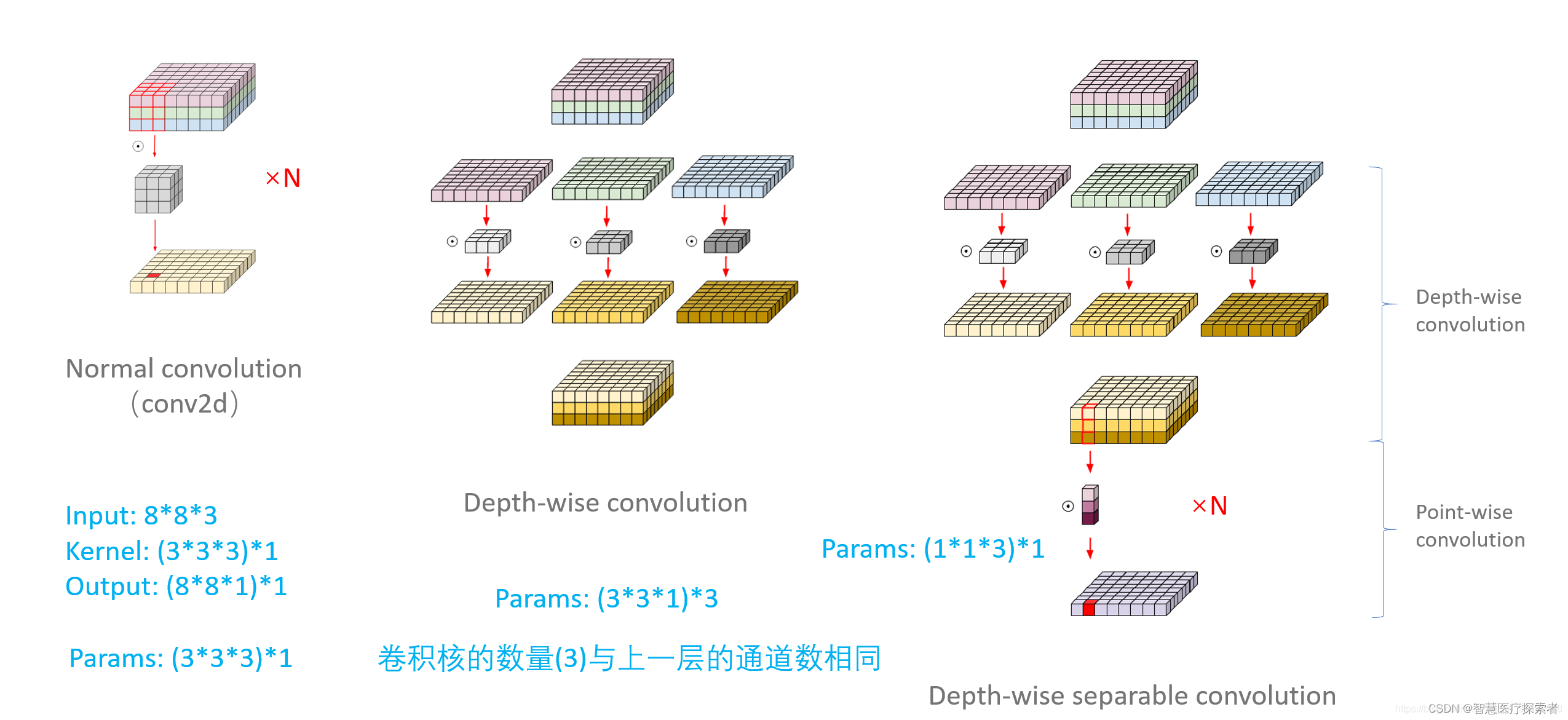
2.6 深度可分离卷积
MobileNet中大量使用的了深度可分离卷积(Depth-wise Separable Convolutions),主要起到降低参数量,增加非线性,跨通道信息融合的作用。