时序预测 | Python实现GA-TCN-LSTM遗传算法-时间卷积神经网络-长短期记忆网络时间序列预测
目录
- 时序预测 | Python实现GA-TCN-LSTM遗传算法-时间卷积神经网络-长短期记忆网络时间序列预测
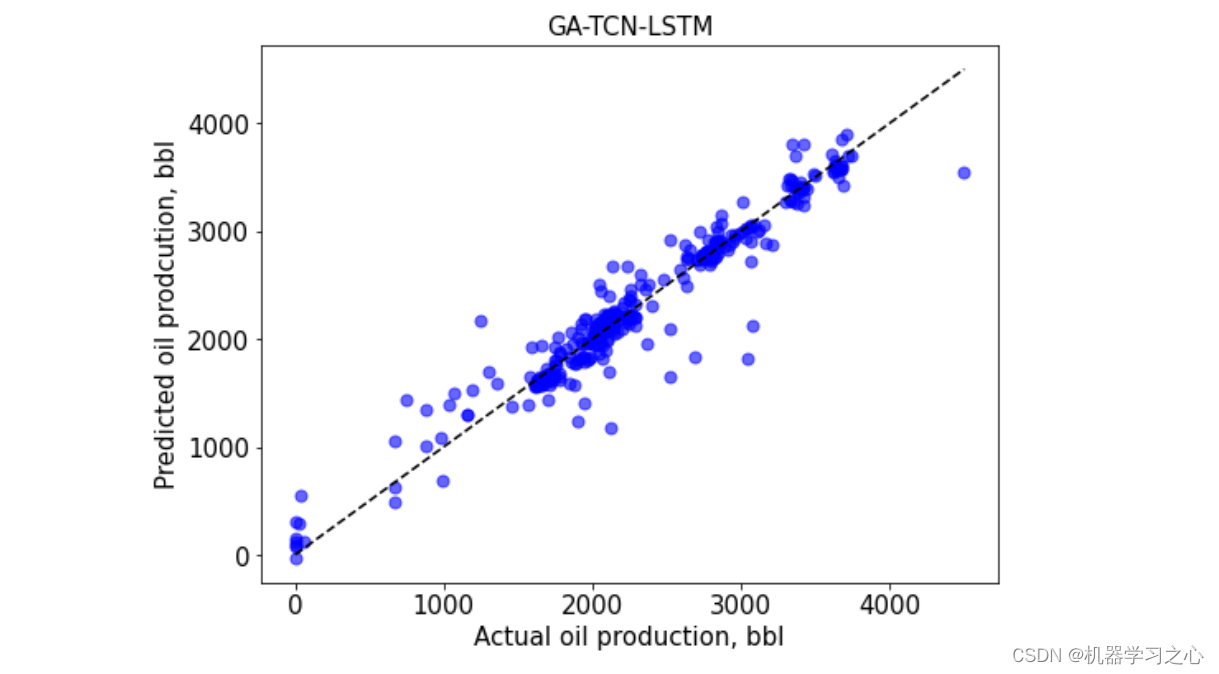
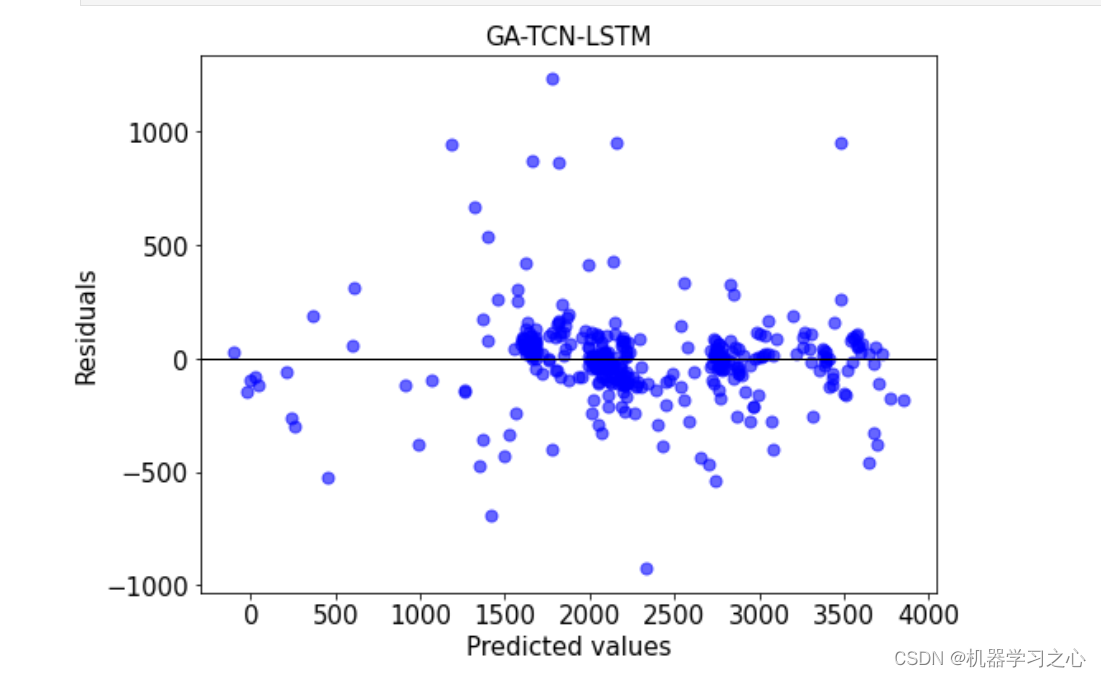
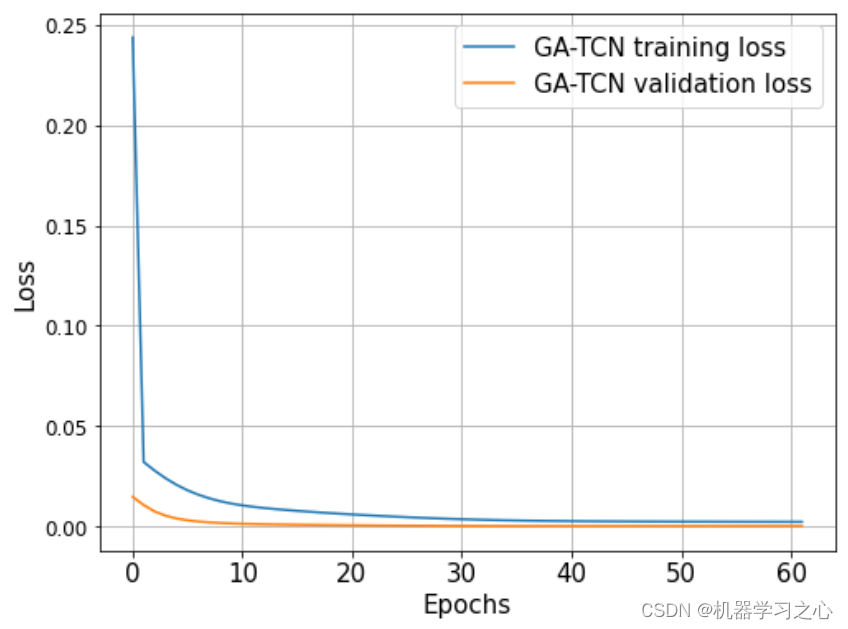
- 预测效果
- 基本介绍
- 程序设计
- 参考资料
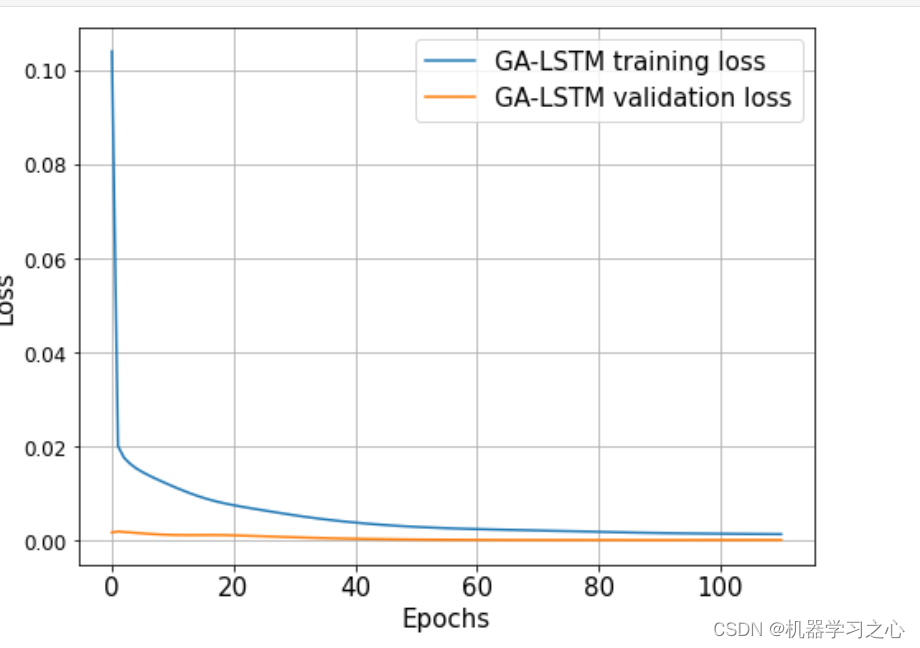
预测效果

基本介绍
使用先进的机器学习技术和优化算法开发石油产量预测模型,包括开发遗传算法-时间卷积神经网络-长短期记忆(GA-TCN-LSTM)集成模型,以及对循环神经网络(RNN)、门控循环单元( GRU)、长短期记忆LSTM)和时间卷积网络(TCN)。 此外,该程序还包括使用探索性数据分析和数据清理,旨在检测、可视化和处理数据集中的异常值。
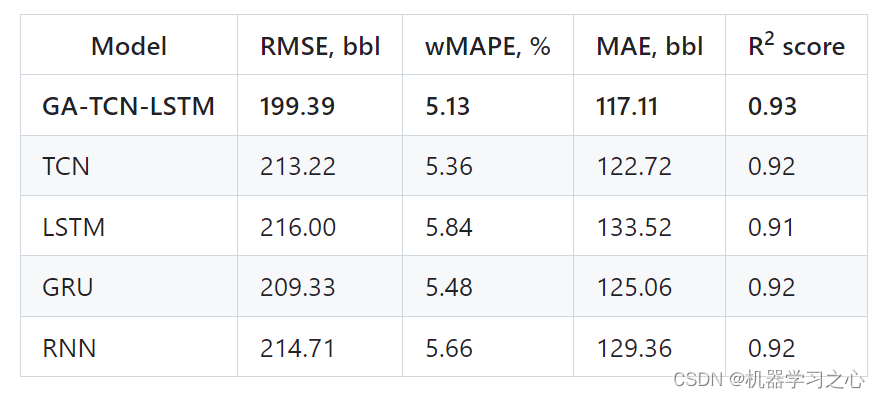
利用先进的机器学习技术和优化算法可以通过考虑这些复杂性来提高预测的准确性 并确定每个模型的最佳超参数组合。
程序设计
- 私信博主回复Python实现GA-TCN-LSTM遗传算法-时间卷积神经网络-长短期记忆网络时间序列预测。
- Python 3.10.7

# (找到将用于 TCN-LSTM 预测的加权平均指标的最佳权重)。
# decode bitstring to numbers
def decode(
bounds: list,
n_bits: int,
bitstring: list
)-> list:
"""
Decodes a bitstring into a list of values that correspond to the variables in an optimization problem.
Args:
bounds (list): A list of lists, where each list represents the lower and upper bounds of a variable in the optimization problem.
n_bits (int): An integer that specifies the number of bits used to represent each variable in the bitstring.
bitstring (list): A list of bits that represents a candidate solution in the optimization problem.
Returns:
list: A list of values that correspond to the variables in the optimization problem.
"""
decoded = list()
largest = 2**n_bits
for i in range(len(bounds)):
# extract the substring
start, end = i * n_bits, (i * n_bits)+n_bits
substring = bitstring[start:end]
# convert bitstring to a string of chars
chars = ''.join([str(s) for s in substring])
# convert string to integer
integer = int(chars, 2)
# scale integer to desired range
value = bounds[i][0] + (integer/largest) * (bounds[i][1] - bounds[i][0])
value = np.round(value)
value = int(value)
# store
decoded.append(value)
return decoded
# tournament selection
def selection(
pop: list,
scores: list,
k: int = 3
)-> list:
"""
Selects a candidate solution from a population using tournament selection.
Args:
pop (list): A list of candidate solutions.
scores (list): A list of fitness scores for the candidate solutions.
k (int): The number of individuals to compete in each tournament.
Returns:
list: The selected candidate solution.
"""
# first random selection
selection_ix = randint(len(pop))
for ix in randint(0, len(pop), k-1):
# check if better (e.g. perform a tournament)
if scores[ix] < scores[selection_ix]: # which individual has the lowest loss
selection_ix = ix
return pop[selection_ix]
# crossover two parents to create two children
def crossover(
p1: list,
p2: list,
r_cross: float
)-> list:
"""
Performs crossover between two parent candidate solutions to create two child candidate solutions.
Args:
p1 (list): The first parent candidate solution.
p2 (list): The second parent candidate solution.
r_cross (float): The crossover rate.
Returns:
list: A list containing the two child candidate solutions.
"""
# children are copies of parents by default
c1, c2 = p1.copy(), p2.copy()
# check for recombination
if rand() < r_cross:
# select crossover point that is not on the end of the string
pt = randint(1, len(p1)-2)
# perform crossover
c1 = np.append(p1[:pt] , p2[pt:])
c2 = np.append(p2[:pt] , p1[pt:])
return [c1, c2]
# mutation operator
def mutation(
bitstring: list,
r_mut: float
)-> list:
"""
Mutates a candidate solution by flipping bits in its bitstring.
Args:
bitstring (list): The bitstring of the candidate solution.
r_mut (float): The mutation rate.
Returns:
None
"""
for i in range(len(bitstring)):
# check for a mutation
if rand() < r_mut:
# flip the bit
bitstring[i] = 1 - bitstring[i]
# genetic algorithm
def genetic_algorithm(
series: pd.Series,
netowrk_type: str,
steps_ahead: int,
evaluate: callable,
bounds: list,
n_bits: int,
n_iter: int,
n_pop: int,
r_cross: float,
r_mut: float
)-> list:
"""
Implements a genetic algorithm to optimize the hyperparameters of a neural network.
Args:
series (pd.Series): The time series data to be used for training and validation.
network_type (str): The type of neural network to be optimized ('lstm' or 'tcn').
steps_ahead (int): The number of steps ahead to forecast.
evaluate (callable): A function that evaluates the fitness of a candidate solution based on the validation loss.
bounds (list): A list of lists, where each list represents the lower and upper bounds of a variable in the optimization problem.
n_bits (int): An integer that specifies the number of bits used to represent each variable in the bitstring.
n_iter (int): The number of generations to run the genetic algorithm.
n_pop (int): The number of candidate solutions in each generation.
r_cross (float): The crossover rate.
r_mut (float): The mutation rate.
Returns:
list: A list containing the best candidate solution and its fitness score.
"""
if network_type not in ['lstm', 'tcn']:
raise ValueError("network_type must be either 'lstm' or 'tcn'")
# initial population of random bitstring
pop = [randint(0, 2, n_bits*len(bounds)).tolist() for _ in range(n_pop)]
# keep track of best solution
best, best_eval = 0, inf
# enumerate generations
for gen in range(1, n_iter+1):
print(f"Generation:{gen}")
# decode population
decoded = [decode(bounds, n_bits, p) for p in pop]
# evaluate all candidates in the population
scores = [evaluate(series, steps_ahead, individual) for individual in decoded]
# check for new best solution
for i in range(n_pop):
if scores[i] < best_eval: # find the lowest validation loss
best, best_eval = pop[i], scores[i]
if network_type == 'lstm':
print(">%d, new best combination, Epoch: %d, num_hidden_layers: %d, num_neurons:%d, batch_size: %d, window_size: %d, Loss = %.8f" % \
(gen, decoded[i][0],decoded[i][1], decoded[i][2], decoded[i][3], decoded[i][4],
scores[i]))
elif network_type == 'tcn':
print(">%d, new best combination, Epoch: %d, n_filters_1: %d, n_filters_2: %d, n_filters_3: %d, batch_size: %d, window_size: %d, Loss = %.8f" % \
(gen, decoded[i][0],decoded[i][1], decoded[i][2], decoded[i][3], decoded[i][4], decoded[i][5],
scores[i]))
# select parents (Tournament selection)
selected = [selection(pop, scores) for _ in range(n_pop)]
# create the next generation
children = list()
for i in range(0, n_pop, 2):
# get selected parents in pairs
p1, p2 = selected[i], selected[i+1]
# crossover and mutation
for c in crossover(p1, p2, r_cross):
# mutation
mutation(c, r_mut)
# store for next generation
children.append(c)
# replace population
pop = children
return [best, best_eval]
#find the optimal weights for the weighted average metric that will be used for the prediction of TCN-LSTM
# Define a range for the weights to be searched
weights = np.linspace(0.0, 1, 100)
weights = np.round(weights,5)
# Initialize the best weights and best performance
# best_weights = (1,1)
best_performance = float('inf')
# Iterate over all possible weight combinations
for w1 in weights:
for w2 in weights:
# Make predictions using the current weight combination
predictions = ((w1 * yhat_tcn_test) + (w2 * yhat_lstm_test)) / (w1+w2+1e-10)
# Evaluate the performance using some metric, e.g. accuracy
performance = sqrt(mean_squared_error(y_tcn_test, predictions))
# Update the best weights and best performance if the current performance is better
if performance < best_performance:
best_weights = (w1, w2)
best_performance = performance
print("Best weights:", best_weights)
print("Best performance:", best_performance)
参考资料
[1] https://blog.csdn.net/kjm13182345320/article/details/128247182