Java基础之常用类
- 一、包装类
- 1.1、Java基本数据类型及其对应的包装类
- 1.2、包装类的自动装箱、自动拆箱机制
- 1.3、包装类的优点
- 二、String类
- 三、StringBuffer类和StringBuilder类
- 3.1、主要区别:
- 3.2、StringBuffer/StringBuilder用法(两者用法一致)
- 四、日期类
- 4.1、Date类
- 4.2、SimpleDateFormate和DateFormate类
- 4.3、Calender类日期类
- 五、JDK8日期类
- 5.1、LocalDate
- 5.2、LocalTime
- 5.3、LocalDateTime
- 5.4、ZoneDateTime
- 六、Math类和Random类
- 6.1、Math类
- 6.2、Random类
- 七、枚举类
- 八、System类
一、包装类
Java包装类(Wrapper Classes)是一组用于将基本数据类型转换为对象的类。均位于java.lang包内
1.1、Java基本数据类型及其对应的包装类
| 基本数据类型 | 包装类 | |
|---|---|---|
| 整数类型 | byte | Byte |
| … | short | Short |
| … | int | Integer |
| … | long | Long |
| 浮点类型 | float | Float |
| … | double | Double |
| 字符类型 | char | Character |
| 布尔类型 | boolean | Boolean |
1.2、包装类的自动装箱、自动拆箱机制
- 创建一个包装类
Integer num = new Integer(0); //创建一个数值为0的Integer对象
- 基本类型数据和包装类对象互换
Integer num1= new Integer(8);//基本数据类型-->包装类
int num2=num1.intValue();//包装类转换成基本数据类型
System.out.println(num1+" "+num2);
//1、包装类中的自动装箱拆箱机制
Integer num1 = 1; //自动装箱
int num2 = num1; //自动拆箱
System.out.println(num1 +" "+ num2);
1.3、包装类的优点
- 某些方法参数必须为对象,包装类使数据类型转换成对象
- 获得类型的最大值:Integer.MAX_VALUE
- 最小值Integer.MIN_VALUE
- 将一个类型转为另一个类型integer.doubleValue()
- 将字符串转化为数字Integer.parseInt(“100”)
- 将数字转化为字符串Integer.toString(100)
二、String类
String 是 Java 中的一个类,用于表示字符串。在 Java 中,字符串是不可变的,这意味着一旦创建了一个字符串对象,就不能再修改它的内容。String 类位于 java.lang 包中,因此在大多数情况下不需要显式导入。
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
/**
* @BelongsProject: Test
* @BelongsPackage: FaceObject
* @Author: Jorya
* @CreateTime: 2023-11-21 22:26
* @Description: TODO
* @Version: 1.0
*/
public class TestString {
public static void main (String[] args){
//①字符串的创建
// 使用字面值创建字符串
String str1 = "Hello, World!";
String str2 = "Hello, World!";//这两个的地址是一样的,并没有重新生成一个字符串
System.out.println(str1==str2);//true
// 使用构造函数创建字符串
String str3 = new String("Hello, World!");
String str4 = new String("Hello, World!");
System.out.println(str3==str4);//判断是否全部一样,因为是不同对象。False
System.out.println(str3.equals(str4));//equals是判断内容是否相等:true
System.out.println(str3.equalsIgnoreCase(str4));// 忽略大小写比较
System.out.println(str3.compareTo(str4));//判断字符串是否相等,区分大小写
//②字符串的链接
// 使用加号进行字符串连接
String fullName = str1 + " " + str2;
// 使用 concat 方法
String fullNameConcat = str1.concat(" ").concat(str2);
System.out.println(fullName);
System.out.println(str1.length());//获取字符串长度
System.out.println(str1.isEmpty());//判断字符串是否为空
System.out.println(str1.endsWith("!"));//判断字符串是否以!结尾
System.out.println(str1.startsWith("H"));//判断字符串是否以H开始
System.out.println(str1.toUpperCase());//全部转换为大写
System.out.println(str1.toLowerCase());//全部转换为小写
System.out.println(str1.charAt(2));//获得字符串的第3个字符l;java的下标是从0开始的
System.out.println(str1.toCharArray());//字符串转数组
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("l"));//查找字符串第一次出现的位置
System.out.println(str1.indexOf("l",2));//从指定位置查找字符串第一次出现的位置
System.out.println(str1.lastIndexOf("o"));//从后往前查找字符串第一次出现的位置
System.out.println(str1.substring(2));//从指定位置截取字符串
System.out.println(str1.substring(2,5));//截取中间某处的字符串
System.out.println(str1.substring(7)); // 从索引 7 开始截取到字符串末尾
System.out.println(str1.contains("World")); //检查字符串包括
System.out.println(str1.replace("World", "Java")); //字符串替换
//字符串分割
String[] split = str1.split(" ");//按指定字符串分割字符串
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(split));
//去掉首尾空格
String str5 = " Trim Me ";
String trimmedStr = str5.trim();
//字符串格式化
String name = "John";
int age = 25;
String formattedString = String.format("Name: %s, Age: %d", name, age);
}
}
三、StringBuffer类和StringBuilder类
StringBuffer和StringBuilder类用法几乎一模一样,都为抽象类、是AbstractStringBuilder的子类
3.1、主要区别:
| StringBuffer | StringBuilder |
|---|---|
| 线程安全 | 线程不安全 |
| 效率较慢 | 效率快、建议使用 |
| 方法同步、适用于多线程 | 不提供同步、适用于单线程 |
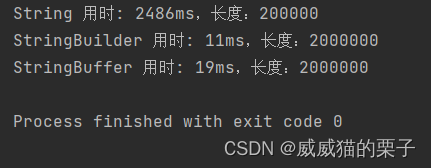
//比较String、StringBuilder、StringBuffer的运行时间
public class StringBufferTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
long startTime, endTime;
// 使用 String 拼接
String s1 = "";
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
s1 = s1.concat("拼接");
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("String 用时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms,长度:" + s1.length());
// 使用 StringBuilder 拼接
StringBuilder s2 = new StringBuilder();
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
s2.append("拼接");
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuilder 用时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms,长度:" + s2.length());
// 使用 StringBuffer 拼接
StringBuffer s3 = new StringBuffer();
startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000000; i++) {
s3.append("拼接");
}
endTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("StringBuffer 用时: " + (endTime - startTime) + "ms,长度:" + s3.length());
}
}
3.2、StringBuffer/StringBuilder用法(两者用法一致)
// 创建一个空的 StringBuffer
StringBuffer buffer = new StringBuffer();
// 添加字符串
buffer.append("Hello");
// 在特定位置插入字符串
buffer.insert(5, ", World!");
// 替换字符串
buffer.replace(0, 5, "Hi");
// 删除字符串
buffer.delete(3, 6);
// 反转字符串
buffer.reverse();
// 获取字符串长度
int length = buffer.length();
// 转换为字符串
String result = buffer.toString();
四、日期类
4.1、Date类
在 Java 中,Date 类用于表示日期和时间。请注意,Date类在 Java 8 之后已经过时,更推荐使用 java.time 包中的新日期和时间 API(java.time 包中的类,如 LocalDate、LocalTime、LocalDateTime 等
import java.util.Date;
//日期类
public class TestDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date currentDate = new Date();
System.out.println(currentDate);
System.out.println(currentDate.getTime());//获取1970年1月1日到现在的毫秒数
System.out.println(currentDate.toLocaleString());//获取当前时间的字符串
int year = currentDate.getYear() + 1900; // 获取年份(从1900开始)
int month = currentDate.getMonth() + 1; // 获取月份(从0开始,需要加1)
int day = currentDate.getDate();// 获取日期
// 获取小时、分钟、秒
int hours = currentDate.getHours();
int minutes = currentDate.getMinutes();
int seconds = currentDate.getSeconds();
java.sql.Date date1 = new java.sql.Date(System.currentTimeMillis());
System.out.println(date1);//只有年月日
String t="2019-8-20";
java.sql.Date date2 = java.sql.Date.valueOf(t);//将字符串转化为日期
System.out.println(date2);
}
}
4.2、SimpleDateFormate和DateFormate类
import java.text.DateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
//日期类
public class TestDate {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Date currentDate = new Date();
// 创建 SimpleDateFormat 对象并指定日期格式
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
// 格式化日期
String formattedDate = sdf.format(currentDate);
System.out.println("SimpleDateFormat Date: " + formattedDate);
//创建格式化日期格式为:"yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss";因为DateFormat是一个抽象类不能new对象,所以new一个他的子类;这叫多态
DateFormat dateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
String format = dateFormat.format(currentDate);//格式化这个日期类,返回String字符串
System.out.println("DateFormat Date: "+format);//2022-05-16 10:03:29
}
}
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat(“日期格式字符串”);
日期格式字符串,如:“yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss”
yyyy 代表4位的年份
MM 代表2位的月份
dd 代表2位的日期
hh/HH 12小时制/24小时制
mm 代表分钟
ss 代表秒钟
a 代表AM/PM
4.3、Calender类日期类
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.*;
public class TestCalendar {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//Calendar这也是一个抽象类,需要new他的子类
Calendar calendar = new GregorianCalendar();
System.out.println(calendar);
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR));//获取年月日
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.MARCH)+1);//月是从0开始的
System.out.println(calendar.get(Calendar.DATE));
System.out.println(calendar.getActualMaximum(Calendar.DATE));//获取当前月最大天数
//日期类和日历类相互转化
// 1. Date 转 Calendar
Date currentDate = new Date();
Calendar calendarFrom = Calendar.getInstance();
calendarFrom.setTime(currentDate);
// 输出 Calendar 对象的日期和时间
System.out.println("1. Calendar from Date:");
printCalendar(calendarFrom);
// 2. Calendar 转 Date
Calendar calendarTo = Calendar.getInstance();
calendarTo.set(2023, Calendar.JANUARY, 1); // 2023-01-01
Date date = calendarTo.getTime();
// 输出转换后的 Date 对象
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println("\n2. Date from Calendar: " + sdf.format(date));
}
private static void printCalendar(Calendar calendar) {
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(" Time: " + sdf.format(calendar.getTime()));
}
}
五、JDK8日期类
在 Java 8 中,引入了新的日期和时间 API,这个 API 位于 java.time 包中。以下是一些 Java 8 中日期和时间 API 的常用类:
| 属性 | 含义 |
|---|---|
| Instant | 代表的是时间相当于Date |
| LocalDate | 代表日期,比如2022-01-14 |
| LocalTime | 代表时间,比如12:20:30 |
| LocalDateTime | 代表具体时间,比如2022-01-14 12:20:30 |
| ZonedDateTime | 代表一个包含时区的完整的日期时间 |
| DateTimeFormatter | 日期和字符串格式转换 |
5.1、LocalDate
import java.time.LocalDate;
public class LocalDateExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前日期
LocalDate currentDate = LocalDate.now();
// 创建指定日期
LocalDate specificDate = LocalDate.of(2023, 1, 1);
// 获取日期属性
int year = specificDate.getYear();
int month = specificDate.getMonthValue();
int dayOfMonth = specificDate.getDayOfMonth();
int dayOfWeek = specificDate.getDayOfWeek().getValue();
int dayOfYear = specificDate.getDayOfYear();
// 在当前日期基础上加上一天
LocalDate nextDay = currentDate.plusDays(1);
// 在当前日期基础上减去一周
LocalDate lastWeek = currentDate.minusWeeks(1);
}
}
5.2、LocalTime
import java.time.LocalTime;
public class LocalTimeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前时间
LocalTime currentTime = LocalTime.now();
// 创建指定时间
LocalTime specificTime = LocalTime.of(12, 30, 45);
// 获取时间属性
int hour = specificTime.getHour();
int minute = specificTime.getMinute();
int second = specificTime.getSecond();
int nano = specificTime.getNano();
// 在当前时间基础上加上一小时
LocalTime nextHour = currentTime.plusHours(1);
// 在当前时间基础上减去半小时
LocalTime halfHourAgo = currentTime.minusMinutes(30);
}
}
5.3、LocalDateTime
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
public class LocalDateTimeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前日期和时间
LocalDateTime currentDateTime = LocalDateTime.now();
// 创建指定日期和时间
LocalDateTime specificDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2023, 1, 1, 12, 30, 45);
// 在当前日期和时间基础上加上一天
LocalDateTime nextDay = currentDateTime.plusDays(1);
// 在当前日期和时间基础上减去一周
LocalDateTime lastWeek = currentDateTime.minusWeeks(1);
}
}
5.4、ZoneDateTime
import java.time.ZonedDateTime;
import java.time.ZoneId;
public class ZonedDateTimeExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前日期和时间(带时区信息)
ZonedDateTime currentDateTimeWithZone = ZonedDateTime.now();
// 创建指定日期和时间(带时区信息)
ZonedDateTime specificDateTimeWithZone = ZonedDateTime.of(2023, 1, 1, 12, 30, 45, 0, ZoneId.of("America/New_York"));
// 在当前日期和时间基础上加上一天(带时区信息)
ZonedDateTime nextDayWithZone = currentDateTimeWithZone.plusDays(1);
// 在当前日期和时间基础上减去一周(带时区信息)
ZonedDateTime lastWeekWithZone = currentDateTimeWithZone.minusWeeks(1);
}
}
六、Math类和Random类
6.1、Math类
java.lang.Math 类包含用于执行基本数学运算的静态方法。这些方法提供了对常见数学函数的访问,如三角函数、指数函数、对数函数等。
public class MathExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 基本数学运算
int sum = Math.addExact(5, 3); // 返回两个整数的和,溢出时抛出异常。
int difference = Math.subtractExact(8, 3); // 返回两个整数的差
int product = Math.multiplyExact(4, 7); //返回两个整数的积
int incremented = Math.incrementExact(10); // 返回参数的值加 1
int decremented = Math.decrementExact(7); //返回参数的值减 1
int negated = Math.negateExact(9); // 返回参数的负值
// 取整和舍入
double ceilValue = Math.ceil(3.14); // 4.0 返回不小于参数的最小整数
double floorValue = Math.floor(3.14); // 3.0 返回不大于参数的最大整数
long roundedValue = Math.round(3.14); // 3 返回参数最接近的整数
// 指数和对数
double expValue = Math.exp(2.0); // 7.3890560989306495 返回自然数底数 e 的指数
double logValue = Math.log(10.0); // 2.302585092994046 返回参数的自然对数
double powValue = Math.pow(2.0, 3.0); // 8.0 返回 a 的 b 次幂
// 三角函数
double sinValue = Math.sin(Math.toRadians(30)); // 0.49999999999999994 返回角的正弦
double cosValue = Math.cos(Math.toRadians(60)); // 0.5000000000000001返回角的余弦
double tanValue = Math.tan(Math.toRadians(45)); // 0.9999999999999999 返回角的正切
}
}
6.2、Random类
-
构造
Random random =new Random(); -
获得随机数
Random.nextInt(100);代码示例:
import java.util.Random; public class TestRandom { public static void main(String[] args) { Random random = new Random(); System.out.println(random.nextInt(100));//获取100以内的随机整数 System.out.println(random.nextFloat());//获取浮点随机 } }
七、枚举类
所有的枚举类型隐性地继承自java.lang.Enum, 枚举的实质还是类。
代码示例:
// 定义一个简单的枚举类型
enum Day {
SUNDAY, MONDAY, TUESDAY, WEDNESDAY, THURSDAY, FRIDAY, SATURDAY
}
public class EnumExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用枚举常量
Day today = Day.MONDAY;
System.out.println("Today is " + today);
// 枚举常量的比较
if (today == Day.MONDAY) {
System.out.println("It's a workday.");
}
// 遍历枚举值
System.out.println("Days of the week:");
for (Day day : Day.values()) {
System.out.println(day);
}
}
}
八、System类
System.in: 标准输入流
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter your name: ");
String name = scanner.nextLine();
System.out.println("Hello, " + name + "!");
System.exit(int status):退出程序
System.exit(0); // 正常退出
System.exit(1); // 异常退出
System.currentTimeMillis():获取当前时间毫秒数
long currentTimeMillis = System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("Current time in milliseconds: " + currentTimeMillis);


![nginx: [alert] could not open error log file](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/direct/28037170e1c744df935d45da7e6cf7d3.png#pic_center)