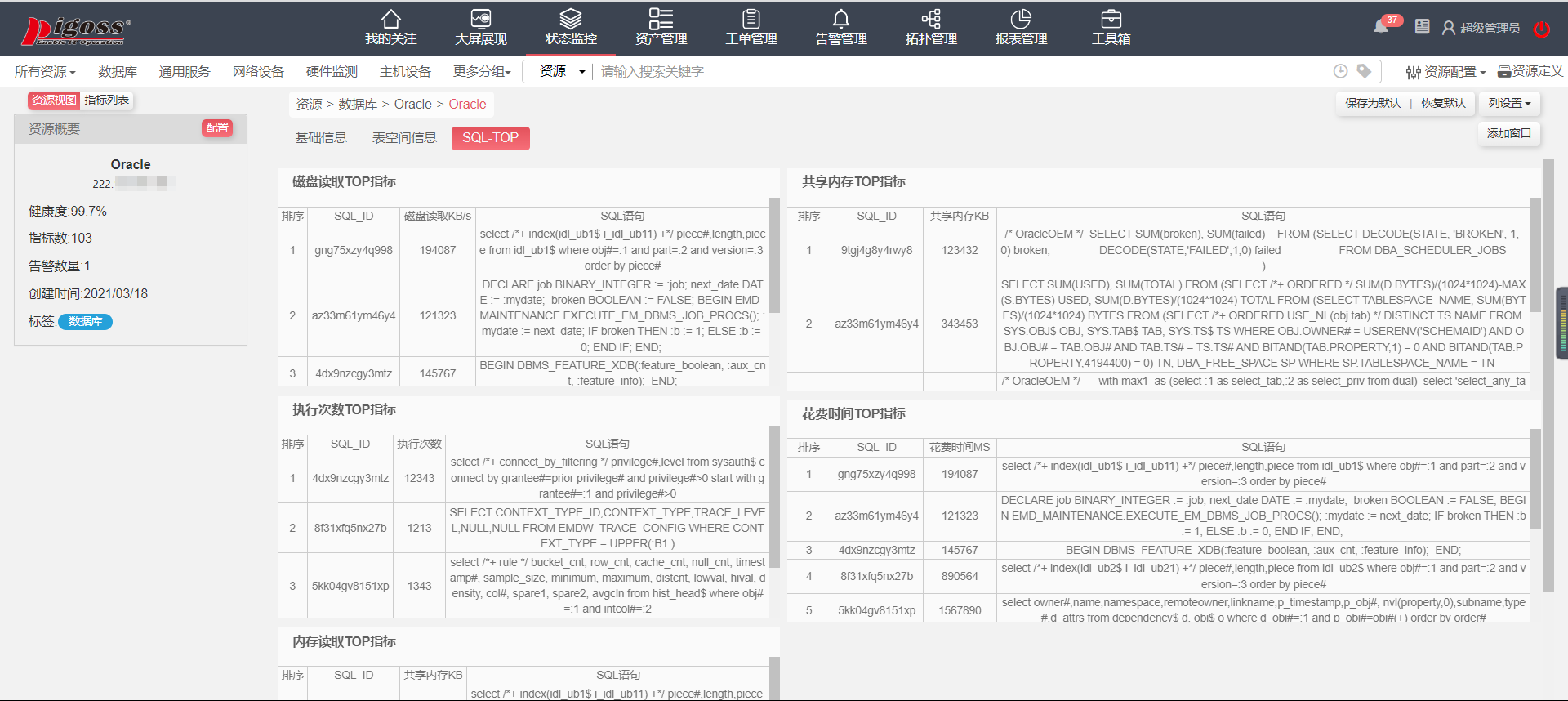
1、自定义MyArrayList类
该类里面基本有两个属性,一个是用来存放数据的数组,另外一个是用来描述已经存放数据的数量。同时设置arraylist表的默认长度为10;代码如下:
public class MyArrayList {
private int[] elem;
private int usedSize;//表示表的实际占用空间
//顺序表的默认大小
public static final int DEFAULT_SIZE = 10;
public MyArrayList(int[] elem) {
elem = new int[DEFAULT_SIZE];
}
}
2. 创建接口
我们创建一个接口,要将arraylist要实现的抽象方法列出来,使得后期直接在自定义类里面能够具体化;
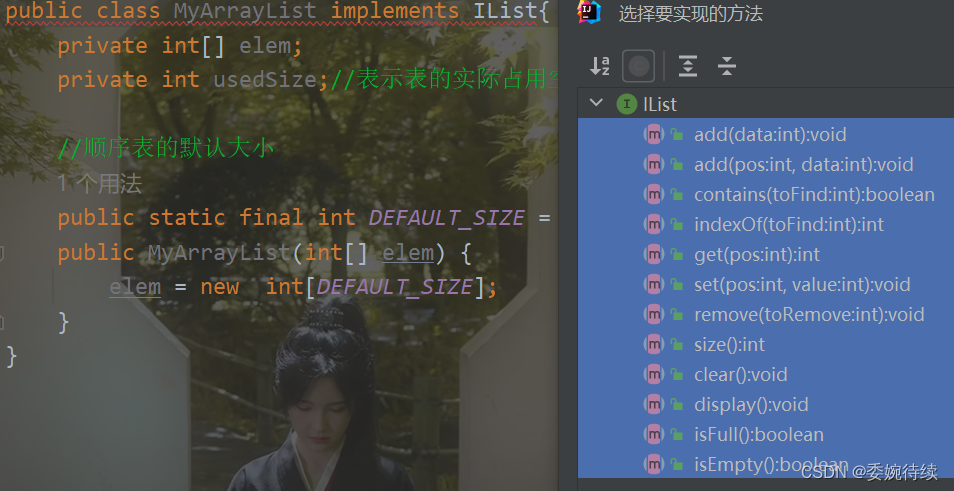
public interface IList {
//新增元素,默认在数组最后新增
public void add(int data);
// 在 pos 位置新增元素
public void add(int pos, int data);
// 判定是否包含某个元素
public boolean contains(int toFind) ;
// 查找某个元素对应的位置
public int indexOf(int toFind);
// 获取 pos 位置的元素
public int get(int pos);
// 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value 更新
public void set(int pos, int value);
//删除第一次出现的关键字key
public void remove(int toRemove) ;
// 获取顺序表长度
public int size();
// 清空顺序表
public void clear() ;
// 打印顺序表,注意:该方法并不是顺序表中的方法,为了方便看测试结果给出的
public void display();
boolean isFull();
public boolean isEmpty();
}
同时我们的自定义类实现该接口,并实现接口中的方法;我们接下来通过自己手敲arraylist的一些方法来从底层深入的学习arraylist表如何完成一系列的方法实现,方便我们了解arraylist表的运行逻辑和优缺点;
3、实现具体方法
3.1 打印顺序表
只要知道当前类对象的实际长度即可完成打印顺序表操作;
@Override
public void display() {
for (int i = 0; i <= this.usedSize-1; i++) {
System.out.print(this.elem[i]+"->");
}
System.out.println();
}3.2新增元素
我们此处的方法默认添加的每一个元素是从底层数组末尾依次添加的
思路:
1、 首先需要确定当前存储在数组中最后一位数据的索引(即usedSize-1),然后下一个存储空间范围合法的话,直接将我们要添加的数据放到接下来的数组索引上即可(数据存放的索引应该为usedSized)
1.1 这时候就要考虑如果我们要存放数据之前要判断数组的空间是否满了(我们之前默认存储容量为10);
1.2 如果判断出数组当前已满,我们就要对数组存空容量进行扩容;
2、添加完成后,usedSize往后移一位;
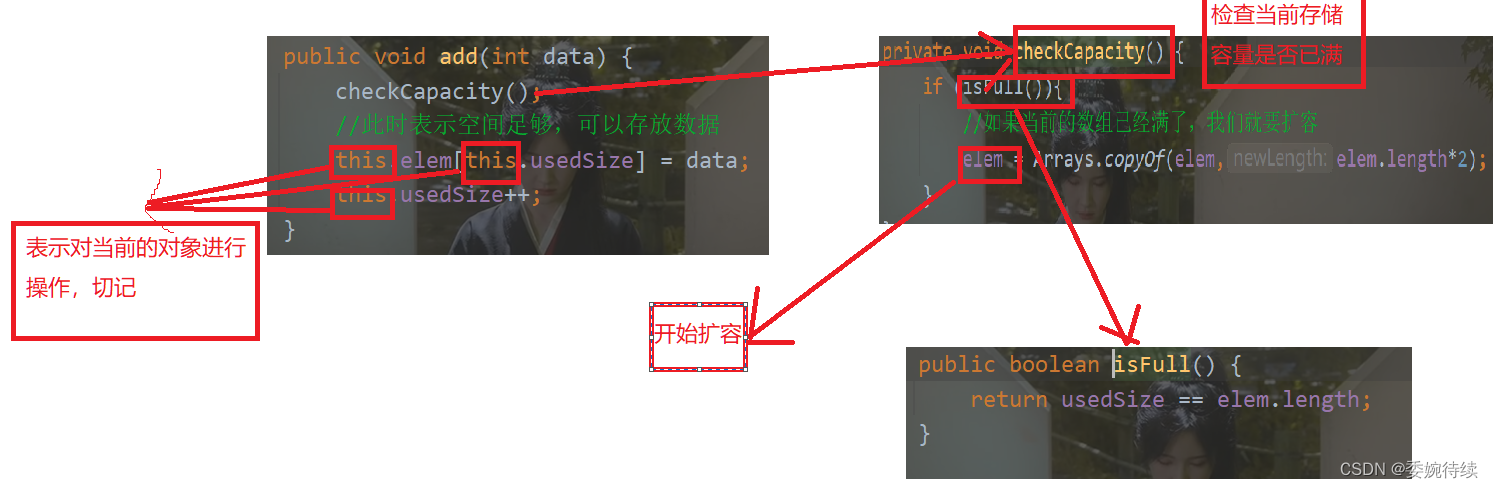
代码如下
@Override
public void add(int data) {
checkCapacity();
//此时表示空间足够,可以存放数据
this.elem[this.usedSize] = data;
this.usedSize++;
}
private void checkCapacity() {
if (isFull()){
//如果当前的数组已经满了,我们就要扩容
elem = Arrays.copyOf(elem,elem.length*2);
}
}
@Override
public boolean isFull() {
return usedSize == elem.length;
}
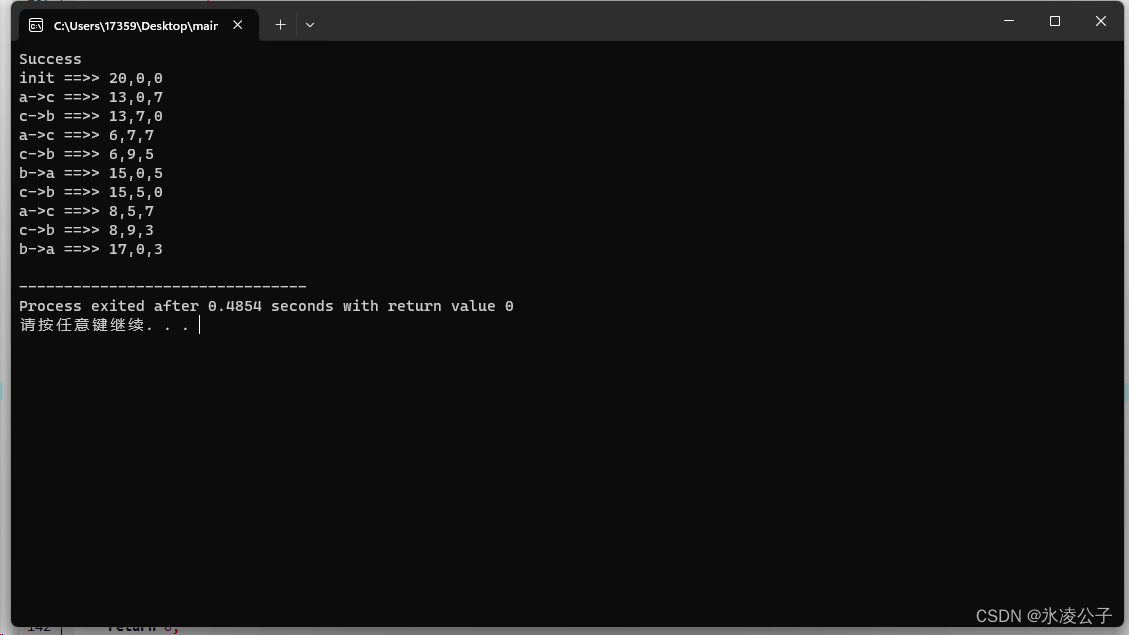
测试及结果:
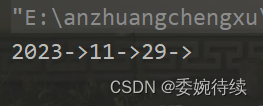
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(2023);
myArrayList.add(11);
myArrayList.add(29);
myArrayList.display();
}
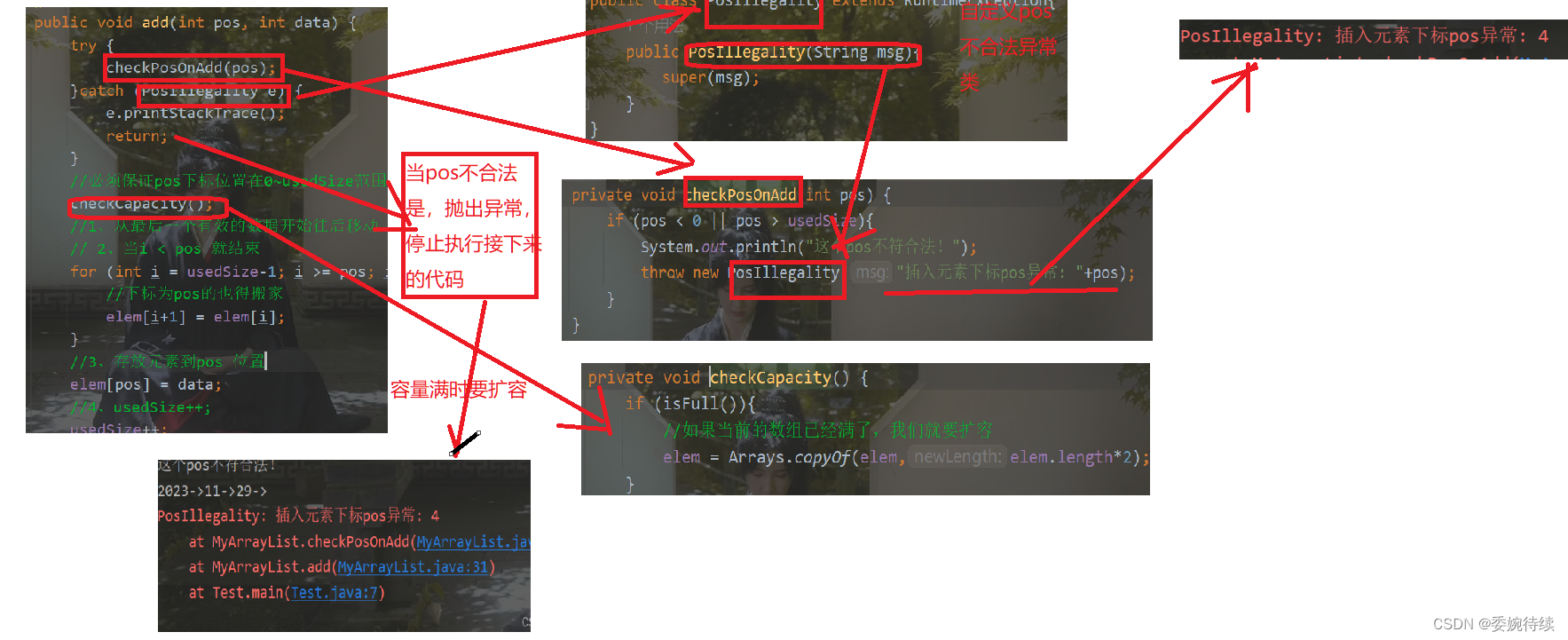
3.3 在 pos 位置新增元素
思路:在pos下标添加data;
1、应该把pos下标到usedSzie-1下标之间的元素往右面移动(包含pos),且得先从最右边的元素开始移动
1、1必须保证pos下标位置在0~usedSize范围之间;(即一个顺序表只有0下标有位置,想要往3下标位置插入数据是不科学的)
1.2 如果要在usedSize-1的位置插入数据,我们要进行扩容操作;
2、最后userSize++;
详细图解如下图所示:
代码如下所示:
public class PosIllegality extends RuntimeException{
public PosIllegality(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
@Override
public void add(int pos, int data) {
try {
checkPosOnAdd(pos);
}catch (PosIllegality e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return;
}
//必须保证pos下标位置在0~usedSize范围之间,所以要检查
checkCapacity();
//1、从最后一个有效的数据开始往后移动
// 2、当i < pos 就结束
for (int i = usedSize-1; i >= pos; i--) {
//下标为pos的也得搬家
elem[i+1] = elem[i];
}
//3、存放元素到pos 位置
elem[pos] = data;
//4、usedSize++;
usedSize++;
}
checkCapacity();
//1、从最后一个有效的数据开始往后移动 //2、当i < pos 就结束
for (int i = usedSize-1; i >= pos; i--) {
elem[i+1] = elem[i];
}
//3、存放元素到pos 位置
elem[pos] = data;
//4、usedSize++;
usedSize++;
}
执行结果:
eg1:
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(2023);
myArrayList.add(11);
myArrayList.add(29);
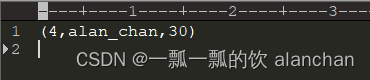
myArrayList.add(4,99);
myArrayList.display();
}
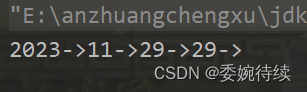
eg2:
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(2023);
myArrayList.add(11);
myArrayList.add(29);
myArrayList.add(2,29);
myArrayList.display();
}
3.4判定是否包含某个元素
思路:先遍历整个数组,再判断是否包含;
注意:首先要判断列表是否为空
此处代码图解:
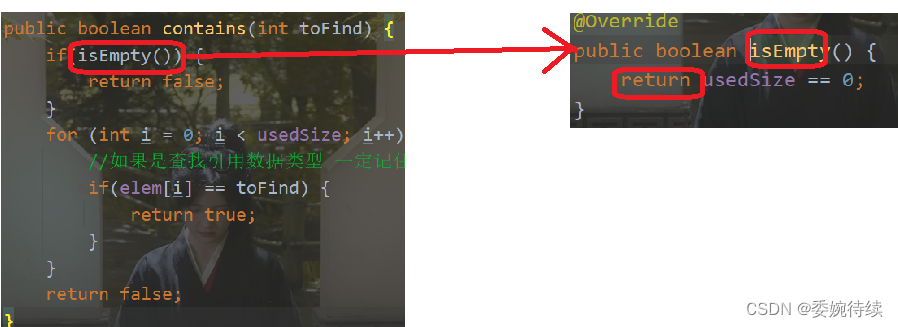
@Override
public boolean contains(int toFind) {
if(isEmpty()) {
return false;
}
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
//如果是查找引用数据类型 一定记住 重写方法
if(elem[i] == toFind) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public boolean isEmpty() {
return usedSize == 0;
}3.5 查找某个元素对应的位置
找到列表中的钙元素,返回其在列表中的索引
思路:
1、如果列表为空,则返回-1;
2、遍历数组,找到返回索引,找不到返回-1;
下图为方法代码和运行结果
@Override
public int indexOf(int toFind) {
if (isEmpty()){
return -1;
}
for (int i = 0; i < usedSize; i++) {
if (elem[i] == toFind){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
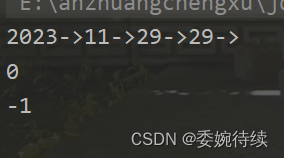
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(2023);
myArrayList.add(11);
myArrayList.add(29);
myArrayList.add(2,29);
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println(myArrayList.indexOf(2023));
System.out.println(myArrayList.indexOf(2024));
}
3.6 获取 pos 位置的元素
思路:
1、检查pos是否合法,当pos不合法时,抛出异常,停止下面的代码运行;
2、检查书序表是否为空,如果链表为空,抛出异常,停止下面的代码运行;
3、除此外,返回pos 位置的元素
下图为代码逻辑图:
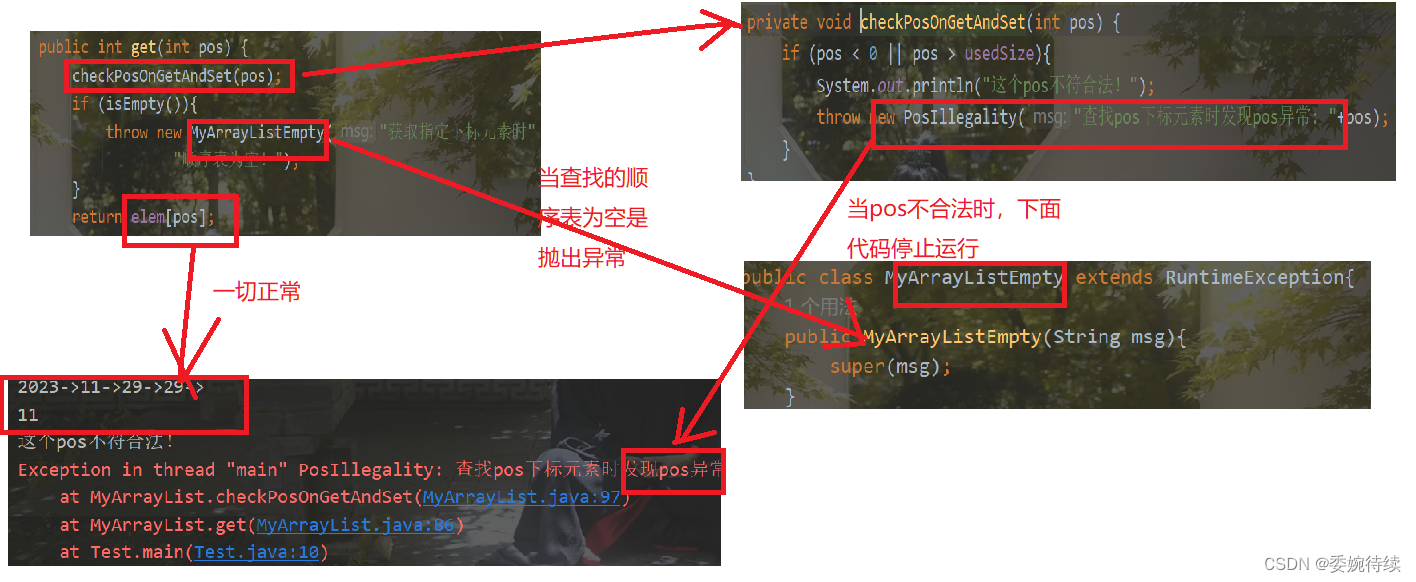
具体方法如下:
public class MyArrayListEmpty extends RuntimeException{
public MyArrayListEmpty(String msg){
super(msg);
}
}
@Override
public int get(int pos) {
checkPosOnGetAndSet(pos);
if (isEmpty()){
throw new MyArrayListEmpty("获取指定下标元素时" +
"顺序表为空!");
}
return elem[pos];
}
private void checkPosOnGetAndSet(int pos) {
if (pos < 0 || pos > usedSize){
System.out.println("这个pos不符合法!");
throw new PosIllegality("查找pos下标元素时发现pos异常: "+pos);
}
}
执行代码及结果:
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(2023);
myArrayList.add(11);
myArrayList.add(29);
myArrayList.add(2,29);
myArrayList.display();
System.out.println(myArrayList.get(1));
System.out.println(myArrayList.get(6));
}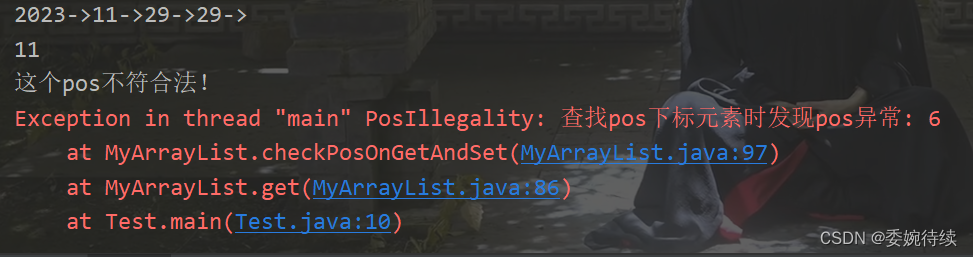 3.7 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
3.7 给 pos 位置的元素设为 value
代码如下:
@Override
public void set(int pos, int value) {
checkPosOnGetAndSet(pos);
elem[pos] = value;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyArrayList myArrayList = new MyArrayList();
myArrayList.add(2023);
myArrayList.add(11);
myArrayList.add(29);
myArrayList.add(2,29);
myArrayList.display();
myArrayList.set(1,2029);
myArrayList.display();
}运行结果如图所示:
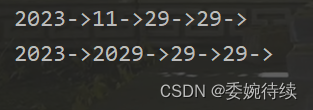
3.8 删除第一次出现的关键字key
思路:
1、先通过查找索引的方法,寻找key在列表中的索引。如果没有找到,停止运行
2、如果找到,开始删除该元素,自这个元素以后得所有元素往前移一个单位
3、删除成功后,usedSize--
@Override
public void remove(int toRemove) {
int index = indexOf(toRemove);
if(index == -1) {
System.out.println("没有这个数字!");
return;
}
for(int i = index; i < usedSize-1;i++) {
elem[i] = elem[i+1];
}
usedSize--;
}3.9 获取顺序表长度
@Override
public int size() {
return this.usedSize;
}3.10 清空顺序表
@Override
public void clear() {
this.usedSize = 0;
}ps:本次内容就到这里结束了,喜欢的话,还请大家一键三连哦!!!