【数据结构】单链表---C语言版
- 一、顺序表的缺陷
- 二、链表的概念和结构
- 1.概念:
- 三、链表的分类
- 四、链表的实现
- 1.头文件:SList.h
- 2.链表函数:SList.c
- 3.测试函数:test.c
- 五、链表应用OJ题
- 1.移除链表元素
- (1)题目描述:
- (2)思路表述:
- (3)代码实现:
- 2.翻转一个单链表
- (1)题目描述:
- (2)思路表述:
- (3)代码实现:
- 3.返回一个链表的中间节点
- (1)题目描述:
- (2)思路表述:
- (3)代码实现:
- 4.链表中倒数第k个结点
- (1)题目描述:
- (2)思路表述:
- (3)代码实现:
- 5.合并两个有序链表
- (1)题目描述:
- (2)思路表述:
- (3)代码实现:
- 6. 链表分割
- (1)题目描述:
- (2)思路表述:
- (3)代码实现:
- 7. 链表的回文结构
- (1)题目描述:
- (2)思路表述:
- (3)代码实现:
- 8.相交链表
- (1)题目描述:
- (2)思路表述:
- (3)代码实现:
- 9.判断链表中是否有环
- (1)题目描述:
- (2)思路表述:
- (3)代码实现:
- 六、链表和顺序表的优缺点对比
一、顺序表的缺陷
(1)挪动数据时间开销较大:如果是头插或者头删,后面的数据都需要挪动时间复杂度为O(N),这样的代价就比较大。
(2)增容有代价:每次扩容都需要向系统申请空间,然后拷贝数据,然后再释放原来的旧空间,这样对系统的消耗还是不小的。
(3)空间浪费:我们每次空间不够,都会扩大原来空间的二倍,如果我只需要两个字节的空间,但是我扩大了原来100的2倍,那98个字节的空间就浪费了。
但是谁能来解决这个问题呢?那么就是接下来要讲的:链表!

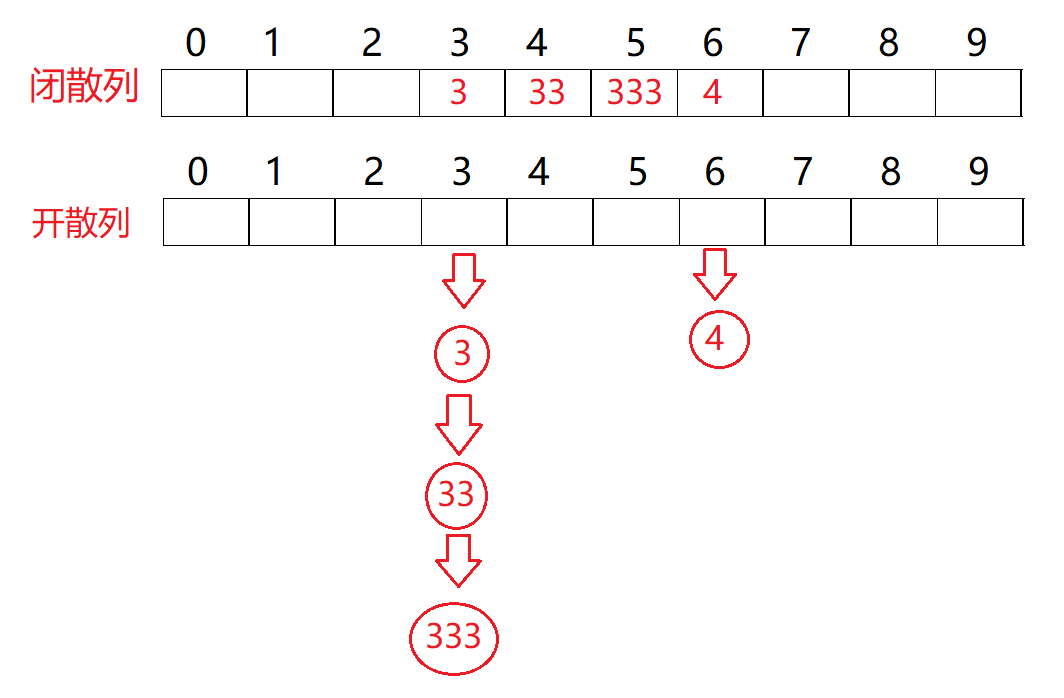
现实中的链表就是这样的:
- 从上面的图片我们可以看出链式结构在逻辑上是连续的,但是在物理上它不一定是连续的。
- 现实中也就是物理上的节点都是从堆上申请出来的。
- 从堆上申请的空间是按照一定的策略来分配的,两次申请的空间:可能连续,也可能不连续。
三、链表的分类
实际中链表的结构非常多样,以下情况组合起来就有8种链表结构:
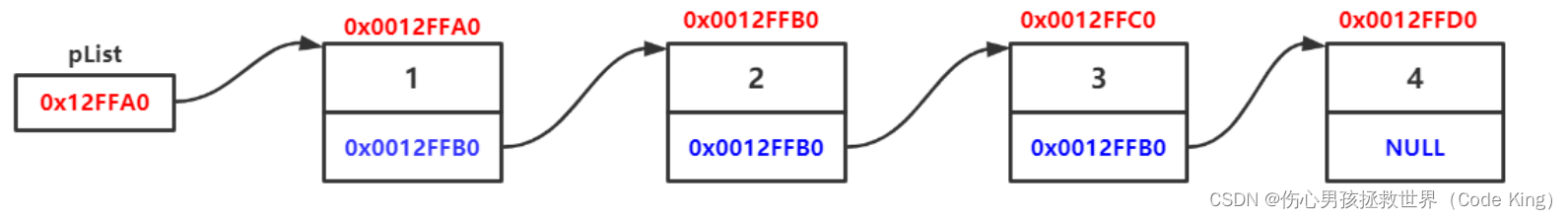
1. 单向或者双向:
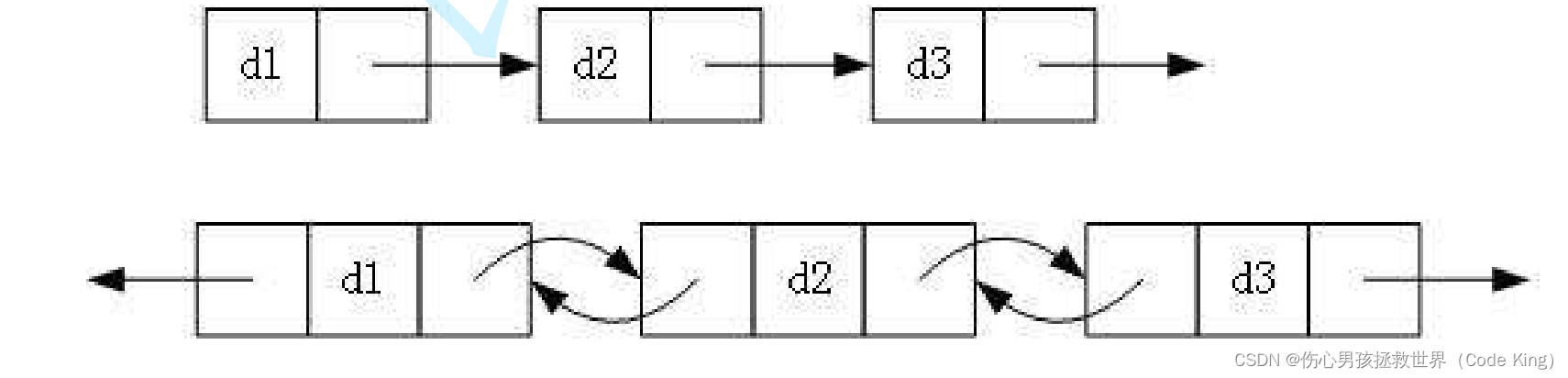
2. 带头或者不带头:
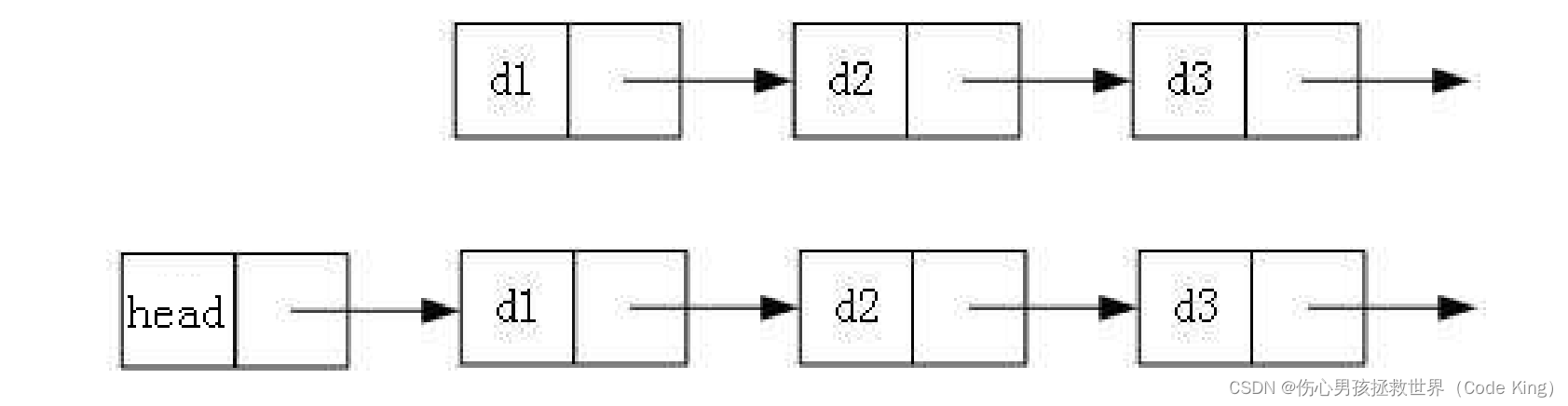
3. 循环或者非循环:
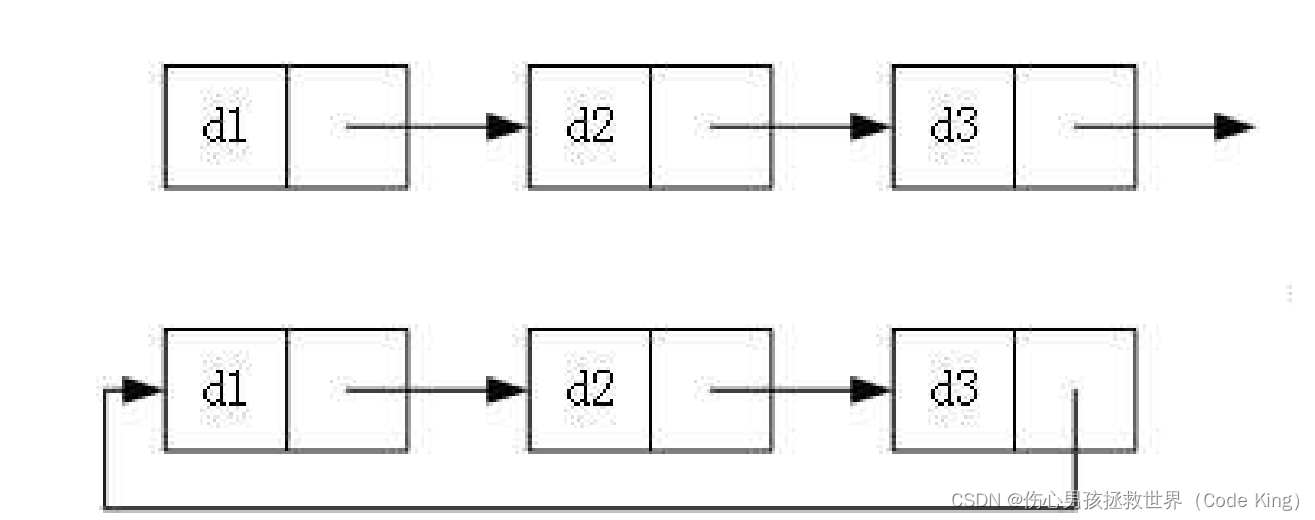
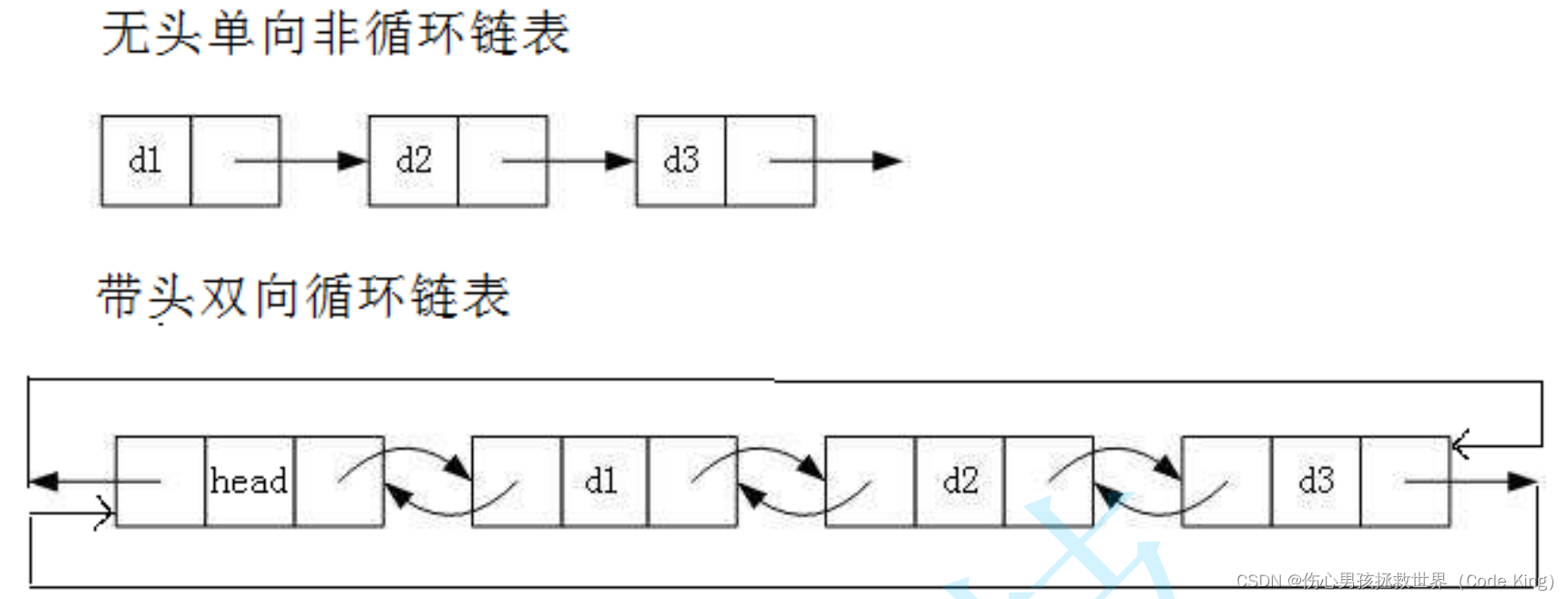
4.虽然有这么多的链表的结构,但是我们实际中最常用还是两种结构:
无头单向非循环链表和带头双向循环链表。
四、链表的实现
1.头文件:SList.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
typedef int SLTDataType;
typedef struct SListNode
{
SLTDataType data;
struct SListNode* next;
}SLTNode;
//打印函数
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead);
//申请新结点函数
SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x);
//头插
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//尾插
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x);
//头删
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead);
//尾删
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead);
//单链表查找
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x);
// 在pos之前插入x
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
//在pos位置之后插入一个数字x
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x);
//删除POS位置的值
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos);
//删除POS位置的下一个值
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos);
2.链表函数:SList.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include "SList.h"
void SLTPrint(SLTNode* phead)
{
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur)
{
printf("%d-> ", cur->data);
cur = cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
}
SLTNode* BuySListNode(SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = (SLTNode*)malloc(sizeof(SLTNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
return newnode;
}
//头插
void SLTPushFront(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
newnode->next = *pphead;
*pphead = newnode;
}
//尾插
//如果我要改变指针的指向,我不可能通过传值调用,我只能通过来改变指针的地址,
//也就是用二级指针才能改变结构体指针的指向。
void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** pphead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);//创建新节点
if (*pphead == NULL)
{
// 改变的结构体的指针,所以要用二级指针
*pphead = newnode;
}
else
{
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next)//tail->next!=NULL
{
tail = tail->next;
}
// 改变的结构体,用结构体的指针即可
tail->next = newnode;//因为tail->next是结构体中的一个成员
}
}
//头删
void SLTPopFront(SLTNode** pphead)
{
//空:
//如果直接指向空指针,那就不用删了
assert(*pphead);
//非空:
// 我们需要运用空瓶思想创建个临时变量来存放,要删那个节点的下一个节点的地址,
//要不然删除那个节点之后,下一个节点的地址就连接不上了。
SLTNode* newnode = (*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead = newnode;
}
//尾删
void SLTPopBack(SLTNode** pphead)
{
//1.空
assert(*pphead);
//1个节点
if ((*pphead)->next == NULL)
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead = NULL;
}
//1个以上结点
else
{
//因为是尾删,所以需要一个前摇标志:tailPrev
SLTNode* tailPrev = NULL;
SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
while (tail->next)
{
tailPrev = tail;
tail = tail->next;
}
free(tail);
tailPrev->next = NULL;
}
//方法2
//SLTNode* tail = *pphead;
//while (tail->next->next)
//{
// tail = tail->next;
//}
//free(tail->next);
//tail->next = NULL;
}
//查找函数
SLTNode* SLTFind(SLTNode* phead, SLTDataType x)
{
SLTNode* cur = phead;
while (cur)//而不是cur->text!=NULL,查找因为我要遍历完!!!
{
if (cur->data == x)
{
return cur;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
return NULL;//当全部都遍历完了,还没找到的话,就直接返回 空 (NULL)
}
//在POS之前插入一个结点
void SLTInsert(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
//SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
if (pos == *pphead)
{
SLTPushFront(pphead, x);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
prev->next = newnode;
newnode->next = pos;
}
}
//在pos位置后插入一个数字
void SLTInsertAfter(SLTNode* pos, SLTDataType x)
{
assert(pos);
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
//while()为啥不用循环????
newnode->next = pos->next;
pos->next = newnode;
}
void SLTErase(SLTNode** pphead, SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
if (pos == *pphead)
{
SLTPopFront(pphead);
}
else
{
SLTNode* prev = *pphead;
while (prev->next != pos)
{
prev = prev->next;
}
prev->next = pos->next;
free(pos);
//pos = NULL;
}
}
//删除pos后位置的一个值
void SLTEraseAfter(SLTNode* pos)
{
assert(pos);
//检查尾节点是否为空
assert(pos->next);
//空瓶思想:需要先做一个标记,posnext就是空瓶存放,在pos的下一个位置
SLTNode* posNext = pos->next;
pos->next = posNext->next;
free(posNext);
posNext = NULL;
}
3.测试函数:test.c
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include <stdio.h>
#include "SList.h"
void TestList1()
{
int n=0;
printf("请输入链表的长度:");
scanf("%d", &n);
printf("\n请依次输入每个节点的值:");
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++)
{
int val = 0;
scanf("%d", &val);
SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(val);
//头插
newnode->next = plist;
plist = newnode;
}
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 10000);
SLTPrint(plist);
}
//void SLTPushBack(SLTNode** phead, SLTDataType x)
//{
// //如果我要改变指针的指向,我不可能通过传值调用,我只能通过来改变指针的地址,也就是用二级指针才能改变结构体指针的指向。
// SLTNode* newnode = BuySListNode(x);
// SLTNode* tail = phead;
// while (tail->next)//tail->next!=NULL
// {
// tail = tail->next;
// }
// tail->next = newnode;
//}
//测试尾插
void TestList2()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushBack(&plist, 10);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 20);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 30);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 40);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPushBack(&plist, 50);
SLTPrint(plist);
}
//测试头插
void TestList3()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushFront(&plist, 10);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 20);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 30);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 40);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 50);
SLTPrint(plist);
}
//测试尾删
void TestList4()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushFront(&plist, 10);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 20);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 30);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 40);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 50);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopBack(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
}
//测试头删
void TestList5()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushFront(&plist, 10);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 20);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 30);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 40);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 50);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopFront(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopFront(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopFront(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopFront(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTPopFront(&plist);
SLTPrint(plist);
}
//测试查找
void TestList6()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushFront(&plist, 10);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 20);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 30);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 40);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 50);
SLTPrint(plist);
SLTNode* pos = SLTFind(plist, 40);
if (pos)
{
pos->data *= 10;
}
SLTPrint(plist);
int x = 0;
printf("请输入要查找数字的位置:");
scanf("%d", &x);
pos = SLTFind(plist, x);
if (pos)
{
SLTInsert(&plist, pos, x * 10);
}
SLTPrint(plist);
}
void TestList7()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushFront(&plist, 10);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 20);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 30);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 40);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 50);
SLTPrint(plist);
int x;
printf("请输入你想要查找的数字:");
scanf("%d", &x);
SLTNode* pos = SLTFind(plist, x);
if (pos)
{
SLTInsertAfter(pos, x * 10);
}
SLTPrint(plist);
}
void TestList8()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushFront(&plist, 10);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 20);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 30);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 40);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 50);
SLTPrint(plist);
int x = 0;
printf("请输入你想要查找的数字:");
scanf("%d", &x);
SLTNode* pos = SLTFind(plist, x);
if (pos)
{
SLTErase(plist, pos);
}
SLTPrint(plist);
}
void TestList9()
{
SLTNode* plist = NULL;
SLTPushFront(&plist, 10);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 20);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 30);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 40);
SLTPushFront(&plist, 50);
SLTPrint(plist);
int x = 0;
printf("请输入你想要查找的数字:");
scanf("%d", &x);
SLTNode* pos = SLTFind(plist, x);
if (pos)
{
SLTEraseAfter(pos);
}
SLTPrint(plist);
}
int main()
{
//TestList1();
//TestList2();
//TestList3();
//TestList4();
//TestList5();
//TestList6();
//TestList7();
TestList8();
//TestList9();
return 0;
}
五、链表应用OJ题
1.移除链表元素
(1)题目描述:
点击链接
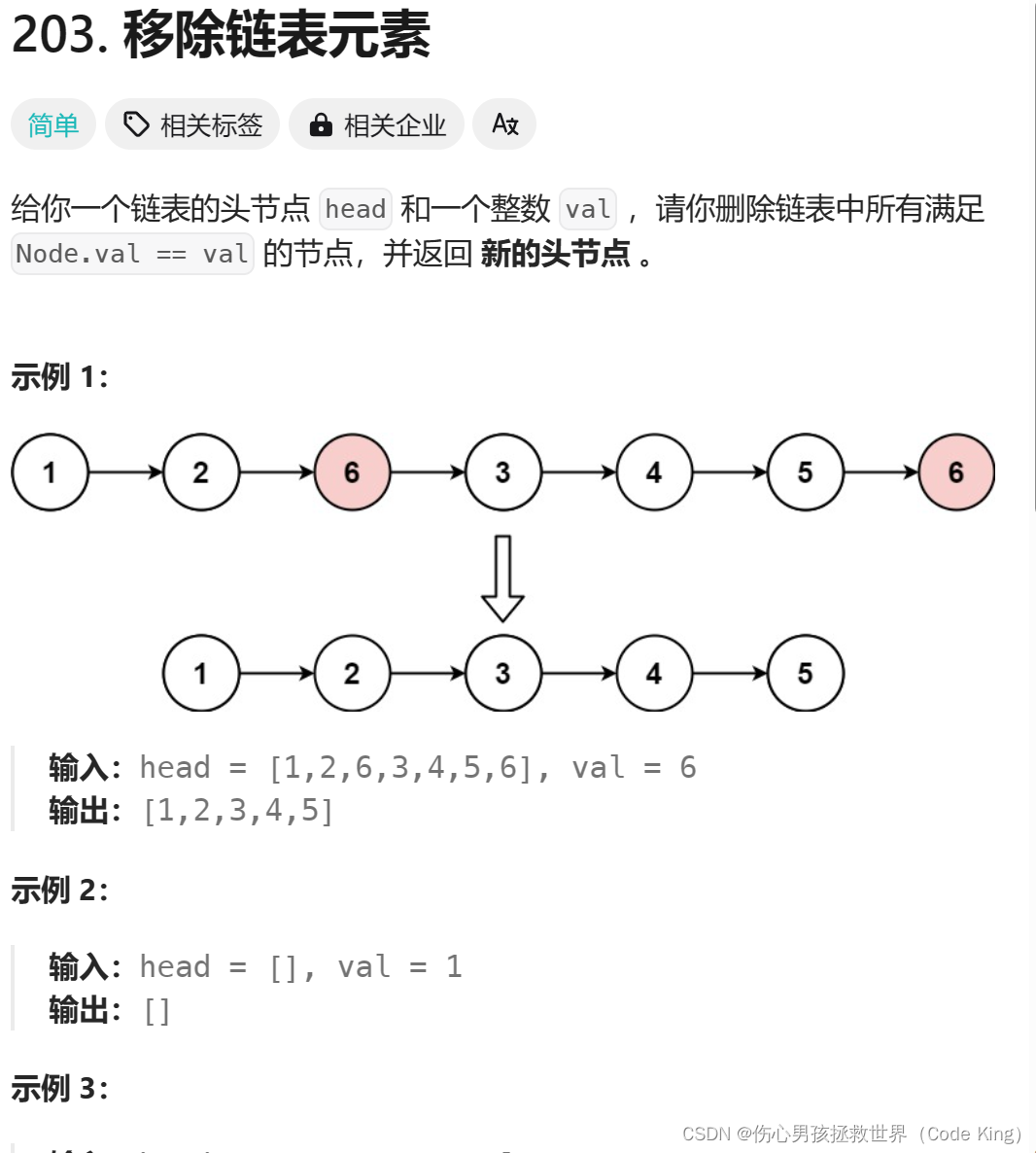
(2)思路表述:
创建的prev和tmp指针都是用来保存 cur当前节点指针的前一个和后一个:因为如果你直接销毁cur的话,他前一个和后一个连接不起来,所以说你要先创建暂时的节点来保存它。
分类讨论:
-
从头往后找,如果没找到要删的目标节点就一直往后走:
prev->next=cur;
cur=cur->next; -
如果找到目标节点,这里面还要分为:如果目标节点是在“头”,我们要进行“头删”,如果在除了“头”的其他位置是另一种情况(注意:只要我找到了要删的目标节点,我一定要先保存,当前要删节点的下一个!)
(3)代码实现:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* removeElements(struct ListNode* head, int val)
{
struct ListNode* prev=NULL;
struct ListNode* cur=head;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->val==val)//只要找到了,我就保存!
{
struct ListNode* tmp=cur->next;
//接下来我就要判断了,
//1.如果他这个链表里面第1个就是我们要删除的节点。prev==NULL就说明第1个就是目标
if(prev==NULL)
{
free(cur);
head=tmp;
cur=tmp;
}
else//2.除了头删的其他任意位置!
{
prev->next=tmp;
free(cur);
cur=tmp;
}
}
else//没找到就都往下一个走
{
prev->next=cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
}
return head;
}
2.翻转一个单链表
(1)题目描述:
点击链接
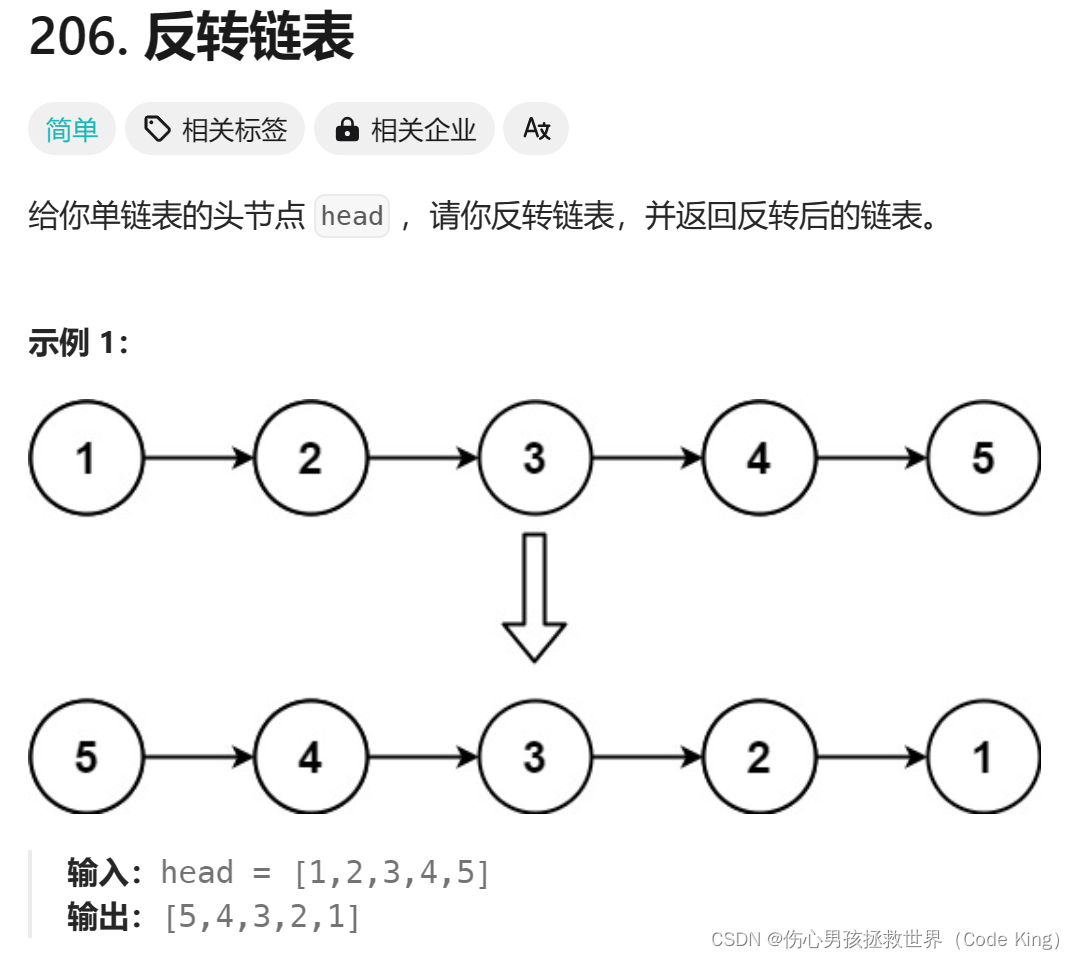
(2)思路表述:
1.
2.
3.
(3)代码实现:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* cur=head;
struct ListNode* newhead=NULL;
while(cur)
{
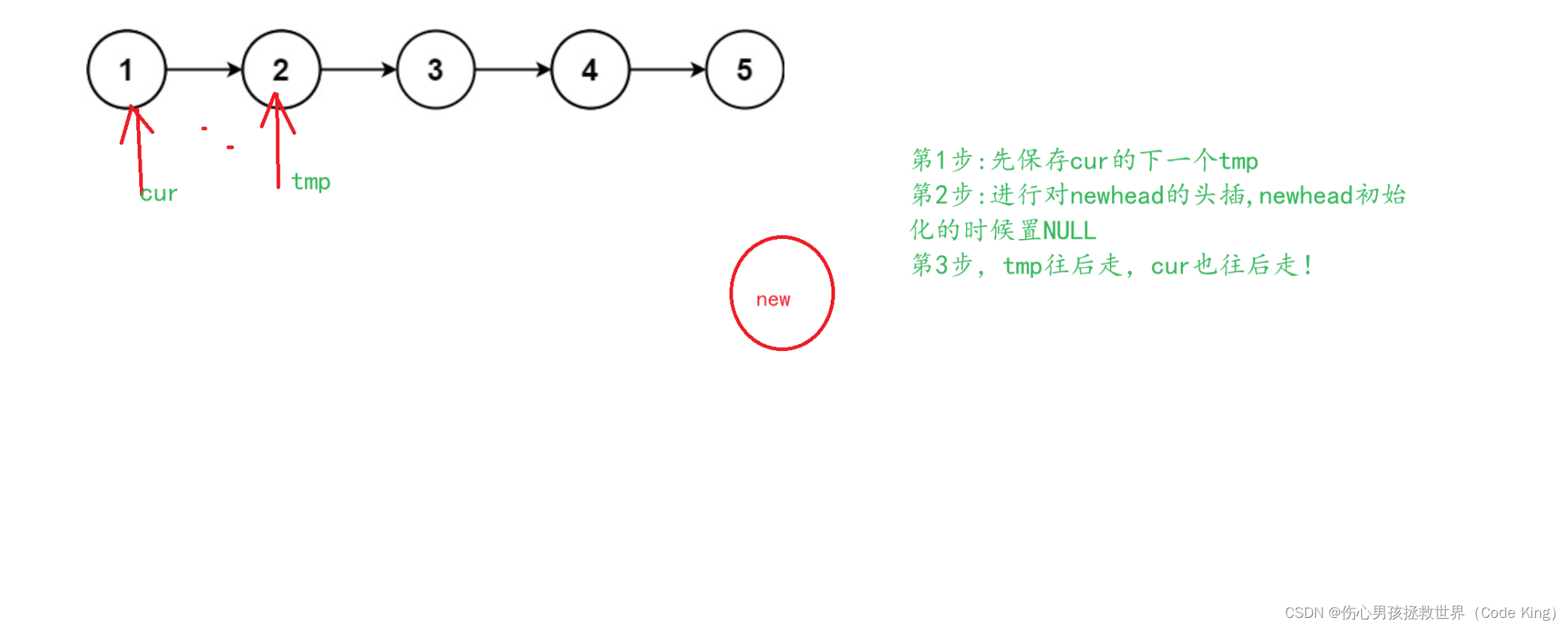
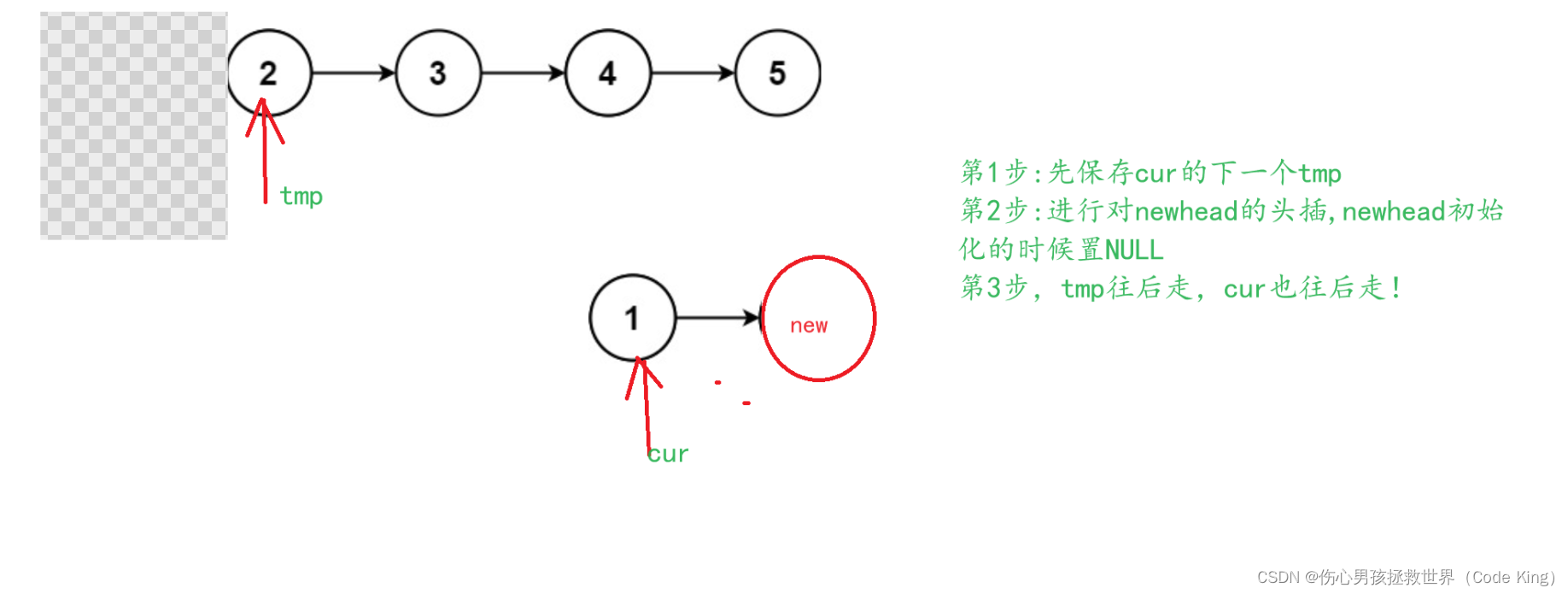
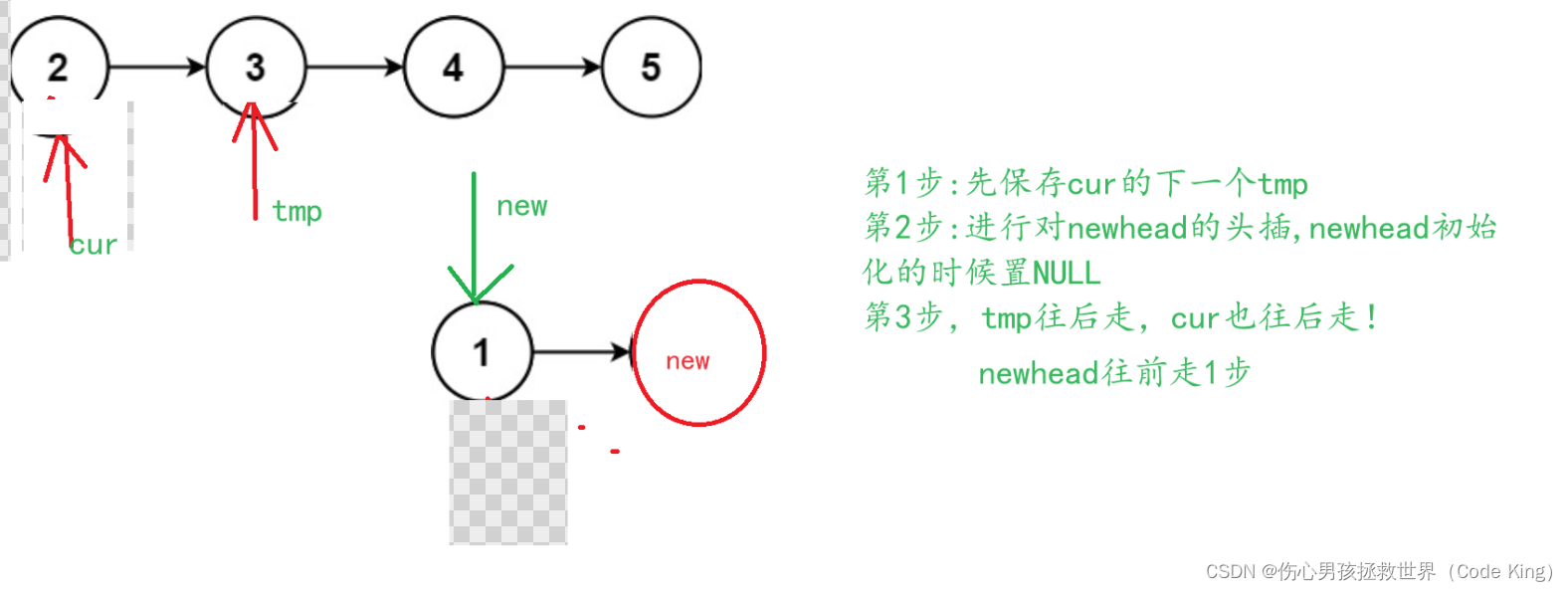
//1.保存cur的下一个结点
struct ListNode* tmp=cur->next;
//2.头插:头插之后一定要记得newhead要往前走一步
cur->next=newhead;
newhead=cur;
//3.原链表中的cur继续往后走!
cur=tmp;
}
return newhead;
}
3.返回一个链表的中间节点
(1)题目描述:
点击链接
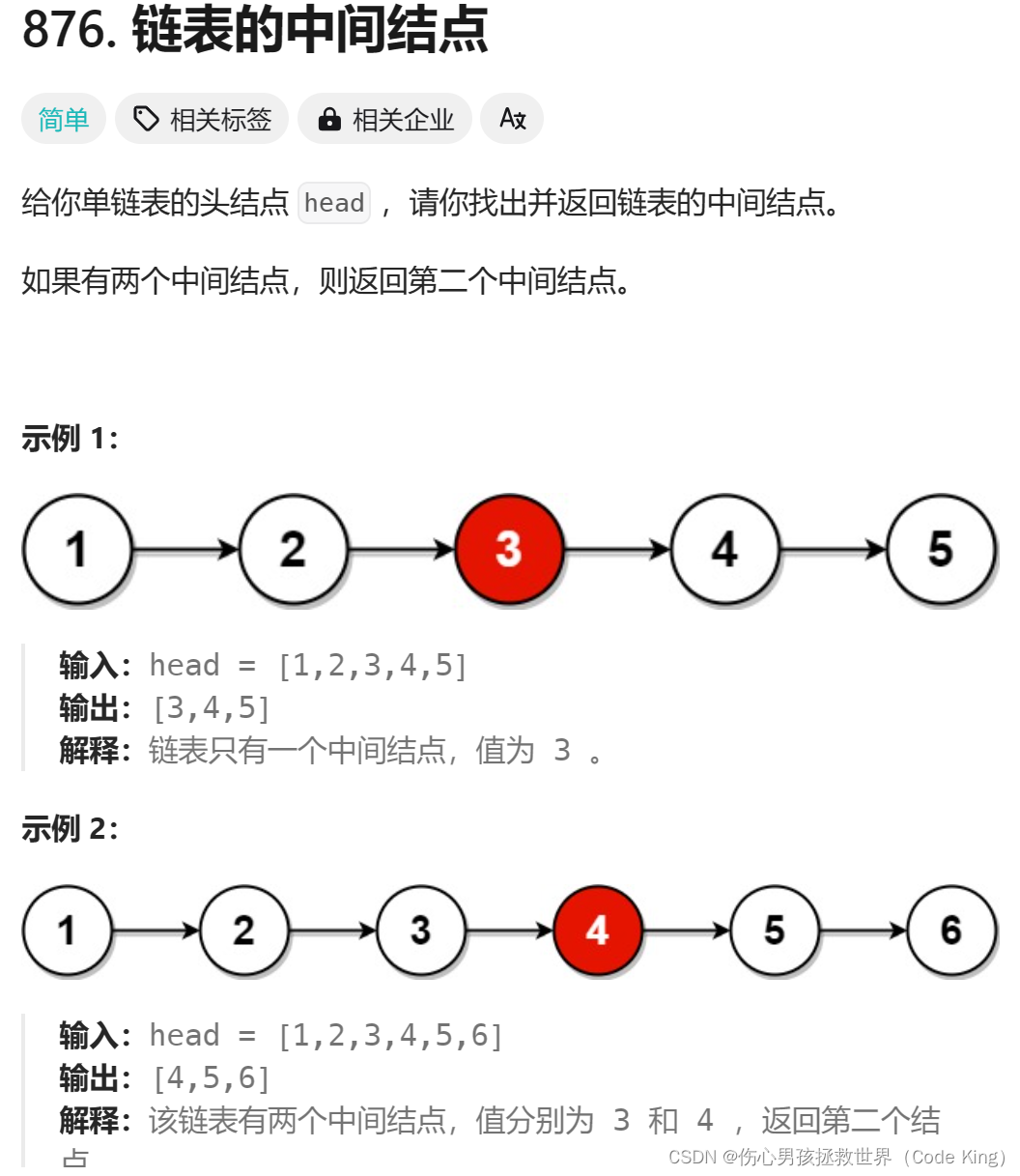
(2)思路表述:
利用两个指针,一个是快指针(fast),一个慢指针(slow),快指针移动的速度是慢指针的二倍!
(3)代码实现:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* fast=head;
struct ListNode* slow=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)//1.fast存在:针对奇数个结点 2.fast—>next存在:针对偶数个结点
{
fast=fast->next->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
4.链表中倒数第k个结点
(1)题目描述:
点击链接
(2)思路表述:
如果要求倒数第k个节点并返回k节点:还是利用快慢指针法,先让fast指针走k步,slow在第一个节点不动,完了之后呢,然后他们再一起走,最后如果fast走到了NULL,那么就直接返回slow就OK了!
自己要尝试画画图
(3)代码实现:
/**
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
/**
*
* @param pListHead ListNode类
* @param k int整型
* @return ListNode类
*/
struct ListNode* FindKthToTail(struct ListNode* pListHead, int k )
{
struct ListNode* fast=pListHead;
struct ListNode* slow=pListHead;
//fast=(fast->next)*k;
//先让fast指针走K步
while(k--)
{
if(fast==NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
fast=fast->next;
}
while(fast)
{
fast=fast->next;
slow=slow->next;
}
return slow;
}
5.合并两个有序链表
(1)题目描述:
题目链接
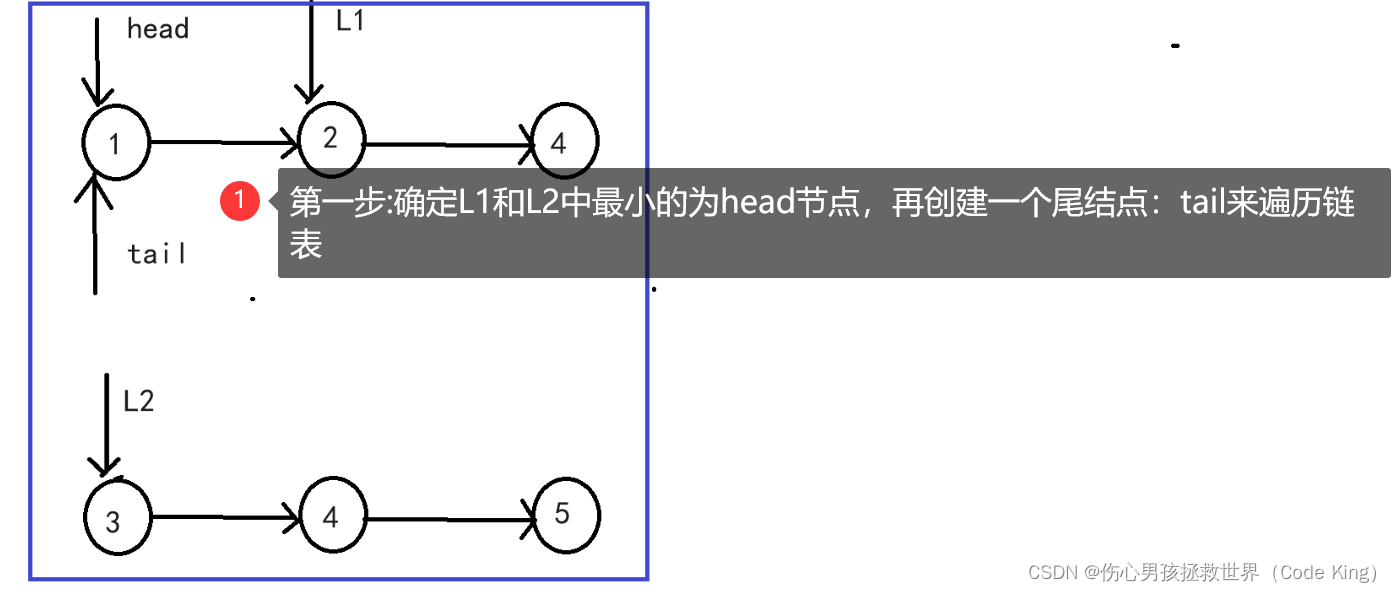
(2)思路表述:
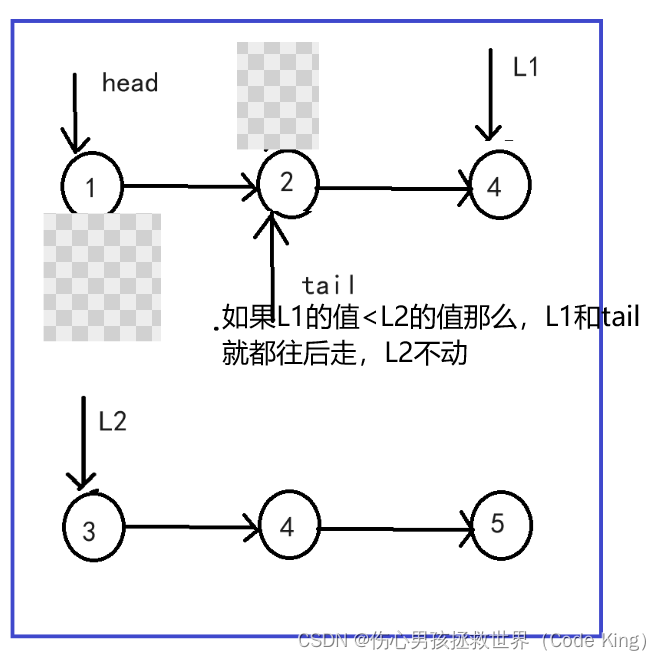
2.
3.
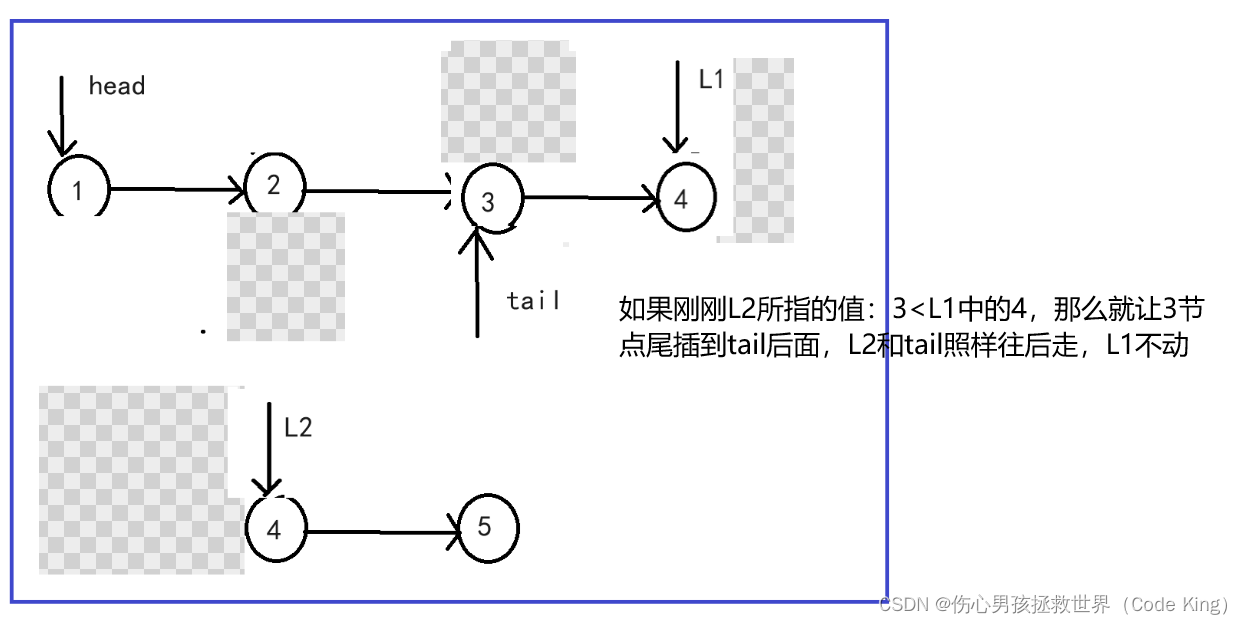
4.
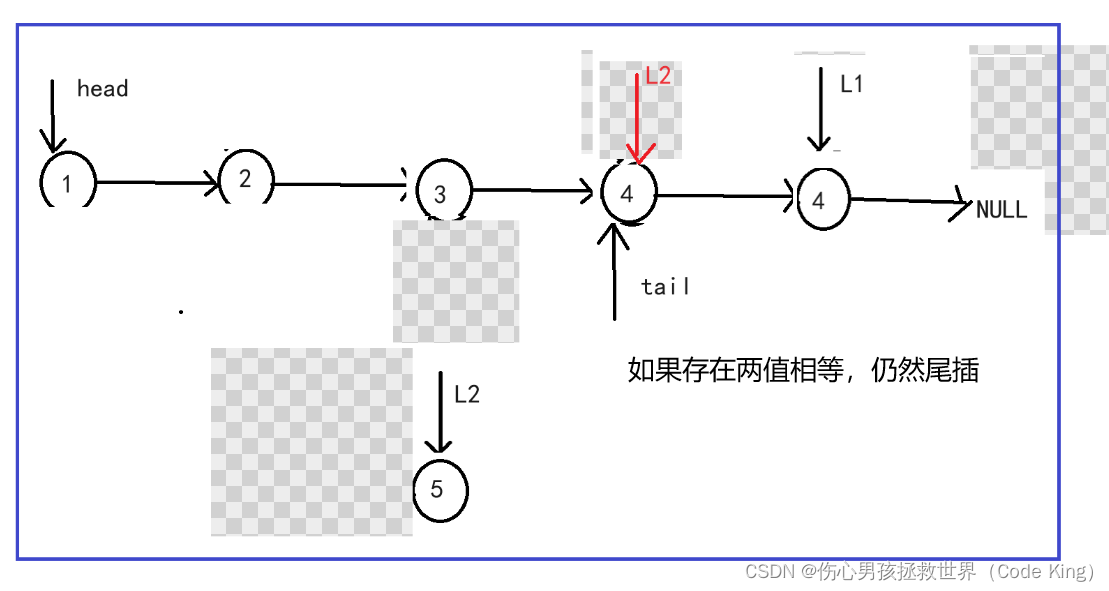
5.
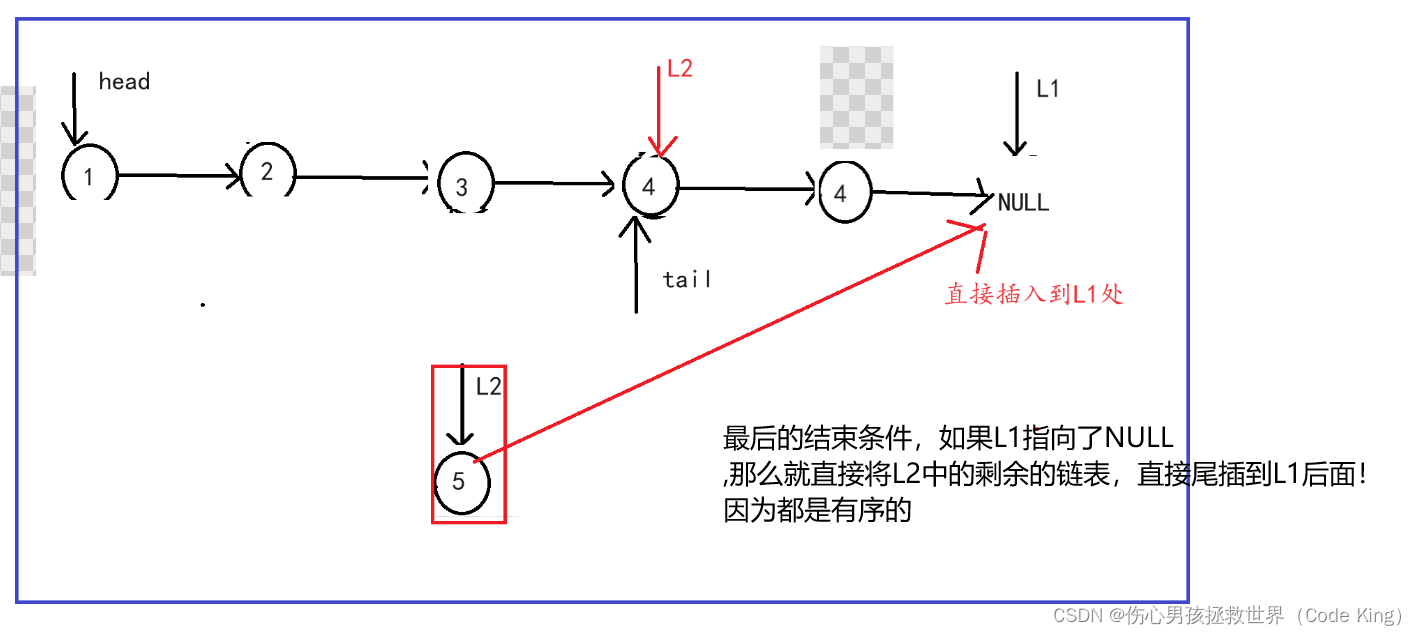
(3)代码实现:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode* mergeTwoLists(struct ListNode* l1, struct ListNode* l2)
{
struct ListNode* head=NULL;
struct ListNode* tail=NULL;
//前提:排除如果有一个链表就是空的咋办?
if(l1==NULL)
{
return l2;
}
if(l2==NULL)
{
return l1;
}
//1.确定好:l1和l2谁为head,tail
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
head=tail=l1;
l1=l1->next;
}
else
{
head=tail=l2;
l2=l2->next;
}
//2.逐个节点判断
while(l1&&l2)
{
if(l1->val<l2->val)
{
tail->next=l1;
l1=l1->next;
tail=tail->next;
}
else
{
tail->next=l2;
l2=l2->next;
tail=tail->next;
}
}
//3.如果跳出了循环,那么肯定有一个指向了NULL
if(l1==NULL)
{
tail->next=l2;
}
if(l2==NULL)
{
tail->next=l1;
}
return head;
}
6. 链表分割
(1)题目描述:
点击链接
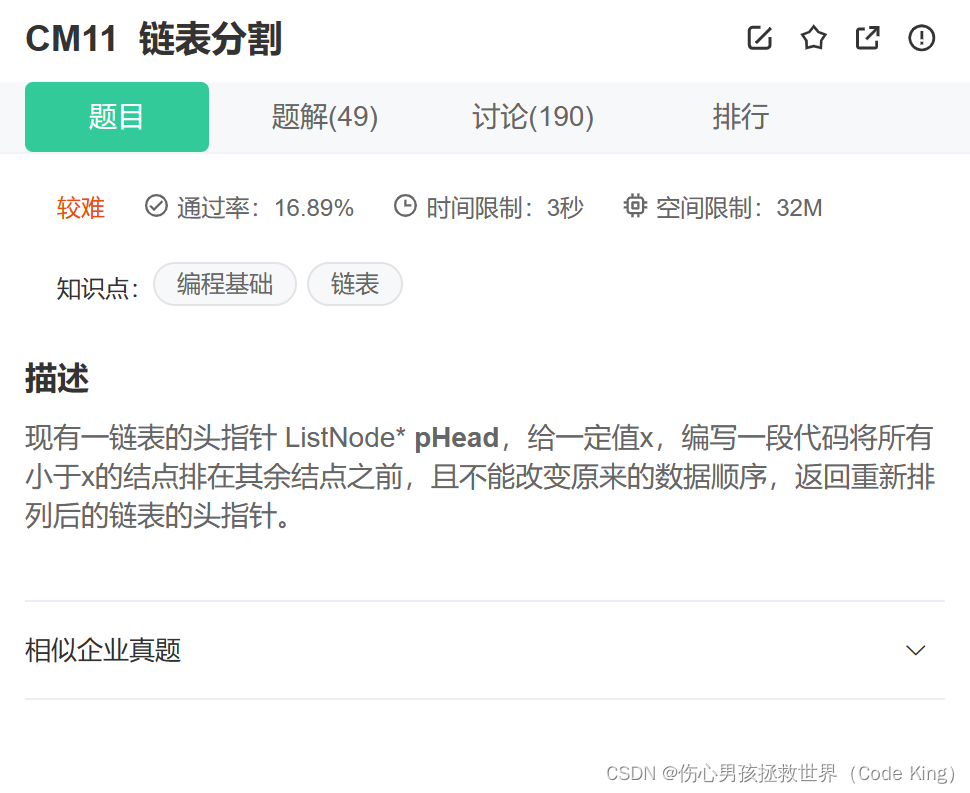
(2)思路表述:
分析:申请两个链表,一个放比x小的节点,一个放比x大的节点,最后将大链表链接在小链表末尾即可。
(3)代码实现:
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
#include <cstddef>
class Partition {
public:
ListNode* partition(ListNode* pHead, int x)
{
struct ListNode* cur = pHead;
struct ListNode* lhead;
struct ListNode* ltail;
struct ListNode* ghead;
struct ListNode* gtail;
lhead= ltail= (struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
ghead= gtail=(struct ListNode*)malloc(sizeof(struct ListNode));
while (cur)
{
if (cur->val < x) {
ltail->next = cur;
ltail = ltail->next;
}
else
{
gtail->next = cur;
gtail = gtail->next;
}
cur = cur->next;
}
ltail->next = ghead->next;
//不置空,会导致死循环
gtail->next = NULL;
//释放哨兵位,但需先创建结构体保存:lhead的第一个
struct ListNode* head = lhead->next;
free(lhead);
free(ghead);
return head;
}
};
7. 链表的回文结构
(1)题目描述:
点击链接
(2)思路表述:
分析:判断链表是否是回文结构,可以结合前面的题:
(1)利用快慢指针找到链表中间结点
(2)将后半部分逆置
(3)将(2)中的链表从第一个节点开始和中间结点开始同时进行访问,如果所有val相等,则链表为回文结构。
(3)代码实现:
/*
struct ListNode {
int val;
struct ListNode *next;
ListNode(int x) : val(x), next(NULL) {}
};*/
class PalindromeList {
public:
bool chkPalindrome(ListNode* head)
{
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode * head);
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode * head);
//找到中间节点
struct ListNode* middleNode(struct ListNode * head) {
struct ListNode* fast = head;
struct ListNode* slow = head;
while (fast && fast->next) {
slow = slow->next;
fast = fast->next->next;
}
return slow;
}
//将中间节点后的都逆置
struct ListNode* reverseList(struct ListNode * head) {
struct ListNode* cur = head;
struct ListNode* newhead = NULL;
while (cur) {
//这个next定义一定要在while循环内部,因为每次头插之前都要保存下一个节点的地址!!!
struct ListNode* next = cur->next;
//头插
cur->next = newhead;
newhead = cur;
cur = next;
}
return newhead;
}
struct ListNode* mid = middleNode(head);
struct ListNode* rmid = reverseList(mid);
//head相当于原来链表的前一半的头指针
//rmid相当于原来链表后一半的头指针
while (head && rmid) {
if (head->val != rmid->val) {
return false;
}
head = head->next;
rmid = rmid->next;
}
return true;
}
};
8.相交链表
(1)题目描述:
点击链接
(2)思路表述:
分别计算出L1链表和L2链表的总长度,然后用两个指针,一个是:fast,一个是:slow,让fast先走他们的差值步,让他们处在同一竖直平行线上,然后他们两个一起走,两个指针一起走后如果所指向的节点的值相同,那么就返回这个公共节点,也就是相交节点!
(3)代码实现:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
struct ListNode *getIntersectionNode(struct ListNode *headA, struct ListNode *headB)
{
//1.极端条件的判断,要么L1为空,要么L2为空,我就返回空,所以说不可能有公共交点。
if(headA == NULL || headB == NULL)
{
return NULL;
}
struct ListNode *curA = headA, *curB = headB;
int lenA = 0,lenB = 0;
while(curA->next)
{
curA = curA->next;
lenA++;
}
while(curB->next)
{
curB = curB->next;
lenB++;
}
//2.此时此刻两个循环都结束了,current a指向的是最后一个节点,current b也指向最后一个节点,如果他们两个不相等的话,走到最后一个节点还没有公共交点,那么他们两个永远远远不可能会有公共节点,所以说我们直接返回空就ok了。
if(curA != curB)
{
return NULL;
}
//3.此时两个指针都指向数值水平线的平行线上处于同一位置,现在不知道lena大?还是lenb大?所以说我先假设lena大
struct ListNode *longList = headA,*shortList = headB;
if(lenA < lenB)
{
longList = headB;
shortList = headA;
}
int gap = abs(lenA - lenB);
while(gap--)
{
longList = longList->next;
}
while(longList != shortList)
{
longList = longList->next;
shortList = shortList->next;
}
return longList;
}
9.判断链表中是否有环
(1)题目描述:
点击链接
(2)思路表述:
分析:
如何判断链表是否有环:使用快慢指针,慢指针一次走1步,快指针一次走2步,如果链表带环,那么快慢同时从链表起始位置开始向后走,一定会在环内相遇,此时快慢指针都有可能在环内打圈,直到相遇;否则,如果链表不带环,那么快指针会先走到链表末尾,慢指针只能在链表末尾追上快指针。
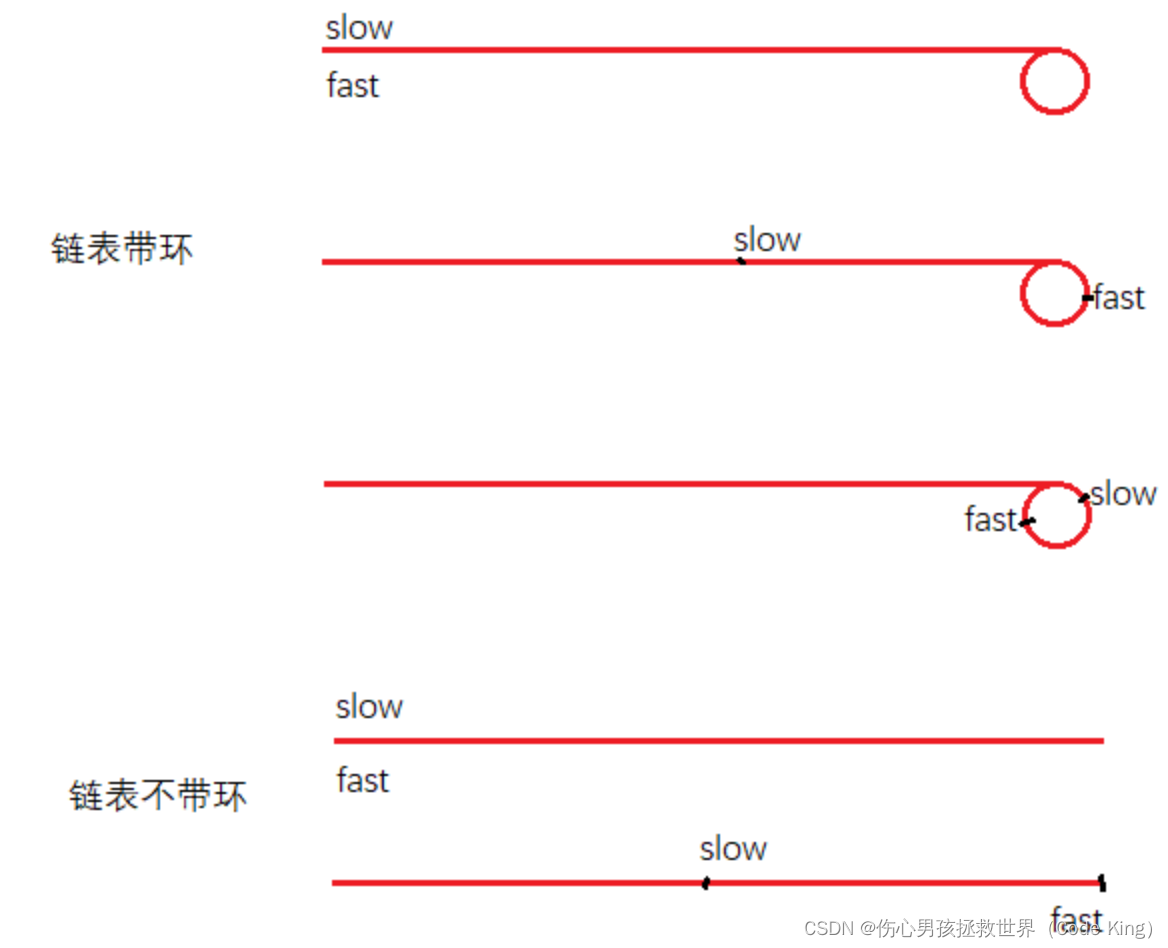
如果快指针不是一次走2步,而是一次走3步,一次走4步一次走x步呢?能不能判断出链表是否带环呢?
如果快指针一次走两步,当slow从直线中间移动到直线末尾时,fast又走了slow的2倍,因此当slow进环时,fast可能在环的任意位置,具体要看直线有多长,环有多大。在环内,一定是fast追slow,因为fast比slow移动的快。
fast一次走3步:假设slow进环的时候,fast跟slow相差N步,环的长度为C,追击时,slow走1步,fast走3步,每走1次,差距就缩小
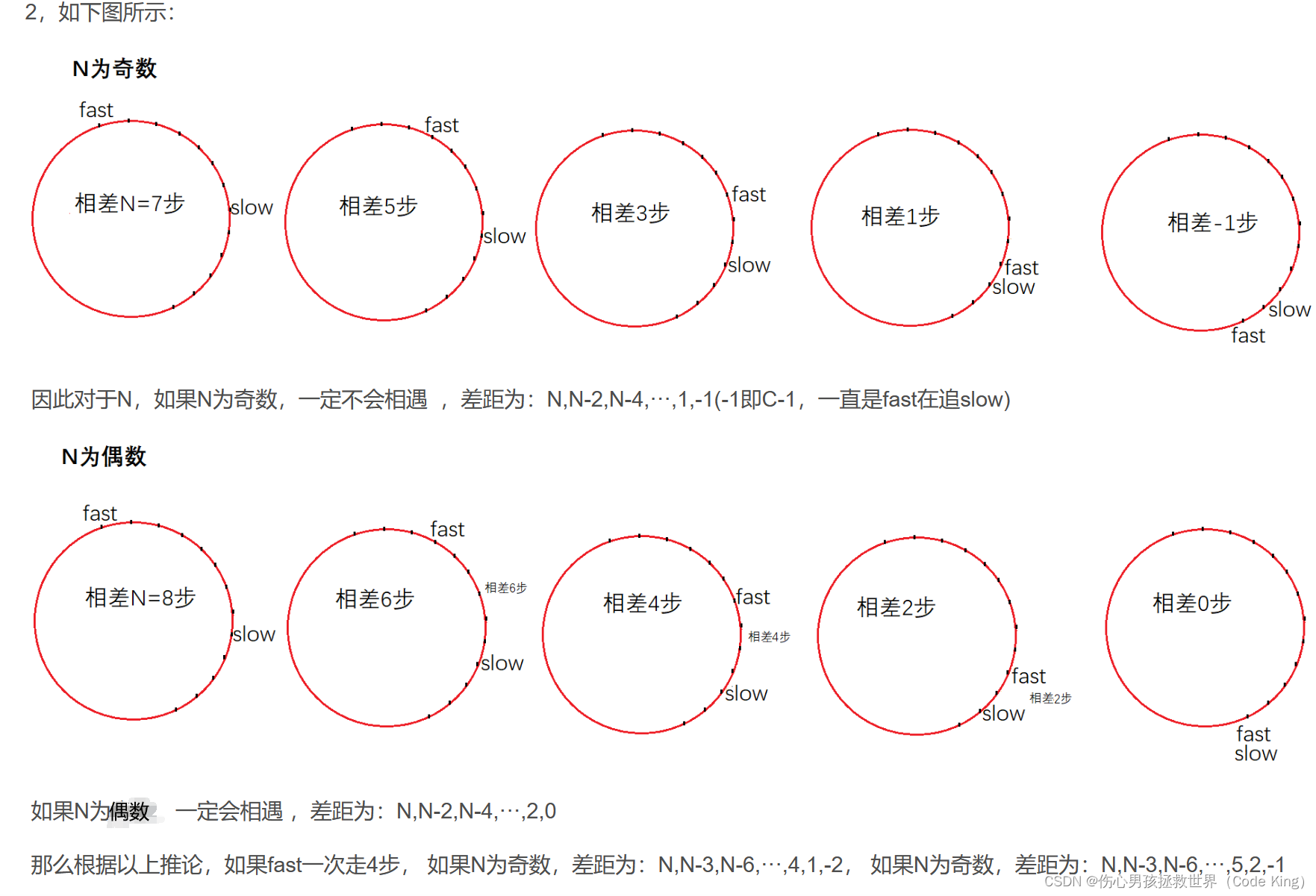
总结:如果slow进环时,slow和fast的差距N是奇数,且环的长度C为偶数(则C-1为奇数,上面举例可以看出差距最小为1或-1),那么就永远追不上了。
(3)代码实现:
/**
* Definition for singly-linked list.
* struct ListNode {
* int val;
* struct ListNode *next;
* };
*/
bool hasCycle(struct ListNode *head)
{
struct ListNode* slow=head;
struct ListNode* fast=head;
while(fast&&fast->next)
{
slow=slow->next;
fast=fast->next->next;
if(fast==slow)
{
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
六、链表和顺序表的优缺点对比

没有谁好谁坏,不同情况具体对待,相辅相成罢了
好了,今天的分享就到这里了
如果对你有帮助,记得点赞👍+关注哦!
我的主页还有其他文章,欢迎学习指点。关注我,让我们一起学习,一起成长吧!