7. 类型转换
7.1 基本类型转换
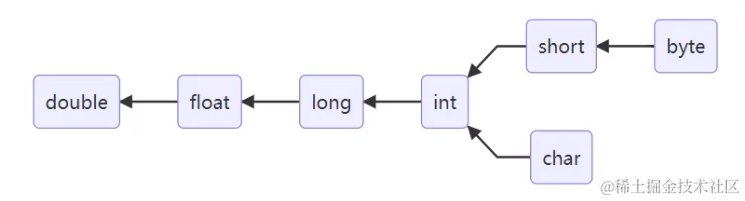
顺箭头:隐式转换(自动)
逆箭头:强制转换(可能造成精度丢失)
byte a = 10;
int b = a;
int c = 1000;
byte d = (byte) c;
System.out.println(d); // -24
7.2 包装类型与基本类型之间的转换
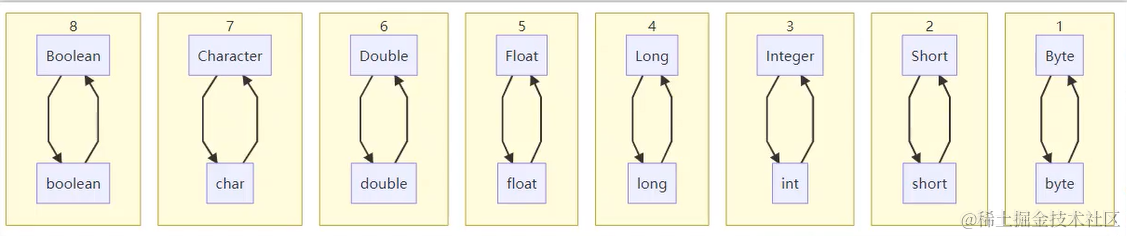
int a = 10;
Integer b = a;
Integer c = new Integer(20);
int d = c;
System.out.println(d);
7.3 引用类型之间的转换规则
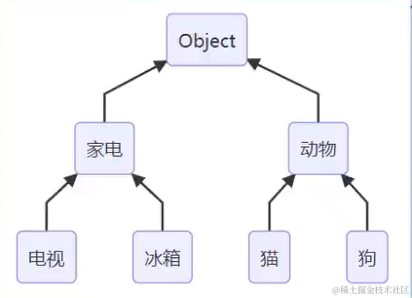
继承特点:
- 单继承:子类只能继承一个父类
- Object 是其他类型直接或者间接的父类型(不写 extends 也是继承 Object)
转换规则:
- 顺箭头:隐式转换
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal a = new Cat(); // 对象还是原本的对象,只是用父类型或者祖先类型来代表它
Object b = new Cat();
// Appliance c = new Cat(); // 不合法
}
}
class Animal extends Object {}
class Cat extends Animal {}
class Dog extends Animal {}
class Appliance {}
- 逆箭头:强制转换
public class TestArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Animal a = new Cat(); // 对象还是原本的对象,只是用父类型或者祖先类型来代表它
Object b = new Cat();
Cat c = (Cat) a;
// Dog d = (Dog) a; // 类型转换错误 ClassCastException
Animal d = (Animal) a;
}
}
class Animal extends Object {}
class Cat extends Animal {}
class Dog extends Animal {}
class Appliance {}
7.4 类型判断
System.out.println(a.getClass()); // class com.example.demo.Cat
System.out.println(b.getClass()); // class com.example.demo.Cat
System.out.println(a instanceof Cat); // true
7.5 字符串和数字的转换
String a = "1";
String b = "2";
System.out.println(a + b); // 12
System.out.println(Integer.parseInt(a) + Integer.parseInt(b)); // 3