SD 卡控制器(SD/SDIO Controller)
ZYNQ 中的 SD 卡控制器符合 SD2.0 协议规范,接口兼容 eMMC、MMC3.31、SDIO2.0、SD2.0、SPI,支持 SDHC、SDHS 器件。SD 卡控制器支持 SDMA(单操作 DMA)、ADMA1(4K 边界限制 DMA)和 ADMA2(在 32 位系统中允许任何位置和任意大小)。ARM 处理器通过 AHB 总线访问 SD 卡控制器,SD 控制器采用读和写通道各自双缓冲 FIFO 的机制提高吞吐带宽。
其内部框图如下图所示:
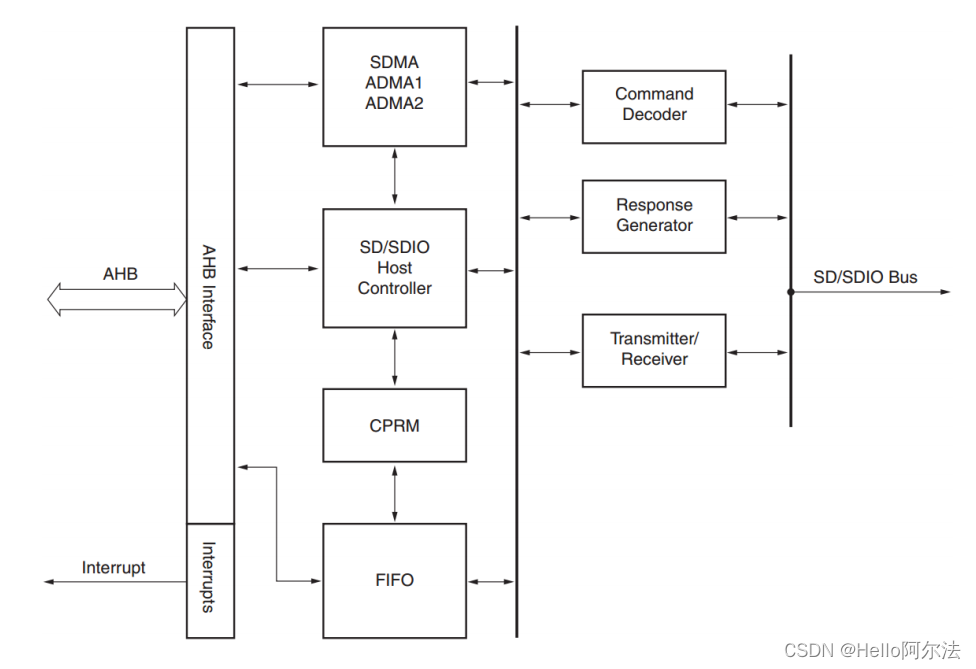
SD 控制器读写通道采用独立的 512 字节深度的双缓冲 FIFO 执行读和写操作。在写操作时,处理器向其中一个 FIFO 写数据,将另一个 FIFO 的数据写到 SD 总线;在读操作时,SD 总线上的数据向其中一个 FIFO 写数据,处理器将数据从另一个 FIFO 读出数据。SD 卡控制器通过双缓冲机制以保证最大带宽。
FATFS 文件系统
FATFS 是一个完全开源免费的 FAT 文件系统模块,专门为小型的嵌入式系统而设计。它完全用标准 C 语言编写,所以具有良好的硬件平台独立性,可以很方便的移植到各种嵌入式处理器中。Xilinx SDK 的 standalone 已经移植好了 FATFS 文件系统,因此在 SDK 中添加 xilffs 库后,就可以在程序中使用 FATFS 中的 API 函数来操作 SD 卡。
FATFS 的特点如下:
- 1、 结构清晰,代码量少,文件系统和 IO 底层分开,特别适合新手入门学习;
- 2、 支持最多 10 个逻辑盘符和两级文件夹;
- 3、 支持 FAT12/FAT16 和 FAT32 文件系统;
- 4、 支持长文件名称。
FATFS 的这些特点,加上开源、免费的原则,使得 FATFS 的应用非常广泛。FATFS 模块的层次结构分为顶层、中间层 FATFS 模块和底层接口。
最顶层是应用层,使用者无需理会 FATFS 的内部结构和复杂的 FAT 协议,只需要调用 FATFS 模块提供给用户的一系列应用接口函数,如 f_open,f_read,f_write 和 f_close 等,就可以像在 PC 上读/写文件那样简单。
中间层 FATFS 模块,实现了 FAT 文件读/写协议。FATFS 模块提供的是 ff.c 和 ff.h。除非有必要,使用者一般不用修改,使用时将头文件直接包含进去即可。
FATFS 模块提供的底层接口,它包括存储媒介读/写接口(disk I/O)和供给文件创建修改时间的实时时钟。
读写实验
- 实验平台:黑金 Zynq7035
- 开发环境:Vivado 2017.4
硬件设计
参考原理图可知,SD 卡接在了 PS_MIO40~45:

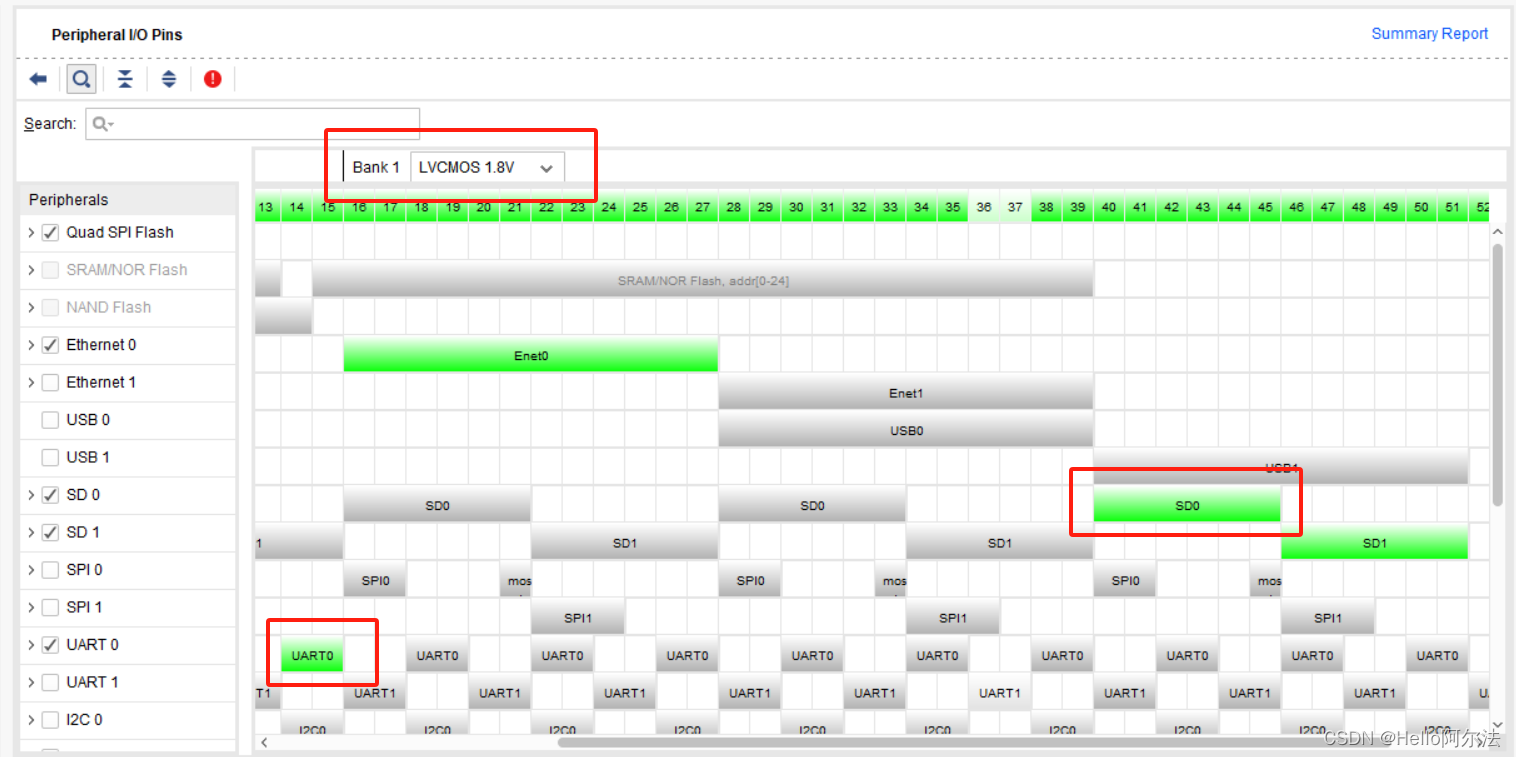
ZYNQ PS 做如下配置,配置 Bank 1 为 LVCMOS 1.8V,打开 UART0 和 SD0:
完善其他配置后生成比特流,导出硬件信息。
软件设计
创建 SDK 工程,在 BSP 设置中选中 xilffs,xilffs 即为 FATFS 库,保存配置:

添加如下代码:
#include "xparameters.h"
#include "ff.h"
#include "xdevcfg.h"
#include "xil_printf.h"
#include "stdio.h"
#define kprintf xil_printf
#define SD_FS "0:/"
#define SD_FILE "0:SD_TEST.txt"
static FATFS sd_fatfs;
static FRESULT fatfs_init(FATFS *fatfs, TCHAR *path)
{
FRESULT res;
res = f_mount(fatfs, path, 1);
if(res != FR_OK)
{
res = f_mkfs(path, 0, 0);
if (res != FR_OK)
{
kprintf("ERROR: Unable to format FATfs.\r\n");
return res;
}
res = f_mount(fatfs, path, 1);
if(res != FR_OK)
{
kprintf("ERROR: f_mount returned %d.\r\n", res);
return res;
}
}
return res;
}
static FRESULT sd_read_data(char *FileName, uint32_t DestinationAddress, uint32_t ByteLength)
{
FIL fil;
FRESULT res;
UINT br;
res = f_open(&fil, FileName, FA_READ);
if(res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: %s f_open returned %d\r\n", FileName, res);
return res;
}
res = f_lseek(&fil, 0);
if(res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: %s f_lseek returned %d\r\n", FileName, res);
return res;
}
res = f_read(&fil, (void*)DestinationAddress, ByteLength, &br);
if(res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: %s f_read returned %d\r\n", FileName, res);
return res;
}
res = f_close(&fil);
if(res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: %s f_close returned %d\r\n", FileName, res);
return res;
}
return res;
}
static FRESULT sd_write_data(char *FileName, uint32_t SourceAddress, uint32_t ByteLength)
{
FIL fil;
FRESULT res;
UINT bw;
res = f_open(&fil, FileName, FA_CREATE_ALWAYS | FA_WRITE);
if(res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: %s f_open returned %d.\r\n", FileName, res);
return res;
}
res = f_lseek(&fil, 0);
if(res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: %s f_lseek returned %d.\r\n", FileName, res);
return res;
}
res = f_write(&fil, (void*) SourceAddress, ByteLength, &bw);
if(res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: %s f_write returned %d.\r\n", FileName, res);
return res;
}
res = f_close(&fil);
if(res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: %s f_close returned %d.\r\n", FileName, res);
return res;
}
return res;
}
static FRESULT sd_rw_test(void)
{
FRESULT res;
const char src_str[] = "ZYNQ test SD card write and read!";
char dest_str[33];
uint32_t len = strlen(src_str);
res = sd_write_data(SD_FILE, (uint32_t)src_str, len);
if(XST_SUCCESS != res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: fail to write SD Card.\r\n");
return res;
}
else
{
kprintf("Success to write SD Card.\r\n");
}
res = sd_read_data(SD_FILE, (uint32_t)dest_str, len);
if(XST_SUCCESS != res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: fail to read SD Card.\r\n");
return res;
}
else
{
kprintf("Success to read SD Card; data: %s \r\n", dest_str);
}
kprintf("SD Card Write and Read test end.\r\n");
return res;
}
static FRESULT scan_files(char *path)
{
FRESULT res;
DIR dir;
UINT i;
static FILINFO fno;
res = f_opendir(&dir, path);
char pathBuff[256];
if(res == FR_OK)
{
for( ; ; )
{
res = f_readdir(&dir, &fno);
if(res != FR_OK || fno.fname[0] == 0)
{
break;
}
if(fno.fattrib & AM_DIR)
{
i = strlen(path);
sprintf(&path[i], "/%s", fno.fname);
kprintf("%s \r\n", path);
res = scan_files(path);
if(res != FR_OK)
{
break;
}
path[i] = 0;
}
else
{
kprintf("%s/%s \r\n", path, fno.fname);
strcpy(pathBuff, fno.fname);
}
}
}
else
{
kprintf("Failed - %s", &res);
}
f_closedir(&dir);
return res;
}
int main(void)
{
kprintf("hello world. \r\n");
FRESULT res;
res = fatfs_init(&sd_fatfs, SD_FS);
if(XST_SUCCESS != res)
{
kprintf("ERROR: fail to open SD Card.\r\n");
}
else
{
kprintf("Success to open SD Card.\r\n");
}
sd_rw_test();
scan_files(SD_FS);
while(1)
{
}
return 0;
}
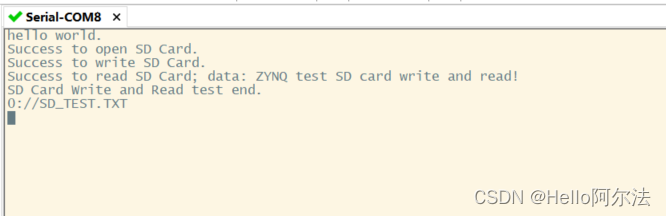
实验现象
- 终端输出: