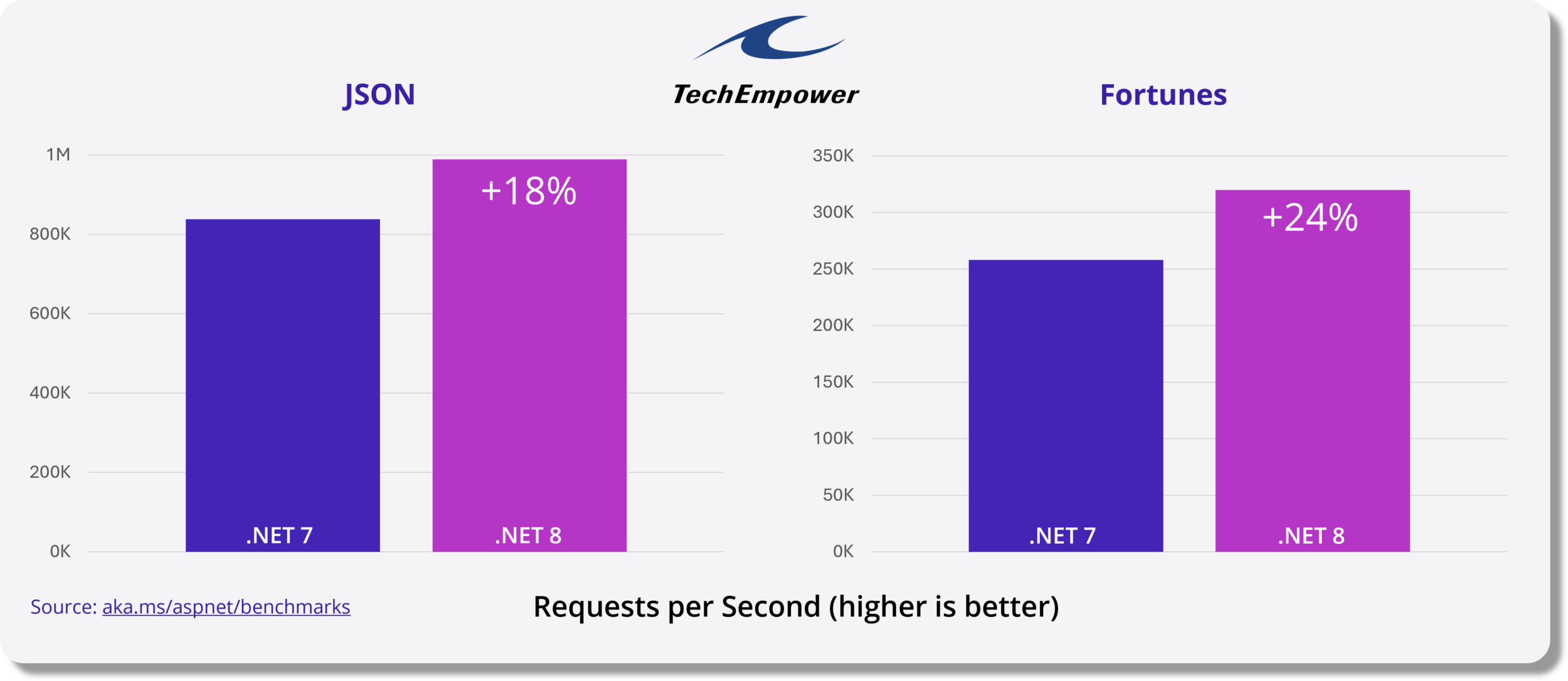
1性能提升
.NET 8在整个堆栈中带来了数千项性能改进 。默认情况下会启用一种名为动态配置文件引导优化 (PGO) 的新代码生成器,它可以根据实际使用情况优化代码,并且可以将应用程序的性能提高高达 20%。现在支持的 AVX-512 指令集能够对 512 位数据向量执行并行操作,这意味着可以在更短的时间内处理更多的数据。原始类型(数字及其他类型)现在实现了新的可格式化和可解析接口,这使它们能够直接格式化和解析为 UTF-8,而无需任何转码开销。
2.NET Aspire
.NET Aspire 是一个用于使用 .NET 构建弹性、可观察和可配置的云原生应用程序的堆栈。它包括一组针对云原生而增强的精选组件,默认情况下包括遥测、弹性、配置和运行状况检查。结合复杂而简单的本地开发人员体验,.NET Aspire 可以在第 1 天和第 100 天轻松发现、获取和配置云原生应用程序的基本依赖项。
点击这里查看.NET Aspire的预览版本。

3.NET 8 容器增强功能 – 更安全、更紧凑、更高效
使用 .NET 比以往更轻松、更安全地使用容器打包应用程序。每个 .NET 映像都包含一个非 root 用户,从而通过单行配置启用更安全的容器。.NET SDK 工具无需 Dockerfile 即可发布容器映像,并且默认情况下是非 root 的。由于 .NET 基础映像更小,因此可以更快地部署容器化应用程序 - 包括我们映像的新实验变体,这些变体可为本机 AOT 提供真正最小的应用程序大小。选择使用新的 Chiseled Ubuntu 映像变体进行更多安全强化,以进一步减少攻击面。使用 Dockerfile 或 SDK 工具,为任何架构构建应用程序和容器映像。

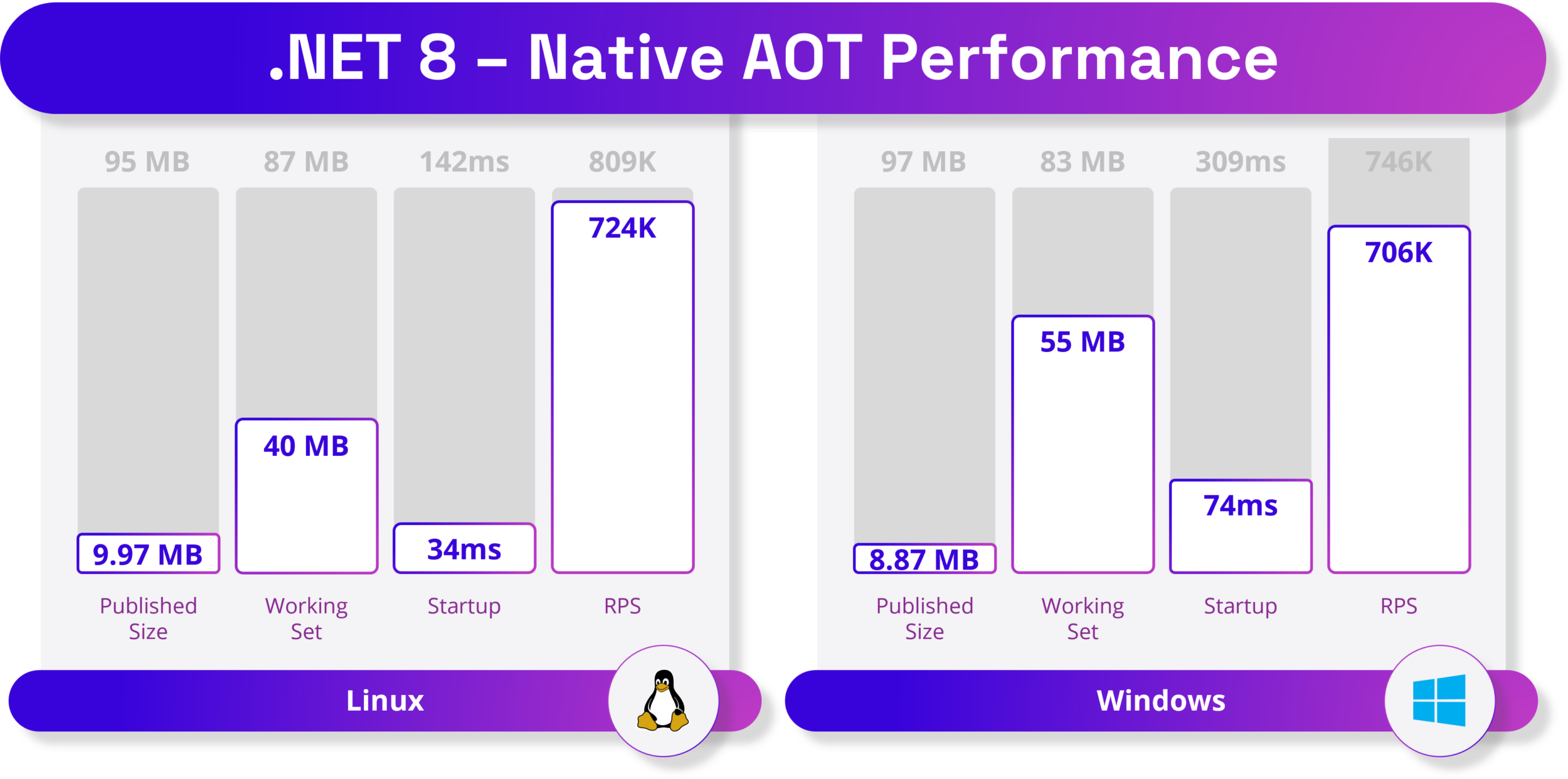
4原生 AoT – 迈向更高密度可持续计算的旅程
无需等待 JIT(即时)编译器在运行时编译代码。无需部署JIT编译器和IL代码。AOT 应用程序仅部署应用程序所需的代码。应用程序现在可以在不允许使用 JIT 编译器的受限环境中运行。
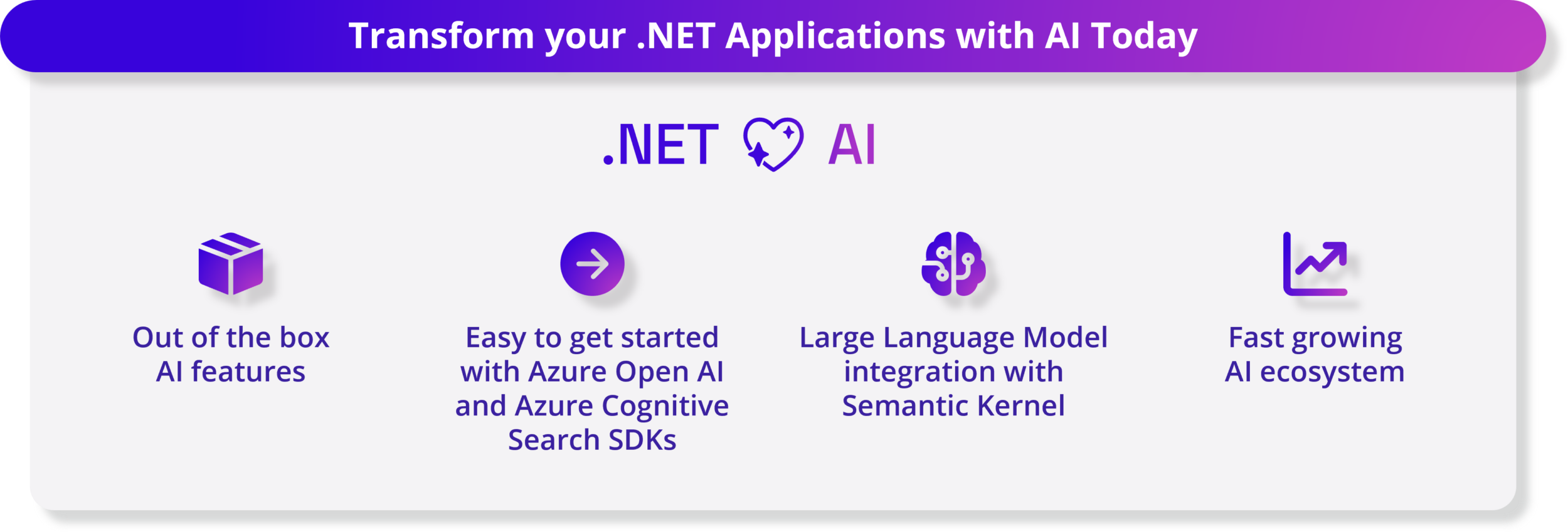
5人工智能 – 将 AI 融入您的 .NET 应用程序
生成式人工智能和大型语言模型正在改变人工智能领域,使开发人员能够在其应用程序中创建独特的人工智能体验。.NET 8 可以通过 .NET SDK 中一流的开箱即用 AI 功能以及与多种工具的无缝集成来轻松利用 AI。
.NET 8 为该 库带来了多项增强功能,以提高其与生成式 AI 工作负载的兼容性,例如集成 Tensor Primitives。随着人工智能应用程序的兴起,新的工具和 SDK 出现了。我们与众多内部和外部合作伙伴合作,例如Azure OpenAI、Azure Cognitive Search、Milvus、Qdrant和Microsoft Teams,以确保 .NET 开发人员可以通过各自的 SDK 轻松访问各种 AI 模型、服务和平台。此外,开源语义内核SDK 简化了这些 AI 组件与新的和现有应用程序的集成,以帮助您提供创新的用户体验。System.Numerics
现在提供各种示例和参考模板,展示模式和实践,以便开发人员轻松入门:
- 客户聊天机器人
- 检索增强生成
- 使用 Azure AI 服务开发应用程序
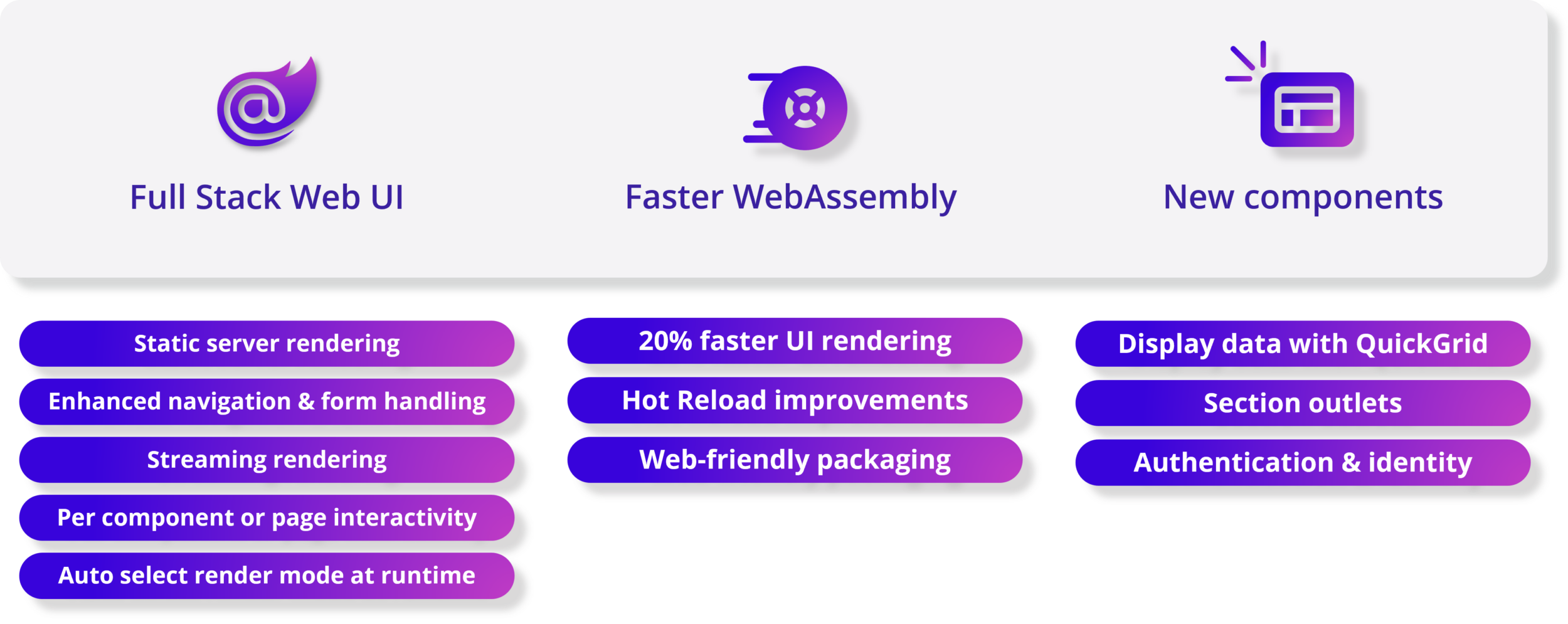
6Blazor – 使用 .NET 构建全栈 Web 应用程序
.NET 8 中的 Blazor 可以同时使用服务器和客户端来处理您的所有 Web UI 需求。这是全栈 Web UI!通过专注于优化页面加载时间、可扩展性和提升用户体验的多项新增强功能,开发人员现在可以在同一应用程序中使用Blazor Server 和 Blazor WebAssembly,在运行时自动将用户从服务器转移到客户端。得益于新的基于“Jiterpreter”的运行时和新的内置组件,您的 .NET 代码在 WebAssembly 上的运行速度显着加快。作为增强.NET 8 中整体身份验证、授权和身份管理的一部分,Blazor 现在支持生成完整的基于 Blazor 的身份 UI。
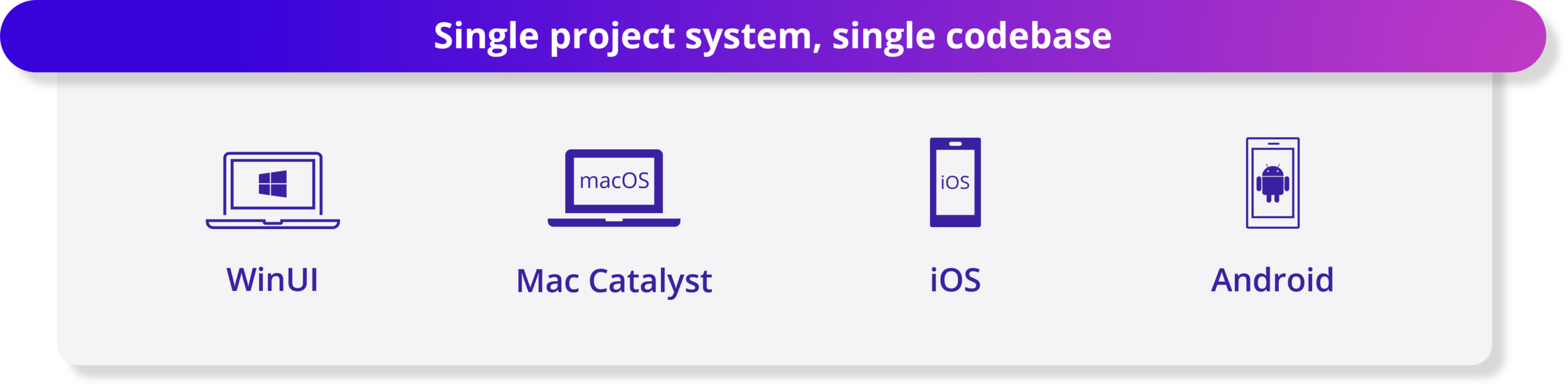
7.NET MAUI – 提升性能、可靠性和开发人员体验
.NET MAUI 提供单一项目系统和单一代码库来构建 WinUI、Mac Catalyst、iOS 和 Android 应用程序。本机 AOT(实验性)现在支持针对类似 iOS 的平台。适用于 .NET MAUI 的新 Visual Studio Code 扩展为您提供了开发跨平台 .NET 移动和桌面应用程序所需的工具。现在支持 Xcode 15 和 Android API 34,允许您瞄准最新版本的 iOS 和 Android。在性能、控件和 UI 元素以及特定于平台的行为方面进行了大量的质量改进,例如桌面交互添加了更好的点击处理、键盘侦听器等。
8 C# 12 功能 – 简化语法以提高开发人员的工作效率
C# 12 让您的编码体验更加高效和愉快。现在,您可以使用简单而优雅的语法在任何类和结构中创建主构造函数。不再需要样板代码来初始化您的字段和属性。使用简洁且富有表现力的语法创建数组、跨度和其他集合类型时会感到高兴。对 lambda 表达式中的参数使用新的默认值。不再需要重载或空检查来处理可选参数。您甚至可以使用usingalias 指令为任何类型添加别名,而不仅仅是命名类型!
8.1集合表达式
在 C# 12 之前,创建集合需要针对不同场景使用不同的语法。初始化所需的与or不同的语法。以下是创建集合的几种方法:List<int>int[]Span<int>
int[] x1 = new int[] { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
int[] x2 = Array.Empty<int>();
WriteByteArray(new[] { (byte)1, (byte)2, (byte)3 });
List<int> x4 = new() { 1, 2, 3, 4 };
Span<DateTime> dates = stackalloc DateTime[] { GetDate(0), GetDate(1) };
WriteByteSpan(stackalloc[] { (byte)1, (byte)2, (byte)3 });
8.2任何类或结构上的主构造函数
C# 12 扩展了主构造函数以适用于所有类和结构,而不仅仅是记录。主构造函数允许在声明类时定义构造函数参数:
public class BankAccount(string accountID, string owner)
{
public string AccountID { get; } = accountID;
public string Owner { get; } = owner;
public override string ToString() => $"Account ID: {AccountID}, Owner: {Owner}";
}
主构造函数参数最常见的用途是:
- 作为 base() 构造函数调用的参数。
- 初始化成员字段或属性。
- 在实例成员中引用构造函数参数。
- 删除依赖注入中的样板。
8.3别名任意类型
别名类型是从代码中删除复杂类型签名的便捷方法。using从 C# 12 开始,其他类型在别名指令中有效。例如,这些别名在早期版本的 C# 中无效:
using intArray = int[]; // Array types.
using Point = (int x, int y); // Tuple type
using unsafe ArrayPtr = int*; // Pointer type (requires "unsafe")
8.4默认 lambda 参数
从 C# 12 开始,您可以在 lambda 表达式中声明默认参数:
var IncrementBy = (int source, int increment = 1) => source + increment;
Console.WriteLine(IncrementBy(5)); // 6
Console.WriteLine(IncrementBy(5, 2)); // 7
8.5内联数组
运行时团队和其他库作者使用内联数组来提高应用的性能。 内联数组使开发人员能够创建固定大小的 struct 类型数组。 具有内联缓冲区的结构应提供类似于不安全的固定大小缓冲区的性能特征。 你可能不会声明自己的内联数组,但当它们从运行时 API 作为 System.Span<T> 或 System.ReadOnlySpan<T> 对象公开时,你将透明地使用这些数组。
[System.Runtime.CompilerServices.InlineArray(10)]
public struct Buffer
{
private int _element0;
}
它们的用法与任何其他数组类似:
var buffer = new Buffer();
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
buffer[i] = i;
}
foreach (var i in buffer)
{
Console.WriteLine(i);
}
区别在于编译器可以利用有关内联数组的已知信息。 你可能会像使用任何其他数组一样使用内联数组。 有关如何声明内联数组的详细信息,请参阅有关 struct 类型的语言参考。
9.反射改进
.NET 5 中引入了函数指针,但当时未添加对反射的相应支持。 对函数指针使用 typeof 或反射时(例如分别使用 typeof(delegate*<void>()) 或 FieldInfo.FieldType),返回了 IntPtr。 从 .NET 8 开始,将改为返回 System.Type 对象。 此类型提供对函数指针元数据的访问,包括调用约定、返回类型和参数。
新功能目前仅在 CoreCLR 运行时和 MetadataLoadContext 中实现。已将新的 API 添加到 System.Type(例如 IsFunctionPointer)以及 System.Reflection.PropertyInfo、System.Reflection.FieldInfo 和 System.Reflection.ParameterInfo。 以下代码演示如何使用一些新 API 进行反射。
// Sample class that contains a function pointer field.
public unsafe class UClass
{
public delegate* unmanaged[Cdecl, SuppressGCTransition]<in int, void> _fp;
}
// ...
FieldInfo fieldInfo = typeof(UClass).GetField(nameof(UClass._fp));
// Obtain the function pointer type from a field.
Type fpType = fieldInfo.FieldType;
// New methods to determine if a type is a function pointer.
Console.WriteLine($"IsFunctionPointer: {fpType.IsFunctionPointer}");
Console.WriteLine($"IsUnmanagedFunctionPointer: {fpType.IsUnmanagedFunctionPointer}");
// New methods to obtain the return and parameter types.
Console.WriteLine($"Return type: {fpType.GetFunctionPointerReturnType()}");
foreach (Type parameterType in fpType.GetFunctionPointerParameterTypes())
{
Console.WriteLine($"Parameter type: {parameterType}");
}
// Access to custom modifiers and calling conventions requires a "modified type".
Type modifiedType = fieldInfo.GetModifiedFieldType();
// A modified type forwards most members to its underlying type.
Type normalType = modifiedType.UnderlyingSystemType;
// New method to obtain the calling conventions.
foreach (Type callConv in modifiedType.GetFunctionPointerCallingConventions())
{
Console.WriteLine($"Calling convention: {callConv}");
}
// New method to obtain the custom modifiers.
foreach (Type modreq in modifiedType.GetFunctionPointerParameterTypes()[0].GetRequiredCustomModifiers())
{
Console.WriteLine($"Required modifier for first parameter: {modreq}");
}
输出:
IsFunctionPointer: True
IsUnmanagedFunctionPointer: True
Return type: System.Void
Parameter type: System.Int32&
Calling convention: System.Runtime.CompilerServices.CallConvSuppressGCTransition
Calling convention: System.Runtime.CompilerServices.CallConvCdecl
Required modifier for first parameter: System.Runtime.InteropServices.InAttribute
10.配置绑定源生成器
.NET 8 引入了一个源生成器,用于在 ASP.NET Core 中提供 AOT 和适合剪裁的配置。 该生成器是现有的基于反射的实现的替代方法。
源生成器探测 Configure(TOptions)、Bind 和 Get 调用来从中检索类型信息。 在项目中启用生成器后,编译器将隐式选择生成的方法,而非预先存在的基于反射的框架实现。
无需更改源代码即可使用生成器。 AOT Web 应用中默认启用该生成器。 对于其他项目类型,源生成器默认关闭,但你可通过在项目文件中将 EnableConfigurationBindingGenerator 属性设置为 true 来选择使用它:
<PropertyGroup>
<EnableConfigurationBindingGenerator>true</EnableConfigurationBindingGenerator>
</PropertyGroup>
以下代码演示了调用绑定器的示例:
using Microsoft.AspNetCore.Builder;
using Microsoft.Extensions.Configuration;
using Microsoft.Extensions.DependencyInjection;
WebApplicationBuilder builder = WebApplication.CreateBuilder(args);
IConfigurationSection section = builder.Configuration.GetSection("MyOptions");
// !! Configure call - to be replaced with source-gen'd implementation
builder.Services.Configure<MyOptions>(section);
// !! Get call - to be replaced with source-gen'd implementation
MyOptions options0 = section.Get<MyOptions>();
// !! Bind call - to be replaced with source-gen'd implementation
MyOptions options1 = new MyOptions();
section.Bind(options1);
WebApplication app = builder.Build();
app.MapGet("/", () => "Hello World!");
app.Run();
public class MyOptions
{
public int A { get; set; }
public string S { get; set; }
public byte[] Data { get; set; }
public Dictionary<string, string> Values { get; set; }
public List<MyClass> Values2 { get; set; }
}
public class MyClass
{
public int SomethingElse { get; set; }
}
11.针对 Android 应用的 AOT 编译
为了减小应用大小,面向 Android 的 .NET 和 .NET MAUI 应用在发布模式下构建时使用分析的预先 (AOT) 编译模式。 与常规 AOT 编译相比,分析的 AOT 编译所影响的方法更少。 .NET 8 引入了 <AndroidStripILAfterAOT> 属性,你可使用它进一步对 Android 应用进行 AOT 编译,从而更进一步减少应用大小。
<PropertyGroup>
<AndroidStripILAfterAOT>true</AndroidStripILAfterAOT>
</PropertyGroup>
默认情况下,将 AndroidStripILAfterAOT 设置为 true 会替代默认的 AndroidEnableProfiledAot 设置,从而允许剪裁已 AOT 编译的(几乎)所有方法。 还可通过将两个属性都显式设置为 true 来结合使用分析的 AOT 和 IL 条带化:
<PropertyGroup>
<AndroidStripILAfterAOT>true</AndroidStripILAfterAOT>
<AndroidEnableProfiledAot>true</AndroidEnableProfiledAot>
</PropertyGroup>
12.代码分析
.NET 8 包括几个新的代码分析器和修复程序,可帮助验证是否正确且高效地使用 .NET 库 API。 下表总结了新的分析器。
| 规则 ID | 类别 | 说明 |
|---|---|---|
| CA1856 | 性能 | 未在参数上正确应用 ConstantExpectedAttribute 属性时触发。 |
| CA1857 | 性能 | 当参数使用 ConstantExpectedAttribute 添加批注但提供的参数不是常量时触发。 |
| CA1858 | 性能 | 若要确定字符串是否以给定前缀开头,最好调用 String.StartsWith,而不是调用 String.IndexOf,然后将结果与零进行比较。 |
| CA1859 | 性能 | 此规则建议尽可能将特定局部变量、字段、属性、方法参数和方法返回类型从接口或抽象类型升级到具体类型。 使用具体类型可生成更高质量的代码。 |
| CA1860 | 性能 | 若要确定集合类型是否具有任何元素,最好使用 Length、Count 或 IsEmpty,而不是调用 Enumerable.Any。 |
| CA1861 | 性能 | 重复调用时,不会重复使用作为参数传递的常量数组,这意味着每次都会创建一个新数组。 若要提高性能,请考虑将数组提取到静态只读字段。 |
| CA1865-CA1867 | 性能 | 对于单字符串,char 重载的性能更好。 |
| CA2021 | 可靠性 | Enumerable.Cast(IEnumerable) 和 Enumerable.OfType(IEnumerable) 需要兼容的类型才能正常运行。 泛型类型不支持扩大转换和用户定义的转换。 |
| CA1510-CA1513 | 可维护性 | 在构造新的异常实例方面,引发帮助程序比 if 块更简单、更高效。 这四个分析器是为以下例外情况创建的:ArgumentNullException、ArgumentException、ArgumentOutOfRangeException 和 ObjectDisposedException。 |
13.Core .NET 库
13.1时间抽象
新的 TimeProvider 类和 ITimer 接口添加了时间抽象功能,让你可以在测试方案中模拟时间。 此外,还可以使用时间抽象,通过 Task.Delay 和 Task.WaitAsync 来模拟依赖于时间进度的 Task 操作。 时间抽象支持以下基本时间操作:
- 检索本地和 UTC 时间
- 获取用于测量性能的时间戳
- 创建计时器
以下代码片段演示了一些使用情况示例。
// Get system time.
DateTimeOffset utcNow = TimeProvider.System.GetUtcNow();
DateTimeOffset localNow = TimeProvider.System.GetLocalNow();
// Create a time provider that works with a
// time zone that's different than the local time zone.
private class ZonedTimeProvider : TimeProvider
{
private TimeZoneInfo _zoneInfo;
public ZonedTimeProvider(TimeZoneInfo zoneInfo) : base()
{
_zoneInfo = zoneInfo ?? TimeZoneInfo.Local;
}
public override TimeZoneInfo LocalTimeZone => _zoneInfo;
public static TimeProvider FromLocalTimeZone(TimeZoneInfo zoneInfo) =>
new ZonedTimeProvider(zoneInfo);
}
// Create a timer using a time provider.
ITimer timer = timeProvider.CreateTimer(callBack, state, delay, Timeout.InfiniteTimeSpan);
// Measure a period using the system time provider.
long providerTimestamp1 = TimeProvider.System.GetTimestamp();
long providerTimestamp2 = TimeProvider.System.GetTimestamp();
var period = GetElapsedTime(providerTimestamp1, providerTimestamp2);
13.2UTF8 改进
如果要启用将类型的类似字符串的表示形式写出到目标范围,请在类型上实现新的 IUtf8SpanFormattable 接口。 此新接口与 ISpanFormattable 密切相关,但面向 UTF8 和 Span<byte>,而不是 UTF16 和 Span<char>。
IUtf8SpanFormattable 已在所有基元类型(以及其他)上实现,无论是面向 string、Span<char> 还是 Span<byte>,其共享逻辑完全一致。 它完全支持所有格式(包括新的“B”二进制说明符)和所有区域性。 这意味着现在可以从 Byte、Complex、Char、DateOnly、DateTime、DateTimeOffset、Decimal、Double、Guid、Half、IPAddress、IPNetwork、Int16、Int32、Int64、Int128、IntPtr、NFloat、SByte、Single、Rune、TimeOnly、TimeSpan、UInt16、UInt32、UInt64、UInt128、UIntPtr 和 Version 直接格式化为 UTF8。
新的 Utf8.TryWrite 方法向现有 MemoryExtensions.TryWrite 方法(基于 UTF16)提供基于 UTF8 的对应方法。 可以使用内插字符串语法将复杂表达式直接格式化为 UTF8 字节范围,例如:
static bool FormatHexVersion(
short major,
short minor,
short build,
short revision,
Span<byte> utf8Bytes,
out int bytesWritten) =>
Utf8.TryWrite(
utf8Bytes,
CultureInfo.InvariantCulture,
$"{major:X4}.{minor:X4}.{build:X4}.{revision:X4}",
out bytesWritten);
13.3加密
.NET 8 添加了对 SHA-3 哈希基元的支持。 (目前,具有 OpenSSL 1.1.1 或更高版本和 Windows 11 Build 25324 或更高版本的 Linux 支持 SHA-3。)可在其中使用 SHA-2 的 API 现在提供对 SHA-3 的补充。 对于哈希,这包括 SHA3_256、SHA3_384 和 SHA3_512;对于 HMAC,这包括 HMACSHA3_256、HMACSHA3_384 和 HMACSHA3_512;对于其中可配置算法的哈希,这包括 HashAlgorithmName.SHA3_256、HashAlgorithmName.SHA3_384 和 HashAlgorithmName.SHA3_512;对于 RSA OAEP 加密,这包括 RSAEncryptionPadding.OaepSHA3_256、RSAEncryptionPadding.OaepSHA3_384 和 RSAEncryptionPadding.OaepSHA3_512。
以下示例演示如何使用 API(包括 SHA3_256.IsSupported 属性)来确定平台是否支持 SHA-3。
// Hashing example
if (SHA3_256.IsSupported)
{
byte[] hash = SHA3_256.HashData(dataToHash);
}
else
{
// ...
}
// Signing example
if (SHA3_256.IsSupported)
{
using ECDsa ec = ECDsa.Create(ECCurve.NamedCurves.nistP256);
byte[] signature = ec.SignData(dataToBeSigned, HashAlgorithmName.SHA3_256);
}
else
{
// ...
}
13.4基于流的 ZipFile 方法
.NET 8 包含 ZipFile.CreateFromDirectory 的新重载,通过它可以收集目录中包含的所有文件并压缩这些文件,然后将生成的 zip 文件存储到提供的流中。 同样,通过新的 ZipFile.ExtractToDirectory 重载,可提供包含压缩文件的流,并将其内容提取到文件系统中。 下面是新的重载:
namespace System.IO.Compression;
public static partial class ZipFile
{
public static void CreateFromDirectory(string sourceDirectoryName, Stream destination);
public static void CreateFromDirectory(string sourceDirectoryName, Stream destination, CompressionLevel compressionLevel, bool includeBaseDirectory);
public static void CreateFromDirectory(string sourceDirectoryName, Stream destination, CompressionLevel compressionLevel, bool includeBaseDirectory, Encoding? entryNameEncoding);
public static void ExtractToDirectory(Stream source, string destinationDirectoryName) { }
public static void ExtractToDirectory(Stream source, string destinationDirectoryName, bool overwriteFiles) { }
public static void ExtractToDirectory(Stream source, string destinationDirectoryName, Encoding? entryNameEncoding) { }
public static void ExtractToDirectory(Stream source, string destinationDirectoryName, Encoding? entryNameEncoding, bool overwriteFiles) { }
}




![BUUCTF [MRCTF2020]ezmisc 1](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/6d4e55a5407c4c839c44252bbbd4d03f.png#pic_center)