行路难!行路难!多歧路,今安在?长风破浪会有时,直挂云帆济沧海。————李白
一 .堆栈
1 什么是堆栈
堆栈是一种特殊的线性表,堆栈中的元素以及元素之间的逻辑关系和线性表完全相同。在操作上的差别是线性表允许在任意位置插入和删除元素,而堆栈只允许在固定一端插入和删除元素,堆栈中允许插入和删除元素的一端称为栈顶,另一端称为栈底。
栈顶的当前位置是动态的,用于标记栈顶当前位置的变量,称为栈顶指示器。堆栈的插入操作,通常称为入栈。堆栈的删除操作通常称为出栈。
根据堆栈的定义,我们可以发现,每次入栈的元素都放在原栈顶元素之前而成为新的栈顶元素,每次出栈的元素都是原栈顶元素。这样最后进入栈的元素总是最先退出栈的,因此堆栈也称作后进先出的线性表,或简称为后进先出表。

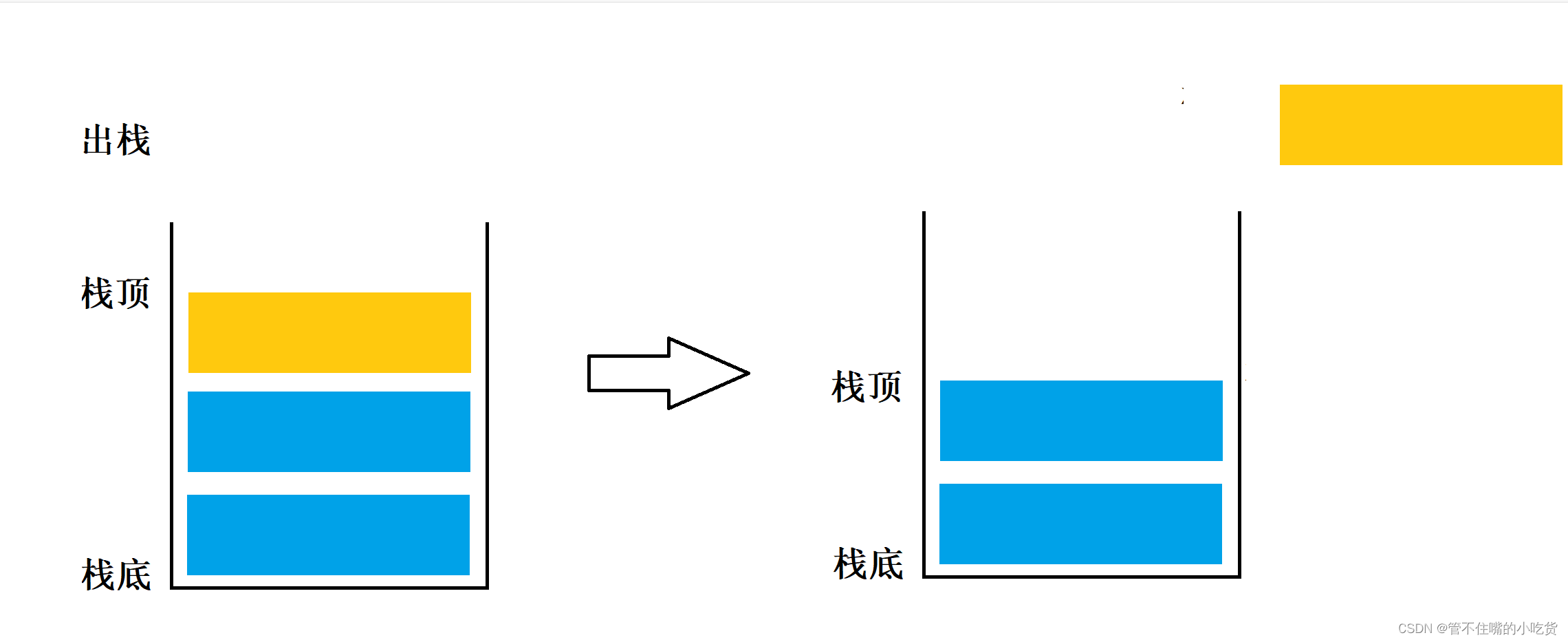
2 堆栈的两种实现方式
栈的实现一般可以使用数组或者链表实现
链式栈:用链表的结构来实现栈。
顺序栈:用数组的结构来实现栈。
优缺点:
单向链式结构的出栈入栈效率比较低,因为我们要先找到尾结点再行插入删除
而顺序栈只需要记录栈顶位置,进行出栈入栈十分方便,不需要多余的空间存储地址。
所以相对而言数组的结构实现更优一些。因为数组在尾上插入数据的代价比较小。
3 堆栈的操作实现
3.1 栈的结构体和初始化
结构体:
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;初始化:
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;
}
3.2 销毁
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
3.3入栈
// 入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
// 满了-》增容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}3.4出栈
// 出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
// 栈空了,调用Pop,直接中止程序报错
assert(ps->top > 0);
//ps->a[ps->top - 1] = 0;
ps->top--;
}
3.5判断栈是否为空
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}3.6取顶部数据
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
// 栈空了,调用Top,直接中止程序报错
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}3.7取栈中有效数据的个数
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}4 完整代码
Stack.h
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int STDataType;
typedef struct Stack
{
STDataType* a;
int top;
int capacity;
}ST;
void StackInit(ST* ps);
void StackDestory(ST* ps);
// 入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x);
// 出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps);
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps);
int StackSize(ST* ps);
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps);Stack.c
#include "Stack.h"
void StackInit(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
ps->a = (STDataType*)malloc(sizeof(STDataType) * 4);
if (ps->a == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
ps->capacity = 4;
ps->top = 0;
}
void StackDestory(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
free(ps->a);
ps->a = NULL;
ps->top = ps->capacity = 0;
}
// 入栈
void StackPush(ST* ps, STDataType x)
{
assert(ps);
// 满了-》增容
if (ps->top == ps->capacity)
{
STDataType* tmp = (STDataType*)realloc(ps->a, ps->capacity * 2 * sizeof(STDataType));
if (tmp == NULL)
{
printf("realloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
else
{
ps->a = tmp;
ps->capacity *= 2;
}
}
ps->a[ps->top] = x;
ps->top++;
}
// 出栈
void StackPop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
// 栈空了,调用Pop,直接中止程序报错
assert(ps->top > 0);
//ps->a[ps->top - 1] = 0;
ps->top--;
}
STDataType StackTop(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
// 栈空了,调用Top,直接中止程序报错
assert(ps->top > 0);
return ps->a[ps->top - 1];
}
int StackSize(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top;
}
bool StackEmpty(ST* ps)
{
assert(ps);
return ps->top == 0;
}二 .队列
1 队列的概念及结构
队列也是一种特殊的线性表,队列中的元素及元素间的逻辑关系和线性表完全相同,在操作上的差异是; 线性表允许在任意位置插入和删除元素。而队列只允许在其一端进行插入操作,在其另一端进行删除操作。
在队列中,允许进行插入操作的一端成为队尾。允许进行删除操作的一端成为队头,队头队尾,分别由队头指针和队尾指针指示。队列的插入操作通常称作入队列,队列的删除操作通常称作出队列,根据队列的定义,我们可以把,队列想象成是一种先进先出的线性表,简称先进先出表
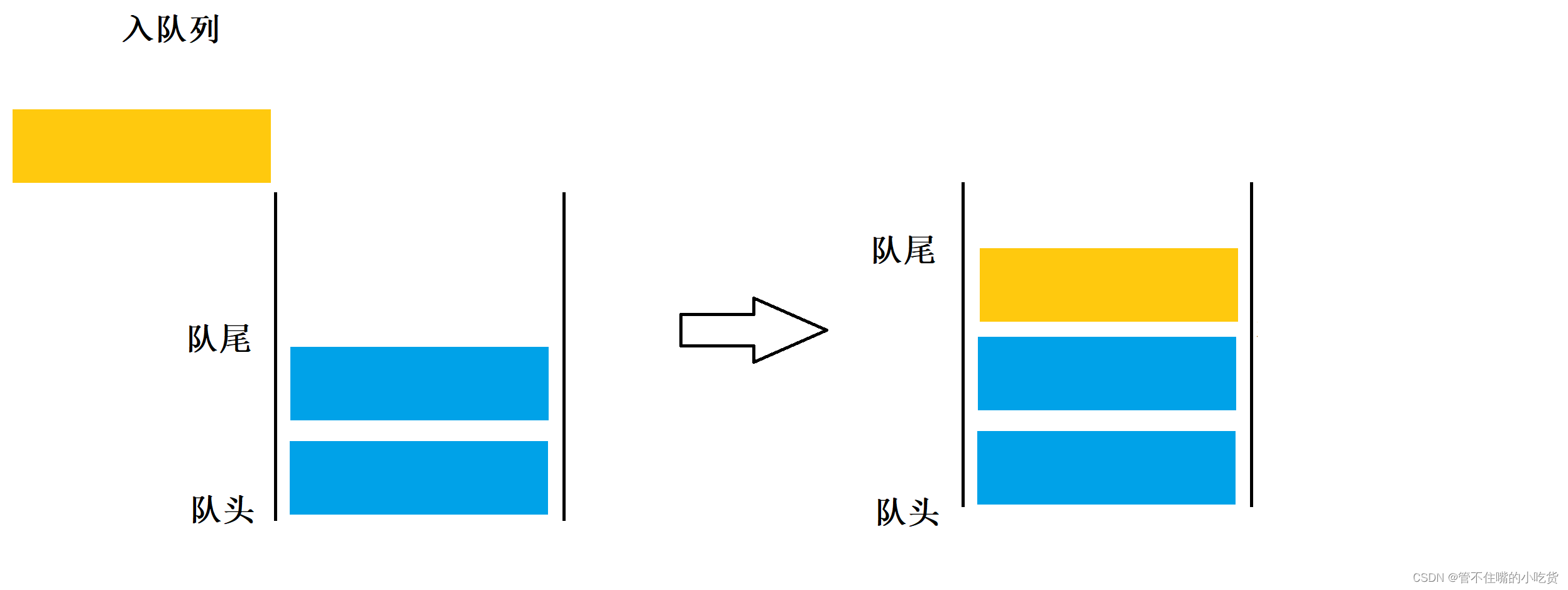
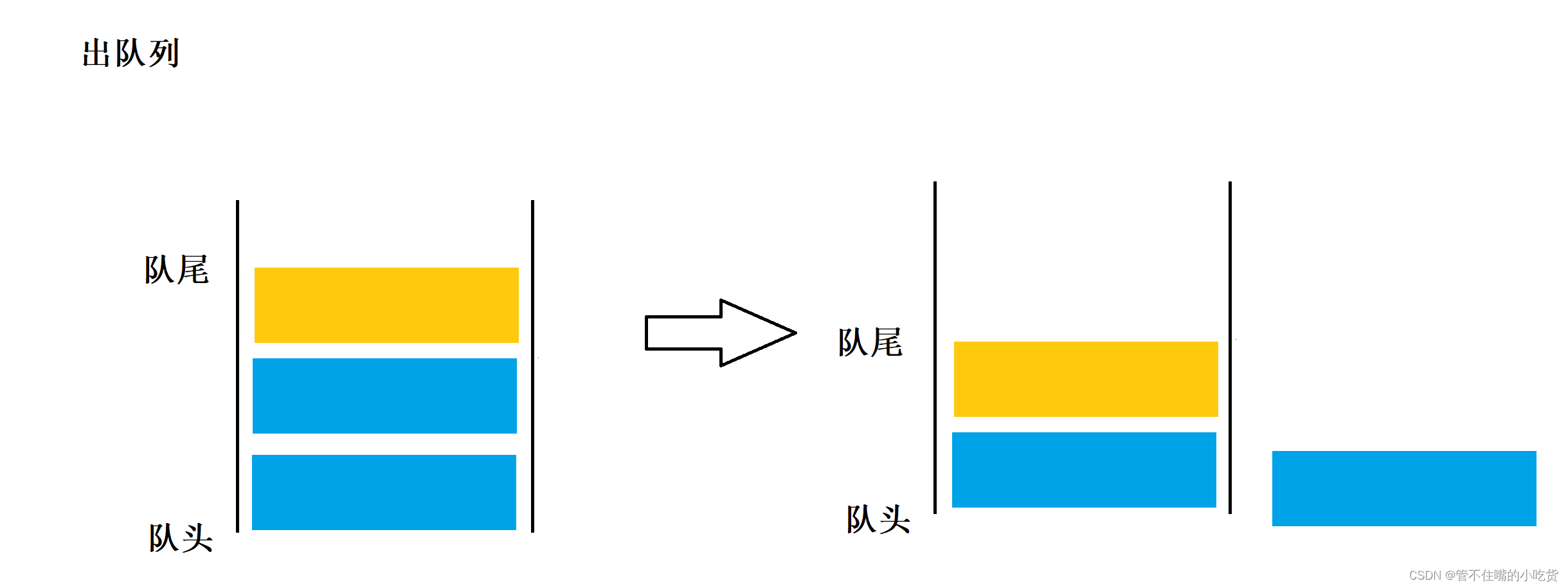
2 队列的实现形式
队列也可以数组和链表的结构实现,但使用链表的结构实现更优一些,因为如果使用数组的结构, 出队列在数组头上出数据,效率会比较低。
3 队列的操作实现
3.1 结构体
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;3.2 队列初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
3.3 队列的销毁
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}3.4 入队列(队尾入)
// 队尾入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}3.5 出队列(队头出)
// 队头出
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}3.6 删除队内数据
3.6.1 前删
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}3.6.2 尾删
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->data;
}
3.7 返回队列大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
++size;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}3.8 清空队列
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}4 完整代码
queue.h:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#pragma once
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
typedef int QDataType;
typedef struct QueueNode
{
struct QueueNode* next;
QDataType data;
}QNode;
typedef struct Queue
{
QNode* head;
QNode* tail;
}Queue;
//队列初始化
void QueueInit(Queue* pq);
//队列销毁
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq);
// 队尾入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x);
// 队头出
void QueuePop(Queue* pq);
//前删
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq);
//后删
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq);
//队列大小
int QueueSize(Queue* pq);
//清空队列
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq);
queue.c:
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include "Queue.h"
void QueueInit(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
void QueueDestory(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
QNode* next = cur->next;
free(cur);
cur = next;
}
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
// 队尾入
void QueuePush(Queue* pq, QDataType x)
{
assert(pq);
QNode* newnode = (QNode*)malloc(sizeof(QNode));
if (newnode == NULL)
{
printf("malloc fail\n");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data = x;
newnode->next = NULL;
if (pq->tail == NULL)
{
pq->head = pq->tail = newnode;
}
else
{
pq->tail->next = newnode;
pq->tail = newnode;
}
}
// 队头出
void QueuePop(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
if (pq->head->next == NULL)
{
free(pq->head);
pq->head = pq->tail = NULL;
}
else
{
QNode* next = pq->head->next;
free(pq->head);
pq->head = next;
}
}
QDataType QueueFront(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->head->data;
}
QDataType QueueBack(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
assert(pq->head);
return pq->tail->data;
}
int QueueSize(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
int size = 0;
QNode* cur = pq->head;
while (cur)
{
++size;
cur = cur->next;
}
return size;
}
bool QueueEmpty(Queue* pq)
{
assert(pq);
return pq->head == NULL;
}