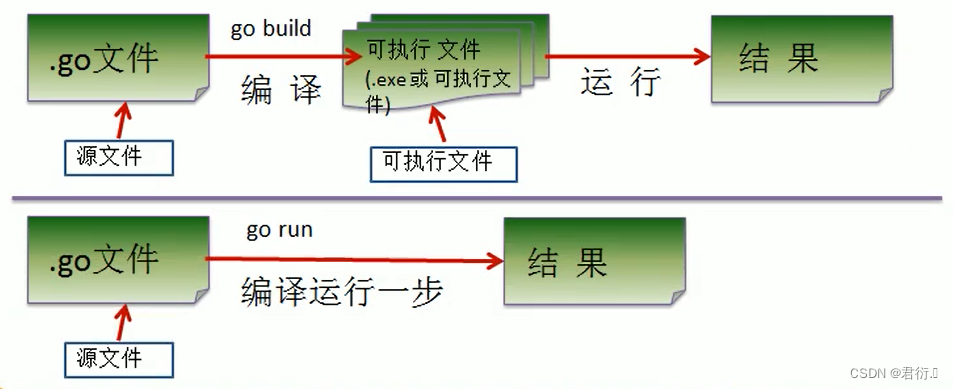
Springboot框架中使用 Redis + Lua 脚本进行限流功能
限流是一种用于控制系统资源利用率或确保服务质量的策略。在Web应用中,限流通常用于控制接口请求的频率,防止过多的请求导致系统负载过大或者防止恶意攻击。
什么是限流?
限流是一种通过限制请求的速率或数量,以防止系统被过度使用或滥用的策略。它可以帮助维护系统的稳定性、可用性和性能。限流的目标通常是平滑请求流量,防止短时间内过多的请求对系统造成冲击。
为什么需要限流?
-
保护系统稳定性: 防止过多的请求导致系统资源耗尽,例如数据库连接、线程池等,从而保护系统的稳定性。
-
防止恶意攻击: 限制请求频率可以防止恶意攻击,例如暴力破解、DDoS攻击等。
-
保障服务质量: 避免因过多请求而导致的服务质量下降,确保正常用户的良好体验。
如何实现限流?
在Spring Boot中,结合Redis和Lua脚本是一种常见的实现方式。具体步骤如下:
-
选择合适的Key: 限流通常需要根据请求的特性选择合适的Key,例如用户ID、接口路径等,以确保限流的粒度和准确性。
-
编写Lua脚本: 使用Lua脚本可以在Redis中原子性地执行限流逻辑。脚本中通常包含对计数器的增加、过期时间的设置和判断是否超过限制的逻辑。
-
在Spring Boot中使用RedisTemplate: 利用Spring Boot的
RedisTemplate来执行Lua脚本,确保在多线程环境下的原子性操作。 -
集成到业务代码中: 在需要进行限流的地方调用限流工具,根据返回结果决定是否继续处理业务逻辑或者拒绝请求。
在Spring Boot框架中,使用Redis和Lua脚本进行限流功能是一种常见的做法,可以有效地控制系统的请求流量,防止突发的大量请求对系统造成压力。下面是一个简单的Spring Boot项目中使用Redis和Lua脚本进行限流的流程说明和示例代码:
步骤1: 添加依赖
首先,在pom.xml文件中添加Redis和Spring Boot的相关依赖:
<dependencies>
<!-- Spring Boot Starter Data Redis -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
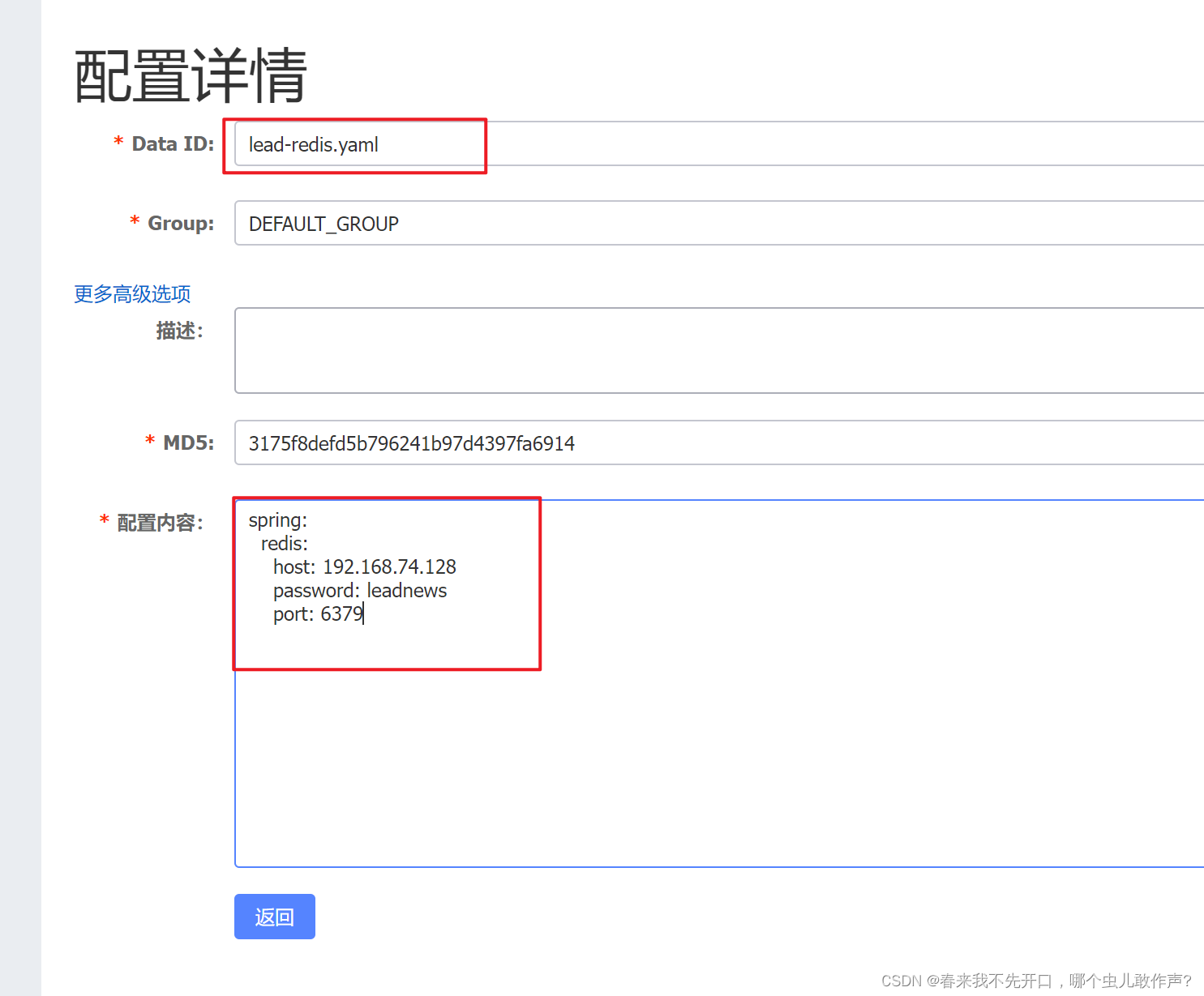
步骤2: 配置Redis连接
在application.properties文件中配置Redis连接信息:
spring.redis.host=localhost
spring.redis.port=6379
步骤3: 编写限流工具类
创建一个RateLimiter类,用于执行Lua脚本进行限流操作:
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.RedisTemplate;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.DefaultRedisScript;
import org.springframework.data.redis.core.script.RedisScript;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
import java.util.Collections;
@Component
public class RateLimiter {
private final RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate;
public RateLimiter(RedisTemplate<String, Object> redisTemplate) {
this.redisTemplate = redisTemplate;
}
public boolean allowRequest(String key, int maxRequests, long timeWindowSeconds) {
String luaScript = "local current = redis.call('incr', KEYS[1])\n" +
"if tonumber(current) == 1 then\n" +
" redis.call('expire', KEYS[1], ARGV[1])\n" +
"end\n" +
"return tonumber(current) <= tonumber(ARGV[2])";
RedisScript<Boolean> redisScript = new DefaultRedisScript<>(luaScript, Boolean.class);
Boolean result = redisTemplate.execute(redisScript, Collections.singletonList(key), String.valueOf(timeWindowSeconds), String.valueOf(maxRequests));
if (result == null) {
// 处理脚本执行失败的情况
return false;
}
return result;
}
}
步骤4: 在Controller中使用限流
在需要进行限流的Controller中,注入RateLimiter并使用它进行限流:
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/api")
public class ApiController {
@Autowired
private RateLimiter rateLimiter;
@GetMapping("/limitedEndpoint")
public String limitedEndpoint() {
String key = "user:1:apiLimitedKey"; // 根据实际情况生成唯一的key,可以使用用户ID等信息
int maxRequests = 10; // 允许的最大请求数
long timeWindowSeconds = 60; // 时间窗口大小,单位秒
if (rateLimiter.allowRequest(key, maxRequests, timeWindowSeconds)) {
// 允许请求的业务逻辑
return "Request allowed!";
} else {
// 请求限流的业务逻辑
return "Request blocked due to rate limiting!";
}
}
}
在上述示例中,limitedEndpoint是一个受限制的接口,通过RateLimiter类进行限流。根据实际需要,可以根据不同的接口、用户等生成不同的key来进行限流。在RateLimiter类中,通过Lua脚本来原子性地执行限流逻辑,确保在多线程环境下的正确性。
示例中完整代码,可以从下面网址获取:
https://gitee.com/jlearning/wechatdemo.git
https://github.com/icoderoad/wxdemo.git