新钛云服已累计为您分享775篇技术干货

概览
日常运维中,我们有时需要关注阿里云中 EIP 和 CEN 的监控数据,如果每次登录到平台查看,不太方便。
可以通过 API 获取监控数据,并输入到 influxDB,然后再到 Grafana 中展示,以便进行实施监控和可视化。
第一步:准备工作
在开始之前,我们需要确保已经完成以下准备工作
准备阿里云的EIP和CEN实例
这一步省略
了解如何获取EIP和CEN数据
了解如何获取 EIP 和 CEN 数据
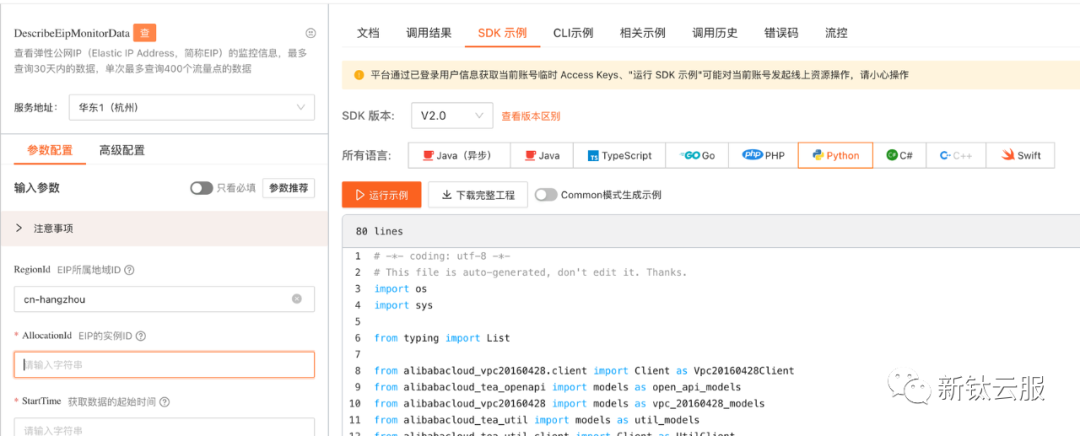
我的方式是 EIP 通过 EIP 产品的 API 获取的,调试链接如下
https://next.api.aliyun.com/api/Vpc/2016-04-28/DescribeEipMonitorData?params={"RegionId":"cn-hangzhou"}
输入 RegionId 和 AllocationId 等必选信息后,复制平台生成的代码,进行更改,下文会介绍如何更改
CEN 的监控数据未找到具体的 API,但可以通过云监控的数据获取,也是很方便的,链接如下
https://api.aliyun.com/api/Cms/2019-01-01/DescribeMetricData
获取 CEN 的具体数据时,可以通过 https://cms.console.aliyun.com/metric-meta/acs_cen/cen_tr?spm=a2c4g.11186623.0.0.252476ab1Ldq0T 得到
实际上,EIP 的数据也可以通过云监控获取
安装Python和所需的依赖库
下面示例的版本是截止发文时间最新版本,实际使用时,可以登录到上面的阿里云开放平台查看最新的版本
pip install alibabacloud_vpc20160428==5.1.0
pip install alibabacloud_cms20190101==2.0.11
安装InfluxDB,并进行初始化配置
1. 为方便使用,我这里是使用 Docker 运行的 Influxdb
cd /data/influxdb
# 生成初始的配置文件
docker run --rm influxdb:2.7.1 influxd print-config > config.yml
# 启动容器
docker run --name influxdb -d -p 8086:8086 --volume `pwd`/influxdb2:/var/lib/influxdb2 --volume `pwd`/config.yml:/etc/influxdb2/config.yml influxdb:2.7.12. 安装完成后,可通过 http://ip:8086 登录到 Influxdb
3. 创建 bucket
只需要创建一个 bucket 就可以了,bucket 类似 MySQL 的 database
4. 获取 API Token,在 Python 插入数据时会用到
安装Grafana,并进行基本的配置
省略
第二步:获取API访问凭证
为了能够通过API访问阿里云的 EIP 和 CEN 数据,我们需要获取访问凭证。具体步骤如下
登录阿里云控制台
创建 RAM 用户并分配相应的权限
获取 RAM 用户的 Access Key ID 和 Access Key Secret
第三步:编写Python脚本
使用Python编写脚本来获取 EIP 和 CEN 的监控数据,并将其存储到 InfluxDB 中
本文仅展示部分代码,如需完整的代码,请联系本公众号获取~
调整从阿里云复制的示例代码
1. 修改构造函数,可以传如 access_key_id 和 access_key_secret
def __init__(self, access_key_id: str=access_key_id, access_key_secret: str=access_key_secret):
self.access_key_id = access_key_id
self.access_key_secret = access_key_secret
2. 修改获取 eip 数据的函数
def get_eip_monitor_data(self, region_id, allocation_id, start_time: str, end_time: str):
'''
参考文档:
https://api.aliyun.com/api/Vpc/2016-04-28/DescribeEipMonitorData?params={%22RegionId%22:%22cn-hangzhou%22}
Args:
region_id (_type_): _description_
allocation_id (_type_): _description_
start_time (str): utc时间
end_time (_type_): utc时间
Yields:
_type_: _description_
eip_tx: 流出的流量。单位: Byte
eip_rx: 流入的流量。单位: Byte
'''
# 请确保代码运行环境设置了环境变量 ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID 和 ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET。
# 工程代码泄露可能会导致 AccessKey 泄露,并威胁账号下所有资源的安全性。以下代码示例使用环境变量获取 AccessKey 的方式进行调用,仅供参考,建议使用更安全的 STS 方式,更多鉴权访问方式请参见:https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/378659.html
client = self.create_client(endpoint=f'vpc.{region_id}.aliyuncs.com', access_key_id=self.access_key_id, access_key_secret=self.access_key_secret)
describe_eip_monitor_data_request = vpc_20160428_models.DescribeEipMonitorDataRequest(
region_id=region_id,
allocation_id=allocation_id,
start_time=start_time,
end_time=end_time
)
log.debug(msg=describe_eip_monitor_data_request)
runtime = util_models.RuntimeOptions()
log.debug(msg=runtime)
try:
# 复制代码运行请自行打印 API 的返回值
results = client.describe_eip_monitor_data_with_options(describe_eip_monitor_data_request, runtime).body.eip_monitor_datas.eip_monitor_data
for result in results:
yield result
except Exception as error:
log.error(msg=error)
return UtilClient.assert_as_string(error.message)
3. 修改获取 cen 数据的函数
def get_cen_monitor_data(self, namespace, metric_name, start_time: str, end_time: str):
# 请确保代码运行环境设置了环境变量 ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_ID 和 ALIBABA_CLOUD_ACCESS_KEY_SECRET。
# 工程代码泄露可能会导致 AccessKey 泄露,并威胁账号下所有资源的安全性。以下代码示例使用环境变量获取 AccessKey 的方式进行调用,仅供参考,建议使用更安全的 STS 方式,更多鉴权访问方式请参见:https://help.aliyun.com/document_detail/378659.html
client = self.create_client(access_key_id=self.access_key_id, access_key_secret=self.access_key_secret)
describe_metric_list_request = cms_20190101_models.DescribeMetricListRequest(
namespace=namespace,
metric_name=metric_name,
start_time=start_time,
end_time=end_time,
)
runtime = util_models.RuntimeOptions()
try:
# 复制代码运行请自行打印 API 的返回值
return client.describe_metric_list_with_options(describe_metric_list_request, runtime).body.datapoints
except Exception as error:
# 如有需要,请打印 error
UtilClient.assert_as_string(error.message)
编写InfluxDB相关的代码
将 InfluxDB 的写入代码独立出来可以方便后续其他业务的调用
下面的代码在获取 token 时,使用了 1password,可视情况进行修改,例如通过环境变量的方式获取 Token
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import influxdb_client, time
import datetime
from influxdb_client import InfluxDBClient, Point, WritePrecision
from influxdb_client.client.write_api import SYNCHRONOUS
from modules.onepassword import OnePassword
my1p = OnePassword()
class InfluxClient:
token = my1p.get_item_by_title(title='my_influxdb')['api']
def __init__(self, url: str='http://10.1.1.1:8086', org: str='tyun', token: str=token):
self.url = url
self.org = org
self.token = token
def create_client(self):
return influxdb_client.InfluxDBClient(url=self.url, token=self.token, org=self.org)
def write_aliyun_eip(self, bucket: str='example', table_name: str='test1', location: str=None, eip_tx: int=None, eip_rx: int=None, time_stamp: str=None):
write_api = self.create_client().write_api(write_options=SYNCHRONOUS)
point = (
Point(table_name)
.tag("location", location)
.field("eip_tx", eip_tx)
.field("eip_rx", eip_rx)
.time(time_stamp)
)
write_api.write(bucket=bucket, org=self.org, record=point)
def write_cen(self, bucket: str='example', table_name: str='test1', location: str=None, tr_instance_id: str=None, value: int=None, time_stamp: str=None):
write_api = self.create_client().write_api(write_options=SYNCHRONOUS)
point = (
Point(table_name)
.tag("location", location)
.tag("tr_instance_id", tr_instance_id)
.field("value", value)
.time(time_stamp)
)
write_api.write(bucket=bucket, org=self.org, record=point)
def main():
influx_client = InfluxClient()
for i in range(5):
influx_client.write_data(bucket='example', table_name='test1', location='hangzhou', EipBandwidth=i, EipFlow=i)
time.sleep(1)
if __name__ == '__main__':
main()
编写主程序
1. 获取 eip 并插入到 influxdb
#!/usr/bin/env python3
from collections import namedtuple
from modules.aliyun.eip import Eip
from modules.database.influxdb.write import InfluxClient
from modules.tools.my_time import MyDatetime as my_time
eip = Eip()
influx_client = InfluxClient()
def insert_data(region_id, location, table_name, allocation_id, start_time, end_time):
'''
_summary_
Args:
region_id (_type_): _description_
location (_type_): _description_
table_name (_type_): _description_
allocation_id (_type_): _description_
start_time (_type_): _description_
interval (int, optional): 取值的范围, 默认是5.
'''
eip_datas = eip.get_eip_monitor_data(region_id=region_id, allocation_id=allocation_id, start_time=start_time, end_time=end_time)
for eip_data in eip_datas:
# print(eip_data)
influx_client.write_aliyun_eip(bucket='example',
table_name=table_name,
location=location,
eip_rx=eip_data.eip_rx,
eip_tx=eip_data.eip_tx,
time_stamp=eip_data.time_stamp)
Instance = namedtuple('Instance', ['region_id', 'allocation_id', 'bandwidth', 'env'])
hangzhou = Instance(region_id='hangzhou', allocation_id='eip-xxxxxxxxx', bandwidth='100m', env='prod')
eip_site_list = [hangzhou]
for eip_site in eip_site_list:
insert_data(region_id=f'cn-{eip_site.region_id}',
location=f'cn-{eip_site.region_id}',
table_name='eip',
allocation_id=eip_site.allocation_id,
start_time=my_time.get_utc_now_str_offset(offset=-60*10),
end_time=my_time.get_utc_now_str()
)
2. 获取 cen 数据并插入到 influxdb
#!/usr/bin/env python3
import ast
from modules.aliyun.metrics import Metrics
from modules.database.influxdb.write import InfluxClient
from modules.tools.my_time import MyDatetime as my_time
from modules.logger.client import LogClient
metrics = Metrics()
influx_client = InfluxClient()
log = LogClient(app='example_traffic')
def tr_instance_id_to_location(tr_instance_id):
if tr_instance_id == 'tr-xxxxxxxxxxxxx':
location = 'hangzhou'
bandwidth = '20m'
else:
location = 'none'
return location, bandwidth
metric_names = ['AttachmentOutRate', 'AttachmentInRate']
for metric_name in metric_names:
results = metrics.get_cen_monitor_data(namespace='acs_cen',
metric_name=metric_name,
start_time=my_time.get_utc_now_str_offset(offset=-60*10),
end_time=my_time.get_utc_now_str())
log.debug(msg=results)
for result in ast.literal_eval(results):
result['metric_name'] = metric_name
trInstanceId = result['trInstanceId']
result['location'] = tr_instance_id_to_location(tr_instance_id=trInstanceId)[0]
result['bandwidth'] = tr_instance_id_to_location(tr_instance_id=trInstanceId)[1]
log.info(msg=metric_name + ' ' + my_time.timestamp_to_str(timestamp=result['timestamp']) + ' ' + ' ' + result['location'] + ' ' + str(result['Value']))
influx_client.write_cen(bucket='example',
table_name=metric_name,
location=result['location'],
tr_instance_id=result['trInstanceId'],
value=result['Value'],
time_stamp=my_time.timestamp_to_str(timestamp=result['timestamp']))第四步:配置Grafana
在Grafana中配置 InfluxDB 数据源,并创建相应的仪表盘来展示 EIP 和 CEN 的监控数据。具体步骤如下:
添加 InfluxDB 数据源,并配置连接信息
我用的是 Flux 的查询语言,配置数据源时,需要注意以下事项
数据源名字推荐使用:InfluxDB-Flux,注明是 Flux 类型的数据源
InfluxDB Details 填写 Organization、Token、Default Bucket 即可
不用填写 HTTP 认证
创建仪表盘,配置 eip 和 cen 的查询语句
· EIP 接收方向的流量
from(bucket: "example")
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "eip")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_field"] == "eip_rx")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["location"] == "cn-hangzhou")
|> aggregateWindow(every: v.windowPeriod, fn: last, createEmpty: false)
|> map(fn: (r) => ({ r with _value: r._value / 8 }))
|> yield(name: "last")· EIP 发送方向的流量
from(bucket: "example")
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "eip")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_field"] == "eip_tx")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["location"] == "cn-hangzhou")
|> aggregateWindow(every: v.windowPeriod, fn: last, createEmpty: false)
|> map(fn: (r) => ({ r with _value: r._value / 8 }))
|> yield(name: "last")
· CEN 发送方向的流量
from(bucket: "example")
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "AttachmentOutRate")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_field"] == "value")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["location"] == "hangzhou")
|> aggregateWindow(every: v.windowPeriod, fn: last, createEmpty: false)
|> yield(name: "last")
· CEN 接收方向流量
from(bucket: "example")
|> range(start: v.timeRangeStart, stop: v.timeRangeStop)
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_measurement"] == "AttachmentInRate")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["_field"] == "value")
|> filter(fn: (r) => r["location"] == "hangzhou")
|> aggregateWindow(every: v.windowPeriod, fn: last, createEmpty: false)
|> yield(name: "last")
eip 和 cen 的数据单位都是 bit/sec(SI)
建议配置 Grafana 面板的 Thresholds
100M为 100000000,配置后会显示一条红线,可以更直观的看到流量的占用情况
总结
通过本文的步骤,我们可以通过API获取阿里云 EIP 和 CEN 的监控数据,将其存储到 InfluxDB,并通过 Grafana 进行实时监控和可视化。这为我们提供了一种自动化的方式来监控和管理阿里云网络资源。
推荐阅读


推荐视频






![[CSS] 文本折行](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/7857f1c49895480a97783fc58a637158.png)