1--源码
import torch
import math
import numpy as np
import torch.nn as nn
class Pos_Embed(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, channels, num_frames, num_joints):
super().__init__()
# 根据帧序和节点序生成位置向量
pos_list = []
for tk in range(num_frames):
for st in range(num_joints):
pos_list.append(st)
position = torch.from_numpy(np.array(pos_list)).unsqueeze(1).float() # num_frames*num_joints, 1
pe = torch.zeros(num_frames * num_joints, channels) # T*N, C
div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0, channels, 2).float() * -(math.log(10000.0) / channels))
pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term) # 偶数列 # 偶数C维度sin
pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term) # 奇数列 # 奇数C维度cos
pe = pe.view(num_frames, num_joints, channels).permute(2, 0, 1).unsqueeze(0) # T N C -> C T N -> 1 C T N
self.register_buffer('pe', pe)
def forward(self, x): # nctv # BCTN
x = self.pe[:, :, :x.size(2)]
return x
if __name__ == "__main__":
B = 2
C = 4
T = 120
N = 25
x = torch.rand((B, C, T, N))
Pos_embed_1 = Pos_Embed(C, T, N)
PE = Pos_embed_1(x)
# print(PE.shape) # 1 C T N
x = x + PE
print("All Done !")2--源码分析与理解
原理理解:Positional Encoding(位置编码)
代码解释:
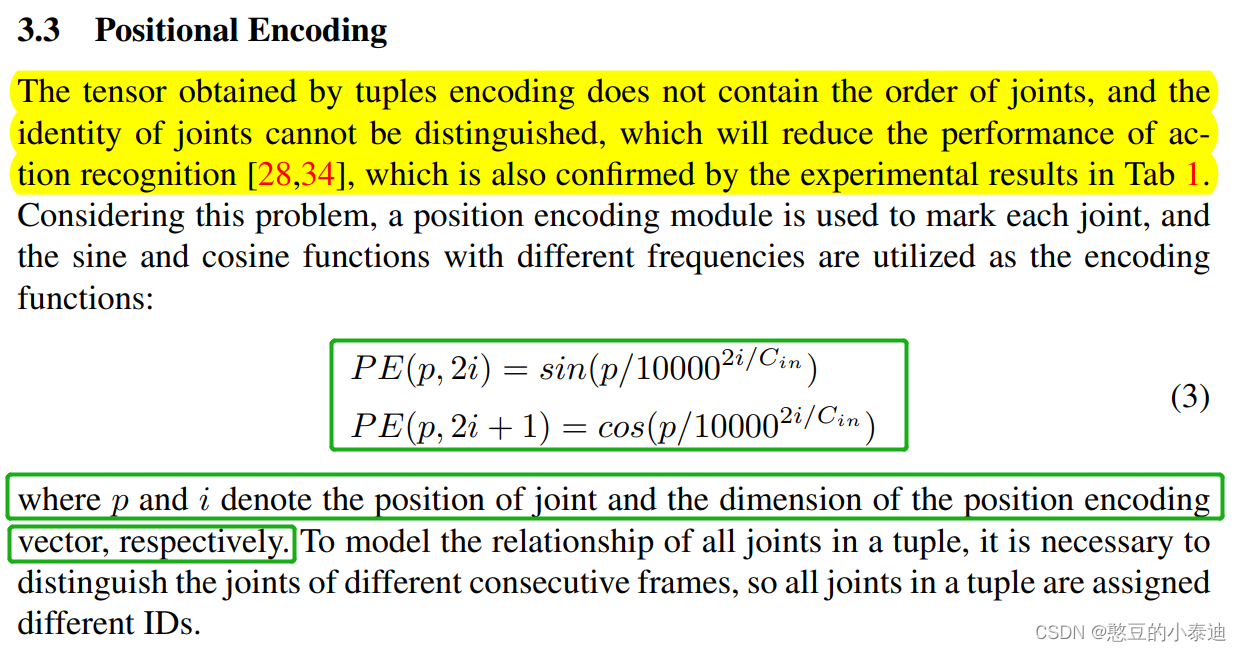
①代码 div_term = torch.exp(torch.arange(0, channels, 2).float() * -(math.log(10000.0) / channels)):
令:channels = C, torch.arange(0, channels, 2).float() = k(则k = 0, 2, ..., C-2);
-(math.log(10000.0) / channels) ;
则:torch.arange(0, channels, 2).float() * -(math.log(10000.0) / channels)
torch.exp(torch.arange(0, channels, 2).float() * -(math.log(10000.0) / channels));
②代码:pe[:, 0::2] = torch.sin(position * div_term) 和 pe[:, 1::2] = torch.cos(position * div_term):
令:position = p,则position * div_term;
将k等价为2i,pe[:, 0::2]和pe[:, 1::2]分别取行数列和奇数列,就可以得到上图绿框所示的公式。
3--参考
参考1
参考2







![[附源码]SSM计算机毕业设计餐厅卫生安全系统JAVA](https://img-blog.csdnimg.cn/d3e9a8c9b6aa49ec891b6703ed24ae77.png)