准备环境
安装jetPack组件
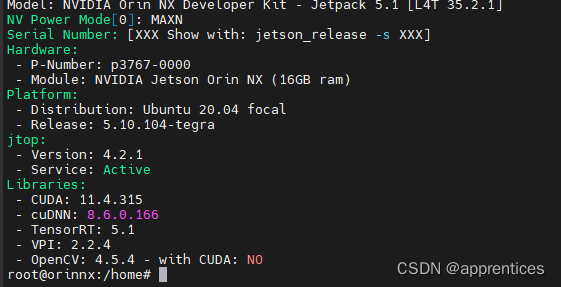
Jetpack 是 Nvidia为 Jetson系列开发板开发的一款软件开发包,常用的开发工具基本都包括了,并在在安装 Jetpack的时候,会自动的将匹配版本的CUDA、cuDNN、TensorRT等。官方提供套件中默认已经安装,可以通过以下命令查看jetPack是否已经安装。
官网指导链接:How to Install JetPack :: NVIDIA JetPack Documentation
# 法一:需要已安装jtop sudo jetson_release # 法二:无需安装jtop sudo apt-cache show nvidia-jetack
配置cuda环境变量
# 配置cuda环境变量 sudo vim ~/.bashrc # 在文本中末尾添加如下代码 export LD_LIBRARY_PATH=$LD_LIBRARY_PATH:/usr/local/cuda/lib64 export PATH=$PATH:/usr/local/cuda/bin export CUDA_HOME=$CUDA_HOME:/usr/local/cuda #使该配置生效 sorce ~/.bashrc # 查看cuda 版本 nvcc -V
配置cuDNN
虽然jetpack安装了cuDNN,但并没有将对应的头文件、库文件放到cuda目录,cuDNN的头文件在:/usr/include,库文件位于:/usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu。将头文件与库文件复制到cuda目录下
# 复制文件到cuda目录下 cd /usr/include && sudo cp cudnn* /usr/local/cuda/include cd /usr/lib/aarch64-linux-gnu && sudo cp libcudnn* /usr/local/cuda/lib64 # 修改文件权限,修改复制完的头文件与库文件的权限,所有用户都可读,可写,可执行: sudo chmod 777 /usr/local/cuda/include/cudnn.h sudo chmod 777 /usr/local/cuda/lib64/libcudnn* # 重新软链接,这里的8.6.0和8对应安装的cudnn版本号和首数字 cd /usr/local/cuda/lib64 sudo ln -sf libcudnn.so.8.6.0 libcudnn.so.8 sudo ln -sf libcudnn_ops_train.so.8.6.0 libcudnn_ops_train.so.8 sudo ln -sf libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8.6.0 libcudnn_ops_infer.so.8 sudo ln -sf libcudnn_adv_train.so.8.6.0 libcudnn_adv_train.so.8 sudo ln -sf libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8.6.0 libcudnn_adv_infer.so.8 sudo ln -sf libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8.6.0 libcudnn_cnn_train.so.8 sudo ln -sf libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8.6.0 libcudnn_cnn_infer.so.8 sudo ldconfig #测试cudnn sudo cp -r /usr/src/cudnn_samples_v8/ ~/ cd ~/cudnn_samples_v8/mnistCUDNN sudo chmod 777 ~/cudnn_samples_v8 sudo make clean && sudo make ./mnistCUDNN
可能存在问题
-
编译时freeImage.h文件不存在
# 执行安装命令 sudo apt-get install libfreeimage3 libfreeimage-dev
查看tensorrt版本
import tensorrt print(tensort.__version__)
部署步骤
1. 拉取代码
#拉取 yolo-tensorRt git clone https://github.com/Monday-Leo/YOLOv7_Tensorrt # 拉取yolo 代码 git clone https://github.com/WongKinYiu/yolov7 #将**YOLOv7_Tensorrt**下的**EfficientNMS.py**和**export_onnx.py**复制到**yolov7**下,导出含有#EfficientNMS的onnx模型。 python3 export_onnx.py --weights ./weights/yolov7.pt
注:
如果遇到:EfficientNMS_TRT type is missing, so it may result in wrong shape inference for the exported graph.异常时,需要安装以下依赖
pip install onnx-simplifier pip install coremltools pip install nvidia-pyindex pip install onnx-graphsurgeon
2. 生成engine模型文件
trtexec --onnx=./yolov7.onnx --saveEngine=./yolov7_fp16.engine --fp16 --workspace=200
3. 运行代码
在YOLOv7_Tensorrt 工程项目中新增trt_model文件夹,并将转换好的yolov7_f16.engine 拷贝到 文件下,修改infer.py代码段
import cv2
import tensorrt as trt
import torch
import numpy as np
from collections import OrderedDict,namedtuple
class TRT_engine():
def __init__(self, weight) -> None:
self.imgsz = [640,640]
self.weight = weight
self.device = torch.device('cuda:0')
self.init_engine()
def init_engine(self):
# Infer TensorRT Engine
self.Binding = namedtuple('Binding', ('name', 'dtype', 'shape', 'data', 'ptr'))
self.logger = trt.Logger(trt.Logger.INFO)
trt.init_libnvinfer_plugins(self.logger, namespace="")
with open(self.weight, 'rb') as self.f, trt.Runtime(self.logger) as self.runtime:
self.model = self.runtime.deserialize_cuda_engine(self.f.read())
self.bindings = OrderedDict()
self.fp16 = False
for index in range(self.model.num_bindings):
self.name = self.model.get_binding_name(index)
self.dtype = trt.nptype(self.model.get_binding_dtype(index))
self.shape = tuple(self.model.get_binding_shape(index))
self.data = torch.from_numpy(np.empty(self.shape, dtype=np.dtype(self.dtype))).to(self.device)
self.bindings[self.name] = self.Binding(self.name, self.dtype, self.shape, self.data, int(self.data.data_ptr()))
if self.model.binding_is_input(index) and self.dtype == np.float16:
self.fp16 = True
self.binding_addrs = OrderedDict((n, d.ptr) for n, d in self.bindings.items())
self.context = self.model.create_execution_context()
def letterbox(self,im,color=(114, 114, 114), auto=False, scaleup=True, stride=32):
# Resize and pad image while meeting stride-multiple constraints
shape = im.shape[:2] # current shape [height, width]
new_shape = self.imgsz
if isinstance(new_shape, int):
new_shape = (new_shape, new_shape)
# Scale ratio (new / old)
self.r = min(new_shape[0] / shape[0], new_shape[1] / shape[1])
if not scaleup: # only scale down, do not scale up (for better val mAP)
self.r = min(self.r, 1.0)
# Compute padding
new_unpad = int(round(shape[1] * self.r)), int(round(shape[0] * self.r))
self.dw, self.dh = new_shape[1] - new_unpad[0], new_shape[0] - new_unpad[1] # wh padding
if auto: # minimum rectangle
self.dw, self.dh = np.mod(self.dw, stride), np.mod(self.dh, stride) # wh padding
self.dw /= 2 # divide padding into 2 sides
self.dh /= 2
if shape[::-1] != new_unpad: # resize
im = cv2.resize(im, new_unpad, interpolation=cv2.INTER_LINEAR)
top, bottom = int(round(self.dh - 0.1)), int(round(self.dh + 0.1))
left, right = int(round(self.dw - 0.1)), int(round(self.dw + 0.1))
self.img = cv2.copyMakeBorder(im, top, bottom, left, right, cv2.BORDER_CONSTANT, value=color) # add border
return self.img,self.r,self.dw,self.dh
def preprocess(self,image):
self.img,self.r,self.dw,self.dh = self.letterbox(image)
self.img = self.img.transpose((2, 0, 1))
self.img = np.expand_dims(self.img,0)
self.img = np.ascontiguousarray(self.img)
self.img = torch.from_numpy(self.img).to(self.device)
self.img = self.img.float()
return self.img
def predict(self,img,threshold):
img = self.preprocess(img)
self.binding_addrs['images'] = int(img.data_ptr())
self.context.execute_v2(list(self.binding_addrs.values()))
nums = self.bindings['num_dets'].data[0].tolist()
boxes = self.bindings['det_boxes'].data[0].tolist()
scores =self.bindings['det_scores'].data[0].tolist()
classes = self.bindings['det_classes'].data[0].tolist()
num = int(nums[0])
new_bboxes = []
for i in range(num):
if(scores[i] < threshold):
continue
xmin = (boxes[i][0] - self.dw)/self.r
ymin = (boxes[i][1] - self.dh)/self.r
xmax = (boxes[i][2] - self.dw)/self.r
ymax = (boxes[i][3] - self.dh)/self.r
new_bboxes.append([classes[i],scores[i],xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax])
return new_bboxes
def visualize(img,bbox_array):
for temp in bbox_array:
xmin = int(temp[2])
ymin = int(temp[3])
xmax = int(temp[4])
ymax = int(temp[5])
clas = int(temp[0])
score = temp[1]
cv2.rectangle(img,(xmin,ymin),(xmax,ymax), (105, 237, 249), 2)
img = cv2.putText(img, "class:"+str(clas)+" "+str(round(score,2)), (xmin,int(ymin)-5), cv2.FONT_HERSHEY_SIMPLEX, 0.5, (105, 237, 249), 1)
return img
def test(path):
import os
out = './runs'
images = os.listdir(path)
engine = TRT_engine("./trt_model/video_fp32.engine")
for item in images:
img = cv2.imread(f'{path}/{item}')
results = engine.predict(img,threshold=0.25)
img = visualize(img,results)
cv2.imwrite(f'{out}/{item}',img)
test('./pictures')