文章底部有个人公众号:热爱技术的小郑。主要分享开发知识、学习资料、毕业设计指导等。有兴趣的可以关注一下。为何分享? 踩过的坑没必要让别人在再踩,自己复盘也能加深记忆。利己利人、所谓双赢。
前言
调用一些方法,进行一些比较耗时的操作时,如果时间超过了规定的时间。要做超时处理。
package A1多线程.B1超时处理.Demo1;
import org.apache.log4j.Logger;
import java.util.Random;
import java.util.concurrent.*;
/**
* @author zyz
* @version 1.0
* @data 2023/11/14 9:52
* @Description: 有些方法的执行 比较费时。执行时间 超过指定时间的时候 主动结束
*/
public class TimeoutProcessing {
static final Logger log = Logger.getLogger(TimeoutProcessing.class); //创建日志对象 Logger
private static ExecutorService executorService = Executors.newSingleThreadExecutor();
public static void main(String[] args) {
long start = System.currentTimeMillis();
String result = timeoutMethod();
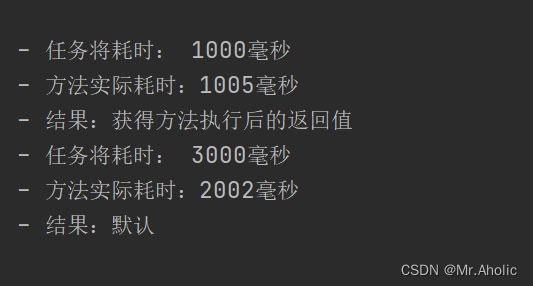
log.info("方法实际耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start) + "毫秒");
log.info("结果:" + result);
try {
Thread.sleep(3000);
long start1 = System.currentTimeMillis();
String result1 = timeoutMethod();
log.info("方法实际耗时:" + (System.currentTimeMillis() - start1) + "毫秒");
log.info("结果:" + result1);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
}
/**
* 有超时时间的方法
* @param
* @return
*/
private static String timeoutMethod() {
String result = "默认";
FutureTask<String> futureTask = new FutureTask<>(new Callable<String>() {
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
return unknowMethod();
}
});
executorService.execute(futureTask);
try {
result = futureTask.get(2000, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS); //2秒后,还未执行完。就当作超时
} catch (InterruptedException | ExecutionException | TimeoutException e) {
futureTask.cancel(true);
result = "默认";
}
return result;
}
/**
* 这个方法的耗时不确定
* @return
*/
private static String unknowMethod() {
Random random = new Random();
int time = (random.nextInt(10) + 1) * 1000;
log.info("任务将耗时: " + time + "毫秒");
try {
Thread.sleep(time);
} catch (Exception e) {
// TODO: handle exception
}
return "获得方法执行后的返回值";
}
}